高并发压力测试工具Locust(蝗虫)
What is Locust?
Locust is an easy-to-use, distributed, user load testing tool. It is intended for load-testing web sites (or other systems) and figuring out how many concurrent users a system can handle.
The idea is that during a test, a swarm of locusts will attack your website. The behavior of each locust (or test user if you will) is defined by you and the swarming process is monitored from a web UI in real-time. This will help you battle test and identify bottlenecks in your code before letting real users in.
Locust is completely event-based, and therefore it’s possible to support thousands of concurrent users on a single machine. In contrast to many other event-based apps it doesn’t use callbacks. Instead it uses light-weight processes, through gevent. Each locust swarming your site is actually running inside its own process (or greenlet, to be correct). This allows you to write very expressive scenarios in Python without complicating your code with callbacks.
蝗虫是什么?
蝗虫是一个易于使用、分发、用户负载测试工具。它是用于负载测试的网站(或其他系统),弄清楚有多少并发用户系统可以处理。
我们的想法是,在测试期间,一群蝗虫会攻击你的网站。每个蝗虫的行为(或测试用户如果你愿意)被定义为你和聚集过程实时监控从web UI。这将帮助你战斗测试和代码中识别瓶颈之前让真正的用户。
蝗虫是完全基于事件,因此可以支持在单个机器上成千上万的并发用户。与许多其他的基于事件的应用程序不使用回调。相反,它使用轻量级进程,通过gevent。每个蝗虫爬你的网站实际上是运行在它自己的进程(或一种绿色小鸟,是正确的)。这允许您编写非常富有表现力的场景在Python中没有复杂的代码和回调。
Installation
Locust is available on PyPI and can be installed through pip or easy_install
pip install locustio
or:
easy_install locustio
When Locust is installed, a locust command should be available in your shell (if you’re not using virtualenv—which you should—make sure your python script directory is on your path).
To see available options, run:
locust --help
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H HOST, --host=HOST Host to load test in the following format:
http://10.21.32.33
--web-host=WEB_HOST Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to '' (all
interfaces)
-P PORT, --port=PORT, --web-port=PORT
Port on which to run web host
-f LOCUSTFILE, --locustfile=LOCUSTFILE
Python module file to import, e.g. '../other.py'.
Default: locustfile
--master Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as master
--slave Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as slave
--master-host=MASTER_HOST
Host or IP address of locust master for distributed
load testing. Only used when running with --slave.
Defaults to 127.0.0.1.
--master-port=MASTER_PORT
The port to connect to that is used by the locust
master for distributed load testing. Only used when
running with --slave. Defaults to 5557. Note that
slaves will also connect to the master node on this
port + 1.
--master-bind-host=MASTER_BIND_HOST
Interfaces (hostname, ip) that locust master should
bind to. Only used when running with --master.
Defaults to * (all available interfaces).
--master-bind-port=MASTER_BIND_PORT
Port that locust master should bind to. Only used when
running with --master. Defaults to 5557. Note that
Locust will also use this port + 1, so by default the
master node will bind to 5557 and 5558.
--no-web Disable the web interface, and instead start running
the test immediately. Requires -c and -r to be
specified.
-c NUM_CLIENTS, --clients=NUM_CLIENTS
Number of concurrent clients. Only used together with
--no-web
-r HATCH_RATE, --hatch-rate=HATCH_RATE
The rate per second in which clients are spawned. Only
used together with --no-web
-n NUM_REQUESTS, --num-request=NUM_REQUESTS
Number of requests to perform. Only used together with
--no-web
-L LOGLEVEL, --loglevel=LOGLEVEL
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL.
Default is INFO.
