HttpClient 源码阅读
在项目中常用的HttpClient,与我们非常的亲密,为了能处理遇到的Http问题,我们应该去了解里面的机制和实现。
官方文档:http://hc.apache.org/httpcomponents-client-ga/tutorial/html/
Maven
<!-- components.httpclient-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.5</version>
</dependency>
HttpClient的看点主要是它的责任链设计、连接池机制、工具类的封装,个人觉得它设计得还比较优雅。
我们从一个简单的Http请求,就可以步步深入得去阅读它的源码。
HttpGet get = new HttpGet("http://localhost:8080/hello/say");
RequestConfig config = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(3000)
.setSocketTimeout(3000)
.build();
get.setConfig(config);
HttpClient client = HttpClientBuilder.create()
.setMaxConnTotal(1<<6)
.setMaxConnPerRoute(1<<3)
.evictExpiredConnections()
.build();
HttpResponse response = client.execute(get);
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
首先,发起一个Get请求,它先要实例化请求方法,然后设置请求的配置(连接时间、读取时间)等,然后使用HttpClient的Builder实例化一个按照你配置的HttpClient,最后发起请求拿到响应,在解析响应的时候,它提供了EntityUtils帮你解析响应体。
当我们从它的execute方法进去的时候,它是一个抽象类CloseableHttpClient;它封装了各式各样发起请求的方法,可以说是走入核心之前的外部接口封装,它的真正功能在doExecute方法里面,这个方法是抽象的,取决与Builder在创建实例的时候,实现类或者内部类实现的这个方法。
我们通过debug可以知道,它实际上是走入了InternalHttpClient中,这个时候已经走入了责任链的头部了,开始走入设计者想好的路径了;这个类的主要作用是封装内部调用使用的Request和Config,在它的return方法中,可以看出它将走入下一个execChain。
protected CloseableHttpResponse doExecute(HttpHost target, HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws IOException, ClientProtocolException {
Args.notNull(request, "HTTP request");
HttpExecutionAware execAware = null;
if(request instanceof HttpExecutionAware) {
execAware = (HttpExecutionAware)request;
}
try {
HttpRequestWrapper wrapper = HttpRequestWrapper.wrap(request, target);
HttpClientContext localcontext = HttpClientContext.adapt((HttpContext)(context != null?context:new BasicHttpContext()));
RequestConfig config = null;
if(request instanceof Configurable) {
config = ((Configurable)request).getConfig();
}
if(config == null) {
HttpParams params = request.getParams();
if(params instanceof HttpParamsNames) {
if(!((HttpParamsNames)params).getNames().isEmpty()) {
