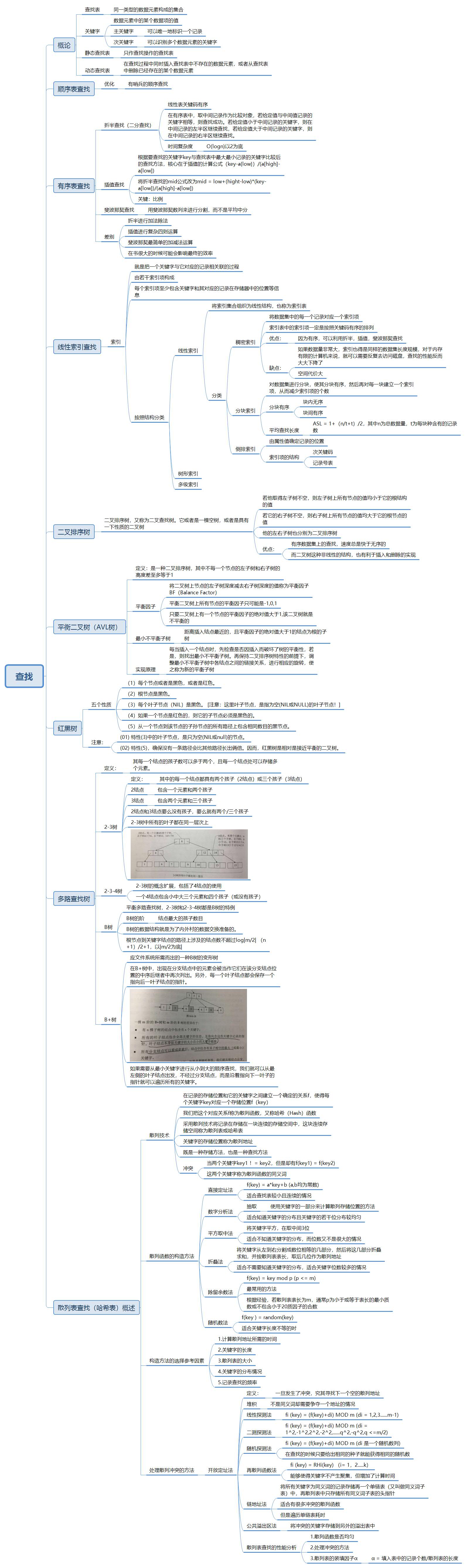
Chapter 8(查找)
//************************Search.h***********************************
#ifndef SEARCH_H
#define SEARCH_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int BiSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
int IVSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
int FibSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
#endif //SEARCH_H
//************************Search.c*************************************
#include "Search.h"
//折半查找
int BiSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
if(NULL == array)return -1;
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid = (left+right)/2;
while(left <= right)
{
if(array[mid] == key)
{
return mid;
}
else if(array[mid] > key)
{
right = mid-1;
}
else if(array[mid] < key)
{
left = mid+1;
}
mid = (left+right)/2;
}
return -1;
}
//插值查找
int IVSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
if(NULL == array)return -1;
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid = left+(right-left)*(key-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left]);
while(left <= right)
{
if(array[mid] == key)
{
return mid;
}
else if(array[mid] > key)
{
right = mid-1;
}
else if(array[mid] < key)
{
left = mid+1;
}
mid = left+(right-left)*(key-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left]);
}
return -1;
}
int FibSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
int F[] = {1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89};
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid;
int k = 0;
while(n>F[k]-1)
{
k++;
}
for(int i=n;i < F[k])
}
//************************SearchTest.c*************************************
#include "Search.h"
int main()
{
int a[10] = {1,16,24,35,47,59,62,73,88,99};
int key = 62;
printf("position: %d \n",BiSearch(a,10,key));
printf("position: %d \n",IVSearch(a,10,key));
}//************************Search.h***********************************
#ifndef SEARCH_H
#define SEARCH_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int BiSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
int IVSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
int FibSearch(int array[],int n,int key);
#endif //SEARCH_H
//************************Search.c*************************************
#include "Search.h"
//折半查找
int BiSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
if(NULL == array)return -1;
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid = (left+right)/2;
while(left <= right)
{
if(array[mid] == key)
{
return mid;
}
else if(array[mid] > key)
{
right = mid-1;
}
else if(array[mid] < key)
{
left = mid+1;
}
mid = (left+right)/2;
}
return -1;
}
//插值查找
int IVSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
if(NULL == array)return -1;
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid = left+(right-left)*(key-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left]);
