0_Simple__clock + 0_Simple__clock_nvrtc
▶ 使用 clock() 函数在CUDA核函数内部进行计时,将核函数封装为PTX并在另外的代码中读取和使用。
▶ 源代码:文件内建核函数计时
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <cuda.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <helper_cuda.h>
#include <helper_string.h> #define NUM_BLOCKS 1
#define NUM_THREADS 1024 __global__ static void timedReduction(const float *input, float *output, clock_t *timer)
{
extern __shared__ float shared[];
const int tid = threadIdx.x, bid = blockIdx.x; if (tid == ) // 0 号线程记录开始时间,调用 time.h 的计时器,一个线程块有一个开始时间和一个结束时间
timer[bid] = clock(); shared[tid] = input[tid];
shared[tid + blockDim.x] = input[tid + blockDim.x]; for (int d = blockDim.x; d > ; d /= ) // 二分规约求最小值,每次循环后较小值保存在前半段上
{
if (tid < d)
{
float f0 = shared[tid], f1 = shared[tid + d];
if (f1 < f0)
shared[tid] = f1;
}
__syncthreads();
} if (tid == ) // 0 号线程输出结果
output[bid] = shared[];
__syncthreads(); if (tid == ) // 0 号线程记录结束时间
timer[bid + gridDim.x] = clock();
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int dev = findCudaDevice(argc, (const char **)argv); // helper_cuda.h 中设置设备的函数 clock_t timer[NUM_BLOCKS * ];
float input[NUM_THREADS * ];
for (int i = ; i < NUM_THREADS * ; i++)
input[i] = (float)i; float *dinput = NULL, *doutput = NULL;
clock_t *dtimer = NULL;
cudaMalloc((void **)&dinput, sizeof(float) * NUM_THREADS * );
cudaMalloc((void **)&doutput, sizeof(float) * NUM_BLOCKS);
cudaMalloc((void **)&dtimer, sizeof(clock_t) * NUM_BLOCKS * ); cudaMemcpy(dinput, input, sizeof(float) * NUM_THREADS * , cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); timedReduction << <NUM_BLOCKS, NUM_THREADS, sizeof(float) * * NUM_THREADS >> >(dinput, doutput, dtimer); cudaMemcpy(timer, dtimer, sizeof(clock_t) * NUM_BLOCKS * , cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaFree(dinput);
cudaFree(doutput);
cudaFree(dtimer); long double sumElapsedClocks = ; // 计算平均耗时
for (int i = ; i < NUM_BLOCKS; i++)
sumElapsedClocks += (long double)(timer[i + NUM_BLOCKS] - timer[i]);
printf("Average clocks/block = %f\n", sumElapsedClocks / NUM_BLOCKS); getchar();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
● 输出结果,比较不同的 blockDim.x 和 threadDim.x 情况结果如下图表所示。
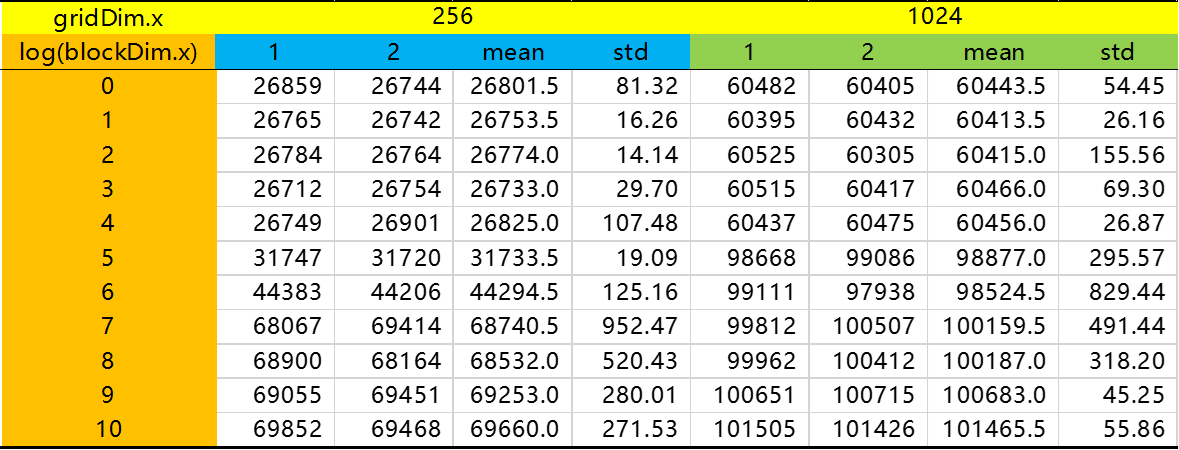

▶ 涨姿势:
● 在核函数中也能使用 time.h 中的 clock_t 变量,并用clock() 函数计时。
▶ 源代码,封装核函数并在另外的代码中使用。分成核函数部分 clock_fernel.cu 和主函数部分 clock.cpp
// clock_kernel.cu
__global__ static void timedReduction(const float *input, float *output, clock_t *timer)
{
extern __shared__ float shared[];
const int tid = threadIdx.x, bid = blockIdx.x; if (tid == )
timer[bid] = clock(); shared[tid] = input[tid];
shared[tid + blockDim.x] = input[tid + blockDim.x]; for (int d = blockDim.x; d > ; d /= )
{
if (tid < d)
{
float f0 = shared[tid], f1 = shared[tid + d];
if (f1 < f0)
shared[tid] = f1;
}
__syncthreads();
} if (tid == )
output[bid] = shared[];
__syncthreads(); if (tid == )
timer[bid + gridDim.x] = clock();
}
