poj——3177Redundant Paths
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 15272 | Accepted: 6436 |
Description
Given a description of the current set of R (F-1 <= R <= 10,000) paths that each connect exactly two different fields, determine the minimum number of new paths (each of which connects exactly two fields) that must be built so that there are at least two separate routes between any pair of fields. Routes are considered separate if they use none of the same paths, even if they visit the same intermediate field along the way.
There might already be more than one paths between the same pair of fields, and you may also build a new path that connects the same fields as some other path.
Input
Lines 2..R+1: Each line contains two space-separated integers which are the fields at the endpoints of some path.
Output
Sample Input
7 7 1 2 2 3 3 4 2 5 4 5 5 6 5 7
Sample Output
2
Hint
One visualization of the paths is:
1 2 3 +---+---+ | | | | 6 +---+---+ 4 / 5 / / 7 +
Building new paths from 1 to 6 and from 4 to 7 satisfies the conditions.
1 2 3 +---+---+ : | | : | | 6 +---+---+ 4 / 5 : / : / : 7 + - - - -
Check some of the routes:
1 – 2: 1 –> 2 and 1 –> 6 –> 5 –> 2
1 – 4: 1 –> 2 –> 3 –> 4 and 1 –> 6 –> 5 –> 4
3 – 7: 3 –> 4 –> 7 and 3 –> 2 –> 5 –> 7
Every pair of fields is, in fact, connected by two routes.
It's possible that adding some other path will also solve the problem (like one from 6 to 7). Adding two paths, however, is the minimum.
Source
描述
为了从一个F(1=f=5000)放牧场(编号为1…F)到另一个场,Bessie和其他牧群被迫越过腐烂的苹果树附近。奶牛现在已经厌倦了常常被迫走一条特定的道路,并且想建立一些新的道路,这样他们就可以在任何一对田地之间选择至少两条独立的路线。他们目前至少有一对路线之间的每一对领域,并希望有至少两个。当然,当他们从一个领域迁移到另一个领域时,他们只能在正式的道路上旅行。
描述了R的电流设定(F-1 <= R <= 10000),每个连接两个不同领域的路径,确定新的路径的最小数目(每个连接两个领域),必须建立,至少有两个独立的路线,任何对田野之间。如果路径没有相同的路径,即使它们在同一个中间区域访问相同的路径,它们也被认为是独立的。
在同一对字段之间可能有不止一条路径,您还可以构建一个新路径,将同一字段与其他路径连接起来。
输入
第1行:两个空间分隔的整数:f和r
第2行…r + 1:每行包含两个空间分隔的整数,这是某个路径端点的字段。
输出
第1行:一个整数,这是必须建立的新路径的数量。
思路:
我们来考虑一下这道题的做法。
由于题目说,给定一张无向强连通图:判断至少需要加多少条边,使得任意两点之间至少有两条相互‘边独立’的道路,也就是说,至少加多少条边,使得这个图成为一个边双连通图。
什么是双连通图?!
双连通图分为两种:双边连通图与双点连通图,双边连通图就是不存在割边的连通图,点双联通图就是不存在割点的连通图。。(差不多是这样吧。。)
首先我们已经有了一个连通图,我们先判断这个强连通图中是否存在环,这个就与tarjan缩点(有向图时有一点差别了)这个图保证是一个强连通图,如果我们还按以前那样缩点的话,我们只会把这个图个缩成一个点,这样肯定不对啊。。。
我们在缩完点以后把它变成了一个树,这样我们只需要把它的子节点连通起来就好了
也就是说:加入的边的条数一定等于:(叶子节点数+1)/2
我们在这个地方所说的叶子结点为入读或出度为0的点。
但在这里我又想到令一种算法:我们可以先求割边,割边的条数就是我们要求的叶子结点的个数
这样说有人可能会不明白了,那好,我们来看一个图
对于这个图来说,我们先将这个图中存在的环缩成一个点,那它就变成了右图的样子
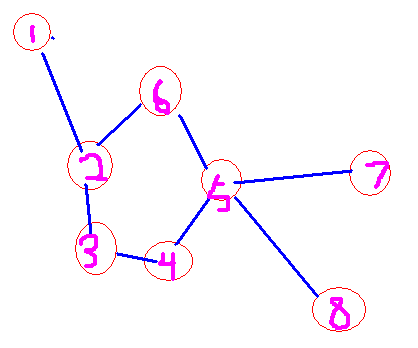 在这里,我们以环缩点后的点5为根节点
在这里,我们以环缩点后的点5为根节点 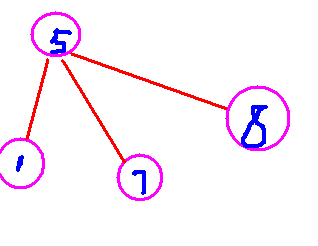
看这个图的子节点是不是3?!