while(left <= right)
{
if(array[mid] == key)
{
return mid;
}
else if(array[mid] > key)
{
right = mid-1;
}
else if(array[mid] < key)
{
left = mid+1;
}
mid = left+(right-left)*(key-array[left])/(array[right]-array[left]);
}
return -1;
}
int FibSearch(int array[],int n,int key)
{
int F[] = {1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89};
int left = 0;
int right= n-1;
int mid;
int k = 0;
while(n>F[k]-1)
{
k++;
}
for(int i=n;i < F[k])
}
//************************SearchTest.c*************************************
#include "Search.h"
int main()
{
int a[10] = {1,16,24,35,47,59,62,73,88,99};
int key = 62;
printf("position: %d \n",BiSearch(a,10,key));
printf("position: %d \n",IVSearch(a,10,key));
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXN 20
/*
*产生斐波那契数列
* */
void Fibonacci(int *f)
{
int i;
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
for(i = 2;i < MAXN; ++i)
f[i] = f[i - 2] + f[i - 1];
}
/*
* 查找
* */
int Fibonacci_Search(int *a, int key, int n)
{
int i, low = 0, high = n - 1;
int mid = 0;
int k = 0;
int F[MAXN];
Fibonacci(F);
while(n > F[k] - 1) //计算出n在斐波那契中的数列
++k;
for(i = n;i < F[k] - 1;++i) //把数组补全
a[i] = a[high];
while(low <= high)
{
mid = low + F[k-1] - 1; //根据斐波那契数列进行黄金分割
if(a[mid] > key)
{
high = mid - 1;
k = k - 1;
}
else if(a[mid] < key)
{
low = mid + 1;
k = k - 2;
}
else
{
if(mid <= high) //如果为真则找到相应的位置
return mid;
else
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int a[MAXN] = {5,15,19,20,25,31,38,41,45,49,52,55,57};
int k, res = 0;
printf("请输入要查找的数字:\n");
scanf("%d", &k);
res = Fibonacci_Search(a,k,13);
if(res != -1)
printf("在数组的第%d个位置找到元素:%d\n", res + 1, k);
else
printf("未在数组中找到元素:%d\n",k);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXN 20
/*
*产生斐波那契数列
* */
void Fibonacci(int *f)
{
int i;
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
for(i = 2;i < MAXN; ++i)
f[i] = f[i - 2] + f[i - 1];
}
/*
* 查找
* */
int Fibonacci_Search(int *a, int key, int n)
{
int i, low = 0, high = n - 1;
int mid = 0;
int k = 0;
int F[MAXN];
Fibonacci(F);
while(n > F[k] - 1) //计算出n在斐波那契中的数列
++k;
for(i = n;i < F[k] - 1;++i) //把数组补全
a[i] = a[high];
while(low <= high)
{
mid = low + F[k-1] - 1; //根据斐波那契数列进行黄金分割
if(a[mid] > key)
{
high = mid - 1;
k = k - 1;
}
else if(a[mid] < key)
{
low = mid + 1;
k = k - 2;
}
else
{
if(mid <= high) //如果为真则找到相应的位置
return mid;
else
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int a[MAXN] = {5,15,19,20,25,31,38,41,45,49,52,55,57};
int k, res = 0;
printf("请输入要查找的数字:\n");
scanf("%d", &k);
res = Fibonacci_Search(a,k,13);
if(res != -1)
printf("在数组的第%d个位置找到元素:%d\n", res + 1, k);
else
printf("未在数组中找到元素:%d\n",k);
return 0;
}
//****************************BiSortTree.h*************************
#ifndef BISORTTREE_H
#define BISORTTREE_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct BiSNode
{
datatype data;
struct BiSNode *left,*right;
}BiSNode,*BiSTree;
//在二叉排序树中查找key
