linux 分区 物理卷 逻辑卷
今天我们主要说说分区、格式化、SWAP、LVM、软件RAID的创建哈~
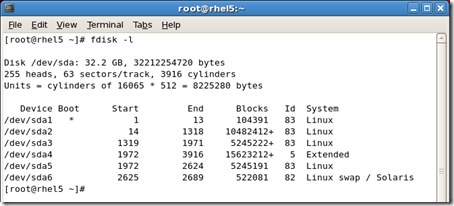

#fdisk /dev/sda
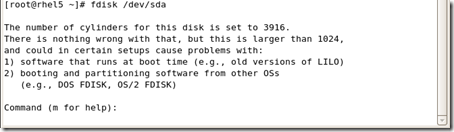
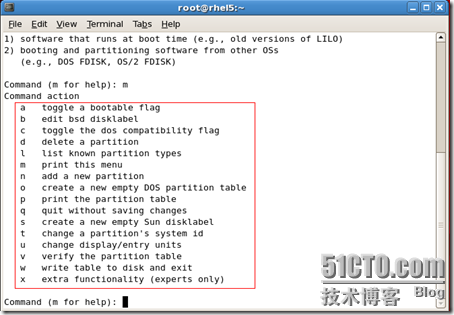
D删除一个分区

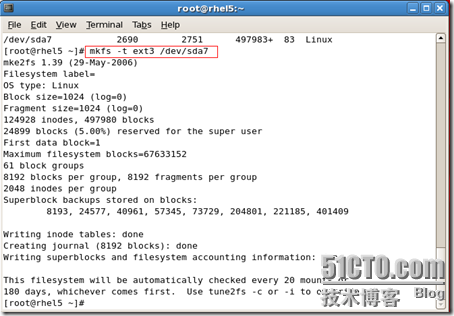

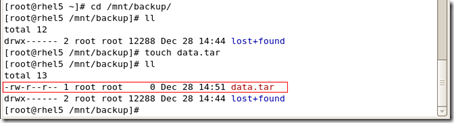

#pvcreate /dev/sdax
sdax就是你刚才创建的分区
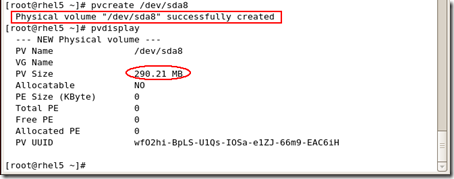
从硬盘驱动器中创建物理卷(physical volumes-PV)。
从物理卷中创建卷组(volume groups-VG)。
从卷组中创建逻辑卷(logical volumes-LV),并分派逻辑卷挂载点
其中只有逻辑卷才可以写数据
#vgcreate myvg /dev/sda8
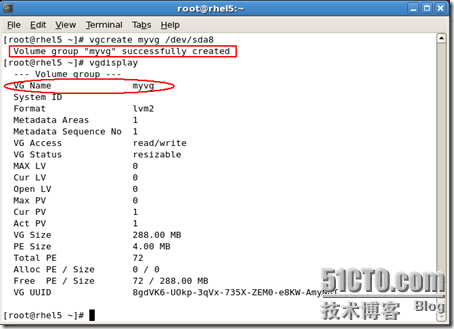
我就从卷组里面分100M出来创建一个逻辑卷
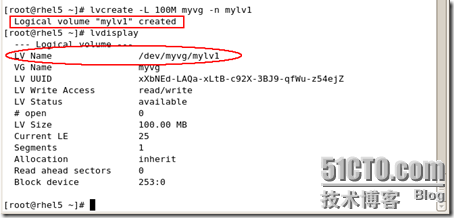
#lvcreate -L 100M myvg -n mylv1
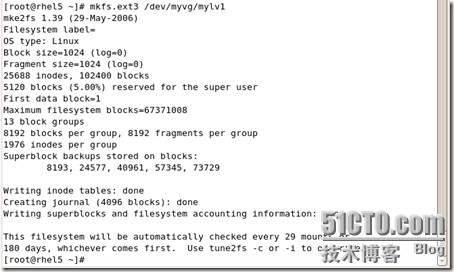
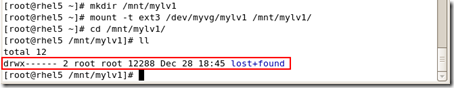
|
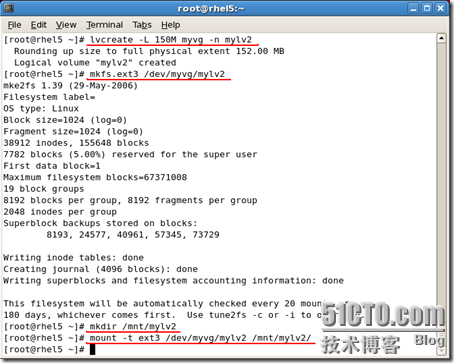
[root@rhel5 /mnt/mylv1]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
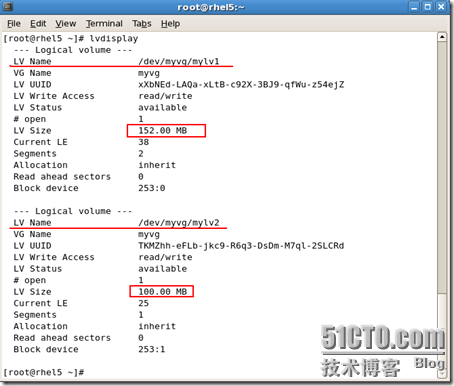
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2752 2788 297171 8e Linux LVM [root@rhel5 /mnt/mylv1]# lvdisplay --- Logical volume --- LV Name /dev/myvg/mylv1 VG Name myvg LV UUID xXbNEd-LAQa-xLtB-c92X-3BJ9-qfWu-z54ejZ LV Write Access read/write LV Status available # open 1 LV Size 100.00 MB Current LE 25 Segments 1 Allocation inherit Read ahead sectors 0 Block device 253:0 [root@rhel5 /mnt/mylv1]# |
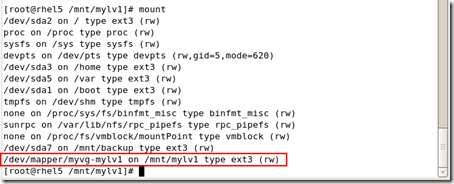
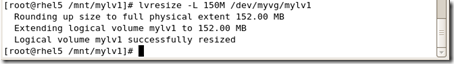
#lvresize -L 绝对大小 对象
#lvresize -L 100M /dev/myvg/mylv2

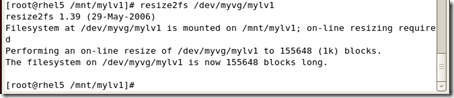
resize2fs /dev/myvg/mylv2
1:不要进行对该分区的任何写入操作,最好是也不read
2:用lvresize2fs重新扩大该分区,且扩大的容量是刚刚缩小的容量(数字一定要和刚刚的一致哈~)。
3:缩小文件系统