config = HttpClientParamConfig.getRequestConfig(params, this.defaultConfig);
}
} else {
config = HttpClientParamConfig.getRequestConfig(params, this.defaultConfig);
}
}
if(config != null) {
localcontext.setRequestConfig(config);
}
this.setupContext(localcontext);
HttpRoute route = this.determineRoute(target, wrapper, localcontext);
return this.execChain.execute(route, wrapper, localcontext, execAware);
} catch (HttpException var9) {
throw new ClientProtocolException(var9);
}
}
再往下走,它将走入RetryClient;这个类的主要作用是控制重试,当下层链出现超时的时候会进行重试。这个重试的次数是之前你创建实例的时候可以指定的,没有指定它也有默认值。
@Override
public CloseableHttpResponse execute(
final HttpRoute route,
final HttpRequestWrapper request,
final HttpClientContext context,
final HttpExecutionAware execAware) throws IOException, HttpException {
Args.notNull(route, "HTTP route");
Args.notNull(request, "HTTP request");
Args.notNull(context, "HTTP context");
final Header[] origheaders = request.getAllHeaders();
for (int execCount = 1;; execCount++) {
try {
return this.requestExecutor.execute(route, request, context, execAware);
} catch (final IOException ex) {
if (execAware != null && execAware.isAborted()) {
this.log.debug("Request has been aborted");
throw ex;
}
if (retryHandler.retryRequest(ex, execCount, context)) {
if (this.log.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.log.info("I/O exception ("+ ex.getClass().getName() +
") caught when processing request to "
+ route +
": "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (!RequestEntityProxy.isRepeatable(request)) {
this.log.debug("Cannot retry non-repeatable request");
throw new NonRepeatableRequestException("Cannot retry request " +
"with a non-repeatable request entity", ex);
}
request.setHeaders(origheaders);
if (this.log.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.log.info("Retrying request to " + route);
}
} else {
if (ex instanceof NoHttpResponseException) {
final NoHttpResponseException updatedex = new NoHttpResponseException(
route.getTargetHost().toHostString() + " failed to respond");