bool SearchBST(BiSTree T,datatype key,BiSTree f,BiSTree *p);
//按顺插入
bool InsertBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key);
//删除节点
bool DeleteBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key);
bool Delete(BiSTree *p);
#endif //BISORTTREE_H
//****************************BiSortTree.c*************************
#include "BiSortTree.h"
//在二叉排序树中查找key
bool SearchBST(BiSTree T,datatype key,BiSTree f,BiSTree *p)
{
if(!T)
{
*p = f;
return false;
}
else if(key == T->data)
{
*p = T;
return true;
}
else if(key < T->data)
{
return SearchBST(T->left,key,T,p);
}
else
{
return SearchBST(T->right,key,T,p);
}
}
//按顺插入
bool InsertBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key)
{
BiSTree p,s;
if(!SearchBST(*T,key,NULL,&p))
{
s = (BiSTree)malloc(sizeof(BiSNode));
s->data = key;
s->left = s->right = NULL;
if(!p)
{
*T = s;
}
else if(key < p->data)
{
p->left = s;
}
else
{
p->right = s;
}
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//删除节点
bool DeleteBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key)
{
if(!*T)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if(key == (*T)->data)
{
return Delete(T);
}
else if(key < (*T)->data)
{
DeleteBST(&(*T)->left,key);
}
else
{
DeleteBST(&(*T)->right,key);
}
}
}
bool Delete(BiSTree *p)
{
BiSTree q,s;
if(NULL == (*p)->left)
{
q = *p;
*p = (*p)->right;
free(q);
}
else if(NULL == (*p)->right)
{
q = *p;
*p = (*p)->left;
free(q);
}
else
{
q = *p;
s = (*p)->left;
while(s->right)
{
q = s;
s = s->right;
}
(*p)->data = s->data;
if(q != *p)
{
q->right = s->left;
}
else
{
q->left = s->left;
}
free(s);
}
return true;
}
//****************************BiSortTreeTest.c*************************
#include "BiSortTree.h"
int main()
{
int i;
int a[10] ={62,88,58,47,35,73,51,99,37,93};
BiSTree T = NULL;
for(i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
InsertBST(&T,a[i]);
}
BiSTree p,f;
printf("%d \n",p->data);
SearchBST(T,58,f,&p);
printf("%d \n",p->data);
DeleteBST(&T,58);
printf("%d \n",p->data);
}//****************************BiSortTree.h*************************
#ifndef BISORTTREE_H
#define BISORTTREE_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct BiSNode
{
datatype data;
struct BiSNode *left,*right;
}BiSNode,*BiSTree;
//在二叉排序树中查找key
bool SearchBST(BiSTree T,datatype key,BiSTree f,BiSTree *p);
//按顺插入
bool InsertBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key);
//删除节点
bool DeleteBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key);
bool Delete(BiSTree *p);
#endif //BISORTTREE_H
//****************************BiSortTree.c*************************
#include "BiSortTree.h"
//在二叉排序树中查找key
bool SearchBST(BiSTree T,datatype key,BiSTree f,BiSTree *p)
{
if(!T)
{
*p = f;
return false;
}
else if(key == T->data)
{
*p = T;
return true;
}
else if(key < T->data)
{
return SearchBST(T->left,key,T,p);
}
else
{
return SearchBST(T->right,key,T,p);
}
}
//按顺插入
bool InsertBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key)