// main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cuda.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <driver_functions.h>
#include <nvrtc_helper.h> #define NUM_BLOCKS 64
#define NUM_THREADS 256 int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
typedef long clock_t;
clock_t timer[NUM_BLOCKS * ]; float input[NUM_THREADS * ];
for (int i = ; i < NUM_THREADS * ; i++)
input[i] = (float)i; char *kernel_file = sdkFindFilePath("clock_kernel.cu", argv[]); // 找到核函数代码文件
char *ptx;
size_t ptxSize;
compileFileToPTX(kernel_file, , NULL, &ptx, &ptxSize, ); // 将指定核函数编译为 PTX,放在指针 ptx 指向的地址,大小为ptxSize CUmodule module = loadPTX(ptx, argc, argv); // 读取编译好的 PTX
CUfunction kernel_name;
cuModuleGetFunction(&kernel_name, module, "timedReduction"); // 取出 PTX 中的函数 timeReducetion() CUdeviceptr dinput, doutput, dtimer; // 内存申请和拷贝
cuMemAlloc(&dinput, sizeof(float) * NUM_THREADS * );
cuMemAlloc(&doutput, sizeof(float) * NUM_BLOCKS);
cuMemAlloc(&dtimer, sizeof(clock_t) * NUM_BLOCKS * );
cuMemcpyHtoD(dinput, input, sizeof(float) * NUM_THREADS * ); dim3 cudaGridSize(NUM_BLOCKS, , ), cudaBlockSize(NUM_THREADS, , );
void *arr[] = { (void *)&dinput, (void *)&doutput, (void *)&dtimer }; // 封装核函数实参的指针 cuLaunchKernel(kernel_name, // 调用核函数,函数名
cudaGridSize.x, cudaGridSize.y, cudaGridSize.z, // gridDim 分量
cudaBlockSize.x, cudaBlockSize.y, cudaBlockSize.z, // blockDim 分量
sizeof(float) * * NUM_THREADS, , // 共享内存和流号
&arr[], ); // 实参和其他参数 cuCtxSynchronize(); // 上下文同步,作用接近 cudaDeviceSynchronize()
cuMemcpyDtoH(timer, dtimer, sizeof(clock_t) * NUM_BLOCKS * );
cuMemFree(dinput);
cuMemFree(doutput);
cuMemFree(dtimer); long double sumElapsedClocks = ; // 计算耗时
for (int i = ; i < NUM_BLOCKS; i++)
sumElapsedClocks += (long double)(timer[i + NUM_BLOCKS] - timer[i]);
printf("Average clocks/block = %Lf\n", sumElapsedClocks / NUM_BLOCKS); getchar();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
● 输出结果:
sdkFindFilePath <clock_kernel.cu> in ./
> Using CUDA Device []: GeForce GTX
> GPU Device has SM 6.1 compute capability
Average clocks/block = 3058.000000
▶ 涨姿势:
● 在外部核函数代码文件中采用 extern "C" __global__ void functionName() 来定义函数
● 使用 PTX 过程中涉及的函数
// 依文件名搜索其绝对路径,传入需要查找的目标文件名 filename 和可选的可执行文件目录 executable_path
inline char *sdkFindFilePath(const char *filename, const char *executable_path)
{
const char *searchPath[] = { "./" }; // 默认搜索路径只有当前目录,源代码中罗列了很多文件目录
std::string executable_name;
if (executable_path != )
{
executable_name = std::string(executable_path); #if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(WIN64) || defined(_WIN64) // 注意 Windows 和 Linux 文件路径的分隔符不同
size_t delimiter_pos = executable_name.find_last_of('\\');
executable_name.erase(, delimiter_pos + );
if (executable_name.rfind(".exe") != std::string::npos)
executable_name.resize(executable_name.size() - );
#else
size_t delimiter_pos = executable_name.find_last_of('/');
executable_name.erase(, delimiter_pos + );
#endif
}
