shell脚本 3 流程控制
shell流程控制
流程控制是改变程序运行顺序的指令。linux shell有一套自己的流程控制语句,其中包括条件语句(if),循环语句(for,while),选择语句(case)。下面我将通过例子介绍下,各个语句使用方法
if语句
格式:
格式:if list; then list; [ elif list; then list; ] ... [ else list; ] fi 1.1 单分支
if 条件表达式; then
命令
fi 实例:
#!/bin/bash
N=10
if [ $N -gt 5 ]; then
echo yes
fi # bash test.sh
yes 1.2 双分支 if 条件表达式; then
命令
else
命令
fi 实例1: #!/bin/bash
N=10
if [ $N -lt 5 ]; then
echo yes
else
echo no
fi # bash test.sh
no 实例2:判断crond进程是否正在运行 -v: 表示取反
-c: 即count,取代通常的输出,显示行数 #!/bin/bash
NAME=crond
NUM=$(ps aux | grep $NAME | grep -vc grep)
if [ $NUM -eq 1 ]; then
echo "$NAME running."
else
echo "$NAME is not running!"
fi 实例3:检查主机是否在线
-c:表示发送几次包
-w:表示等待时间。当试图检测不可达主机时此选项很有用。 #!/bin/bash
if ping -c 1 192.168.1.1 &>/dev/null; then
echo "OK."
else
echo "NO!"
fi
if 语句可以直接对命令状态进行判断,就省去了获取$?这一步! 1.3 多分支 if 条件表达式; then
命令
elif 条件表达式; then
命令
else
命令
fi 当不确定条件符合哪一个时,就可以把已知条件判断写出来,做相应的处理。 实例1:
$1:表示接受用户输入参数 #!/bin/bash
N=$1
if [ $N -eq 3 ]; then
echo "eq 3"
elif [ $N -eq 5 ]; then
echo "eq 5"
elif [ $N -eq 8 ]; then
echo "eq 8"
else
echo "no"
fi 如果第一个条件符合就不再向下匹配。
shell编程之if语句实战案例
需求:
1. 完成用户输入文件或者目录的自动复制,并可以实现用户指定复制目标位置。
2. 用户体验佳。 #!/bin/bash
read -p "please enter a file you want to copy:" file
if [ -f $file -o -d $file ];then
read -p "do you want to copy the $file?(y/n)" sure
confirm=$(echo ${sure} | tr A-Z a-z)
if [ "$confirm" == "y" ];then
read -p "where do you want to copy?" dire
if [ -d $dire ];then
cp -a $file $dire
echo "the $file copied to $dire"
else
echo "the $dire is not exists"
exit 1
fi
elif [ "$confirm" == "n" ];then
echo "bye"
else
echo "pls input y or n"
fi
else
echo "the $file is not exists"
fi
练习题1:尝试写一个shell简单的计算器,实现加减乘除。
请输入一个数字: 7
请输入运算符:+
请输入第二个数字:7
7+7=14

练习题2:输入一个用户,用脚本判断判断该用户是否存在。

for语句
格式:for name [ [ in [ word ... ] ] ; ] do list ; done for 变量名 in 取值列表; do
命令
done 或者
for 变量名 in 取值列表 do 命令 done 实例1:
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..3}; do
echo $i
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3 实例2:计算100以内偶数和
#!/bin/bash
sum=0
for i in `seq 2 2 100`
do
let sum+=$i
done
echo "$sum" shell编程之for语句实战案例 需求:
1. 批量检查当前教室主机是否在线 #!/bin/bash
. /etc/init.d/functions
ip=192.168.7.
for i in {100..150}
do
if ping -c 1 -w 1 $ip$i &>/dev/null;then
echo -n "$ip$i在线!"
success
echo ""
else
echo -n "$ip$i不在线!"