{
BiSTree p,s;
if(!SearchBST(*T,key,NULL,&p))
{
s = (BiSTree)malloc(sizeof(BiSNode));
s->data = key;
s->left = s->right = NULL;
if(!p)
{
*T = s;
}
else if(key < p->data)
{
p->left = s;
}
else
{
p->right = s;
}
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//删除节点
bool DeleteBST(BiSTree *T,datatype key)
{
if(!*T)
{
return false;
}
else
{
if(key == (*T)->data)
{
return Delete(T);
}
else if(key < (*T)->data)
{
DeleteBST(&(*T)->left,key);
}
else
{
DeleteBST(&(*T)->right,key);
}
}
}
bool Delete(BiSTree *p)
{
BiSTree q,s;
if(NULL == (*p)->left)
{
q = *p;
*p = (*p)->right;
free(q);
}
else if(NULL == (*p)->right)
{
q = *p;
*p = (*p)->left;
free(q);
}
else
{
q = *p;
s = (*p)->left;
while(s->right)
{
q = s;
s = s->right;
}
(*p)->data = s->data;
if(q != *p)
{
q->right = s->left;
}
else
{
q->left = s->left;
}
free(s);
}
return true;
}
//****************************BiSortTreeTest.c*************************
#include "BiSortTree.h"
int main()
{
int i;
int a[10] ={62,88,58,47,35,73,51,99,37,93};
BiSTree T = NULL;
for(i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
InsertBST(&T,a[i]);
}
BiSTree p,f;
printf("%d \n",p->data);
SearchBST(T,58,f,&p);
printf("%d \n",p->data);
DeleteBST(&T,58);
printf("%d \n",p->data);
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define EH 0 /*等高*/
#define LH 1 /*左高*/
#define RH -1 /*右高*/
typedef int ElemType; /*数据类型*/
typedef struct BiTree{
ElemType data; /*数据元素*/
int BF; /*平衡因子*/
struct BiTree *lchild,*rchild; /*左右子女指针*/
}*Bitree,BitreeNode;
int InsertAVL(Bitree *T,ElemType e,bool *taller);
void LeftBalance(Bitree *T);
void RightBalance(Bitree *T);
void R_Rotate(Bitree *T);
void L_Rotate(Bitree *T);
bool *taller;
//bool *taller= (bool *)malloc(sizeof(bool));
int main(void)
{
taller= (bool *)malloc(sizeof(bool));
int data;
Bitree T=NULL;
while(1)
{
printf("enter the number(zero to exit):");
scanf("%d",&data);
if(0==data)break;
InsertAVL(&T,data,taller);
}
return 0;
}
/*若在平衡的二叉排序树T 中不存在和e 有相同关键码的结点,则插入一个数据元素为e 的*/
/*新结点,并反回1,否则反回0。若因插入而使二叉排序树失去平衡,则作平衡旋转处理,*/
/*布尔型变量taller 反映T 长高与否*/
int InsertAVL(Bitree *T,ElemType e,bool *taller)
{
if(!*T) /*插入新结点,树“长高”,置taller 为TURE*/
{
(*T)=(Bitree)malloc(sizeof(BitreeNode));
(*T)->data = e;
(*T)->lchild = (*T)->rchild = NULL;
(*T)->BF = EH;
*taller = true;
}
else
{
if(e==(*T)->data) /*树中存在和e 有相同关键码的结点,不插入*/
{
*taller = false;
return 0;
}
if(e<(*T)->data)
{
if(!InsertAVL(&(*T)->lchild,e,taller)) return 0; /*未插入*/
if(*taller)
switch((*T)->BF)
{
case EH : /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=LH;
*taller=true;
break;
case LH : /*原本左子树高,需作左平衡处理*/
LeftBalance(T);
*taller=false;
break;
case RH : /*原本右子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
(*T)->BF=EH;
*taller=false;
break;
}
}
else
{
if(!InsertAVL(&(*T)->rchild,e,taller)) return 0; /*未插入*/
if(*taller)
switch((*T)->BF)
{
case EH : /*原本左、右子树等高,因右子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=RH;