4:最后缩小逻辑卷哈。
5:确认文件系统和逻辑卷大小一致。
|
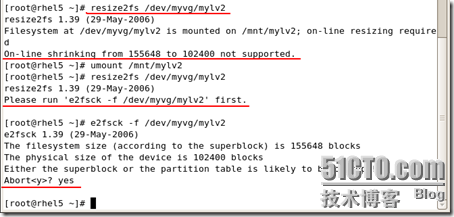
[root@rhel5 ~]# umount /mnt/mylv2
[root@rhel5 ~]# lvresize -L 150M /dev/myvg/mylv2 Rounding up size to full physical extent 152.00 MB Extending logical volume mylv2 to 152.00 MB Logical volume mylv2 successfully resized [root@rhel5 ~]# e2fsck -f /dev/myvg/mylv2 e2fsck 1.39 (29-May-2006) Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes Pass 2: Checking directory structure Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity Pass 4: Checking reference counts Pass 5: Checking group summary information /dev/myvg/mylv2: 12/38912 files (8.3% non-contiguous), 10580/155648 blocks [root@rhel5 ~]# resize2fs /dev/myvg/mylv2 100M resize2fs 1.39 (29-May-2006) Resizing the filesystem on /dev/myvg/mylv2 to 102400 (1k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/myvg/mylv2 is now 102400 blocks long. [root@rhel5 ~]# lvresize -L 100M /dev/myvg/mylv2
WARNING: Reducing active logical volume to 100.00 MB THIS MAY DESTROY YOUR DATA (filesystem etc.) Do you really want to reduce mylv2? [y/n]: y Reducing logical volume mylv2 to 100.00 MB Logical volume mylv2 successfully resized [root@rhel5 ~]# e2fsck -f /dev/myvg/mylv2 e2fsck 1.39 (29-May-2006) Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes Pass 2: Checking directory structure Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity Pass 4: Checking reference counts Pass 5: Checking group summary information /dev/myvg/mylv2: 12/26624 files (8.3% non-contiguous), 9032/102400 blocks [root@rhel5 ~]# mount -t ext3 /dev/myvg/mylv2 /mnt/mylv2 [root@rhel5 ~]# |
