剑指 offer 第 2 天
第 2 天
链表(简单)
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
题解思路:辅助栈、反向填充、递归
辅助栈:利用栈先进后出的性质,实现反向节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] print = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
print[i] = stack.pop().val;
}
return print;
}
}
反向填充:反向填充数组下标
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode currNode = head;
int len = 0;
while (currNode != null) {
len ++;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
int[] print = new int[len];
for (int i = len-1; i >= 0; i --) {
print[i] = head.val;
head = head.next;
}
return print;
}
}
递归:利用递归走到链表最后结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ArrayList<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
recur(head, tmp);
int[] res = new int[tmp.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++)
res[i] = tmp.get(i);
return res;
}
void recur(ListNode head, ArrayList<Integer> tmp) {
if(head == null) return;
recur(head.next, tmp);
tmp.add(head.val);
}
}
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 5000
题解思路:辅助栈、递归、迭代
辅助栈:利用栈结构先进后出的特点反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode curr = head;
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode listNode = stack.pop();
ListNode res = listNode;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
listNode.next = stack.pop();
listNode = listNode.next;
listNode.next = null;
}
return res;
}
}
递归:通过递归利用系统栈反转链表,递归到最后一个节点中止,途中完成 head.next.next = head 的交换
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
迭代:通过头插法再次重建链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
// 暂存后续节点
ListNode next = curr.next;
// 修改节点指向
curr.next = prev;
// 暂存当前头节点
prev = curr;
// 访问下一个节点
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
反转链表的题目不止于此,目前常考察的还有区间反转、多次区间反转等
92. 反转链表 II
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
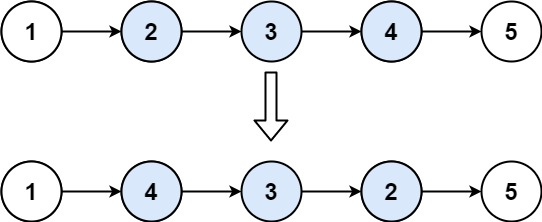
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]
提示:
- 链表中节点数目为
n 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
进阶: 你可以使用一趟扫描完成反转吗?
题解思路:两次遍历、一次遍历
两次遍历:先断链,然后反转中间部分,再接上链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
// 使用额外头节点
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
// 得到left的前一个节点
for (int i = 0; i < left-1; i ++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
// 得到right节点
ListNode rightNode = pre;
for (int i = 0; i < right-left+1; i ++) {
rightNode = rightNode.next;
}
// 截断链表
ListNode leftNode = pre.next;
// 保存rightNode后续节点
ListNode curr = rightNode.next;
// 截断链接
pre.next = null;
rightNode.next = null;
// 反转链表
reverseLinkedList(leftNode);
// 恢复连接
pre.next = rightNode;
leftNode.next = curr;
return dummyNode.next;
}
// 反转链表
private void reverseLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