*taller=true;
break;
case LH : /*原本左子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
(*T)->BF=EH;
*taller=false;
break;
case RH : /*原本右子树高,需作右平衡处理*/
RightBalance(T);
*taller=false;
break;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
/*对以*p 指向的结点为根的子树,作左平衡旋转处理,处理之后,*p 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void LeftBalance(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree L=(*T)->lchild,Lr; /*L 指向*T左子树根结点*/
switch(L->BF) /*检查L 平衡度,并作相应处理*/
{
case LH: /*新结点插在*p 左子树的左子树上,需作单右旋转处理*/
(*T)->BF=L->BF=EH;
R_Rotate(T);
break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=LH; //这里的EH好像没有写的必要
*taller=true;
break;
case RH: /*新结点插在*T 左孩子的右子树上,需作先左后右双旋处理*/
Lr=L->rchild; /*Lr 指向*p 左孩子的右子树根结点*/
switch(Lr->BF) /*修正*T 及其左子树的平衡因子*/
{
case LH:
(*T)->BF = RH;
L->BF = EH;
break;
case EH:
(*T)->BF = L->BF= EH;
break;
case RH:
(*T)->BF = EH;
L->BF = LH;
break;
}
Lr->BF = EH;
L_Rotate(&L); /*对*T 的左子树作左旋转处理*/
R_Rotate(T); /*对*T 作右旋转处理*/
}
}
//这里和leftbalance一个道理,试着自己写一下
void RightBalance(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree Lr= (*T)->rchild,L;
switch(Lr->BF)
{
case EH:
*taller = true;
(*T)->BF = RH;
break;
case RH:
(*T)->BF=Lr->BF=EH;
L_Rotate(T);
break;
case LH:
L = Lr->lchild;
switch(L->BF)
{
case EH:
(*T)->BF=Lr->BF= EH;
break;
case RH:
Lr->BF= EH;
(*T)->BF = LH;
break;
case LH:
(*T)->BF = LH;
Lr->BF = EH;
break;
}
L->BF = EH;
R_Rotate(&Lr);
L_Rotate(T);
}
}
/*对以*T 指向的结点为根的子树,作右单旋转处理,处理之后,*T 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void R_Rotate(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree L=(*T)->lchild; /*L 指向*T 左子树根结点*/
(*T)->lchild=L->rchild; /*L 的右子树挂接*T 的左子树*/
L->rchild=*T; *T=L; /* *L 指向新的根结点*/
}
/*对以*p 指向的结点为根的子树,作左单旋转处理,处理之后,*p 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void L_Rotate(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree Lr=(*T)->rchild; /*Lr 指向*T 右子树根结点*/
(*T)->rchild=Lr->lchild; /*L 的左子树挂接*p 的右子树*/
Lr->lchild=*T;
*T=Lr; /* *L 指向新的根结点*/
}#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define EH 0 /*等高*/
#define LH 1 /*左高*/
#define RH -1 /*右高*/
typedef int ElemType; /*数据类型*/
typedef struct BiTree{
ElemType data; /*数据元素*/
int BF; /*平衡因子*/
struct BiTree *lchild,*rchild; /*左右子女指针*/
}*Bitree,BitreeNode;
int InsertAVL(Bitree *T,ElemType e,bool *taller);
void LeftBalance(Bitree *T);
void RightBalance(Bitree *T);
void R_Rotate(Bitree *T);
void L_Rotate(Bitree *T);
bool *taller;
//bool *taller= (bool *)malloc(sizeof(bool));
int main(void)
{
taller= (bool *)malloc(sizeof(bool));
int data;
Bitree T=NULL;
while(1)
{
printf("enter the number(zero to exit):");
scanf("%d",&data);
if(0==data)break;
InsertAVL(&T,data,taller);
}
return 0;
}
/*若在平衡的二叉排序树T 中不存在和e 有相同关键码的结点,则插入一个数据元素为e 的*/
/*新结点,并反回1,否则反回0。若因插入而使二叉排序树失去平衡,则作平衡旋转处理,*/
/*布尔型变量taller 反映T 长高与否*/
int InsertAVL(Bitree *T,ElemType e,bool *taller)
{
if(!*T) /*插入新结点,树“长高”,置taller 为TURE*/