updatedex.setStackTrace(ex.getStackTrace());
throw updatedex;
} else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
}
继续往下,它到达了MainClientExec类;这个类厉害了,控制着连接池的获取、socket连接的建立、链接的释放,可以说是HttpClient的核心了。它的下层调用是HttpRequestExecutor,里面控制着Http请求头的发送,Http Request Line的发送,以及响应的收集。至此,我们可以梳理一个路径。
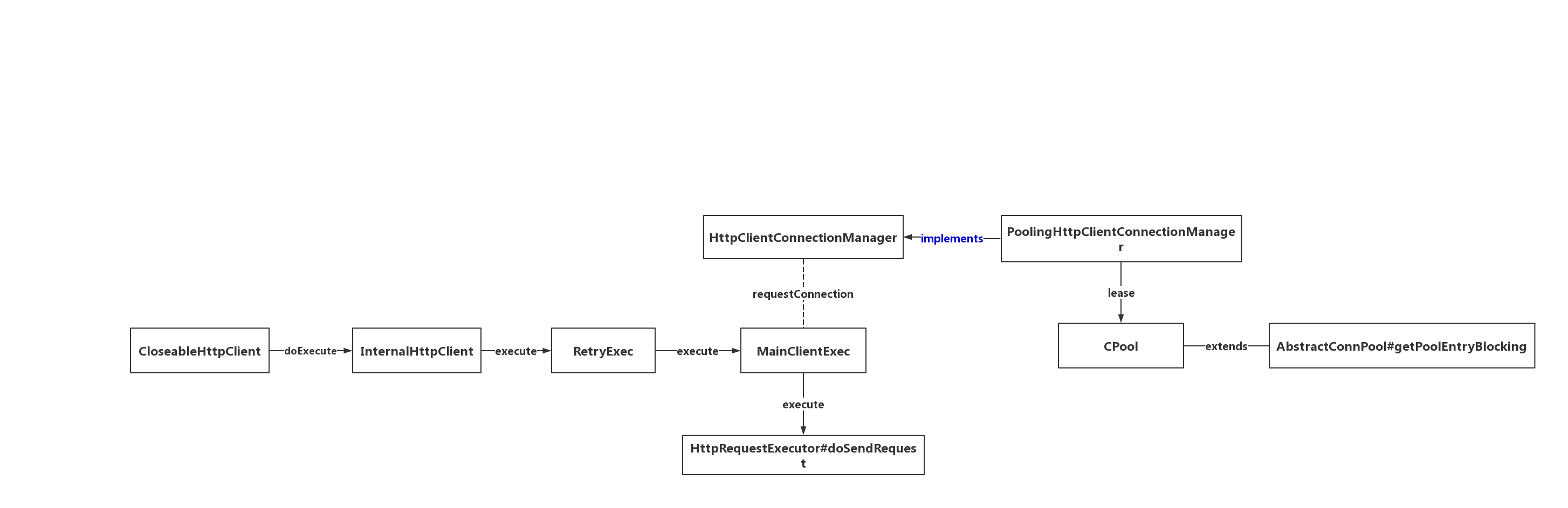
它使用了责任链进行拼装,并且每个链条上的抽象很干净,只做它负责的范围的工作。而它们这个链条的形成,是在builder里面组装的。
我们把调用链抽象出来,结合builder,它的设计是比较优雅的。
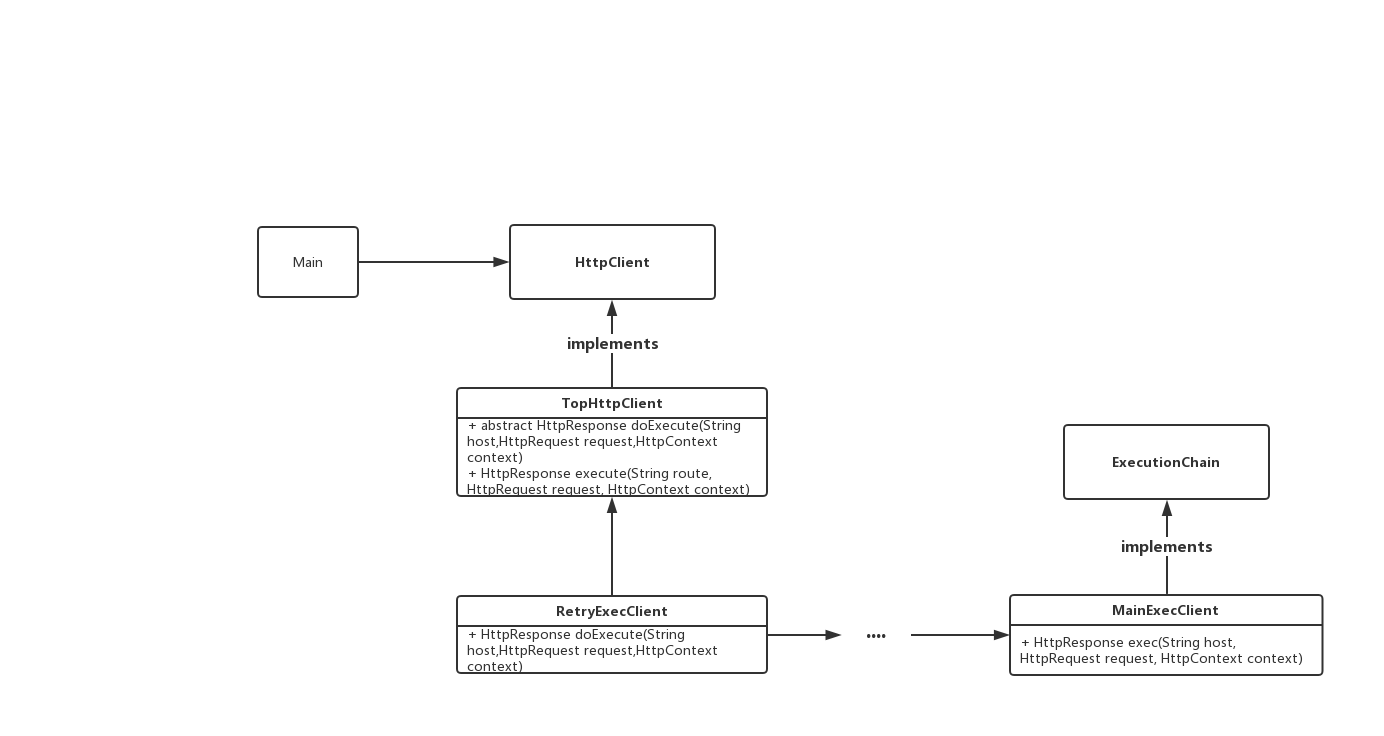
package execChain;
public interface ExecutionChain {
HttpResponse exec(String host,HttpRequest request,HttpContext context);
}
package execChain;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface HttpClient {
HttpResponse execute(String route,HttpRequest request,HttpContext context)
throws IOException;
}
package execChain;
import java.io.IOException;
public abstract class TopHttpClient implements HttpClient{
protected abstract HttpResponse doExecute(String host,HttpRequest request,HttpContext context);
@Override
public HttpResponse execute(String route, HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) throws IOException {
return doExecute(route,request,context);
}
}
package execChain;
public class RetryExecClient extends TopHttpClient{
private ExecutionChain requestExecChain;
public RetryExecClient(ExecutionChain requestExecChain) {
this.requestExecChain = requestExecChain;
}
@Override
protected HttpResponse doExecute(String host, HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) {
return this.requestExecChain.exec(host,request,context);
}
}
package execChain;
public class MainExecClient implements ExecutionChain{
@Override
public HttpResponse exec(String host, HttpRequest request, HttpContext context) {
System.out.println("host : "+host);
return new HttpResponse();
}
}
package execChain;
public class MyHttpClientBuilder {
public static MyHttpClientBuilder create() {
return new MyHttpClientBuilder();
}
public TopHttpClient build(){
MainExecClient client = new MainExecClient();
// append chain ....
