Hdu.1325.Is It A Tree?(并查集)
Is It A Tree?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s): 16702 Accepted Submission(s): 3761
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
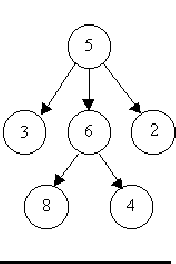
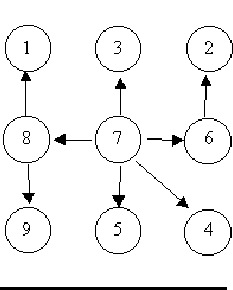
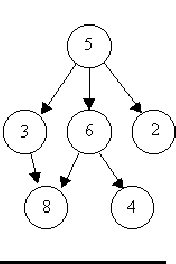 In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not. 5 6 0 0
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
const int M = + ;
int f[M] ;
int path[M] ;
int in[M] ;
bool vis[M] ; int Union (int x)
{
return x == f[x] ? x : f[x] = Union (f[x]) ;
}
int main ()
{
freopen ("a.txt" , "r" , stdin ) ;
int u , v ;
int cas = ;
while (~ scanf ("%d%d" , &u , &v)) {
if (u < || v < ) break ;
for (int i = ; i < M ; i ++) f[i] = i ;
memset (vis , , sizeof(vis));
memset (in , , sizeof(in)) ;
int tot = ;
if (!vis[u]) {
vis[u] = ;
path[tot ++] = u ;
}
if (!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = ;
path[tot ++] = v ;
}
in[v] ++ ;
// printf ("%d ----> %d\n" , u , v);
int x = Union (u) , y = Union (v) ;
f[y] = x ;
if (u != && v != ) {
while () {
scanf ("%d%d" , &u , &v) ;
// printf ("%d ----> %d\n" , u , v);
if (u == && v == ) break ;
if (!vis[u]) {
vis[u] = ;
path[tot ++] = u ;
}
if (!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = ;
path[tot ++] = v ;
}
in[v] ++ ;
int x = Union (u) , y = Union (v) ;
f[y] = x ;
}
for (int i = ; i < tot ; i ++) Union (path[i]) ;
// for (int i = 0 ; i < tot ; i ++) printf ("%d " , path[i]) ; puts ("") ;
// for (int i = 0 ; i < tot ; i ++) printf ("%d " , in[path[i]]); puts ("") ;
// for (int i = 0 ; i < tot ; i ++) printf ("%d " , f[path[i]]) ; puts ("") ;
bool flag = ;
int cnt = ;
int father = f[path[]] ;
for (int i = ; i < tot && !flag; i ++)
if (f[path[i]] != father )
flag = ; for (int i = ; i < tot && !flag ; i ++) {
if (in[path[i]] > ) flag = ;
if (in[path[i]] == ) cnt ++ ;
if (cnt > ) flag = ;
}
if (cnt == ) flag = ;
// printf ("flag = %d\n" , flag );
if (flag) printf ("Case %d is not a tree.\n" , cas ++);
else printf ("Case %d is a tree.\n" , cas ++) ;
}
else printf ("Case %d is a tree.\n" , cas ++) ;
}
return ;
}
检查入度,和每个结点的祖先。
终于解决了并查集压缩路径的不完全的问题。hahahaha。。。
另外没有结点,也被认为是树。
Hdu.1325.Is It A Tree?(并查集)的更多相关文章
- hdu 1325 Is It A Tree? 并查集
Is It A Tree? Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- hdu 5458 Stability(树链剖分+并查集)
Stability Time Limit: 3000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/102400 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- [HDU 3712] Fiolki (带边权并查集+启发式合并)
[HDU 3712] Fiolki (带边权并查集+启发式合并) 题面 化学家吉丽想要配置一种神奇的药水来拯救世界. 吉丽有n种不同的液体物质,和n个药瓶(均从1到n编号).初始时,第i个瓶内装着g[ ...
- HDU 5606 tree 并查集
tree 把每条边权是1的边断开,发现每个点离他最近的点个数就是他所在的连通块大小. 开一个并查集,每次读到边权是0的边就合并.最后Ansi=size[findset(i)],size表示每个并 ...
- tree(并查集)
tree Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- hdu 5652 India and China Origins 并查集
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5652 题目大意:n*m的矩阵上,0为平原,1为山.q个询问,第i个询问给定坐标xi,yi,表示i年后这 ...
- Is It A Tree?(并查集)
Is It A Tree? Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 26002 Accepted: 8879 De ...
- CF109 C. Lucky Tree 并查集
Petya loves lucky numbers. We all know that lucky numbers are the positive integers whose decimal re ...
- hdu - 1829 A Bug's Life (并查集)&&poj - 2492 A Bug's Life && poj 1703 Find them, Catch them
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1829 http://poj.org/problem?id=2492 臭虫有两种性别,并且只有异性相吸,给定n条臭 ...
随机推荐
- memcached的分布式
今天写点周末在火车上看的memcached的东西: 一:memcached的分布式 虽然memcached被称为“分布式”缓存服务器,但是服务器端并没有“分布式”的功能.而是通过客户端来实现的. Me ...
- MyEclipse取消自动跳到Console窗口
在Myeclipse中当全屏查看其它文件时,如果控制台有东西输出,就会弹出控制台窗口,如何取消? 方法1: -->右键在console窗口中点Preferences, -->将Show w ...
- Codeforces 719B Anatoly and Cockroaches(元素的交叉排列问题)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/719/B 题目大意: 有一队蟑螂用字符串表示,有黑色 ‘b’ 和红色 'r' 两种颜色,你想使这队蟑螂颜色 ...
- jquery.cookie使用方法
jquery.cookie 使用方法 一个轻量级的 cookie 插件,可以读取.写入.删除 cookie . jquery.cookie.js 的配置 首先包含 jQuery 的库文件,在后面包含 ...
- sql FOR XML PATH
FOR XML PATH 有的人可能知道有的人可能不知道,其实它就是将查询结果集以XML形式展现,有了它我们可以简化我们的查询语句实现一些以前可能需要借助函数活存储过程来完成的工作.那么以一个实例为主 ...
- NestIn VS插件 visual studio 中将同类CS文件放在一起显示
https://visualstudiogallery.msdn.microsoft.com/9d6ef0ce-2bef-4a82-9a84-7718caa5bb45 Nest files in So ...
- SaltStack安装篇
一.基础介绍1.简介 salt 是一个基础平台管理工具 salt是一个配置管理系统,能够维护预定于状态的远程节点 salt是一个分布式远程执行系统,用来在远程节点上执行命令和查询数据 2.salt的核 ...
- php实现发送邮件
smtp.php: <?php class smtp { /* Public Variables */ var $smtp_port; var $time_out; ...
- 全选,全不选,反选的js实现
全选练习 ** 使用复选框上面一个属性判断是否选中 - checked属性 - checked=true:选中 ...
- Nginx反向代理模板
nginx反向代理模板,修改nginx.conf #Basic reverse proxy server # upstream wcf{ server localhost:8080; #wcf1 ...