--logfile=LOGFILE Path to log file. If not set, log will go to
stdout/stderr
--print-stats Print stats in the console
--only-summary Only print the summary stats
-l, --list Show list of possible locust classes and exit
--show-task-ratio print table of the locust classes' task execution
ratio
--show-task-ratio-json
print json data of the locust classes' task execution
ratio
-V, --version show program's version number and exit
Quick start
Example locustfile.py
Below is a quick little example of a simple locustfile.py:
from locust import HttpLocust, TaskSet def login(l):
l.client.post("/login", {"username":"ellen_key", "password":"education"}) def index(l):
l.client.get("/") def profile(l):
l.client.get("/profile") class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
tasks = {index:2, profile:1} def on_start(self):
login(self) class WebsiteUser(HttpLocust):
task_set = UserBehavior
min_wait = 5000
max_wait = 9000
The HttpLocust class inherits from the Locust class, and it adds a client attribute which is an instance of HttpSession, that can be used to make HTTP requests.
Another way we could declare tasks, which is usually more convenient, is to use the @task decorator. The following code is equivalent to the above:
from locust import HttpLocust, TaskSet, task class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
def on_start(self):
""" on_start is called when a Locust start before any task is scheduled """
self.login() def login(self):
self.client.post("/login", {"username":"ellen_key", "password":"education"}) @task(2)
def index(self):
self.client.get("/") @task(1)
def profile(self):
self.client.get("/profile") class WebsiteUser(HttpLocust):
task_set = UserBehavior
min_wait = 5000
max_wait = 9000
Start Locust
To run Locust with the above locust file, if it was named locustfile.py and located in the current working directory, we could run:
locust --host=http://example.com
If the locust file is located under a subdirectory and/or named different than locustfile.py, specify it using -f:
locust -f locust_files/my_locust_file.py --host=http://example.com
To run Locust distributed across multiple processes we would start a master process by specifying--master:
locust -f locust_files/my_locust_file.py --master --host=http://example.com
and then we would start an arbitrary number of slave processes:
locust -f locust_files/my_locust_file.py --slave --host=http://example.com
If we want to run locust distributed on multiple machines we would also have to specify the master host when starting the slaves (this is not needed when running locust distributed on a single machine, since the master host defaults to 127.0.0.1):
locust -f locust_files/my_locust_file.py --slave --master-host=192.168.0.100 --host=http://example.com
Open up Locust’s web interface
Once you’ve started Locust using one of the above command lines, you should open up a browser and point it to http://127.0.0.1:8089 (if you are running Locust locally). Then you should be greeted with something like this:
from locust import HttpLocust, TaskSet, task class WebSite(TaskSet):
def on_start(self):
self.login() def login(self):
login_data = {'log':'admin','pwd':'admin'}
res = self.client.post('/wordpress/wp-login.php',login_data) @task()
def create_task(self):
self.client.get("/") @task(1)
def profile(self):
res = self.client.get("/wordpress/wp-admin")
print res.urlclass Wordpress(HttpLocust):
task_set = WebSite
min_wait = 1000
max_wait = 1000
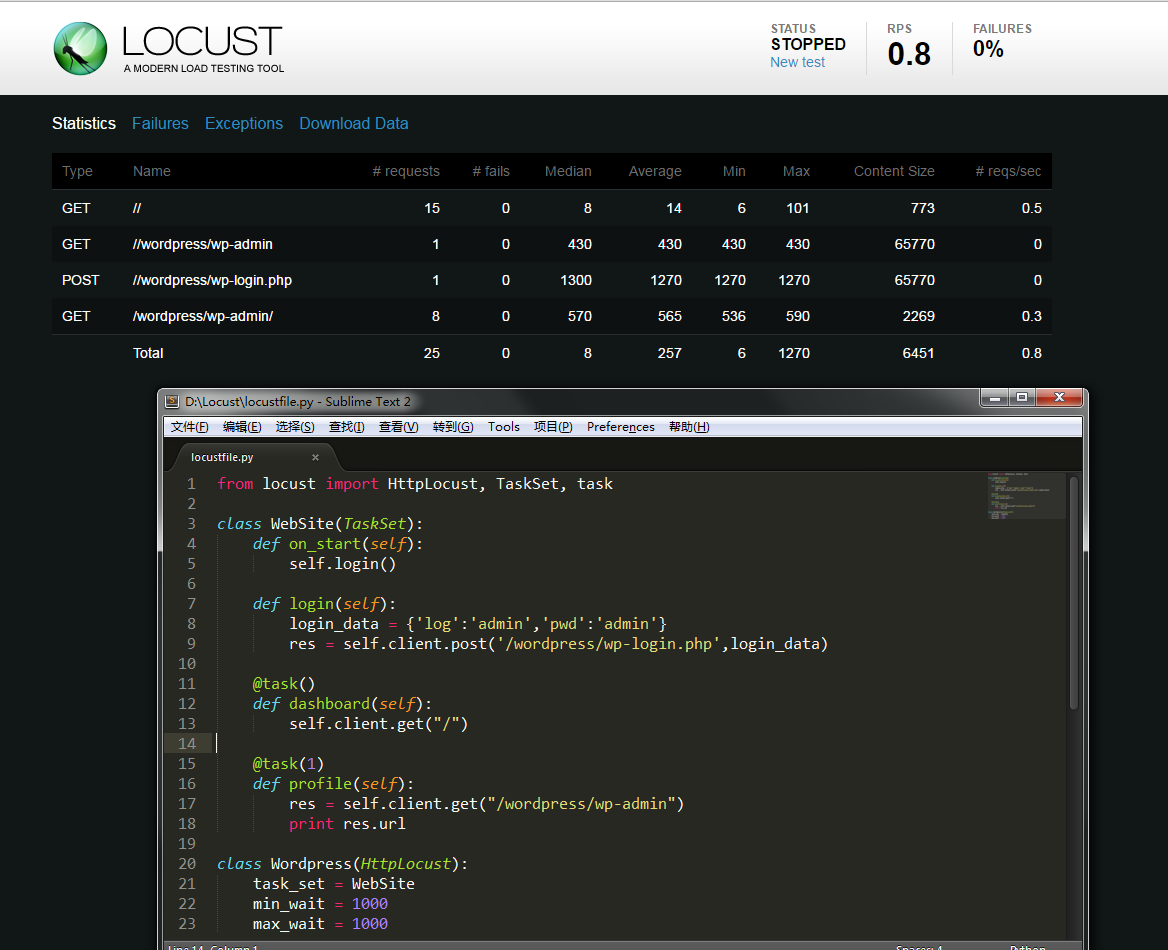
蝗虫比Jmeter好的一点就是 高并发,但是相对的不好的地方也有,就是需要另外的工具去监控服务器,而且需要去编写代码,
locust还需要再去深入研究琢磨,Locust使用好了 是一款非常强大的性能测试工具
http://docs.locust.io/en/latest/
高并发压力测试工具Locust(蝗虫)的更多相关文章
- 面向Web应用的并发压力测试工具——Locust实用攻略
1. 概述 该方案写作目的在于描述一个基于Locust实现的压力测试,文中详细地描述了如何利用locustfile.py文件定义期望达成的测试用例,并利用Locust对目标站点进行并发压力测试. 特别 ...
- 6步完成压力测试工具Locust部署和使用
1,准备安装python,安装过程略 已安装的,查看安装目录: cmd输入where Python 2,pip安装locust 1.进入python所在目录,如果没有配置环境变量,需要进入到C:\Us ...
- HTTP压力测试工具
HttpTest4Net是一款基于C#实现的和HTTP压力测试工具,通过工具可以简单地对HTTP服务进行一个压力测试.虽然VS.NET也集成了压力测试项目,但由于VS自身占用的资源导致了在配置不高的P ...
- Http压力测试工具HttpTest4Net
HttpTest4Net是一款基于C#实现的和HTTP压力测试工具,通过工具可以简单地对HTTP服务进行一个压力测试.虽然VS.NET也集成了压力测试项目,但由于VS自身占用的资源导致了在配置不高的P ...
- Linux下进行Web服务器压力(并发)测试工具http_load、webbench、ab、Siege、autobench简单使用教程(转)
一.http_load 程序非常小,解压后也不到100K http_load以并行复用的方式运行,用以测试web服务器的吞吐量与负载.但是它不同于大多数压力测试工 具,它可以以一个单一的进程运行,一般 ...