return new RetryExecClient(client);
}
}
TopHttpClient client = MyHttpClientBuilder.create().build();
client.execute("http://www.baidu.com",new HttpRequest(),new HttpContext());
有关连接池的操作,是在PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager里边,它把对链接的申请称呼为lease,也就是租借的意思。
@Override
public ConnectionRequest requestConnection(
final HttpRoute route,
final Object state) {
Args.notNull(route, "HTTP route");
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug("Connection request: " + format(route, state) + formatStats(route));
}
final Future<CPoolEntry> future = this.pool.lease(route, state, null);
return new ConnectionRequest() { @Override
public boolean cancel() {
return future.cancel(true);
} @Override
public HttpClientConnection get(
final long timeout,
final TimeUnit tunit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, ConnectionPoolTimeoutException {
final HttpClientConnection conn = leaseConnection(future, timeout, tunit);
if (conn.isOpen()) {
final HttpHost host;
if (route.getProxyHost() != null) {
host = route.getProxyHost();
} else {
host = route.getTargetHost();
}
final SocketConfig socketConfig = resolveSocketConfig(host);
conn.setSocketTimeout(socketConfig.getSoTimeout());
}
return conn;
} }; }
我们观察到它的池子pool是CPool这个类,它的继承关系如下。
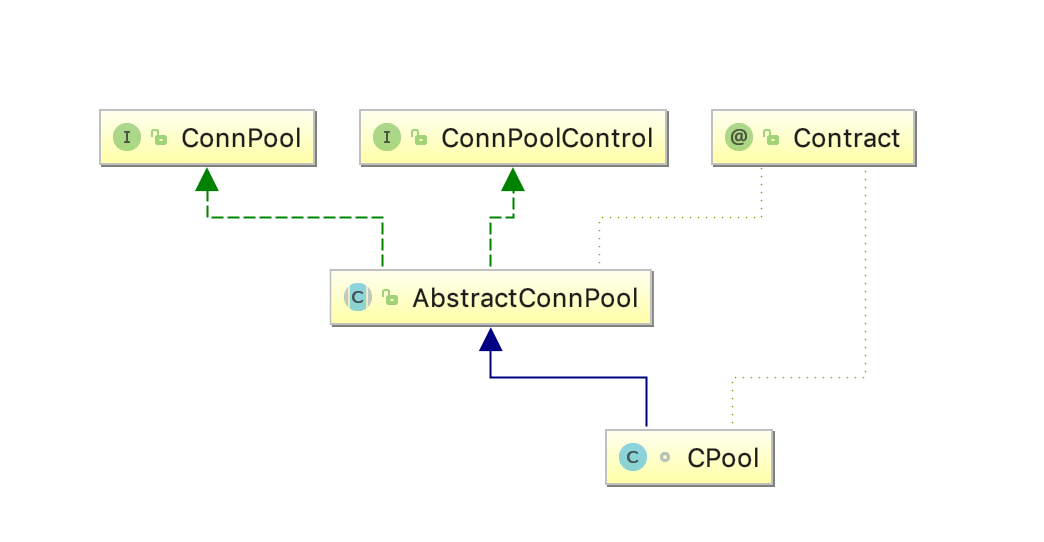
发现大部分的逻辑实在AbstractConnPool里边,租借的时候走了这个方法org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool#getPoolEntryBlocking。在这个方法中,我们发现它往一个RouteSpecificPool中通过route获取了一个池子。
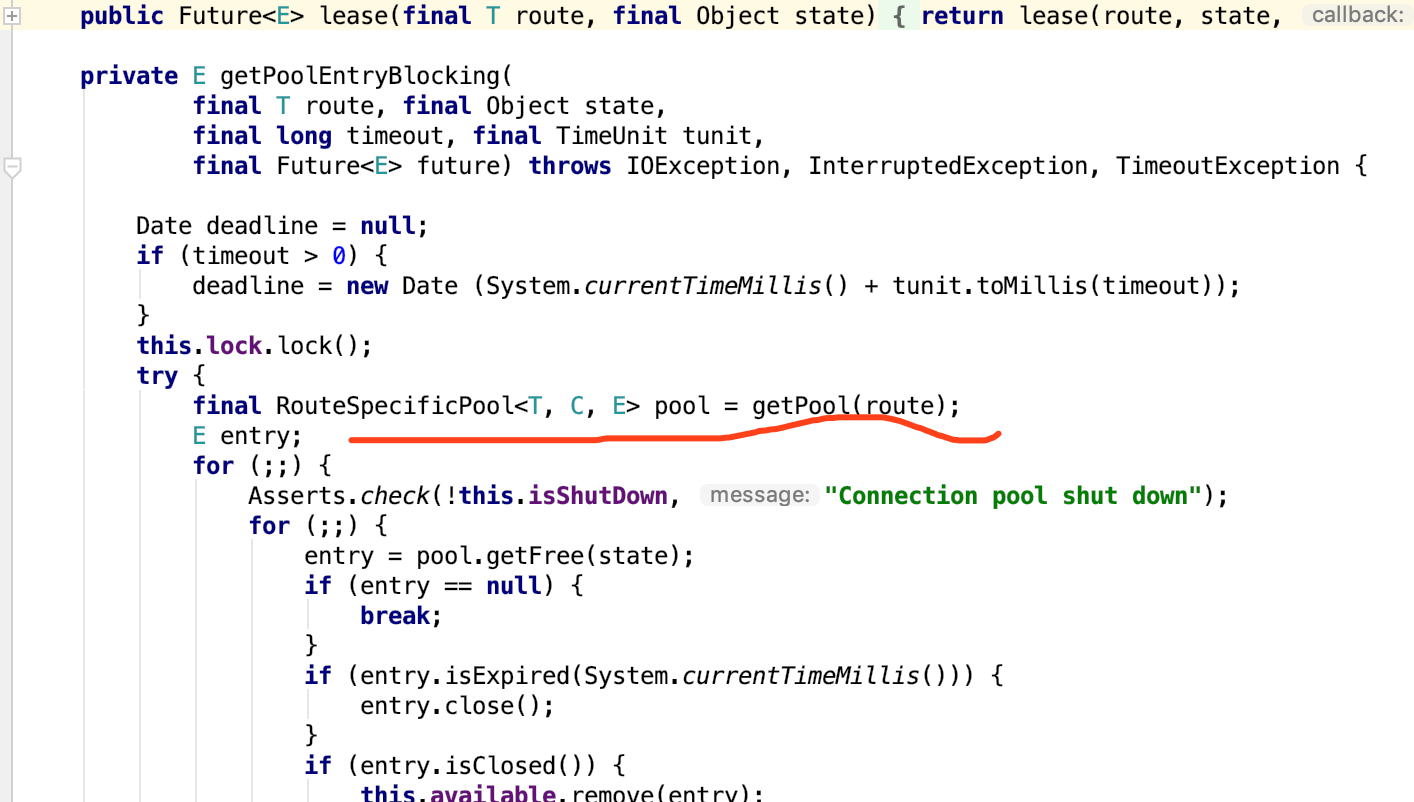
然后进去看到它池子的定义,结合代码可以看出,它把链接的状态分为:已租借、可用链接、等待三种状态。梳理了一下lease方法,它是将avalible的链接拿出来放到lease中,如果可用队列没有链接,那它将创建一个并放入租借队列,这里如果它这个route的连接数超过了你设置的MaxPerRoute配置,那么它将会方法pending队列,并且await当前线程,直到有hold链接的线程调用了releaseConnection等方法才会被notify。

这个getPoolEntityBlocking方法,就是申请连接池链接的核心代码了。
private E getPoolEntryBlocking(
final T route, final Object state,
final long timeout, final TimeUnit tunit,
final Future<E> future) throws IOException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException { Date deadline = null;
if (timeout > 0) {
deadline = new Date (System.currentTimeMillis() + tunit.toMillis(timeout));