failure
echo ""
fi
done
练习题1:计算100以内的偶数和
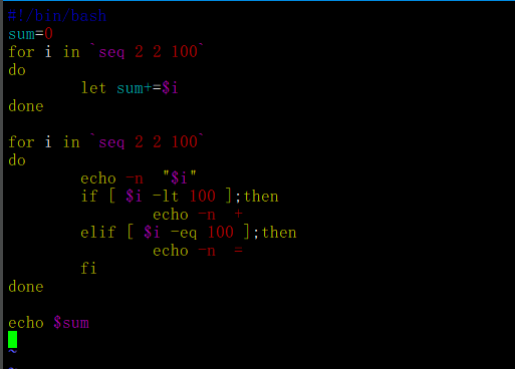
练习题2:判断/root目录下面的文件类型

while语句 条件为真就进入死循环;条件为假就退出循环 格式:while list; do list; done
while 条件表达式; do
命令
done 实例1: #!/bin/bash
N=0
while [ $N -lt 5 ]; do
let N++
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3
4
5 当条件表达式为 false 时,终止循环。 实例2:条件表达式为 true,将会产生死循环
#!/bin/bash
while [ 1 -eq 1 ]; do
echo "yes"
done 也可以条件表达式直接用 true: #!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo "yes"
done 死循环有什么作用那?
可以用来后台运行检测脚本,如下是是一个检测脑裂的脚本 我们只需要在命令行中输入 nohup bash naolie.sh & 即可在后台持续运行该脚本 例子1:检测脑裂 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
ip=`ip a s eth0 | awk -F " +" 'NR==4{print $3}' | awk -F "/" '{print $1}' | awk -F "." '{print $4}'`1
ping -c 3 -i 1 -W 1 10.220.5.166 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ] && [ $ip = 1001 ];then
echo "happed naolie"
else
echo "everything is ok"
fi
done 例子2:检测终端数量 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
num=`who | wc -l`
echo "当前打开终端数量为:$num"
sleep 5
done 要想使用 while 循环逐行读取 a.txt 文件,有三种方式: 方式 1: #!/bin/bash
cat ./a.txt | while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done
方式2: #!/bin/bash
while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done < ./a.txt
方式3: exec < ./a.txt # 读取文件作为标准输出
while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done
与 while 关联的还有一个 until 语句,它与 while 不同之处在于,是当条件表达式为 false 时才循环,实际使用中比较少,这里不再讲解。 #!/bin/bash
n=0
until [ $n -eq 5 ]
do
let n++
echo "$n" done break和continue语句
break 是终止循环。
continue 是跳出当前循环。 示例 1:在死循环中,满足条件终止循环 #!/bin/bash
N=0
while true; do
let N++
if [ $N -eq 5 ]; then
break
fi
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3
4 里面用了 if 判断,并用了 break 语句,它是跳出循环。与其关联的还有一个 continue 语句,它是跳出本次循环。 示例 2:举例子说明 continue 用法
#!/bin/bash
N=0
while [ $N -lt 5 ]; do
let N++
if [ $N -eq 3 ]; then
continue
fi
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
4 当变量 N 等于 3 时,continue 跳过了本次循环,没有执行下面的 echo。 注意:continue 与 break 语句只能循环语句中使用。 [root@ken-node1 ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
st=0
while true
do
let st++
if [ $st -eq 5 ];then
continue
elif [ $st -eq 10 ];then
break
else
echo "$st"
fi done
[root@ken-node1 ~]# bash test.sh
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9 case语句
case 语句一般用于选择性来执行对应部分块命令。
case 模式名 in
模式 1)
命令
;;
模式 2)
命令
;;
*)
不符合以上模式执行的命令
esac 每个模式必须以右括号结束,命令结尾以双分号结束,最后一个模式不需要添加;;。 示例1:根据位置参数匹配不同的模式
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
start)
echo "start."
;;
stop)
echo "stop."
;;
restart)
echo "restart."
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
esac # bash test.sh
Usage: test.sh {start|stop|restart} # bash test.sh start
start. # bash test.sh stop
stop. # bash test.sh restart
restart. 实例2:
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
[0-9])
echo "match number."
;;
[a-z])
echo "match letter."
