Understanding about numerical stability, convergence and consistency
In a computer simulation of the real world, physical quantities, which usually have continuous distributions governed by partial differential equations (PDEs), can be solved by numerical methods such as finite element method (FEM) and boundary element method (BEM). Whether the obtained solution is a good approximation of the reality and whether the numerical schemes can proceed properly under perturbations of different error sources, such as numerical quadrature error and round-off error, should be clarified before any code implementation. To answer these questions, this post will introduce the fundamental concepts of numerical stability, convergence and consistency according to the following figure.
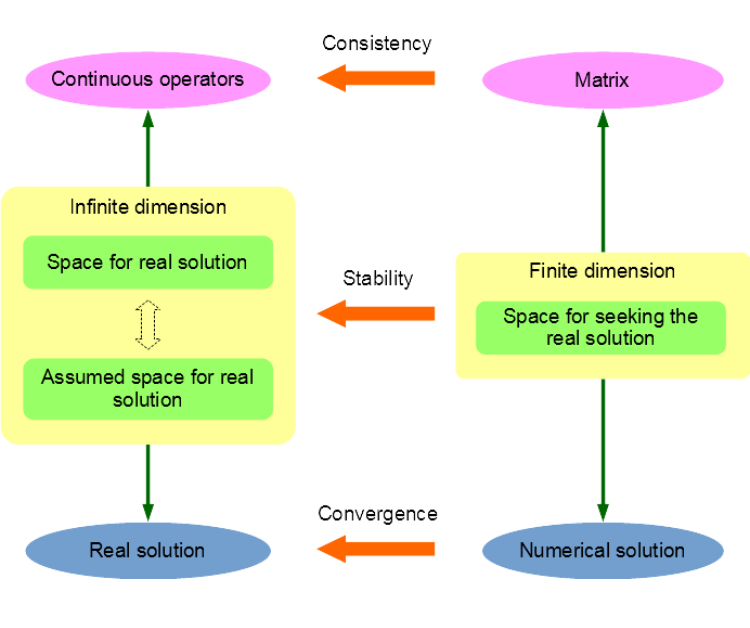
Let \(u\) be the real solution of the following general variational problem for a PDE:
\[
\text{Solve $u \in U$: } a(u, v) = (f, v) \quad (\forall v \in W),
\]
where both \(U\) and \(W\) are Hilbert spaces, \(a(\cdot, \cdot): U \times W \rightarrow \mathbb{K}\) with \(\mathbb{K} \in \{\mathbb{R}, \mathbb{C}\}\) is a sesquilinear or bilinear form and \(f: W \rightarrow \mathbb{K}\) is a continuous linear functional on \(W\). The solution \(u\) belongs to the space \(U\) of continuous functions with infinite dimension. For ease of further analysis, priori assumption is usually adopted for such function space thus we have the assumed function space \(V\). For example, the countably normed spaces \(V = B_{\varrho}(\Gamma)\) used in the \(hp\)-BEM is defined as
\[
B_{\varrho}(\Gamma) = \{ v \in L^2(\Gamma): v \circ \kappa_K \in B_{\varrho}(K_0) \},
\]
where
- \(\Gamma\) is the boundary manifold of the solution domain, which is covered by the mesh \(\{K_i\}_{i=1}^{N_M}\) with \(N_M\) as the number of mesh elements;
- \(K_0\) is the reference cell and \(K\) is the real cell which may be curved;
- \(\kappa_K: K_0 \rightarrow K\) is the mapping from the reference cell to the real cell;
- \(B_{\varrho}(K_0)\) is the countably normed space restricted on the reference cell, which has constraints on the norm of all the derivatives of \(v\). Its formulation is given as below:
\[
B_{\varrho}(K_0) = \big\{ v \in L^2(K_0): \Norm{r_X^{k - \varrho} \left( \Pd{}{r_X} \right)^k \left( \vartheta (\alpha_X - \vartheta_X) \right)^{l - \varrho} \left( \Pd{}{\vartheta_X} \right)^l v}_{L^2(U_X)} \leq C d^{k+l+1} k! l!\big\},
\]
for which I do not provide more explanation in this post, but just give you an impression that the construction of the assumed solution function space can be quite complicated.