}
this.lock.lock();
try {
final RouteSpecificPool<T, C, E> pool = getPool(route);
E entry;
for (;;) {
Asserts.check(!this.isShutDown, "Connection pool shut down");
for (;;) {
entry = pool.getFree(state);
if (entry == null) {
break;
}
if (entry.isExpired(System.currentTimeMillis())) {
entry.close();
}
if (entry.isClosed()) {
this.available.remove(entry);
pool.free(entry, false);
} else {
break;
}
}
if (entry != null) {
this.available.remove(entry);
this.leased.add(entry);
onReuse(entry);
return entry;
} // New connection is needed
final int maxPerRoute = getMax(route);
// Shrink the pool prior to allocating a new connection
final int excess = Math.max(0, pool.getAllocatedCount() + 1 - maxPerRoute);
if (excess > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < excess; i++) {
final E lastUsed = pool.getLastUsed();
if (lastUsed == null) {
break;
}
lastUsed.close();
this.available.remove(lastUsed);
pool.remove(lastUsed);
}
} if (pool.getAllocatedCount() < maxPerRoute) {
final int totalUsed = this.leased.size();
final int freeCapacity = Math.max(this.maxTotal - totalUsed, 0);
if (freeCapacity > 0) {
final int totalAvailable = this.available.size();
if (totalAvailable > freeCapacity - 1) {
if (!this.available.isEmpty()) {
final E lastUsed = this.available.removeLast();
lastUsed.close();
final RouteSpecificPool<T, C, E> otherpool = getPool(lastUsed.getRoute());
otherpool.remove(lastUsed);
}
}
final C conn = this.connFactory.create(route);
entry = pool.add(conn);
this.leased.add(entry);
return entry;
}
} boolean success = false;
try {
if (future.isCancelled()) {
throw new InterruptedException("Operation interrupted");
}
pool.queue(future);
this.pending.add(future);
if (deadline != null) {
success = this.condition.awaitUntil(deadline);
} else {
this.condition.await();
success = true;
}
if (future.isCancelled()) {
throw new InterruptedException("Operation interrupted");
}
} finally {
// In case of 'success', we were woken up by the
// connection pool and should now have a connection
// waiting for us, or else we're shutting down.
