hdu 1828 线段树扫描线(周长)
Picture
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3897 Accepted Submission(s): 1978
Write a program to calculate the perimeter. An example with 7 rectangles is shown in Figure 1.
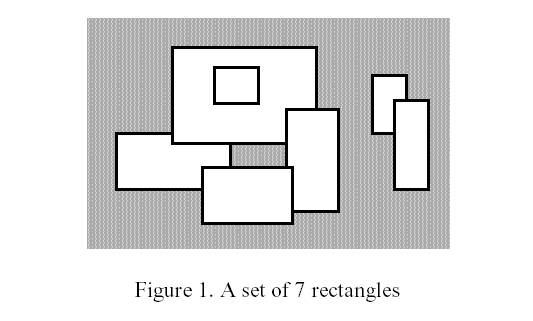
The corresponding boundary is the whole set of line segments drawn in Figure 2.
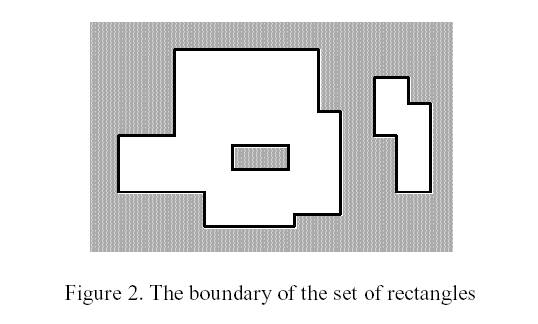
The vertices of all rectangles have integer coordinates.
0 <= number of rectangles < 5000
All coordinates are in the range [-10000,10000] and any existing rectangle has a positive area.
Please process to the end of file.
Sample Input
7
-15 0 5 10
-5 8 20 25
15 -4 24 14
0 -6 16 4
2 15 10 22
30 10 36 20
34 0 40 16
Sample Output
228
First
/*
hdu 1828 线段树扫描线(周长) 给你一些矩阵,有部分or全部重叠.求最终图形的周长 对于x轴的边,矩阵的下边标为1,矩阵的上边标为-1.每次插入后用当前覆盖面积
减去上一次的覆盖面积(即新增长度),扫描过一个矩阵的上边后便能消除下边的
影响。
对x,y轴分别扫描一次即可 最开始没考虑重边的问题,结果C++ AC(G++ WR)
然后更改后G++才过 - - 2
0 0 1 1
1 0 2 1 2
0 0 1 1
0 1 1 2 hhh-2016-03-26 16:35:21
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#define lson (i<<1)
#define rson ((i<<1)|1)
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 20050;
int a[maxn];
struct node
{
int l,r;
int sum,len;
int mid()
{
return (l+r)>>1;
}
} tree[maxn*5]; void push_up(int i)
{
if(tree[i].sum)
tree[i].len = (tree[i].r-tree[i].l+1);
else if(tree[i].l == tree[i].r)
tree[i].len = 0;
else
tree[i].len = tree[lson].len+tree[rson].len;
} void build(int i,int l,int r)
{
tree[i].l = l;
tree[i].r = r;
tree[i].sum = 0;
tree[i].len = 0;
if(l == r)
return ; int mid = tree[i].mid();
build(lson,l,mid);
build(rson,mid+1,r);
push_up(i);
} void push_down(int i)
{
// if(tree[i].sum)
// {
// tree[lson].sum += tree[i].sum;
// tree[rson].sum += tree[i].sum;
// tree[lson].len = tree[lson].r-tree[lson].l;
// tree[rson].len = tree[rson].r-tree[rson].l;
// }
} void Insert(int i,int l,int r,int val)
{
if(tree[i].l >= l && tree[i].r <=r )
{
tree[i].sum += val;
push_up(i);
return ;
}
int mid = tree[i].mid();
push_down(i);
if(l <= mid)
Insert(lson,l,r,val);
if(r > mid)
Insert(rson,l,r,val);
push_up(i);
} struct edge
{
int l,r;
int va,high;
};
edge tx[maxn*2];
edge ty[maxn*2]; bool cmp(edge a,edge b)
{
if(a.high != b.high)
return a.high < b.high;
else //如果有重边则要先插入在删除
return a.va > b.va;
} int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
int tox = 0,lx=0x3f3f3f3f,rx=0;
int toy = 0,ly=0x3f3f3f3f,ry=0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
lx = min(x1,lx),rx = max(rx,x2);
ly = min(y1,ly),ry = max(ry,y2);
tx[tox].l = x1,tx[tox].r = x2,tx[tox].high=y1,tx[tox++].va=1;
tx[tox].l = x1,tx[tox].r = x2,tx[tox].high=y2,tx[tox++].va=-1;
ty[toy].l = y1,ty[toy].r = y2,ty[toy].high=x1,ty[toy++].va=1;
ty[toy].l = y1,ty[toy].r = y2,ty[toy].high=x2,ty[toy++].va=-1;
}
sort(tx,tx+tox,cmp);
sort(ty,ty+toy,cmp);
int ans=0,prelen = 0;