for (unsigned int i = ; i < sizeof(searchPath) / sizeof(char *); ++i) // 遍历查找路径,找到第一个匹配的路径
{
std::string path(searchPath[i]);
size_t executable_name_pos = path.find("<executable_name>");
if (executable_name_pos != std::string::npos)
{
if (executable_path != ) // 额外路径非空,替换掉path中的值
path.replace(executable_name_pos, strlen("<executable_name>"), executable_name);
else // 额外路径为空,不做调整
continue;
} #ifdef _DEBUG
printf("sdkFindFilePath <%s> in %s\n", filename, path.c_str());
#endif path.append(filename); // 根据搜索的结果测试文件是否存在
FILE *fp;
FOPEN(fp, path.c_str(), "rb"); // 在 helper_strings.h 中 #define FOPEN(fHandle,filename,mode) fopen_s(&fHandle, filename, mode)
if (fp != NULL)
{
fclose(fp);
char *file_path = (char *)malloc(path.length() + );
STRCPY(file_path, path.length() + , path.c_str()); // #define STRCPY(sFilePath, nLength, sPath) strcpy_s(sFilePath, nLength, sPath)
return file_path;
}
if (fp) // ?
fclose(fp);
}
return ; // 没有找到文件,返回 0
} // 文本编译为PTX,输入文件名,编译参数,指向编译结果的指针,指向存放编译结果大小的指针
// 新版本中还多了一个参数 int requiresCGheaders,是否要用到 cooperative_groups.h,即向编译选项中添加 --include-path=cooperative_groups.h
void compileFileToPTX(char *filename, int argc, const char **argv, char **ptxResult, size_t *ptxResultSize)
{
std::ifstream inputFile(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
if (!inputFile.is_open())
{
std::cerr << "\nerror: unable to open " << filename << " for reading!\n";
exit();
} std::streampos pos = inputFile.tellg();
size_t inputSize = (size_t)pos;
char * memBlock = new char[inputSize + ]; inputFile.seekg(, std::ios::beg);
inputFile.read(memBlock, inputSize);
inputFile.close();
memBlock[inputSize] = '\x0'; nvrtcProgram prog; // 编译
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcCreateProgram", nvrtcCreateProgram(&prog, memBlock, filename, , NULL, NULL));
nvrtcResult res = nvrtcCompileProgram(prog, argc, argv); size_t logSize; // 写日志
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcGetProgramLogSize", nvrtcGetProgramLogSize(prog, &logSize));
char *log = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * logSize + );
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcGetProgramLog", nvrtcGetProgramLog(prog, log));
log[logSize] = '\x0';
//std::cerr << "\n compilation log ---\n";
//std::cerr << log;
//std::cerr << "\n end log ---\n";
free(log); NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcCompileProgram", res);
// fetch PTX
size_t ptxSize;
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcGetPTXSize", nvrtcGetPTXSize(prog, &ptxSize));
char *ptx = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * ptxSize);
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcGetPTX", nvrtcGetPTX(prog, ptx));
NVRTC_SAFE_CALL("nvrtcDestroyProgram", nvrtcDestroyProgram(&prog));
*ptxResult = ptx;
*ptxResultSize = ptxSize;
} // 传入文件名和错误信息内容,向std_err中输出
#define NVRTC_SAFE_CALL(Name, x) \
do \
{ \
nvrtcResult result = x; \
if (result != NVRTC_SUCCESS) \
{ \
