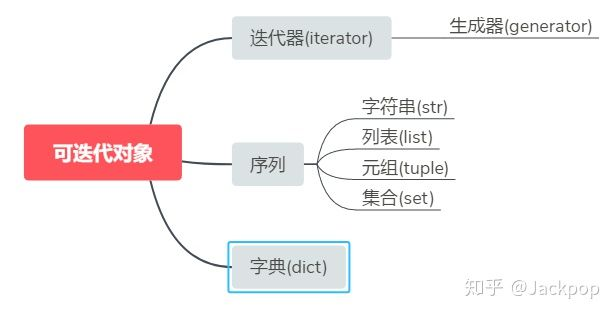
Iterables vs. Iterators vs. Generators
Reprinted from:
Iterables vs. Iterators vs. Generators
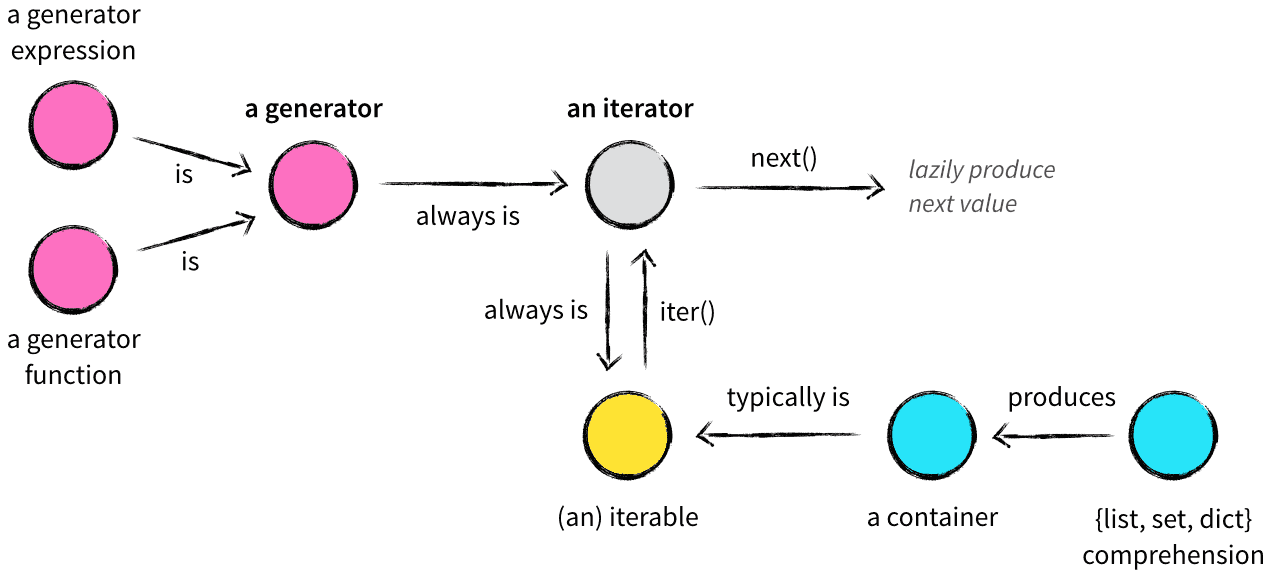
Occasionally I've run into situations of confusion on the exact differences between the following related concepts in Python:
- a container
- an iterable
- an iterator
- a generator
- a generator expression
- a {list, set, dict} comprehension
I'm writing this post as a pocket reference for later.
Containers
Containers are data structures holding elements, and that support membership tests. They are data structures that live in memory, and typically hold all their values in memory, too. In Python, some well known examples are:
- list, deque, …
- set, frozensets, …
- dict, defaultdict, OrderedDict, Counter, …
- tuple, namedtuple, …
- str
Containers are easy to grasp, because you can think of them as real life containers: a box, a cubboard, a house, a ship, etc.
Technically, an object is a container when it can be asked whether it contains a certain element. You can perform such membership tests on lists, sets, or tuples alike:
>>> assert 1 in [1, 2, 3] # lists
>>> assert 4 not in [1, 2, 3]
>>> assert 1 in {1, 2, 3} # sets
>>> assert 4 not in {1, 2, 3}
>>> assert 1 in (1, 2, 3) # tuples
>>> assert 4 not in (1, 2, 3)
Dict membership will check the keys:
>>> d = {1: 'foo', 2: 'bar', 3: 'qux'}
>>> assert 1 in d
>>> assert 4 not in d
>>> assert 'foo' not in d # 'foo' is not a _key_ in the dict
Finally you can ask a string if it "contains" a substring:
>>> s = 'foobar'
>>> assert 'b' in s
>>> assert 'x' not in s
>>> assert 'foo' in s # a string "contains" all its substrings
The last example is a bit strange, but it shows how the container interface renders the object opaque. A string does not literally store copies of all of its substrings in memory, but you can certainly use it that way.