}
}
复杂度: 时间 O(n) 空间 O(1)
一次遍历:头插法建立链表的方式完成反转
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i ++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode curr = pre.next;
// 步骤记熟即可
for (int i = 0; i < right-left; i ++) {
// 保存后续节点
ListNode next = curr.next;
// 改变当前节点指向
curr.next = next.next;
// 改变next节点指向
next.next = pre.next;
// 改变pre节点指向
pre.next = next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
复杂度: 时间 O(n) 空间 O(1)
25. K 个一组翻转链表
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
进阶:
- 你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
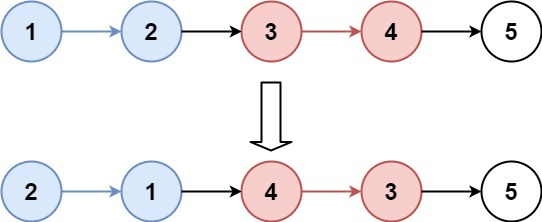
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
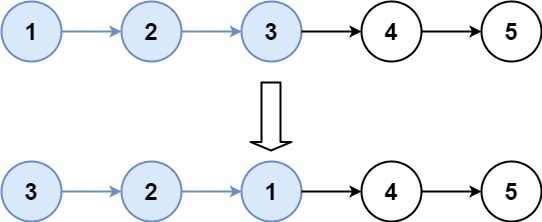
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 4:
输入:head = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
- 列表中节点的数量在范围
sz内 1 <= sz <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 10001 <= k <= sz
题解思路:多次区间反转
多次区间反转:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(-1);
dummyNode.next = head;
// pre 代表待翻转链表的前驱
ListNode pre = dummyNode;
// end 代表待翻转链表的末尾
ListNode end = dummyNode;
while (end.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i ++) {
end = end.next;
}
if (end == null) {
break;
}
// 区间反转类似,保存反转前节点,反转后接上
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(start);
start.next = next;
pre = start;
end = pre;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
复杂度:时间 O(n) 空间 O(1)
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
示例 1:
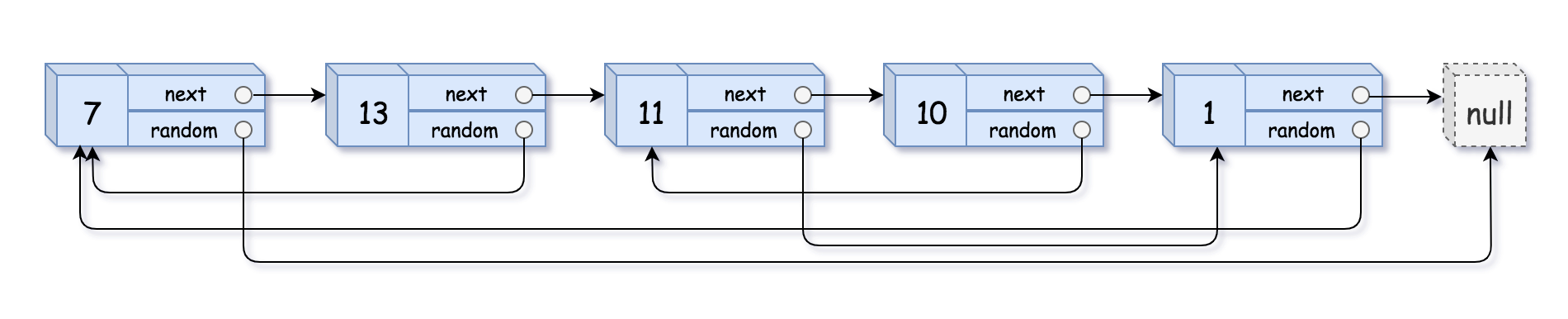
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
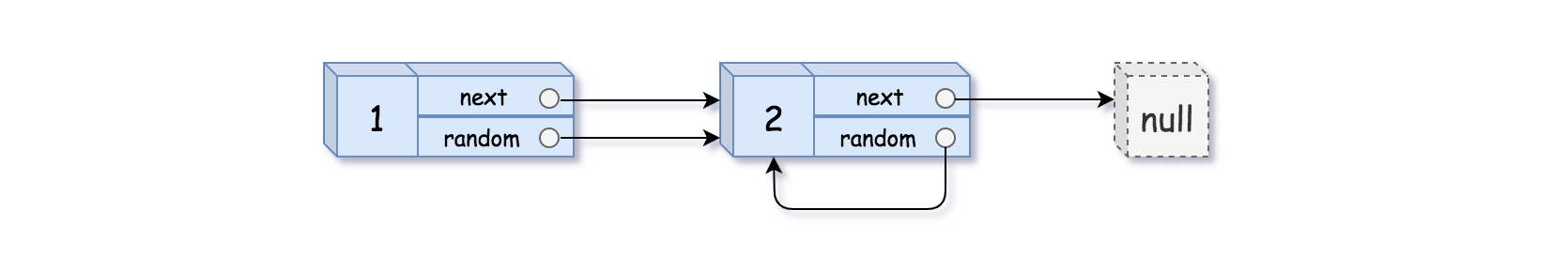
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
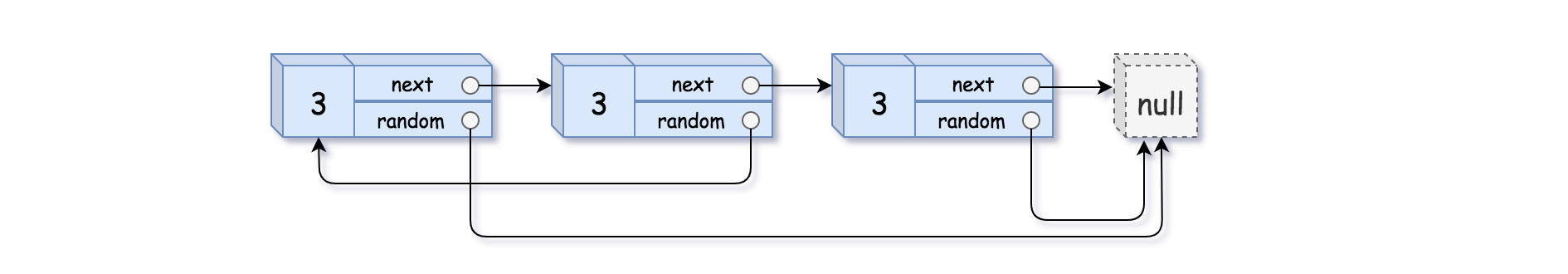
输入:head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
输出:[[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
示例 4:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
解释:给定的链表为空(空指针),因此返回 null。
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。- 节点数目不超过 1000 。
解题思路:哈希表复制、节点拆分
哈希表复制:利用HashMap先存储一次全部节点,再将其取出重建链表即可
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// key存放原节点,value存放待复制节点
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 节点复制val
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
}
// 遍历链表,利用key中原节点信息填充value节点中的next和random
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
// 取出并赋值
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
复杂度:时间 O(n) 空间 O(n)
节点拆分:在每个节点相邻位置创建一个相同节点,先复制 next 和 val 域,再遍历一次复制random域,最后拆分两条链表
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
}
复杂度:时间 O(n) 空间 O(1)
剑指 offer 第 2 天的更多相关文章
- 剑指Offer面试题:1.实现Singleton模式
说来惭愧,自己在毕业之前就该好好看看<剑指Offer>这本书的,但是各种原因就是没看,也因此错过了很多机会,后悔莫及.但是后悔是没用的,现在趁还有余力,把这本书好好看一遍,并通过C#通通实 ...