#resize2fs /dev/myvg/mylv1
|
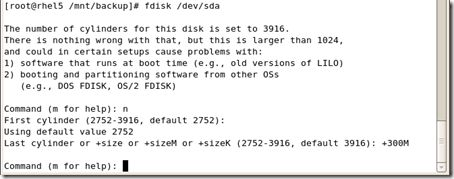
[root@rhel5 /mnt/mylv1]# fdisk /dev/sda
The number of cylinders for this disk is set to 3916.
There is nothing wrong with that, but this is larger than 1024, and could in certain setups cause problems with: 1) software that runs at boot time (e.g., old versions of LILO) 2) booting and partitioning software from other OSs (e.g., DOS FDISK, OS/2 FDISK) Command (m for help): n
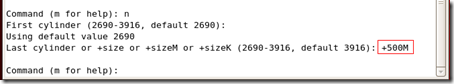
First cylinder (2789-3916, default 2789): Using default value 2789 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2789-3916, default 3916): +500M Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
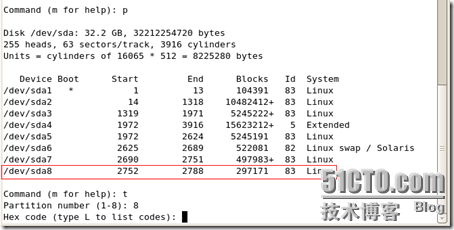
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2752 2788 297171 8e Linux LVM /dev/sda9 2789 2850 497983+ 83 Linux Command (m for help): t
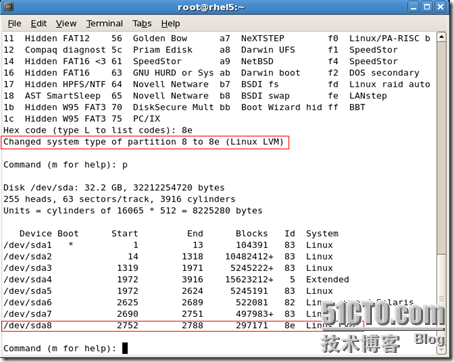
Partition number (1-9): 9 Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e Changed system type of partition 9 to 8e (Linux LVM) Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
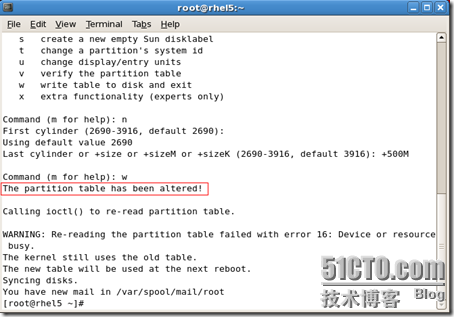
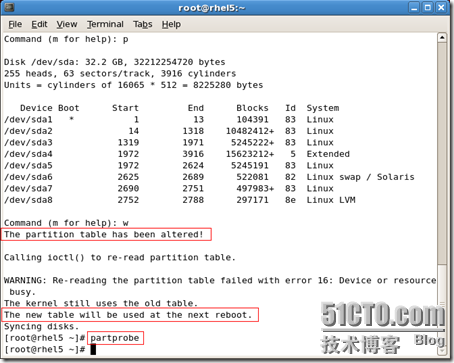
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2752 2788 297171 8e Linux LVM /dev/sda9 2789 2850 497983+ 8e Linux LVM Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at the next reboot. Syncing disks. [root@rhel5 /mnt/mylv1]# |
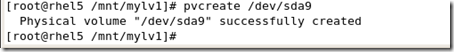
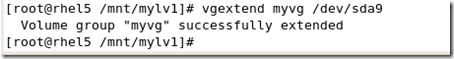
#vgedtend myvg /dev/sda9
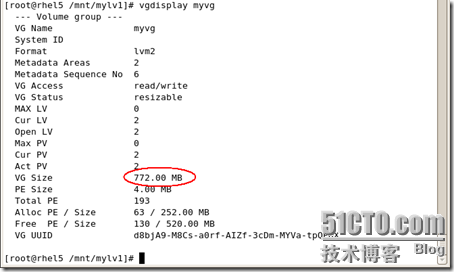