;;
'-h'|'--help')
echo "help"
;;
*)
echo "Input error!"
exit
esac # bash test.sh 1
match number. # bash test.sh a
match letter. # bash test.sh -h
help # bash test.sh --help
help
模式支持的正则有:*、?、[ ]、[.-.]、|。后面有章节单独讲解 Shell 正则表达式。 shell编程高级实战 实战1:写一个猜数字的小游戏
要求:
1. 猜对退出
2. 数字随机
3. 使用体验佳 #!/bin/bash
clear
num=`echo $RANDOM`
count=0
while true
do
let count++
read -p "pls enter a num you guess:" guessnum
if [ $guessnum -lt $num ]; then
echo "the num is so smaller!"
elif [ $guessnum -gt $num ];then
echo "the num is so bigger!"
elif [ $guessnum -eq $num ];then
echo "right!wonderful! "
break
else
echo "good bye"
exit
fi
done
echo -e "\033[36myou guess $count times\033[0m" #-e允许对下面列出的加反斜线转义的字符进行解释. 实战2:检测当前教室在线IP地址
要求:
1.显示美观 #!/bin/bash
. /etc/init.d/functions
ip=172.20.10.
for i in {1..255}
do
if ping -c 1 $ip$i &>/dev/null ;then
echo -n "$ip$i" #-n表示不输出行尾的换行符
success
echo ""
else
echo -n "$ip$i"
failure
echo ""
fi
done
实战3:检查软件包是否安装
要求:
1.用户输入软件名即可进行查询
#!/bin/bash
read -p "pls enter a softname:" softname
if rpm -q $softname &>/dev/null ;then
echo "the $softname is already installed"
else
echo "the $softname" is not installed
fi 实战4:打印九九乘法表
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq 9`
do
for a in `seq 9`
do
if [ $a -le $i ];then
echo -n "$a*$i=$(($i*$a)) "
fi
done
echo ""
done 补充练习题
1.实现简单计算器(加减乘除) #!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入第一个数字:" a
read -p "请输入运算符[+-*/]:" b
read -p "请输入第二个数字:" c
if [ -n $a -a -n $b -a -n $c ];then
if [ "$b" == "+" ];then
echo "$a+$c=$(($a+$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "-" ];then
echo "$a-$c=$(($a-$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "*" ];then
echo "$a*$c=$(($a*$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "/" ];then
echo "$a/$c=$(($a/$c))"
else
echo "请输入+—*%"
fi
else
echo "请按照要求输入内容!"
fi 2. 批量创建100个以数字开头的文件,并每隔一秒钟输出到终端 #!/bin/bash
for i in {1..100}
do
touch ${i}.txt
echo "${i}.txt"
sleep 1
done 3.动态持续监测本机linux系统内存剩余量(仅显示数值),并在终端输出 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
mem=`free -h | grep "Mem" | cut -d "M" -f 4 | tr -d " "`
echo $mem
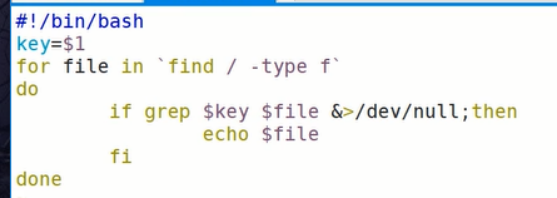
sleep 1 done nohup bash 脚本名 & # 可以将脚本挂在后台运行 4.搜索带有指定的关键词的文件,并且输出文件名
shell脚本 3 流程控制的更多相关文章
- shell脚本之流程控制
shell脚本之流程控制 shell脚本之流程控制 条件语句 条件判断 循环语句for,while,until for循环 while循环 until循环 循环控制语句continue 循环控制语 ...
- Shell脚本学习 - 流程控制和函数
继续Shell的学习.上两篇是关于基本数据类型,基本语法以及运算符相关,这一篇是流程控制相关(if, for, while) 流程控制 if else 流程控制不可为空,如果else没有语句执行,就不 ...
- Shell脚本之流程控制(if、for、while)
if 判断 if语句的三种格式: (1)if (2)if else (3)if elif else 语法格式如下: #if 语法格式 if 条件 then 命令1... 命令2... fi #if e ...
- shell脚本(10)-流程控制while
一.while循环介绍 while循环与for一样,一般不知道循环次数使用for,不知道循环的次数时推荐使用while 二.while语法 while [ condition ] #条件为真才会循环, ...