// Just continue in the loop, both cases are checked.
pool.unqueue(future);
this.pending.remove(future);
}
// check for spurious wakeup vs. timeout
if (!success && (deadline != null && deadline.getTime() <= System.currentTimeMillis())) {
break;
}
}
throw new TimeoutException("Timeout waiting for connection");
} finally {
this.lock.unlock();
}
}
回过头来,在MainClient里边的这一行,是建立Tcp链接的代码。
他们将链接的各种类型作为一种常量也可以说是一种枚举,然后通过while循环全部处理,这里边的状态跳转就不理了。
/** Indicates that the route can not be established at all. */
public final static int UNREACHABLE = -1; /** Indicates that the route is complete. */
public final static int COMPLETE = 0; /** Step: open connection to target. */
public final static int CONNECT_TARGET = 1; /** Step: open connection to proxy. */
public final static int CONNECT_PROXY = 2; /** Step: tunnel through proxy to target. */
public final static int TUNNEL_TARGET = 3; /** Step: tunnel through proxy to other proxy. */
public final static int TUNNEL_PROXY = 4; /** Step: layer protocol (over tunnel). */
public final static int LAYER_PROTOCOL = 5;
/**
* Establishes the target route.
*/
void establishRoute(
final AuthState proxyAuthState,
final HttpClientConnection managedConn,
final HttpRoute route,
final HttpRequest request,
final HttpClientContext context) throws HttpException, IOException {
final RequestConfig config = context.getRequestConfig();
final int timeout = config.getConnectTimeout();
final RouteTracker tracker = new RouteTracker(route);
int step;
do {
final HttpRoute fact = tracker.toRoute();
step = this.routeDirector.nextStep(route, fact); switch (step) { case HttpRouteDirector.CONNECT_TARGET:
this.connManager.connect(
managedConn,
route,
timeout > 0 ? timeout : 0,
context);
tracker.connectTarget(route.isSecure());
break;
case HttpRouteDirector.CONNECT_PROXY:
this.connManager.connect(
managedConn,
route,
timeout > 0 ? timeout : 0,
context);
final HttpHost proxy = route.getProxyHost();
tracker.connectProxy(proxy, false);
break;
case HttpRouteDirector.TUNNEL_TARGET: {
final boolean secure = createTunnelToTarget(
proxyAuthState, managedConn, route, request, context);
this.log.debug("Tunnel to target created.");
tracker.tunnelTarget(secure);
} break; case HttpRouteDirector.TUNNEL_PROXY: {
// The most simple example for this case is a proxy chain
// of two proxies, where P1 must be tunnelled to P2.