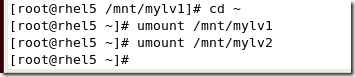
#umount /mnt/mylv1
#umount /mnt/mylv2
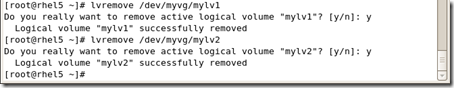
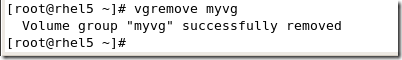
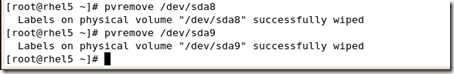
|
[root@rhel5 ~]# fdisk /dev/sda
The number of cylinders for this disk is set to 3916.
There is nothing wrong with that, but this is larger than 1024, and could in certain setups cause problems with: 1) software that runs at boot time (e.g., old versions of LILO) 2) booting and partitioning software from other OSs (e.g., DOS FDISK, OS/2 FDISK) Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2752 2788 297171 8e Linux LVM /dev/sda9 2789 2850 497983+ 8e Linux LVM Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-9): 9 Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2752 2788 297171 8e Linux LVM Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-8): 8 Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
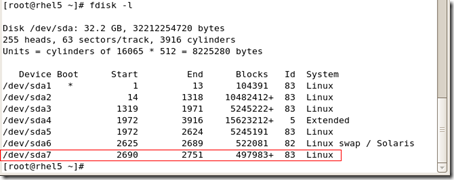
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2751 497983+ 83 Linux Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at the next reboot. Syncing disks. [root@rhel5 ~]# partprobe [root@rhel5 ~]# |
RAID0
RAID1
RAID5
优点:廉价
缺点:不稳定,如果系统坏了,RAID整列也就损坏,容易造成数据丢失
相对于软件RAID
优点:可靠性高,易管理。稳定
缺点:成本过高
因为RAID5至少需要3个或者更多的硬盘,我们就要分3个分区,然后再加一个热备份的分区,就是4个分区
the new table will be used at the next reboot
warning: unable to open /dev/h dc read-wirte ( read-only file system)
|
[root@rhel5 ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris [root@rhel5 ~]# fdisk /dev/sda The number of cylinders for this disk is set to 3916.