- shell脚本(11)-流程控制case
一.case介绍 生产环境下,遇到要根据不同的状况执行不同的预案的情况,首先根据可能出现的情况写出对应预案,根据出现的情况来加载不同的预案 特点:根据给予的不同的代码块 二.case语法 case 变 ...
- 【Shell 编程基础第二部分】Shell里的流程控制、Shell里的函数及脚本调试方法!
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaominghimi/article/details/7603003 本站文章均为李华明Himi原创,转载务必在明显处注明:转载自[黑米GameDev街区 ...
- Shell命令和流程控制
Shell命令和流程控制 在shell脚本中可以使用三类命令: 1)Unix 命令: 虽然在shell脚本中可以使用任意的unix命令,但是还是由一些相对更常用的命令.这些命令通常是用来进行文件和文字 ...
- Shell脚本的条件控制和循环语句
条件判断:if语句 语法格式: if [ expression ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true fi 注意:expre ...
- Shell命令和流程控制[linux常用命令的使用]
在shell脚本中使用三类命令: unix命令 概念:管道.重定向.backtick 流程控制 1 unix命令 echo "some text":在屏幕上输出信息 ls:文件列表 ...
随机推荐
- 学习String源码的部分方法
先看构造器: private final char value[]; //char类型的数组 以下均会用到 private int hash; //缓存字符串的哈希值 //以下均会用到 public ...
- 使用sun.net.ftp.FtpClient进行上传功能开发,在jdk1.7上不适用问题的解决
问题如下图片: 之前项目上开发了一个上传文件的功能,使用的是sun.net.ftp.FtpClient这个类 连接服务器的代码大概如下: public static FtpClient ftpClie ...
- 读懂框架设计的灵魂—Java反射机制
尽人事,听天命.博主东南大学硕士在读,热爱健身和篮球,乐于分享技术相关的所见所得,关注公众号 @ 飞天小牛肉,第一时间获取文章更新,成长的路上我们一起进步 本文已收录于 CS-Wiki(Gitee 官 ...
- Sapper:迈向理想的 Web 应用框架
扎稳阵脚,再进一步. 注意:原文发表于2017-12-31,随着框架不断演进,部分内容可能已不适用. 给迫不及待的小伙伴们的快速入门:Sapper 文档 和快速模板 starter template ...
- Lua C++交互 应用实例步骤(UserData使用)
一.配置Lua C++交互环境 1.下载Lua 包环境 地址: https://www.lua.org/download.html ,我们这里用的是5.4.2版本. 2.新建C++ 控制台应用程序 3 ...
- MVC模式从Controller返回内容协商格式(Json或者Xml)
WebAPI默认的返回格式Json,但是MVC是View,如果在MVC的控制器中,想要返回Json格式该怎么操作呢 在MVC的控制器中返回json数据只需要然会JsonResult而不是ActionR ...
- 一款免费的在线 Markdown 笔记,类似 typora 编辑体验
为什么要开发一款新的编辑器 自从我开始使用 Markdown,就爱上了这种标记语法,轻量.纯文本兼容是最大的优点,哪里都可以编辑,一开始是在 IDE 上直接编辑,后来笔记越来越多,需要上传图片,有云同 ...
- 性能追击:万字长文30+图揭秘8大主流服务器程序线程模型 | Node.js,Apache,Nginx,Netty,Redis,Tomcat,MySQL,Zuul
本文为<高性能网络编程游记>的第六篇"性能追击:万字长文30+图揭秘8大主流服务器程序线程模型". 最近拍的照片比较少,不知道配什么图好,于是自己画了一个,凑合着用,让 ...
- redis集群(redis_cluster)
一.为什么要使用redis-cluster? 1.数据并发问题 2.数据量太大 新浪微博作为世界上最大的redis存储,就超过1TB的数据,去哪买这么大的内存条?各大公司有自己的解决方案,推出各自的集 ...
- Sequelize 和 MySQL 对照Sequelize 和 MySQL 对照
安装 这篇文章主要使用MySQL.Sequelize.co来进行介绍.安装非常简单: $ npm install --save co $ npm install --save sequelize $ ...