我们下面再来看看这个图的割边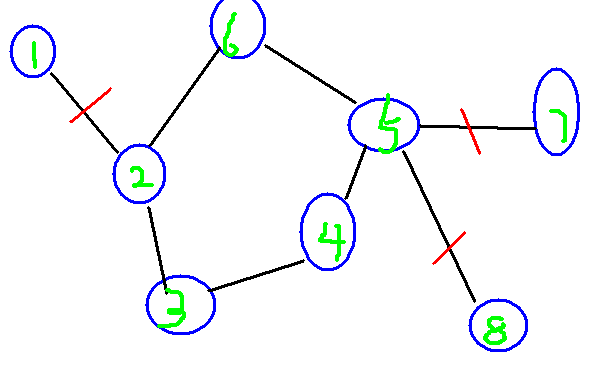 各大佬应该都能看出来我用红线割掉的边是这个图的割边吧。
各大佬应该都能看出来我用红线割掉的边是这个图的割边吧。
他割边的个数是不是也是三?! 也就是说我们上面的结论成立。
那么这个题就变成一个很裸的求割边的板子了。。
好我们来看看代码吧。。
代码:(然而这个思路只能得63分,为什么?!)我们来考虑一下上面的思路的错误所在。
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define N 5005
using namespace std;
bool vis[N][N];
,tim;
long long dfn[N],low[N];
],cut_edge[];
int read()
{
,f=; char ch=getchar();
; ch=getchar();}
+ch-';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct Edge
{
int from,next,to;
}edge[];
void add(int x,int y)
{
tot++;
edge[tot].to=y;
edge[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
int tarjan(int now,int pre)
{
;
dfn[now]=low[now]=++tim;
for(int i=head[now];i;i=edge[i].next)
{
^pre)) continue;
int t=edge[i].to;
if(!dfn[t])
{
tarjan(t,i);
low[now]=min(low[now],low[t]);
]=;
}
else low[now]=min(low[now],dfn[t]);
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
;i<=m;i++)
{
x=read(),y=read();
if(!vis[x][y]&&!vis[y][x]) add(x,y),add(y,x);
vis[x][y]=vis[y][x]=true;
}
tarjan(,);
;i<=m;i++)
)
ans++;
///printf("%d\n",ans);
printf()>>);
;
}
样例的图有些不是很明显,我们来看另一个图
对于这样一个图的话: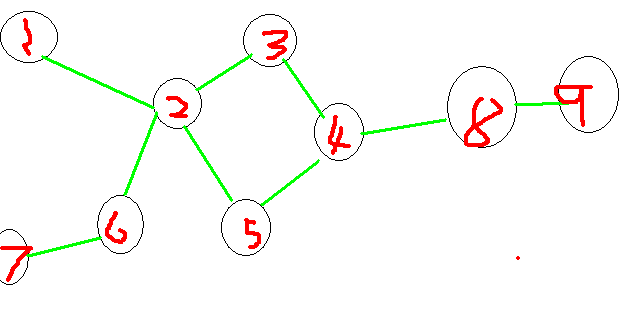 我们缩点之后把它变成了这样一个图:
我们缩点之后把它变成了这样一个图: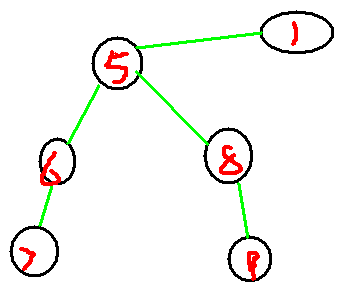
这个图割边的条数为:5条,如果按照我们刚刚的结论来看的话,我们要添3条边,然而我们只需要添2条边就可以了
为什么?!
看这个图: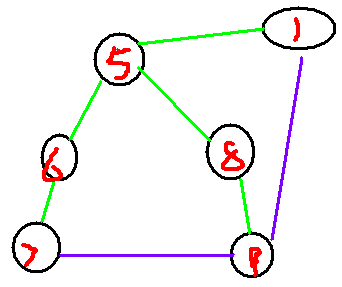 我们只需要在7~9,1~9之间添一条边就可以了。
我们只需要在7~9,1~9之间添一条边就可以了。
那么我们还是乖乖地统计入读为2的点的个数吧。。。。。。(其实这个地方应该是度数为一的点,但是这个地方由于我们建的是双向边,每一个点都会统计两次,所以这个地方最小的将会是入读为2)
这个地方肯定有人就会问这样一个问题:为什么这个地方建的是双向边我们还能用tarjan缩点啊?! 缩点的时候所得不是一个强连通分量吗??这样的一个绝对联通的无向图不就是直接把他缩成了一个点了吗?!这样怎么还能这样做?!
想一下这个地方我们在缩点的时候为什么可以用tarjan??
这样缩点主要是归功于这一句话:if(i==(1^pre)) continue; 对,他是用两条边,但是我们这个地方只让他走一条边,这样不就和有向图缩点一样了吗?!