To solve the PDE on a computer, a finite dimensional subspace \(V^L\) of \(V\) must be constructed, in which a solution is to be sought as an approximation of the real solution by using some sort of numerical method. Then the stability condition means, for any function \(u\) in the real space \(U\) or the assumed space \(V\) of infinite dimension, whether there exists a function \(v\) in the finite dimensional space \(V^L\), such that the norm of their difference can be controlled to be arbitrarily small as \(N_L\), the dimension of space \(V^L\), increases. For example, in the \(hp\)-BEM, a subspace \(V^L\) can be constructed to have the following exponential stability condition:
\[
\begin{equation}
\label{eq:stability-condition}
\forall u \in B_{\varrho}(\Gamma): \inf_{v \in V^L} \norm{u - v}_{L^2(\Gamma)} \leq C \exp(-b N_L^{1/4}).
\end{equation}
\]
Once the solution \(u^L \in V^L\) for the finite dimensional problem is obtained from a general method such as the Galerkin method, i.e.
\[
\text{Solve $u^L \in V^L$: } a(u^L, v) = (f, v) \quad (\forall v \in V^L),
\]
the concept of convergence comes into play, which ensures that the difference between this \(u^L\) and the real solution \(u\) can be controlled. For example, if the following condition can be satisfied:
\[
\Norm{P_L A u^L} \geq C_s \Norm{u^L} \quad (\forall u^L \in V^L),
\]
where \(P_L: V \rightarrow V^L\) is the projection operator, \(A: V^L \rightarrow (V^L)'\) is the associated operator of the sesquilinear or bilinear form \(a(\cdot, \cdot)\) and \(C_s > 0\) is a constant, it can be proved that the solution obtained from the Galerkin method satisfies
\[
\begin{equation}
\label{eq:convergence-condition}
\norm{u - u^L} \leq C \inf_{v \in V^L} \Norm{u - v}.
\end{equation}
\]
This means the real solution can be properly approximated by the Galerkin solution with the error norm controlled by the approximation capability of the adopted finite dimensional space \(V^L\), and we say the method is convergent. In addition, combing equation \eqref{eq:stability-condition} and \eqref{eq:convergence-condition}, we know the solution has the exponential convergence property:
\[
\begin{equation}
\label{eq:exponential-convergence}
\norm{u - u^L} \leq C \exp(-b N_L^{1/4}).
\end{equation}
\]
Finally, we introduce the concept of consistency. During the discretization of the problem, the sesquilinear or bilinear form \(a(\cdot, \cdot)\), or rather, its associated operator \(A\), is to be approximated by its discrete version, i.e. the stiffness matrix \(A^L\). The evaluation of \(A^L\)'s coefficients usually needs numerical quadrature techniques, which introduces additional numerical error. Even though there is an analytical formula for integration, round-off error limited by the finite computer byte length is unavoidable. Hence, an operator \(\tilde{A}^L\) is obtained being different from \(A^L\). The error between \(A^L\) and \(\tilde{A}^L\) will perturb the adopted numerical method. If the error between the real and numerical solutions \(\Norm{u - \tilde{u}^L}\) can still be controlled, we say the method is consistent. For example, in the \(hp\)-BEM, if the stiffness matrix coefficient error satisfies the following consistent condition
\[
\abs{A^L_{ij} - \tilde{A}^L_{ij}} < \Phi(L) \quad (i,j = 1, \cdots, N_L)
\]
with
\[
\lim_{L \rightarrow \infty} N_L \Phi(L) = 0 \; \text{and} \; \Phi(L) = N_L^{-1} L \sigma^{\varrho L},
\]
the exponential convergence as shown in \eqref{eq:exponential-convergence} can be preserved.