- 剑指Offer面试题:14.链表的倒数第k个节点
PS:这是一道出境率极高的题目,记得去年参加校园招聘时我看到了3次,但是每次写的都不完善. 一.题目:链表的倒数第k个节点 题目:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点.为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题 ...
- 《剑指offer》面试题12:打印1到最大的n位数
面试题12:打印1到最大的n位数 剑指offer题目12,题目如下 输入数字n,按顺序打印出1到最大的n位十进制数,比如输入3,则打印出1,2,3一直到最大的三位数999 方法一 和面试题11< ...
- 《剑指offer》面试题11: 数值的整数次方
面试题11: 数值的整数次方 剑指offer面试题11,题目如下 实现函数double power(double base,int exponent),求base的exponent次方, 不得使用库 ...
- 剑指 Offer 题目汇总索引
剑指 Offer 总目录:(共50道大题) 1. 赋值运算符函数(或应说复制拷贝函数问题) 2. 实现 Singleton 模式 (C#) 3.二维数组中的查找 4.替换空格 ...
- 面试题目——《剑指Offer》
1.把一个字符串转换成整数——<剑指Offer>P29 2.求链表中的倒数第k个结点——<剑指Offer>P30 3.实现Singleton模式——<剑指Offer> ...
- 剑指offer习题集2
1.把数组排成最小的数 class Solution { public: static bool compare(const string& s1, const string& s2) ...
- 剑指offer习题集1
1.打印二叉树 程序很简单,但是其中犯了一个小错误,死活找不到,写代码要注意啊 这里左右子树,要注意是node->left,结果写成root->left vector<int> ...
- 剑指Offer:面试题20——顺时针打印矩阵(java实现)
题目描述: 输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数 字,例如,如果输入如下矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1, ...
- 牛客网上的剑指offer题目
题目:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序.请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数. 题目:请实现一个函数,将一 ...
随机推荐
- 关于JDK1.8 java HashMap的tableSizeFor的解析:一个数最近2的幂次数方法
简介 一个数的最近2的幂次数,是java hashmap初始化方法指定容量里面对容量进行处理采用的方法 1.位运算符号介绍 符号 描述 运算规则 & 与 两个位都为1时,结果才为1 | 或 两 ...
- sonar使用
代码质量检查工具 sonar 1. 下载,版本sonar 4.5.1 运行bin下的bat文件,浏览器中访问: http://localhost:9000 , 成功. 2. 修改数据库为mysql数据 ...
- 算法题:消除字符串中全部的b和连续的ac
最近碰到了一道面试题,虽然不难但是临试没想出好的解法,记录下来以作分享. 题目:消除字符串中全部的b和连续的ac 用例: 'aabbc' -> 'a' 'aaabbbccc' -> '' ...
- mysql的隔离级别以及存储引擎
一.隔离级别 1.可序列化:(SERIALIZABLE):如果隔离级别为序列化,则用户之间通过一个接一个顺序地执行当前的事务,这种隔离级别提供了事务之间最大限度的隔离. 2.可重复读(REPEATAB ...
- 狐漠漠养成日记 Cp.00002 第一周
主要目标 (1)考研 考研数学二16-22年的真题卷(已完成真题卷:0/7) 记忆考研英语中高频词汇(已记忆词汇:高频:0/10:中频:0/10) 考研英语二16-22年的真题卷(已完成真题卷:0/7 ...
- MySql 自动设置时间(自动获取时间,填充时间)
应用场景: 1.在数据表中,要记录每条数据是什么时候创建的,不需要应用程序去特意记录,而由数据数据库获取当前时间自动记录创建时间: 2.在数据库中,要记录每条数据是什么时候修改的,不需要应用程序去特意 ...
- C++11新特新-varitable template
C++11新特新-varitable template应用 可变参模板原理可以仔细阅读C++primer 第5版相关部分 应用1 一个万用的HashFun 通过不断调用可变模板函数进行参数包的运算,最 ...
- Arduino教程目录
目录 第一节.安装Arduino开发环境 第二节.第一个HelloWorld 第二节续.LED操作 呼吸灯 流水灯 正在加快制作,大家可以先看下面的视频了解基本语法,我准备基础课程和实际项目结合讲解. ...
- Collectors类的静态工厂方法-《Java 8实战》笔记
- Ubuntu 22.04 安装 VMWare 16.2.3 后无法启动
异常日志: 2022-06-13T03:49:56.019Z In(05) host-29676 In file included from /tmp/modconfig-XR2GVI/vmmon-o ...