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define N 5005
using namespace std;
bool vis[N];
,tim,sum,top;
long long du[N],dfn[N],low[N],stack[N],belong[N];
];
int read()
{
,f=; char ch=getchar();
; ch=getchar();}
+ch-';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct Edge
{
int from,next,to;
}edge[];
void add(int x,int y)
{
tot++;
edge[tot].to=y;
edge[tot].next=head[x];
head[x]=tot;
}
int tarjan(int now,int pre)
{
dfn[now]=low[now]=++tim;
stack[++top]=now;
for(int i=head[now];i;i=edge[i].next)
{
int t=edge[i].to;
^pre)) continue;
if(!dfn[t]) tarjan(t,i),low[now]=min(low[now],low[t]);
else low[now]=min(low[now],dfn[t]);
}
if(low[now]==dfn[now])
{
sum++; belong[now]=sum;
for(;stack[top]!=now;top--)
belong[stack[top]]=sum;
top--;
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
;i<=m;i++)
x=read(),y=read(),add(x,y),add(y,x);
tarjan(,);
;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=head[i];j;j=edge[j].next)
if(belong[i]!=belong[edge[j].to]) du[belong[i]]++,du[belong[edge[j].to]]++;
;i<=n;i++)
) ans++;
printf()>>);
;
}
poj——3177Redundant Paths的更多相关文章
- POJ 3177--Redundant Paths【无向图添加最少的边成为边双连通图 && tarjan求ebc && 缩点构造缩点树】
Redundant Paths Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10798 Accepted: 4626 ...
- POJ 1942 Paths on a Grid(组合数)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1942 题意 :在一个n*m的矩形上有n*m个网格,从左下角的网格划到右上角的网格,沿着边画,只能向上或向右走,问有多少条不重复的路 . 思路 : ...
- poj 1924 Paths on a Grid(组合数学)
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=1942 题意:给定一个矩形网格的长m和高n,其中m和n都是unsigned int32类型,一格代表一个单位,就是一步,求从左下角到右上角有 ...
- [ACM] POJ 1942 Paths on a Grid (组合)
Paths on a Grid Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 21297 Accepted: 5212 ...
- POJ 1942 Paths on a Grid
// n*m 的格子 从左下角走到右上角的种数// 相当于从 n+m 的步数中选 m 步往上走// C(n+m,m) #include <iostream> #include <st ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths(边双连通的构造)
Redundant Paths Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 13717 Accepted: 5824 ...
- tarjan算法求桥双连通分量 POJ 3177 Redundant Paths
POJ 3177 Redundant Paths Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 12598 Accept ...
- (poj 3177) Redundant Paths
题目链接 :http://poj.org/problem?id=3177 Description In order to <= F <= ,) grazing fields (which ...
- POJ 3177 Redundant Paths POJ 3352 Road Construction(双连接)
POJ 3177 Redundant Paths POJ 3352 Road Construction 题目链接 题意:两题一样的.一份代码能交.给定一个连通无向图,问加几条边能使得图变成一个双连通图 ...
随机推荐
- Hibernate核心接口和工作原理
Hibernate核心接口和工作原理 Hibernate有五大核心接口,分别是:Session .Transaction .Query .SessionFactory .Configuration . ...
- 自欺欺人的使用 NSTimer 销毁
自欺欺人的使用 NSTimer 销毁 Demo地址 1.NSTimer是要加到runloop中才会起作用. 常见的创建timer方式 // 第一种方式 @property (nonatomic , s ...
- SQLite – DISTINCT 关键字
SQLite – DISTINCT关键字 使用SQLite DISTINCT关键字与SELECT语句来消除所有重复的记录和获取唯一的记录. 可能存在一种情况,当你有多个表中重复的记录. 获取这些记录, ...
- (转)编码剖析@Resource注解的实现原理
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52860046 上文我们已经学会使用@Resource注解注入属性.学是学会了,但也仅限于会使用 ...
- Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a computer code running on top of a blockchain containing a set of rules under w ...
- CFBundleURLTypes URL scheme
https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/General/Reference/InfoPlistKeyReference/Ar ...
- python的特殊数字类型(无穷大、无穷小等)
float('inf') 表示正无穷 -float('inf') 或 float('-inf') 表示负无穷 其中,inf 均可以写成 Inf 起步python中整型不用担心溢出,因为python理论 ...
- idea创建和部署tomcat项目
小编今天花费了一上午,参悟出了如何快速的在idea上面创建并部署一个属于自己的maven项目,很荣幸能将自己的开发经验推而广之,希望能够帮助到大家! 前言 小编参考博文: Intellij Idea ...
- python基础一day3 字符串
对字符串进行的任何操作都是形成新的字符串. 切片顾头不顾尾 倒着取: 因为顾头不顾尾,所以4要取到 当步长省略时,可以同时省略最后一个冒号 写0时,取不到,什么都不写,可以取到 倒着取出全部的值,两种 ...
- Java集合(四)--基于JDK1.8的ArrayList源码解读
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess ...
