Codeforces 937.D Sleepy Game
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Petya and Vasya arranged a game. The game runs by the following rules. Players have a directed graph consisting of n vertices and medges. One of the vertices contains a chip. Initially the chip is located at vertex s. Players take turns moving the chip along some edge of the graph. Petya goes first. Player who can't move the chip loses. If the game lasts for 106 turns the draw is announced.
Vasya was performing big laboratory work in "Spelling and parts of speech" at night before the game, so he fell asleep at the very beginning of the game. Petya decided to take the advantage of this situation and make both Petya's and Vasya's moves.
Your task is to help Petya find out if he can win the game or at least draw a tie.
The first line of input contain two integers n and m — the number of vertices and the number of edges in the graph (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2·105).
The next n lines contain the information about edges of the graph. i-th line (1 ≤ i ≤ n) contains nonnegative integer ci — number of vertices such that there is an edge from i to these vertices and ci distinct integers ai, j — indices of these vertices (1 ≤ ai, j ≤ n, ai, j ≠ i).
It is guaranteed that the total sum of ci equals to m.
The next line contains index of vertex s — the initial position of the chip (1 ≤ s ≤ n).
If Petya can win print «Win» in the first line. In the next line print numbers v1, v2, ..., vk (1 ≤ k ≤ 106) — the sequence of vertices Petya should visit for the winning. Vertex v1 should coincide with s. For i = 1... k - 1 there should be an edge from vi to vi + 1 in the graph. There must be no possible move from vertex vk. The sequence should be such that Petya wins the game.
If Petya can't win but can draw a tie, print «Draw» in the only line. Otherwise print «Lose».
5 6
2 2 3
2 4 5
1 4
1 5
0
1
Win
1 2 4 5
3 2
1 3
1 1
0
2
Lose
2 2
1 2
1 1
1
Draw
In the first example the graph is the following:
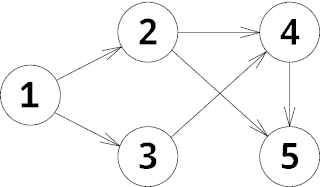
Initially the chip is located at vertex 1. In the first move Petya moves the chip to vertex 2, after that he moves it to vertex 4 for Vasya. After that he moves to vertex 5. Now it is Vasya's turn and there is no possible move, so Petya wins.
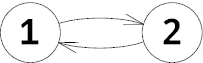
In the second example the graph is the following:

Initially the chip is located at vertex 2. The only possible Petya's move is to go to vertex 1. After that he has to go to 3 for Vasya. Now it's Petya's turn but he has no possible move, so Petya loses.
In the third example the graph is the following:
Petya can't win, but he can move along the cycle, so the players will draw a tie.
题目大意:在一个有向图上,从起点出发,先手走一步,后手在前者的基础上再走一步,不能走的人算输. 现在你既操控了先手,又操控了后手,问你能不能让先手赢,如果不行能不能让这个游戏一直进行下去?
分析:最后走到的点肯定是出度为0的点.我一开始的想法是从起点出发bfs,如果走到一个出度为0的点并且路径的长度为奇数,则能赢.否则就看图中是否存在环,如果有环并且和起点连通,那么游戏就能一直进行下去了.否则就会输掉.
这个想法有一种情况没有考虑到:走到出度为0的点并且路径长度为偶数,按照之前的判断应该是不行的,但是如果这个路径上套一个奇环就不一样了,可以在奇环上走一圈那么路径长度就为奇数了. 直接统计点数为奇数的环不是很容易,需要换一个思路.
从起点开始dfs,记录走到当前点的路径的奇偶性.vis数组记录走到点u并且经过路径的奇偶性为p这个状态是否访问过.枚举u的下一个点v,那么走到v的话奇偶性就变成了p ^ 1 = q.如果vis[v][q]没有被标记,就走到v,记录路径. 如果被标记了1,说明有环,游戏能够一直下去.如果u的所有后继点都被访问完了,就将vis[u][p]标记为2.
为什么还要让标记为2呢?考虑下面一种情况:
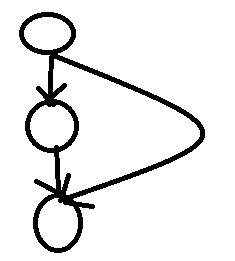 ,对于最下面的一个点,先走左边的路径,那么它被标记为了1,再从右边走,发现它已经被标记为了1,就会认为这是一个环!如果打上2标记就不会出现这种情况.
,对于最下面的一个点,先走左边的路径,那么它被标记为了1,再从右边走,发现它已经被标记为了1,就会认为这是一个环!如果打上2标记就不会出现这种情况.
get到了找奇环的新技巧,找环问题要考虑好vis数组到底会不会用到标记2!