{
(*T)=(Bitree)malloc(sizeof(BitreeNode));
(*T)->data = e;
(*T)->lchild = (*T)->rchild = NULL;
(*T)->BF = EH;
*taller = true;
}
else
{
if(e==(*T)->data) /*树中存在和e 有相同关键码的结点,不插入*/
{
*taller = false;
return 0;
}
if(e<(*T)->data)
{
if(!InsertAVL(&(*T)->lchild,e,taller)) return 0; /*未插入*/
if(*taller)
switch((*T)->BF)
{
case EH : /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=LH;
*taller=true;
break;
case LH : /*原本左子树高,需作左平衡处理*/
LeftBalance(T);
*taller=false;
break;
case RH : /*原本右子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
(*T)->BF=EH;
*taller=false;
break;
}
}
else
{
if(!InsertAVL(&(*T)->rchild,e,taller)) return 0; /*未插入*/
if(*taller)
switch((*T)->BF)
{
case EH : /*原本左、右子树等高,因右子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=RH;
*taller=true;
break;
case LH : /*原本左子树高,使左、右子树等高*/
(*T)->BF=EH;
*taller=false;
break;
case RH : /*原本右子树高,需作右平衡处理*/
RightBalance(T);
*taller=false;
break;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
/*对以*p 指向的结点为根的子树,作左平衡旋转处理,处理之后,*p 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void LeftBalance(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree L=(*T)->lchild,Lr; /*L 指向*T左子树根结点*/
switch(L->BF) /*检查L 平衡度,并作相应处理*/
{
case LH: /*新结点插在*p 左子树的左子树上,需作单右旋转处理*/
(*T)->BF=L->BF=EH;
R_Rotate(T);
break;
case EH: /*原本左、右子树等高,因左子树增高使树增高*/
(*T)->BF=LH; //这里的EH好像没有写的必要
*taller=true;
break;
case RH: /*新结点插在*T 左孩子的右子树上,需作先左后右双旋处理*/
Lr=L->rchild; /*Lr 指向*p 左孩子的右子树根结点*/
switch(Lr->BF) /*修正*T 及其左子树的平衡因子*/
{
case LH:
(*T)->BF = RH;
L->BF = EH;
break;
case EH:
(*T)->BF = L->BF= EH;
break;
case RH:
(*T)->BF = EH;
L->BF = LH;
break;
}
Lr->BF = EH;
L_Rotate(&L); /*对*T 的左子树作左旋转处理*/
R_Rotate(T); /*对*T 作右旋转处理*/
}
}
//这里和leftbalance一个道理,试着自己写一下
void RightBalance(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree Lr= (*T)->rchild,L;
switch(Lr->BF)
{
case EH:
*taller = true;
(*T)->BF = RH;
break;
case RH:
(*T)->BF=Lr->BF=EH;
L_Rotate(T);
break;
case LH:
L = Lr->lchild;
switch(L->BF)
{
case EH:
(*T)->BF=Lr->BF= EH;
break;
case RH:
Lr->BF= EH;
(*T)->BF = LH;
break;
case LH:
(*T)->BF = LH;
Lr->BF = EH;
break;
}
L->BF = EH;
R_Rotate(&Lr);
L_Rotate(T);
}
}
/*对以*T 指向的结点为根的子树,作右单旋转处理,处理之后,*T 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void R_Rotate(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree L=(*T)->lchild; /*L 指向*T 左子树根结点*/
(*T)->lchild=L->rchild; /*L 的右子树挂接*T 的左子树*/
L->rchild=*T; *T=L; /* *L 指向新的根结点*/
}
/*对以*p 指向的结点为根的子树,作左单旋转处理,处理之后,*p 指向的结点为子树的新根*/
void L_Rotate(Bitree *T)
{
Bitree Lr=(*T)->rchild; /*Lr 指向*T 右子树根结点*/
(*T)->rchild=Lr->lchild; /*L 的左子树挂接*p 的右子树*/
Lr->lchild=*T;
*T=Lr; /* *L 指向新的根结点*/
}
附件列表
Chapter 8(查找)的更多相关文章
- Chapter 5 查找
Chapter 5 查找 1- 顺序查找法 O(n) 2- 折半查找O(logn) :二分查找 要求:关键字有序 过程: 判定树:叶子结点为方框,代表不成功的结点. 3- 分块查找:索引顺 ...
- 【ASP.NET Identity系列教程(一)】ASP.NET Identity入门
注:本文是[ASP.NET Identity系列教程]的第一篇.本系列教程详细.完整.深入地介绍了微软的ASP.NET Identity技术,描述了如何运用ASP.NET Identity实现应用程序 ...