std::cerr << "\nerror: " << Name << " failed with error " << nvrtcGetErrorString(result); \
exit(); \
} \
} while() // 读取编译好的PTX为模块,传入指向 ptx 代码的指针和额外参数
CUmodule loadPTX(char *ptx, int argc, char **argv)
{
CUdevice cuDevice = findCudaDeviceDRV(argc, (const char **)argv);// 查找设备,返回设备信息 int major = , minor = ;
char deviceName[];
cuDeviceComputeCapability(&major, &minor, cuDevice);
cuDeviceGetName(deviceName, , cuDevice);
printf("> GPU Device has SM %d.%d compute capability\n", major, minor); cuInit(); // cuda 设备初始化 CUresult CUDAAPI cuInit(unsigned int Flags);
cuDeviceGet(&cuDevice, ); // 返回设备编号 CUresult CUDAAPI cuDeviceGet(CUdevice *device, int ordinal);
CUcontext context;
cuCtxCreate(&context, , cuDevice); // 创建上下文 CUresult CUDAAPI cuCtxCreate(CUcontext *pctx, unsigned int flags, CUdevice dev); CUmodule module;
cuModuleLoadDataEx(&module, ptx, , , ); // 读取模块信息 CUresult CUDAAPI cuModuleLoadDataEx(CUmodule *module, const void *image, unsigned int numOptions, CUjit_option *options, void **optionValues); return module;
} CUresult CUDAAPI cuModuleGetFunction(CUfunction *hfunc, CUmodule hmod, const char *name); // 从模块中取出指定的函数 CUresult CUDAAPI cuMemAlloc(CUdeviceptr *dptr, size_t bytesize); // 类似cudaMalloc // 调用核函数的完整格式
CUresult CUDAAPI cuLaunchKernel(CUfunction f,
unsigned int gridDimX, unsigned int gridDimY, unsigned int gridDimZ, unsigned int blockDimX, unsigned int blockDimY, unsigned int blockDimZ,
unsigned int sharedMemBytes, CUstream hStream, void **kernelParams, void **extra); CUresult CUDAAPI cuCtxSynchronize(void); // 上下文同步 CUresult CUDAAPI cuMemFree(CUdeviceptr dptr); // 类似 cudaFree
0_Simple__clock + 0_Simple__clock_nvrtc的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- textarea文本域值中含有大量\t\n问题
最近在发现了一个问题,很是头疼,textarea值中有大量的制表符,尝试了很多办法,最终找到了解决办法,希望能帮到同样有此困扰的你. <textarea> <c:out value= ...
- Linux入门之常用命令(3)
df 查看硬盘总容量.已用容量和inode [-ikm] du 查看文件已用容量,显示所有文件 每块硬盘最多四个分区. fdisk [-l] [设备名称] 硬盘分区工具 (-l 显示这张硬盘的分区) ...
- Muddy Fields
Muddy Fields Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Submi ...
- Java中Math.round()函数
Math.round(11.5) = 12; Math.round(-11.5) = -11; Math.round()函数是求某个数的整数部分,且四舍五入.
- MongoDB学习教程(2)-常用命令
1.MongoDB 创建数据库 use DATABASE_NAME,如果数据库不存在,则创建数据库,否则切换到指定数据库. > use test_0902 switched to db test ...
- Python3常用学习网站总结(随时更新)
Python资源大全 http://python.jobbole.com/84464/ https://github.com/jobbole/awesome-python-cn scrapy: h ...
- Revit二次开发初体验
最近换了下工作,由之前的互联网企业转入了BIM软件开发行列.具体原因不多说,作为一个程序员来说学习永无止境.下面来一个Hello World体验下Revit的二次开发 事前准备 VS Revit 20 ...
- Sqlserver中存储过程和游标的一些使用例子
/*带输入输出参数存储过程*/ ALTER PROCEDURE pro_test2 @userID INT, @maxUserID INT OUTPUT, @countUser INT OUTPUT ...
- C#仪器数据文件解析-Word文件(doc、docx)
不少仪器数据报告输出为Word格式文件,同Excel文件,Word文件doc和docx的存储格式是不同的,相应的解析Word文件的方式也类似,主要有以下方式: 1.通过MS Word应用程序的DCOM ...
- 记一次vscode升级后,格式化Vue出现的问题
一.VSCode中使用vetur插件格式化vue文件时,stylus代码会自动加上大括号.冒号和分号 本来就是简写比较方便舒服,结果一个格式化回到十年前 解决方案: vscode 文件 ->首 ...