NOTE:
Even though most containers provide a way to produce every element they contain, that ability does not make them a container but an iterable (we'll get there in a minute).Not all containers are necessarily iterable. An example of this is a Bloom filter. Probabilistic data structures like this can be asked whether they contain a certain element, but they are unable to return their individual elements.
Iterables
As said, most containers are also iterable. But many more things are iterable as well. Examples are open files, open sockets, etc. Where containers are typically finite, an iterable may just as well represent an infinite source of data.
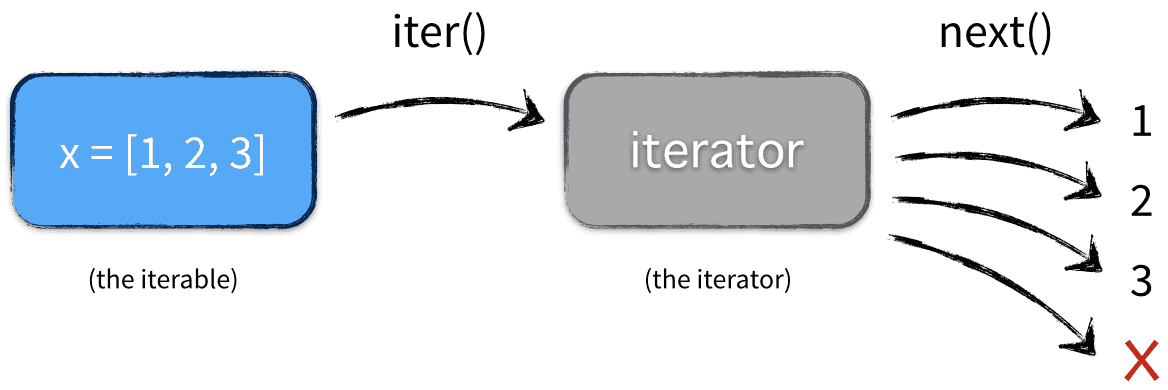
An iterable is any object, not necessarily a data structure, that can return an iterator (with the purpose of returning all of its elements). That sounds a bit awkward, but there is an important difference between an iterable and an iterator. Take a look at this example:
>>> x = [1, 2, 3]
>>> y = iter(x)
>>> z = iter(x)
>>> next(y)
1
>>> next(y)
2
>>> next(z)
1
>>> type(x)
<class 'list'>
>>> type(y)
<class 'list_iterator'>
Here, x is the iterable, while y and z are two individual instances of an iterator, producing values from the iterable x. Both y and z hold state, as you can see from the example. In this example, x is a data structure (a list), but that is not a requirement.
NOTE:
Often, for pragmatic reasons, iterable classes will implement both__iter__()and__next__()in the same class, and have__iter__()returnself, which makes the class both an iterable and its own iterator. It is perfectly fine to return a different object as the iterator, though.
Finally, when you write:
x = [1, 2, 3]
for elem in x:
...
This is what actually happens:
When you disassemble this Python code, you can see the explicit call to GET_ITER, which is essentially like invoking iter(x). The FOR_ITER is an instruction that will do the equivalent of calling next() repeatedly to get every element, but this does not show from the byte code instructions because it's optimized for speed in the interpreter.
>>> import dis
>>> x = [1, 2, 3]
>>> dis.dis('for _ in x: pass')
1 0 SETUP_LOOP 14 (to 17)
3 LOAD_NAME 0 (x)
6 GET_ITER
>> 7 FOR_ITER 6 (to 16)
10 STORE_NAME 1 (_)
13 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 7
>> 16 POP_BLOCK
>> 17 LOAD_CONST 0 (None)
20 RETURN_VALUE
Iterators
So what is an iterator then? It's a stateful helper object that will produce the next value when you call next() on it. Any object that has a __next__() method is therefore an iterator. How it produces a value is irrelevant.
So an iterator is a value factory. Each time you ask it for "the next" value, it knows how to compute it because it holds internal state.