- ASP.NET Identity 一 (转载)
来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/r01cn/p/5194257.html 注:本文是[ASP.NET Identity系列教程]的第一篇.本系列教程详细.完整.深入地介绍了微软的A ...
- ASP.NET Identity系列教程-2【Identity入门】
https://www.cnblogs.com/r01cn/p/5177708.html13 Identity入门 Identity is a new API from Microsoft to ma ...
- Chapter 3: Connector(连接器)
一.概述 Tomcat或者称之为Catalina(开发名称),可以简化为两个主要的模块,如下图: 多个Connector关联一个Container.之所以需要多个Connector,是为了处理多种协议 ...
- Chapter Schema
Chapter Schema Schema是XF的核心,每一个读写方法都有一个相关联的Schema.方法首先解析Schema,然后再根据Schema的配置的执行. 那Schema是什么呢?Schema ...
- Chapter 1 Securing Your Server and Network(9):使用Kerberos用于身份验证
原文:Chapter 1 Securing Your Server and Network(9):使用Kerberos用于身份验证 原文出处:http://blog.csdn.net/dba_huan ...
- Linux - 在当前系统内查找信息的方法
查找文本 使用grep命令 grep命令 - 示例 grep命令 - 正则表达式 grep命令 - 统计匹配字符串的行数 grep命令 - 搜索多个单词 结合正则表达式使用grep命令 注意:在搜索指 ...
- 《Linux内核设计与实现》Chapter 18 读书笔记
<Linux内核设计与实现>Chapter 18 读书笔记 一.准备开始 一个bug 一个藏匿bug的内核版本 知道这个bug最早出现在哪个内核版本中. 相关内核代码的知识和运气 想要成功 ...
随机推荐
- route命令详情
基础命令学习目录首页 原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/lpfuture/p/5857738.html 考试题一:linux下如何添加路由(百度面试题) 以上是原题,老男孩老师 ...
- MegaCli64/MegaCli命令详解
基础命令学习目录首页 MegaCli64 -LDInfo -Lall -aALL这个命令能看到RAID的状态MegaCli64 -LDSetProp ForcedWB -L0 -a0MegaCli64 ...
- Ubuntu 1804 本地显示远程服务器文件
本地是 Ubuntu 1804 最近想查看服务器上的图片,之前都是scp到本地,感觉太麻烦,于是查到有一种方法,ssh图形界面那种: 1.在File 界面下,左侧文件栏的最后一列有 “+ Other ...
- python处理xml实例
""" Author = zyh FileName = read_xml_1.py Time = 18-9-26 下午5:19 """ fr ...
- Android笔记-4-实现登陆页面并跳转和简单的注册页面
实现登陆页面并跳转和简单的注册页面 首先我们来看看布局的xml代码 login.xml <span style="font-family:Arial;font-size:18px; ...
- windows和RedHat双系统安装说明
该博客记录了安装windows和RedHat双系统的方法.这里的windows系统是win8.1,RedHat是RHEL-server-7.0-x86_64-LinuxProbe.Com.iso,该i ...
- java中的互斥锁和信号量的区别
互斥锁和信号量都是操作系统中为并发编程设计基本概念,互斥锁和信号量的概念上的不同在于,对于同一个资源,互斥锁只有0和1 的概念,而信号量不止于此.也就是说,信号量可以使资源同时被多个线程访问,而互斥锁 ...
- grunt入门讲解2:如何使用 Gruntfile 配置任务
Grunt的task配置都是在 Gruntfile 中的grunt.initConfig方法中指定的.此配置主要包括以任务名称命名的属性,和其他任意数据.一旦这些代表任意数据的属性与任务所需要的属性相 ...
- Prism框架的优点
以我粗略的了解,prism/mvvm可以做到完全的逻辑和ui分离.即便是事件都是如此.这是主要优点.mvc是从本质上ui框架(当前大量半吊子把业务逻辑写在里面是不对的),mvvm包含客户端的业务逻辑. ...
- appium启动sdk的android模拟器
(1)启动sdk安装目录下的AVD Manager.exe (2)如下图,点击[create]按钮 (3)如下图,设置虚拟机的配置,至于Target中的:Android 4.4.2是在安装sdk的时候 ...