build(1,lx,rx-1);
for(int i = 0; i < tox; i++)
{
Insert(1,tx[i].l,tx[i].r-1,tx[i].va);
ans += abs(tree[1].len-prelen);
prelen = tree[1].len;
}
//cout << ans <<endl;
build(1,ly,ry-1);
prelen = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < toy; i++)
{
Insert(1,ty[i].l,ty[i].r-1,ty[i].va);
ans += abs(tree[1].len-prelen);
prelen = tree[1].len;
}
cout << ans <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Second
/*
hdu 1828 线段树扫描(周长)2 在向上扫描的过程中我们可以计算出平行于x轴的长度
然后在两条线之间我们只需要计算出有多少条竖线便能得带这两条线之间平行于
y轴的长度。
用ls和rs来表示当前节点左右端点是否被覆盖
在处理竖线数量时,注意合并带来的影响,假设lson.rs和rson.ls都存在值的话
说明存在重叠的部分 hhh-2016-03-26 17:58:50
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#define lson (i<<1)
#define rson ((i<<1)|1)
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 20050;
int a[maxn];
struct node
{
int l,r;
int sum,len;
int num,ls,rs;
int mid()
{
return (l+r)>>1;
}
} tree[maxn*5]; void push_up(int i)
{
if(tree[i].sum)
{
tree[i].len = (tree[i].r-tree[i].l+1);
tree[i].ls = tree[i].rs = 1;
tree[i].num = 1;
}
else if(tree[i].l == tree[i].r)
{
tree[i].len= 0;
tree[i].num=tree[i].rs=tree[i].ls=0;
}
else
{
tree[i].len = tree[lson].len+tree[rson].len;
tree[i].ls = tree[lson].ls;
tree[i].rs = tree[rson].rs;
tree[i].num = tree[lson].num+tree[rson].num;
tree[i].num -= (tree[lson].rs&tree[rson].ls);
//减去重叠的部分
}
} void build(int i,int l,int r)
{
tree[i].l = l;
tree[i].r = r;
tree[i].sum = tree[i].len = 0;
tree[i].ls = tree[i].rs = tree[i].num = 0;
if(l == r)
return ; int mid = tree[i].mid();
build(lson,l,mid);
build(rson,mid+1,r);
push_up(i);
} void push_down(int i)
{ } void Insert(int i,int l,int r,int val)
{
if(tree[i].l >= l && tree[i].r <=r )
{
tree[i].sum += val;
push_up(i);
return ;
}
int mid = tree[i].mid();
push_down(i);
if(l <= mid)
Insert(lson,l,r,val);
if(r > mid)
Insert(rson,l,r,val);
push_up(i);
} struct edge
{
int l,r;
int va,high,id;
};
edge tx[maxn*2]; bool cmp(edge a,edge b)
{
if(a.high != b.high)
return a.high < b.high;
else
return a.va > b.va;
} int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
int tox = 0,lx=0x3f3f3f3f,rx=0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
lx = min(x1,lx),rx = max(rx,x2);
tx[tox].l = x1,tx[tox].r = x2,tx[tox].high=y1,tx[tox++].va=1;
tx[tox].l = x1,tx[tox].r = x2,tx[tox].high=y2,tx[tox++].va=-1;
}
sort(tx,tx+tox,cmp);
int ans=0,prelen = 0;
build(1,lx,rx-1);
//tx[tox] = tx[tox+1];
for(int i = 0; i < tox; i++)
{
Insert(1,tx[i].l,tx[i].r-1,tx[i].va);
ans += abs(tree[1].len-prelen);
if(i != tox-1)
ans += (tx[i+1].high-tx[i].high)*tree[1].num*2;
prelen = tree[1].len;
}
cout << ans <<endl;
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1828 线段树扫描线(周长)的更多相关文章
- HDU 1828 线段树+扫描线(计算矩形周长并)
题意:给你n个矩形,然后矩形有可能重叠,要你求周长 思路:首先碰到这种矩形在数轴上那么第一反应应该想到的是扫描线, 做周长我们有两种方法 第一种,我们可以分开两部分求,第一遍求x轴上的贡献,第二遍求y ...
