Fibonacci Heaps
Mergeable heaps
A mergeable heap is any data structure that supports the following five operations,
in which each element has a key:
MAKE-HEAP./ creates and returns a new heap containing no elements.
INSERT.H; x/ inserts element x, whose key has already been filled in, into heap H.
MINIMUM.H/ returns a pointer to the element in heap H whose key is minimum.
EXTRACT-MIN.H/ deletes the element from heap H whose key is minimum, returning
a pointer to the element.
UNION.H1;H2/ creates and returns a new heap that contains all the elements of
heaps H1 and H2. Heaps H1 and H2 are “destroyed” by this operation.
In addition to the mergeable-heap operations above, Fibonacci heaps also support
the following two operations:
DECREASE-KEY.H; x; k/ assigns to element x within heap H the new key
value k, which we assume to be no greater than its current key value.1
DELETE.H; x/ deletes element x from heap H.


Each node has two other attributes. We store the number of children in the child
list of node x in x:degree. The boolean-valued attribute x:mark indicates whether
node x has lost a child since the last time x was made the child of another node.
Newly created nodes are unmarked, and a node x becomes unmarked whenever it
is made the child of another node. Until we look at the DECREASE-KEY operation
in Section 19.3, we will just set all mark attributes to FALSE.


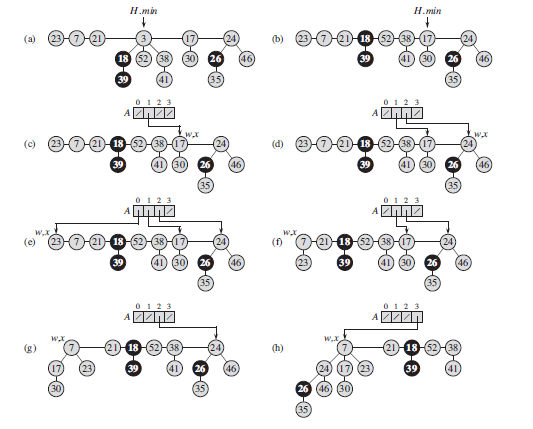
In detail, the CONSOLIDATE procedure works as follows. Lines 1–3 allocate
and initialize the array A by making each entry NIL. The for loop of lines 4–14
processes each root w in the root list. As we link roots together, w may be linked
to some other node and no longer be a root. Nevertheless, w is always in a tree
rooted at some node x, which may or may not be w itself. Because we want at
most one root with each degree, we look in the array A to see whether it contains
a root y with the same degree as x. If it does, then we link the roots x and y but
guaranteeing that x remains a root after linking. That is, we link y to x after first
exchanging the pointers to the two roots if y’s key is smaller than x’s key. After
we link y to x, the degree of x has increased by 1, and so we continue this process,
linking x and another root whose degree equalsx’s new degree, until no other root
that we have processed has the same degree as x. We then set the appropriate entry
of A to point to x, so that as we process roots later on, we have recorded that x is
the unique root of its degree that we have already processed. When this for loop
terminates, at most one root of each degree will remain, and the array A will point
to each remaining root.
The while loop of lines 7–13 repeatedly links the root x of the tree containing
node w to another tree whose root has the same degree as x, until no other root has
the same degree. This while loop maintains the following invariant:
At the start of each iteration of the while loop, d D x:degree.