- 压力测试工具ab,wrk,locust简介
ab 无疑是目前最常见的压力测试工具.其典型用法如下: shell> ab -k -c 100 -t 10 http://domain/path 其中,参数「c」表示的是并发, 参数「t」表示的 ...
- Apache压力(并发)测试工具ab的使用教程收集
说明:用ab的好处,在处理多并发的情况下不用自己写线程模拟.其实这个世界除了LoadRunner之外还是有很多方案可以选择的. 官网: http://httpd.apache.org/(Apache服 ...
- 九款Web服务器性能压力测试工具
一.http_load 程序非常小,解压后也不到100Khttp_load以并行复用的方式运行,用以测试web服务器的吞吐量与负载.但是它不同于大多数压力测试工具,它可以以一个单一的进程运行,一般不会 ...
- Linux下四款Web服务器压力测试工具(http_load、webbench、ab、siege)介绍
一.http_load程序非常小,解压后也不到100Khttp_load以并行复用的方式运行,用以测试web服务器的吞吐量与负载.但是它不同于大多数压力测试工具,它可以以一个单一的进程运行,一般不会把 ...
随机推荐
- Webstorm设置Node.js智能提示
这两天在学习Node.js,在Webstorm上进行编辑时发现竟然没有智能提示!所以写这篇文章来帮助大家度过这个坑! File -> Settings -> Languages&F ...
- 【WPF】推荐一款拖拉缩放控件的DEMO
引言 在CodeProject上有个实现了控件拖拉缩放的DEMO,界面很漂亮,里面对Thumb和Adorner运用得很精彩.我觉得,使用WPF的开发者都可以去学习一下.下面放出链接. WPF Diag ...
- hbase_异常_04_util.FSUtils: Waiting for dfs to exit safe mode...
一.异常现象 启动hbase的时,hbase的日志中可以发现: Waiting for dfs to exit safe mode... 然后就抛异常了 2018-03-22 17:00:28,994 ...
- XML DOM学习
XML 文档对象模型定义访问和操作XML文档的标准方法. XML DOM 是 XML Document Object Model 的缩写,即 XML 文档对象模型. DOM 将 XML 文档作为一个树 ...
- JavaScript--收藏栏添加按钮,放大hdu题目字体
觉得HDOJ的题目字体太小了,一波小操作 在收藏栏添加:添加网页->网址改为: javascript: void((function() { var element = document.get ...
- Network Saboteur (深搜递归思想的特殊使用)
个人心得:对于深搜的使用还是不到位,对于递归的含义还是不太清楚!本来想着用深搜构成一个排列,然后从一到n分割成俩个数组,然后后面发现根本实现不了,思路太混乱.后来借鉴了网上的思想,发现用数组来标志,当 ...
- [独孤九剑]Oracle知识点梳理(五)数据库常用对象之Table、View
本系列链接导航: [独孤九剑]Oracle知识点梳理(一)表空间.用户 [独孤九剑]Oracle知识点梳理(二)数据库的连接 [独孤九剑]Oracle知识点梳理(三)导入.导出 [独孤九剑]Oracl ...
- 类和对象(12)—— this指针
首先,我们都知道类的成员函数可以访问类的数据(限定符只是限定于类外的一些操作,类内的一切对于成员函数来说都是透明的),那么成员函数如何知道哪个对象的数据成员要被操作呢,原因在于每个对象都拥有一个指针: ...
- C++对C语言的拓展(2)—— inline内联函数
C语言中有宏函数的概念.宏函数的特点是内嵌到调用代码中去,避免了函数调用 的开销.但是由于宏函数的处理发生在预处理阶段,缺失了语法检测和有可能带来的语意差错. 1.内联函数基本概念 C++提供了 in ...
- Python函数-all()
all(iterable) 作用: 如果iterable的所有元素不为0.''.False或者iterable为空,all(iterable)返回True,否则返回False:函数等价于: def a ...