- hdu 4052 线段树扫描线、奇特处理
Adding New Machine Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
- hdu 5091(线段树+扫描线)
上海邀请赛的一道题目,看比赛时很多队伍水过去了,当时还想了好久却没有发现这题有什么水题的性质,原来是道成题. 最近学习了下线段树扫描线才发现确实是挺水的一道题. hdu5091 #include &l ...
- HDU 5107 线段树扫描线
给出N个点(x,y).每一个点有一个高度h 给出M次询问.问在(x,y)范围内第k小的高度是多少,没有输出-1 (k<=10) 线段树扫描线 首先离散化Y坐标,以Y坐标建立线段树 对全部的点和询 ...
- hdu 1542 线段树+扫描线 学习
学习扫描线ing... 玄学的东西... 扫描线其实就是用一条假想的线去扫描一堆矩形,借以求出他们的面积或周长(这一篇是面积,下一篇是周长) 扫描线求面积的主要思想就是对一个二维的矩形的某一维上建立一 ...
- hdu 1255(线段树 扫描线) 覆盖的面积
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1255 典型线段树辅助扫描线,顾名思义扫描线就是相当于yy出一条直线从左到右(也可以从上到下)扫描过去,此时先将所 ...
- HDU 5091 线段树扫描线
给出N个点.和一个w*h的矩形 给出N个点的坐标,求该矩形最多能够覆盖多少个点 对每一个点point(x.y)右边生成相应的点(x+w,y)值为-1: 纵向建立线段树,从左到右扫描线扫一遍.遇到点则用 ...
- hdu 4419 线段树 扫描线 离散化 矩形面积
//离散化 + 扫描线 + 线段树 //这个线段树跟平常不太一样的地方在于记录了区间两个信息,len[i]表示颜色为i的被覆盖的长度为len[i], num[i]表示颜色i 『完全』覆盖了该区间几层. ...
- hdu 3265 线段树扫描线(拆分矩形)
题意: 给你n个矩形,每个矩形上都有一个矩形的空洞,所有的矩形都是平行于x,y轴的,最后问所有矩形的覆盖面积是多少. 思路: 是典型的矩形覆盖问题,只不过每个矩形上多了一个矩 ...
随机推荐
- 团队作业4——第一次项目冲刺(Alpha版本)2017.11.19
第三次会议:2017-11-16 第二次会议讨论的还没有完全实现,于是在第三次会议上对此进行了一些对我们工作上的看法,得出结论:多花时间啊!!!! 又没照照片图: 会议主要内容: 1.登录注册完善 2 ...
- android 自定义ScrollView实现背景图片伸缩(阻尼效果)
android 自定义ScrollView实现强调内容背景图片伸缩(仿多米,qq空间背景的刷新) 看到一篇文章,自己更改了一下bug: 原文地址:http://www.aiuxian.com/arti ...
- raid5 / raid5e / raid5ee的性能对比及其数据恢复原理
RAID 5 是一种存储性能.数据安全和存储成本兼顾的存储解决方案. RAID 5可以理解为是RAID 0和RAID 1的折中方案.RAID 5可以为系统提供数据安全保障,但保障程度要比Mirror低 ...
- CentOS搭建Git服务器及权限管理
声明:本教程,仅作为配置的记录,细节不展开,需要您有一点linux的命令基础,仅作为配置参考. 1. 系统环境 系统: Linux:CentOS 7.2 64位 由于CentOS已经内置了OpenSS ...
- monog和github学习
1.导出服务器数据库到本地以json的格式储存:mongoexport -h ip -d dbname -c user -o D:\mondb\user.json2.导入本地Json到本地项目中:D: ...
- LAMP 搭建
p { margin-bottom: 0.25cm; line-height: 120% } LAMP 搭建 承 Ubuntu 17.10.1安装, 定制. 参考 电子工业出版社, Ubuntu完美应 ...
- maven常见问题处理(3-4)配置代理服务器
有的公司基于安全因素考虑,要求员工使用通过安全认证的代理访问因特网. 这时就需要为Maven配置HTTP代理. 在目录~/.m2/setting.xml文件中编辑如下(如果没有该文件,则复制$M2_H ...
- Mysql官方文档翻译系列14.18--MySql备份与恢复
原文链接: (https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-backup-recovery.html) The key to safe database ...
- C#的扩展方法简介
顾名思义,这是一种可以扩展C#类的操作,MSDN上的说法是: "扩展方法使您能够向现有类型"添加"方法,而无需创建新的派生类型.重新编译或以其他方式修改原始类型.&quo ...
- 南京邮电大学java程序设计作业在线编程第一次作业
王利国的"Java语言程序设计第1次作业(2018)"详细 作业结果详细 总分:100 选择题得分:40 1. Java语言中,基本数据类型一共有( )种. A.16 B.2 C ...