// route: Source -> P1 -> P2 -> Target (3 hops)
// fact: Source -> P1 -> Target (2 hops)
final int hop = fact.getHopCount()-1; // the hop to establish
final boolean secure = createTunnelToProxy(route, hop, context);
this.log.debug("Tunnel to proxy created.");
tracker.tunnelProxy(route.getHopTarget(hop), secure);
} break; case HttpRouteDirector.LAYER_PROTOCOL:
this.connManager.upgrade(managedConn, route, context);
tracker.layerProtocol(route.isSecure());
break; case HttpRouteDirector.UNREACHABLE:
throw new HttpException("Unable to establish route: " +
"planned = " + route + "; current = " + fact);
case HttpRouteDirector.COMPLETE:
this.connManager.routeComplete(managedConn, route, context);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown step indicator "
+ step + " from RouteDirector.");
} } while (step > HttpRouteDirector.COMPLETE);
}
最近遇到了一个问题,设置了最大超时时间为5s,但是由于触发了某种条件,监控显示Http调用有长达12s也能成功的,因为阅读了源码,所以马上想到了是连接池的PerRoute设置得太小了,导致同一域名的请求超过了这个设置,引起了线程的await事件,所以Http层面的超时时间只能保证通信的超时,如果触发了线程排队,那么设置的超时时间并没有生效,而且在源码中也没找到能快速失败的路径,正在寻找这一问题的解决方案。
HttpClient 源码阅读的更多相关文章
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(四)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(四) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇还遗留了很多问题,包括AFURLSessionManagerTaskDe ...
- 【原】FMDB源码阅读(三)
[原]FMDB源码阅读(三) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 FMDB比较优秀的地方就在于对多线程的处理.所以这一篇主要是研究FMDB的多线程处理的实现.而 ...
- 【原】FMDB源码阅读(二)
[原]FMDB源码阅读(二) 本文转载请注明出处 -- polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇只是简单地过了一下FMDB一个简单例子的基本流程,并没有涉及到FMDB的所有方方面面,比 ...
- 【原】FMDB源码阅读(一)
[原]FMDB源码阅读(一) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 说实话,之前的SDWebImage和AFNetworking这两个组件我还是使用过的,但是对于 ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(六)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(六) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 这一篇的想讲的,一个就是分析一下AFSecurityPolicy文件,看看AF ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(五)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(五) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇中提及到了Multipart Request的构建方法- [AFHTTP ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(三)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(三) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇的话,主要是讲了如何通过构建一个request来生成一个data tas ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(二)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(二) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇中我们在iOS Example代码中提到了AFHTTPSessionMa ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(一)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(一) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 AFNetworking版本:3.0.4 由于我平常并没有经常使用AFNetw ...
随机推荐
- Hive explode
- Spark算子与RDD基本转换
map 将一个RDD中的每个数据项,通过map中的函数映射变为一个新的元素. 输入分区与输出分区一对一,即:有多少个输入分区,就有多少个输出分区. flatMap 属于Transformation算子 ...
- Java Unsigned Bytes
Having had to use unsigned bytes for the first time, I also had to learn how Java references these d ...
- 使用rabbit mq.模拟dubbo,使MQ异步调用代码写起来像是同步方法.
最近在改造老系统,遇到了需要使用rabbitMq的场景.在以前使用的过程中需要在发送端和消费端各种配置,感觉比较麻烦,然后突然想到了dubbo中@Reference注解的形式,可不可以做一个类似的架子 ...
- vue中自定义指令的使用
原文地址 vue中除了内置的指令(v-show,v-model)还允许我们自定义指令 想要创建自定义指令,就要注册指令(以输入框获取焦点为例) 一.注册全局指令: // 注册一个全局自定义指令 `v- ...
- sql server 备份语句
1.BACKUP DATABASE your_database TO DISK = 'diff.bak'with DIFFERENTIAL #差异备份,仅备份数据2.BACKUP DATABASE y ...
- dfs入门-cogs1640[黑白图像]
题目链接:http://cogs.pro:8081/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=vxSmxkeqa [题目描述] 输入一个n×n的黑白图像(1表示黑色,0表示白色),任务 ...
- Windows Server 2019远程桌面服务配置和授权激活
参考Windows Server 2016远程桌面服务配置和授权激活方法可适用于Windows Server 2019 Server 2016默认远程桌面连接数是2个用户,如果多余两个用户进行 ...
- python安装第三方库报错:Cannot uninstall '***'. It is a distutils installed project and thus we cannot accurately determine which files belong to it which would lead to only a partial uninstall.
pip install --ignore-installed ${PACKAGE_NAME}
- C#规范整理·资源管理和序列化
资源管理(尤其是内存回收)曾经是程序员的噩梦,不过在.NET平台上这个噩梦似乎已经不复存在.CLR在后台为垃圾回收做了很多事情,使得我们现在谈起在.NET上进行开发时,都会说还是new一个对象吧!回收 ...