There is nothing wrong with that, but this is larger than 1024, and could in certain setups cause problems with: 1) software that runs at boot time (e.g., old versions of LILO) 2) booting and partitioning software from other OSs (e.g., DOS FDISK, OS/2 FDISK) Command (m for help): n
First cylinder (2690-3916, default 2690): Using default value 2690 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2690-3916, default 3916): +100M Command (m for help): n
First cylinder (2703-3916, default 2703): Using default value 2703 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2703-3916, default 3916): +100M Command (m for help): n
First cylinder (2716-3916, default 2716): Using default value 2716 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2716-3916, default 3916): +100M Command (m for help): n
First cylinder (2729-3916, default 2729): Using default value 2729 Last cylinder or +size or +sizeM or +sizeK (2729-3916, default 3916): +100M Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2702 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda8 2703 2715 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda9 2716 2728 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda10 2729 2741 104391 83 Linux Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-10): 7 Hex code (type L to list codes): fd Changed system type of partition 7 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-10): 8 Hex code (type L to list codes): fd Changed system type of partition 8 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-10): 9 Hex code (type L to list codes): fd Changed system type of partition 9 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-10): 10 Hex code (type L to list codes): fd Changed system type of partition 10 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sda: 32.2 GB, 32212254720 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 3916 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux /dev/sda2 14 1318 10482412+ 83 Linux /dev/sda3 1319 1971 5245222+ 83 Linux /dev/sda4 1972 3916 15623212+ 5 Extended /dev/sda5 1972 2624 5245191 83 Linux /dev/sda6 2625 2689 522081 82 Linux swap / Solaris /dev/sda7 2690 2702 104391 fd Linux raid autodetect /dev/sda8 2703 2715 104391 fd Linux raid autodetect /dev/sda9 2716 2728 104391 fd Linux raid autodetect /dev/sda10 2729 2741 104391 fd Linux raid autodetect Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at the next reboot. Syncing disks. [root@rhel5 ~]# partprobe Warning: Unable to open /dev/hdc read-write (Read-only file system). /dev/hdc has been opened read-only. [root@rhel5 ~]# partprobe [root@rhel5 ~]# |
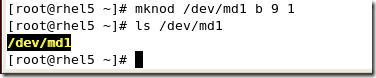
#mdadm --detail /dev/md1
查看RAID状态
|
[root@rhel5 ~]# mdadm -C /dev/md1 -l 5 -n 3 -x 1 /dev/sda7 /dev/sda8 /dev/sda9 /dev/sda10
mdadm: array /dev/md1 started. [root@rhel5 ~]# mdadm --detail /dev/md1 /dev/md1: Version : 00.90.03 Creation Time : Mon Dec 29 17:25:41 2008 Raid Level : raid5 Array Size : 208640 (203.78 MiB 213.65 MB) Device Size : 104320 (101.89 MiB 106.82 MB) Raid Devices : 3 Total Devices : 4 Preferred Minor : 1 Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Mon Dec 29 17:25:44 2008
State : clean Active Devices : 3 Working Devices : 4 Failed Devices : 0 Spare Devices : 1 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 64K UUID : 2f7e30d2:f3f54047:e22d6b9f:16f2b256
Events : 0.2 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 7 0 active sync /dev/sda7 1 8 8 1 active sync /dev/sda8 2 8 9 2 active sync /dev/sda9 3 8 10 - spare /dev/sda10
[root@rhel5 ~]# |
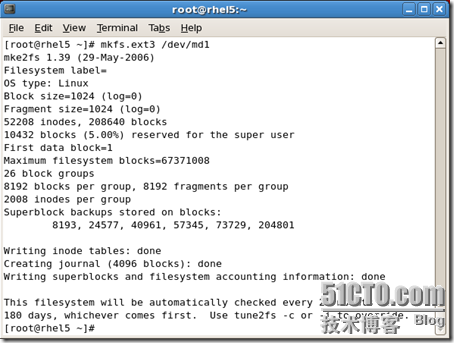
#mount -t ext3 /dev/md1 /mnt/raid
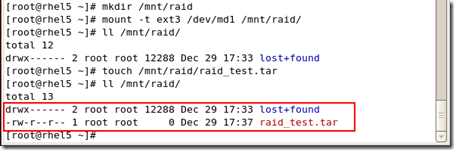
- 顶
- 0
- 踩
linux 分区 物理卷 逻辑卷的更多相关文章
- linux运维基础知识-系统分区及LVM逻辑卷的创建
系统分区及LVM逻辑卷的创建 分区 创建逻辑卷 LVM简介:逻辑卷管理器(LogicalVolumeManager)本质上是一个虚拟设备驱动,是在内核中块设备和物理设备之间添加的一个新的抽象层次,如图 ...
- Linux下对lvm逻辑卷分区大小的调整(针对xfs和ext4不同文件系统)
当我们在安装系统的时候,由于没有合理分配分区空间,在后续维护过程中,发现有些分区空间不够使用,而有的分区空间却有很多剩余空间.如果这些分区在装系统的时候使用了lvm(前提是这些分区要是lvm逻辑卷分区 ...
- 1.4 Linux下对lvm逻辑卷分区大小的调整(针对xfs和ext4不同文件系统)
当我们在安装系统的时候,由于没有合理分配分区空间,在后续维护过程中,发现有些分区空间不够使用,而有的分区空间却有很多剩余空间.如果这些分区在装系统的时候使用了lvm(前提是这些分区要是lvm逻辑卷 ...