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std;
const int maxn = ;
int n,m,head[maxn],to[maxn],nextt[maxn],tot = ,s;
int vis[maxn][],pre[maxn][],du[maxn],ansnode,cnt,anss[maxn];
bool flag = false,can = false; void add(int x,int y)
{
to[tot] = y;
nextt[tot] = head[x];
head[x] = tot++;
} bool dfs(int u,int p)
{
vis[u][p] = ;
int q = p ^ ;
for (int i = head[u];i;i = nextt[i])
{
int v = to[i];
if (!vis[v][q])
{
pre[v][q] = u;
if (dfs(v,q))
return true;
}
else
if (vis[v][q] == )
flag = true;
}
if (du[u] == && p == )
{
can = ;
ansnode = u;
return true;
}
vis[u][p] = ;
return false;
} int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
int num;
scanf("%d",&num);
du[i] = num;
for (int j = ; j <= num; j++)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
add(i,x);
}
}
scanf("%d",&s);
if (dfs(s,))
{
puts("Win");
int x = ;
while (ansnode != )
{
anss[++cnt] = ansnode;
ansnode = pre[ansnode][x];
x ^= ;
}
for (int i = cnt; i >= ; i--)
printf("%d ",anss[i]);
}
else
if (flag)
puts("Draw");
else
puts("Lose"); return ;
}
Codeforces 937.D Sleepy Game的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 937 D. Sleepy Game(DFS 判断环)
题目链接: Sleepy Game 题意: Petya and Vasya 在玩移动旗子的游戏, 谁不能移动就输了. Vasya在订移动计划的时候睡着了, 然后Petya 就想趁着Vasya睡着的时候 ...
- CodeForces 937D 936B Sleepy Game 有向图判环,拆点,DFS
题意: 一种游戏,2个人轮流控制棋子在一块有向图上移动,每次移动一条边,不能移动的人为输,无限循环则为平局,棋子初始位置为$S$ 现在有一个人可以同时控制两个玩家,问是否能使得第一个人必胜,并输出一个 ...
- Codeforces 937.C Save Energy!
C. Save Energy! time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard inpu ...
- Codeforces 937.B Vile Grasshoppers
B. Vile Grasshoppers time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces 937D - Sleepy Game
937D - Sleepy Game 思路: dfs. vis[u][0]==1表示u这个点能从s点偶数路径到达 vis[u][1]==1表示u这个点能从s点奇数路径到达 这个样就能保证dfs时每个点 ...
- 【codeforces】【比赛题解】#937 CF Round #467 (Div. 2)
没有参加,但是之后几天打了哦,第三场AK的CF比赛. CF大扫荡计划正在稳步进行. [A]Olympiad 题意: 给\(n\)个人颁奖,要满足: 至少有一个人拿奖. 如果得分为\(x\)的有奖,那么 ...
- Codeforces Round #467 (Div. 1) B. Sleepy Game
我一开始把题目看错了 我以为是博弈.. 这题就是一个简单的判环+dfs(不简单,挺烦的一题) #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> #i ...
- Sleepy Game CodeForces - 936B
大意: 给定有向图, 初始点S, 两个人轮流移动, 谁不能移动则输, 但后手睡着了, 先手可以控制后手操作, 求最后先手结果. 刚开始看错了, 还以为后手也是最优策略.... 实际上判断是否有偶数个节 ...
- Codeforces 390A( 模拟题)
Inna and Alarm Clock Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 262144KB 64bit IO Format: %I64d & %I64 ...
随机推荐
- 搭建RTSP服务器时nginx的nginx.conf文件配置
worker_processes 1; events { worker_connections 1024;} http { include mime.types; default_type appli ...
- DruidDataSource源码分析
最近公司要求基于阿里的DruidDataSource来做一个连接池监控 , 正好之前没有看过DruidDataSource的源码 , 便自己看了四个多小时写了一些自己的理解 , 给大家分享一下 , 如 ...
- 如何更改Arcmap里经纬度小数点后面的位数?
customize>arcmap option>data view >round coordinate to 改成想要显示的小数位数
- ES6的新特性(11)——Class 的继承
Class 的继承 简介 Class 可以通过extends关键字实现继承,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多. class Point { } class ColorPoint ...
- Python:Python的运行过程
1.Python是什么 和Java以及c#一样,Python也是一门基于虚拟机的语言.熟悉Java开发的人在命令行执行一个Java程序的过程通常如下: javac hello.java java he ...
- postion一句话很管用
relative和absolute有本质区别,relative是相对与postion为默认值的时候元素自身位置来定位:而absolute是相对最近position为relative或absolute的 ...
- 404_NOTE_Foung_软工6
目录 NABCD分析引用 N(Need,需求): A(Approach,做法): B(Benefit,好处): C(Competitors,竞争): D(Delivery,交付): 初期 中期 个人贡 ...
- EF动态排序
转载的代码,改天再研究 public PageData<T> FindAll(int PageIndex, int PageSize, Expression<Func<T, b ...
- C#控件之Repeater控件使用
歡迎大家來討論,修改,一定虛心接受. 1.為什麼使用Repeater控件? 關於把從數據庫讀取的數據綁定到前台頁面,我們可以使用DataGrid.DataGridView以及Repeater來佈局,三 ...
- PAT 甲级 1132 Cut Integer
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805347145859072 Cutting an integer mea ...