Understanding about numerical stability, convergence and consistency的更多相关文章
- Softmax vs. Softmax-Loss VS cross-entropy损失函数 Numerical Stability(转载)
http://freemind.pluskid.org/machine-learning/softmax-vs-softmax-loss-numerical-stability/ 卷积神经网络系列之s ...
- Softmax vs. Softmax-Loss: Numerical Stability
http://freemind.pluskid.org/machine-learning/softmax-vs-softmax-loss-numerical-stability/ softmax 在 ...
- Understanding Convolution in Deep Learning
Understanding Convolution in Deep Learning Convolution is probably the most important concept in dee ...
- [C4] Andrew Ng - Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization
About this Course This course will teach you the "magic" of getting deep learning to work ...
- 【转】Artificial Neurons and Single-Layer Neural Networks
原文:written by Sebastian Raschka on March 14, 2015 中文版译文:伯乐在线 - atmanic 翻译,toolate 校稿 This article of ...
- AP(affinity propagation)研究
待补充…… AP算法,即Affinity propagation,是Brendan J. Frey* 和Delbert Dueck于2007年在science上提出的一种算法(文章链接,维基百科) 现 ...
- 提高神经网络的学习方式Improving the way neural networks learn
When a golf player is first learning to play golf, they usually spend most of their time developing ...
- 【Caffe 测试】Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe
Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe We will assume that you have Caffe successfully compiled. If not, ...
- MR for Baum-Welch algorithm
The Baum-Welch algorithm is commonly used for training a Hidden Markov Model because of its superior ...
随机推荐
- git与eclipse集成之保存快照
1.1. 保存快照 在个分支进行编码,然后需要紧急切换到另外一个分支进行快速修复一个问题,此时可以先将当前分支的修改进行保存快照. 在分支A进行编码,保存快照 切换到另外分支B进行修改 切换回A分支继 ...
- 修改JDK版本配置
我使用的maven是3.0.5版本的,在创建项目的时候,默认使用的jdk为1.5版本 在项目的pom.xml中添加如下配置可修改使用的jdk版本. <properties> <!-- ...
- MySQL 索引原理相关文章
CSDN的整理: http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/392265880 引擎在磁盘中存储顺序的图解: http://blog.csdn.net/php_lzr/article/de ...
- NodeJS+Express+MySQL开发小记(2):服务器部署
http://borninsummer.com/2015/06/17/notes-on-developing-nodejs-webapp/ NodeJS+Express+MySQL开发小记(1)里讲过 ...
- 使用Filezilla搭建FTP服务器
1.FTP over TLS is not enabled, users cannot securely http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_4cd978f90102vtwl ...
- laravel sql复杂语句,原生写法----连表分组
### 使用了临时表.又分组又连表的感觉好难写,使用拉 ravel 但是现在越来也相信,没解决一个新的难题,自己又进步了一点点 ### 原生的sql: select user_code, realna ...
- HttpServletResponse设置下载文件
// path是指欲下载的文件的路径. File file = new File(path); // 取得文件名. String fi ...
- vue 安装之路
vue 来源 1.安装node.js(http://www.runoob.com/nodejs/nodejs-install-setup.html) 2.基于node.js,利用淘宝npm镜像安装相关 ...
- 洛谷P3317 [SDOI2014]重建 [Matrix-Tree定理]
传送门 思路 相信很多人像我一样想直接搞Matrix-Tree定理,而且还过了样例,然后交上去一分没有. 但不管怎样这还是对我们的思路有一定启发的. 用Matrix-Tree定理搞,求出的答案是 \[ ...
- ORA-00379: no free buffers available in buffer pool DEFAULT for block size 16K
SYS@orcl> select TABLESPACE_NAME ,AUTOEXTENSIBLE from dba_data_files ; ERROR: ORA-00379: no free ...