There are countless examples of iterators. All of the itertools functions return iterators. Some produce infinite sequences:
>>> from itertools import count
>>> counter = count(start=13)
>>> next(counter)
13
>>> next(counter)
14
Some produce infinite sequences from finite sequences:
>>> from itertools import cycle
>>> colors = cycle(['red', 'white', 'blue'])
>>> next(colors)
'red'
>>> next(colors)
'white'
>>> next(colors)
'blue'
>>> next(colors)
'red'
Some produce finite sequences from infinite sequences:
>>> from itertools import islice
>>> colors = cycle(['red', 'white', 'blue']) # infinite
>>> limited = islice(colors, 0, 4) # finite
>>> for x in limited: # so safe to use for-loop on
... print(x)
red
white
blue
red
To get a better sense of the internals of an iterator, let's build an iterator producing the Fibonacci numbers:
>>> class fib:
... def __init__(self):
... self.prev = 0
... self.curr = 1
...
... def __iter__(self):
... return self
...
... def __next__(self):
... value = self.curr
... self.curr += self.prev
... self.prev = value
... return value
...
>>> f = fib()
>>> list(islice(f, 0, 10))
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
Note that this class is both an iterable (because it sports an __iter__() method), and its own iterator (because it has a __next__() method).
The state inside this iterator is fully kept inside the prev and curr instance variables, and are used for subsequent calls to the iterator. Every call to next() does two important things:
- Modify its state for the next
next()call; - Produce the result for the current call.
Central idea: a lazy factory
From the outside, the iterator is like a lazy factory that is idle until you ask it for a value, which is when it starts to buzz and produce a single value, after which it turns idle again.
Generators
Finally, we've arrived at our destination! The generators are my absolute favorite Python language feature. A generator is a special kind of iterator—the elegant kind.
A generator allows you to write iterators much like the Fibonacci sequence iterator example above, but in an elegant succinct syntax that avoids writing classes with __iter__() and __next__() methods.
Let's be explicit:
- Any generator also is an iterator (not vice versa!);
- Any generator, therefore, is a factory that lazily produces values.
Here is the same Fibonacci sequence factory, but written as a generator:
>>> def fib():
... prev, curr = 0, 1
... while True:
... yield curr
... prev, curr = curr, prev + curr
...
>>> f = fib()
>>> list(islice(f, 0, 10))
[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
Wow, isn't that elegant? Notice the magic keyword that's responsible for the beauty:
yield
Let's break down what happened here: first of all, take note that fib is defined as a normal Python function, nothing special. Notice, however, that there's no return keyword inside the function body. The return value of the function will be a generator (read: an iterator, a factory, a stateful helper object).
Now when f = fib() is called, the generator (the factory) is instantiated and returned. No code will be executed at this point: the generator starts in an idle state initially. To be explicit: the line prev, curr = 0, 1 is not executed yet.
Then, this generator instance is wrapped in an islice(). This is itself also an iterator, so idle initially. Nothing happens, still.
Then, this iterator is wrapped in a list(), which will consume all of its arguments and build a list from it. To do so, it will start calling next() on the islice() instance, which in turn will start calling next() on our f instance.
But one step at a time. On the first invocation, the code will finally run a bit: prev, curr = 0, 1 gets executed, the while True loop is entered, and then it encounters the yield curr statement. It will produce the value that's currently in the curr variable and become idle again.
This value is passed to the islice() wrapper, which will produce it (because it's not past the 10th value yet), and list can add the value 1 to the list now.
Then, it asks islice() for the next value, which will ask f for the next value, which will "unpause" f from its previous state, resuming with the statement prev, curr = curr, prev + curr. Then it re-enters the next iteration of the while loop, and hits the yield curr statement, returning the next value of curr.
This happens until the output list is 10 elements long and when list() asks islice()for the 11th value, islice() will raise a StopIteration exception, indicating that the end has been reached, and list will return the result: a list of 10 items, containing the first 10 Fibonacci numbers. Notice that the generator doesn't receive the 11th next() call. In fact, it will not be used again, and will be garbage collected later.
Types of Generators
There are two types of generators in Python: generator functions and generator expressions. A generator function is any function in which the keyword yield appears in its body. We just saw an example of that. The appearance of the keyword yield is enough to make the function a generator function.
The other type of generators are the generator equivalent of a list comprehension. Its syntax is really elegant for a limited use case.
Suppose you use this syntax to build a list of sqaures:
>>> numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> [x * x for x in numbers]
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
You could do the same thing with a set comprehension:
>>> {x * x for x in numbers}
{1, 4, 36, 9, 16, 25}
Or a dict comprehension:
>>> {x: x * x for x in numbers}
{1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16, 5: 25, 6: 36}
But you can also use a generator expression (note: this is not a tuple comprehension):
>>> lazy_squares = (x * x for x in numbers)
>>> lazy_squares
<generator object <genexpr> at 0x10d1f5510>
>>> next(lazy_squares)
1
>>> list(lazy_squares)
[4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
Note that, because we read the first value from lazy_sqaures with next(), it's state is now at the "second" item, so when we consume it entirely by calling list(), that will only return the partial list of sqaures. (This is just to show the lazy behaviour.) This is as much a generator (and thus, an iterator) as the other examples above.