- Linux增加LV(逻辑卷)容量
Linux增加LV(逻辑卷)容量 2017-09-29-17:34:13 个人原创博客,转载请注明出处. 查看逻辑卷的相关命令: lvs vgs 命令: [root@arch ~]# vgs VG # ...
- aliyun添加数据盘后的物理分区和lvm逻辑卷两种挂载方式
一.普通磁盘分区管理方式 1.对磁盘进行分区 列出磁盘 # fdisk -l # fdisk /dev/vdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Change ...
- linux LVM:物理卷逻辑卷
逻辑卷管理器,当分区不够用的时候,可以新建一个更大的分区再复制进去,但是浪费时间.Lvm可以弹性调整分区大小,可以动态组合分区.分区大小固定了就无法调整, apt-get update & a ...
- Linux磁盘分区与lvm逻辑卷
硬盘接口的种类分四类:(价格由低到高) IDE SATA硬盘:别名串口硬盘,具有较强的纠错能力. SCSI硬盘:即采用SCSI接口的硬盘,SCSI接口具有应用范围广,多任务,带宽大,CPU占用率低. ...
- 管理员技术(六): 硬盘分区及格式化、 新建一个逻辑卷、调整现有磁盘的分区、扩展逻辑卷的大小、添加一个swap分区
一.硬盘分区及格式化 问题: 本例要求熟悉硬盘分区结构,使用fdisk分区工具在磁盘 /dev/vdb 上按以下要求建立分区: 1> 采用默认的 msdos 分区模式 2> ...
- Linux基础学习-LVM逻辑卷管理遇到的问题
LVM学习逻辑卷管理创建逻辑卷遇到的问题 1 实验环境 系统 内核 发行版本 CentOS 2.6.32-754.2.1.el6.x86_64 CentOS release 6.10 (Final) ...
随机推荐
- Linux命令详解之—less命令
Linux下还有一个与more命令非常类似的命令--less命令,相比于more命令,less命令更加灵活强大一些,今天就给大家介绍下Linux下的less命令. 更多Linux命令详情请看:Linu ...
- 局域网ping Linux主机名
1.Windows ping Linux主机名 #ubuntu 下 sudo apt-get install winbind #centos 下 yum install samba service n ...
- 【HTML5】浅析HTML5应用程序缓存(ApplicationCache)
一.为什么需要Web应用程序缓存 在移动互联网时代,设备终端位置不再固定,依赖无线信号,网络的可靠性变得降低,比如坐在火车上,过了一个隧道(15分钟),便无法访问网站,这对于web的伤害是很大的 ...
- js获取页面中图片的总数
查看效果:http://keleyi.com/keleyi/phtml/image/9.htm 下面是完整代码: <html><body><div id="ke ...
- 定时器相关 setTimeout setInterval 函数节流
这个问题也是在参加百度的前端技术学院中遇到的 任务中需要用js实现动画 导师给的评价中setInterval会导致bug 当时不理解 下面把自己学习的过程分享出来 再次理解单线程 老是说js ...
- 如何对sharepoint图片库的文件夹的图片按照时间排序并分页显示
/// <summary> /// 获取图片库第一层文件夹--根据文件夹名称排序 /// </summary> /// <param name="siteUrl ...
- 数据连接到 Web 服务 InfoPath 2010 窗体中的 SharePoint 服务器上运行时的错误消息:"401-未经授权"解决方案
症状: 请考虑以下情形: Web 窗体发布到 SharePoint 服务器. 您创建 Microsoft InfoPath 2010 表单所在的 SharePoint 服务器上使用到位于数据的数据连接 ...
- 如何:在 SharePoint 中创建外部列表
在创建外部内容类型后创建外部列表是一项非常简单的任务,有如下4种方式进行: 可使用 Microsoft SharePoint Designer 2010 浏览器来完成 VS2010的列表实例 采用代码 ...
- Xcode中XVim的常用操作
- yii create url (一)
1.$this->redirect这里的$this是当前的controller.可能是应用程序的也 可能是模块下的 这里仅将解一下第一个参能是url,当url是一个字符串时,它会自己动跳转 如$ ...