Fibonacci Heaps的更多相关文章
- 一些鲜为人知却非常实用的数据结构 - Haippy
原文:http://www.udpwork.com/item/9932.html 作为程序猿(媛),你必须熟知一些常见的数据结构,比如栈.队列.字符串.链表.二叉树.哈希,但是除了这些常见的数据结构以 ...
- .NET中的泛型集合总结
最近对集合相关的命名空间比较感兴趣,以前也就用下List<T>, Dictionary<Tkey, TValue>之类,总之,比较小白.点开N多博客,MSDN,StackOve ...
- 【推荐】Data Structure Visualizations
University of San Francisco David Galles 功能:可视化数据结构&算法实现过程 网站地址 https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~ga ...
- [Algorithm] 如何正确撸<算法导论>CLRS
其实算法本身不难,第一遍可以只看伪代码和算法思路.如果想进一步理解的话,第三章那些标记法是非常重要的,就算要花费大量时间才能理解,也不要马马虎虎略过.因为以后的每一章,讲完算法就是这样的分析,精通的话 ...
- 某Facebook工程师写的攻略。
Chapter 1 Interesting read, but you can skip it. Chapter 2 2.1 Insertion Sort - To be honest you sho ...
- Programmer Competency Matrix--ref--http://sijinjoseph.com/programmer-competency-matrix/
Note that the knowledge for each level is cumulative; being atlevel n implies that you also know eve ...
- JAVA工程师技能要求
近期做了个JAVA工程师分类, JAVA工程师可能是市场上最多类的程序员: 初级JAVA工程师的基本要求 Good basic programming skills 良好基本编程技能 Founda ...
- 算法与数据结构(九) 查找表的顺序查找、折半查找、插值查找以及Fibonacci查找
今天这篇博客就聊聊几种常见的查找算法,当然本篇博客只是涉及了部分查找算法,接下来的几篇博客中都将会介绍关于查找的相关内容.本篇博客主要介绍查找表的顺序查找.折半查找.插值查找以及Fibonacci查找 ...
- #26 fibonacci seqs
Difficulty: Easy Topic: Fibonacci seqs Write a function which returns the first X fibonacci numbers. ...
随机推荐
- ELK学习笔记之基于kakfa (confluent)搭建ELK
0x00 概述 测试搭建一个使用kafka作为消息队列的ELK环境,数据采集转换实现结构如下: F5 HSL–>logstash(流处理)–> kafka –>elasticsear ...
- Python RabbitMQ消息持久化
RabbitMQ消息持久化:就是将队列中的消息永久的存放在队列中. 处理方案: # 在实例化时加入durable=True来确认消息的实例化,客户端服务端都要写 channel.queue_dec ...
- xshell的优化和连接
远程连接linux ###远程连接工具---xshell/SecureCRT/Putty 商业版(收费) 家庭版(免费) 一.xshell进行优化 1.打开文件属性 2.设置终端类型问linux,输入 ...
- kubeflow 创建tensorflow过程
online deployable ,install k8s 代码 Kubeflow有三个核心组件 TFJob Operator 和 Controller: 作为Kubernetes的扩展,来简化分布 ...
- centos etcd 启动失败
chmod -R 777 /var/lib/etcd systemctl daemon-reload cat /etc/systemd/system/etcd.service " [Unit ...
- tp剩余未验证内容-7
bash脚本中 的 set -e表示 exit immediately if a simple command returns a non-zero value.主要是为了防止错误被忽略.会被立即退出 ...
- Excel 表格查找重复数据,去重复统计
找出表格是否有重复数据: =IF(AND(G20=G19,D20=D19),"是","否") 筛选移除[重复的数据]然后开始统计 =SUBTOTAL(9,E2: ...
- 关于MVC RouteExistingFiles疑问后续
前两天写了<关于MVC RouteExistingFiles疑问>,本来希望寻求大佬快速解答,奈何无人问津. 只能查看.NET 源代码,可以使用反编译工具(我用IL spy),也可以在线查 ...
- Java使用Socket进行通信
什么是Socket 网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的交换,这个连接的一端称为一个socket.通常也称作"套接字",用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,可以 ...
- Windows Server 2008环境下Apache2.4+Tomcat8配置
安装步骤 1. 安装配置JDK2. 安装配置Apache3. 安装配置Tomcat4. 启动服务并测试 一.Apache安装与配置 1.Apache解压在D盘根目录下建立一个文件夹Apache Gro ...