Summary
Generators are an incredible powerful programming construct. They allow you to write streaming code with fewer intermediate variables and data structures. Besides that, they are more memory and CPU efficient. Finally, they tend to require fewer lines of code, too.
Tip to get started with generators: find places in your code where you do the following:
def something():
result = []
for ... in ...:
result.append(x)
return result
And replace it by:
def iter_something():
for ... in ...:
yield x # def something(): # Only if you really need a list structure
# return list(iter_something())
Python 的关键字 yield 有哪些用法和用途?
Iterables vs. Iterators vs. Generators的更多相关文章
- Python高级特性(1):Iterators、Generators和itertools(转)
译文:Python高级特性(1):Iterators.Generators和itertools [译注]:作为一门动态脚本语言,Python 对编程初学者而言很友好,丰富的第三方库能够给使用者带来很大 ...
- iterators和generators
iterators >>> mylist=[x*x for x in range(3)] >>> mylist [0, 1, 4] generators >& ...
- ES6中的新特性:Iterables和iterators
目录 简介 什么是iteration Iterable对象 普通对象不是可遍历的 自定义iterables 关闭iterators 总结 简介 为了方便集合数据的遍历,在ES6中引入了一个iterat ...
- Python标准模块--Iterators和Generators
1 模块简介 当你开始使用Python编程时,你或许已经使用了iterators(迭代器)和generators(生成器),你当时可能并没有意识到.在本篇博文中,我们将会学习迭代器和生成器是什么.当然 ...
- Python高级特性(1):Iterators、Generators和itertools(参考)
对数学家来说,Python这门语言有着很多吸引他们的地方.举几个例子:对于tuple.lists以及sets等容器的支持,使用与传统数学类 似的符号标记方式,还有列表推导式这样与数学中集合推导式和集的 ...
- 004_Python高级特性(1):Iterators、Generators和itertools(参考)
对数学家来说,Python这门语言有着很多吸引他们的地方.举几个例子:对于tuple.lists以及sets等容器的支持,使用与传统数学类 似的符号标记方式,还有列表推导式这样与数学中集合推导式和集的 ...
- What's the Difference Between Iterators and Generators in Python
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-iterators-and-generators-in-Python
- python模块学习:Iterators和Generators
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhbzz2007/p/6102695.html 1 迭代器: 迭代器,允许你在一个容器上进行迭代的对象. python的迭代器主要是通过__ite ...
- 理解Python迭代对象、迭代器、生成器
作者:zhijun liu链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24376869来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处. 本文源自RQ作 ...
随机推荐
- 机器学习-随机梯度下降(Stochastic gradient descent)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003& ...
- [JUC-2]AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
AbstactQueuedSynchronizer的基本数据结构 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的基本数据结构为Node,关于Node,JDK作者写了详细的注释,这里我大致总结几 ...
- mysql:insert插入数据过慢如何解决,设置innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit为0就能解决
问题: 最近在做性能测试,造数据,发现insert好慢,只有几十条每秒,很奇怪,最后再网上找到了原因. 网文如下: MY SQL insert 速度过慢 最近在用MySQL做存储,测试中发现插入数据太 ...
- [Android] Android 使用 Greendao 操作 db sqlite(2)-- 封装DaoUtils类
继续接上文: Android 使用 Greendao 操作 db sqlite(1)-- 直接在MainActivity中调用 布局文件同上文一致,这里就不贴了. 一.封装DaoUtils类 User ...
- [ASNI C] [常用宏定义] [define技巧]
1. 打印变量名及其值 #define Inquire(var, mode) fprintf(stdout, #var" = "#mode". \n", var ...
- Newtonsoft.Json 的高级用法
Ø 简介 接着前一篇http://www.cnblogs.com/abeam/p/8295765.html,继续研究 Newtonsoft.Json 的一些高级用法.主要包括: 1. JSON ...
- getnameinfo函数
一.函数原型 #include <netdb.h> int getnamefo(const struct sockaddr *sockaddr, socklen_t addrlen, ch ...
- JS创建对象之组合使用构造函数模式和原型模式
function Person(name, age, job) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.friends = { ...
- 简单回射程序之处理accept返回EINTR错误的服务器程序版本
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include <errno.h> ...
- MySQL Out-of-Band 攻击
概述 当涉及到MSSQL与Oracle时,Out-of-Band 注入是非常好的方式.但我注意到MySQL注入的情况并非如此,于是我准备以自己在SQL注入方面的经验做相关的研究.我们可以利用诸如loa ...