第 15 章 位操作(dualview)
/*-----------------------------------
dualview.c -- 位字段和按位运算符
-----------------------------------*/ #include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h> //边框线样式
#define SOLID 0
#define DOTTED 1
#define DASHED 2 //三原色
#define BLUE 4
#define GREEN 2
#define RED 1 //混合颜色
#define BLACK (RED & GREEN & BLUE)
#define YELLOW (RED | GREEN)
#define MAGENTA (RED | BLUE)
#define CYAN (GREEN | BLUE)
#define WHITE (RED | BLUE | GREEN) //按位方法中用到的符号常量
#define OPAQUE 0x1
#define FILL_BLUE 0x8
#define FILL_GREEN 0x4
#define FILL_RED 0x2
#define FILL_MASK 0xE //掩码
#define BORDER 0x100
#define BORDER_BLUE 0x800
#define BORDER_GREEN 0x400
#define BORDER_RED 0x200
#define BORDER_MASK 0xE00
#define B_SOLID 0
#define B_DOTTED 0x1000
#define B_DASHED 0x2000
#define STYLE_MASK 0x3000 struct box_props
{
unsigned int opaque : ;
unsigned int fill_color : ;
unsigned int : ;
unsigned int show_border : ;
unsigned int border_color : ;
unsigned int border_style : ;
unsigned int : ;
}; //把数据看作结构或 unsigned short 类型的变量
union Views
{
struct box_props st_view;
unsigned short us_view;
}; const char *color[] =
{
"black", "red", "green", "yellow", "blue", "magenta", "cyan", "white"
}; void show_settings(const struct box_props *pb);
void show_setting1(unsigned short);
char* itobs(int n, char *ps);
void show_bstr(const char *str); int main()
{
printf("size of struct box_props is %d bit\n", CHAR_BIT * sizeof(struct box_props));
printf("size of unsigned short is %d bit\n", CHAR_BIT * sizeof(unsigned short)); //创建 Vies 联合,并初始化 initialize struct box view
union Views box = {{true, YELLOW, true, GREEN, DASHED}};
char bin_str[ * sizeof(unsigned int) + ]; printf("\nOriginal box settings:\n");
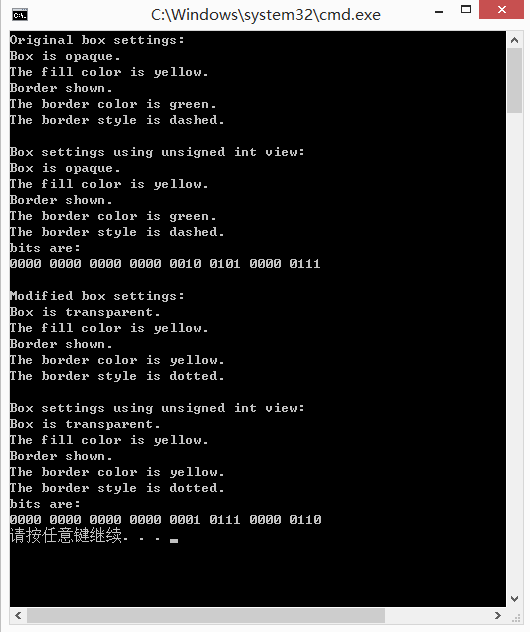
show_settings(&box.st_view);
printf("\nBox settings using unsigned int view:\n");
show_setting1(box.us_view);
//printf("bits are %s\n", itobs(box.us_view, bin_str));
printf("bits are:\n");
show_bstr(itobs(box.us_view, bin_str)); box.us_view &= ~FILL_MASK; //把表示填充色的位清零
box.us_view |= CYAN; //重置填充色
box.us_view ^= OPAQUE; //切换透明位
box.us_view &= ~BORDER_MASK; //边框颜色位清零
box.us_view |= BORDER_RED;
box.us_view &= ~STYLE_MASK; //样式位清零
box.us_view |= B_DOTTED; //边框样式设置为点
printf("\nModified box settings:\n");
show_settings(&box.st_view);
printf("\nBox settings using unsigned int view:\n");
show_setting1(box.us_view);
//printf("bits are %s\n", itobs(box.us_view, bin_str));
printf("bits are:\n");
show_bstr(itobs(box.us_view, bin_str)); return ;
} void show_settings(const struct box_props *pb)
{
printf("Box is %s.\n", pb->opaque ? "opaque" : "transparent");
printf("The fill color is %s.\n", color[pb->fill_color]);
printf("Border %s.\n", pb->show_border ? "shown" : "not shown");
printf("The border color is %s.\n", color[pb->border_color]); printf("The border style is ");
switch (pb->border_style)
{
case SOLID:
printf("solid.\n");
break; case DOTTED:
printf("dotted.\n");
break; case DASHED:
printf("dashed.\n");
break; default:
printf("unknown type.\n");
break;
}
} void show_setting1(unsigned short us)
{
printf("Box is %s.\n", (us & OPAQUE) ? "opaque" : "transparent");
printf("The fill color is %s.\n", color[(us >> ) & 0x07]);
printf("Border %s.\n", (us & BORDER) == BORDER ? "shown" : "not shown");
printf("The border color is %s.\n", color[us >> & 0x07]); printf("The border style is ");
switch (us & STYLE_MASK)
{
case B_SOLID:
printf("solid.\n");
break; case B_DOTTED:
printf("dotted.\n");
break; case B_DASHED:
printf("dashed.\n");
break; default:
printf("unknown style");
break;
}
} char* itobs(int n, char *ps)
{
const static int size = CHAR_BIT * sizeof(int); for (int i(size - ); i >= ; --i, n >>= )
ps[i] = ( & n) + ''; ps[size] = '\0'; return ps;
} //以 4 位为一组,显示二进制字符串
void show_bstr(const char *str)
{
int i = ; while (str[i]) //str[i] 不是空字符
{
putchar(str[i]); if (++i % == && str[i])
putchar(' ');
} putchar('\n');
}
dualview.c
第 15 章 位操作(dualview)的更多相关文章
- 第 15 章 位操作(invert4)
/*------------------------------------ invert4.c -- 使用位操作显示二进制 ------------------------------------* ...
- 第 15 章 位操作(binbit)
/*------------------------------------ binbit.c -- 使用位操作显示二进制 ------------------------------------*/ ...
- 第 15 章 位操作(fields)
/*----------------------------------- fields.c -- 定义并使用字段 -----------------------------------*/ #inc ...
- Linux就这个范儿 第15章 七种武器 linux 同步IO: sync、fsync与fdatasync Linux中的内存大页面huge page/large page David Cutler Linux读写内存数据的三种方式
Linux就这个范儿 第15章 七种武器 linux 同步IO: sync.fsync与fdatasync Linux中的内存大页面huge page/large page David Cut ...
- 【STM32H7教程】第15章 STM32H7的GPIO基础知识(重要)
完整教程下载地址:http://www.armbbs.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=86980 第15章 STM32H7的GPIO基础知识(重要) ...
- 第15章 LinkedList类(暂无)
第15章 LinkedList类 LinkedList类是
- ASM:《X86汇编语言-从实模式到保护模式》第15章:任务切换
15章其实应该是和14章相辅相成的(感觉应该是作者觉得14章内容太多了然后切出来了一点).任务切换和14章的某些概念是分不开的. ★PART1:任务门与任务切换的方法 1. 任务管理程序 14章的时候 ...
- 第15章 设备无关位图_15.3 DIB和DDB的结合
第15章 设备相关位图_15.3 DIB和DDB的结合 15.3.1 从DIB创建DDB (1)hBitmap =CreateDIBitmap(…)——注意这名称会误导,实际上创建的是DDB 参数 说 ...
- unix network programming(3rd)Vol.1 [第13~15章]《读书笔记系列》
第13章 守护进程和inetd 超级服务器 syslog() daemon_init() setuid() setgid() 第14章 高级IO 标准I/O函数库,支持3种缓冲 缓冲(读写存储设备(硬 ...
随机推荐
- maven snapshot和release版本的区别
Maven的Snapshot版本与Release版本 1. Snapshot版本代表不稳定.尚处于开发中的版本 2. Release版本则代表稳定的版本 3. 什么情况下该用SNAPSHOT? 协同开 ...
- Docker构建Java web应用服务
1.构建一个Java应用服务,包含两个步骤:a.一个镜像从URL拉取指定的WAR文件并保存到卷里b.一个含有Tomcat服务器的镜像运行这些下载的WAR文件 2.构建下载WAR的镜像 FROM cen ...
- linux下软件包管理
挂载光盘:mkdir /mnt/cdrommount /dev/cdrom /mnt/cdrom 1.rpm包管理1.安装一个包 rpm –ivh < rpm package name> ...
- 精读JavaScript模式(三),new一个构造函数居然发生了什么?
一.前言 上个月底,爸爸因为事故突然离世,说心里话,现在看到'去世','爸爸'这样的字眼,眼泪都会忍不住在眼眶打转,还是需要时间治愈.最近也只是零碎的看了下东西,始终沉不下心去读书,直到今天还是决定捡 ...
- php手撸轻量级开发(二)框架加载
先上图,有图有真相 1. 加载index文件 index文件是整个项目的唯一入口,任何请求进入项目都是走的index,只是带的参数不一样,然后再在index文件里加载其他文件,相当于把其他文件整个复制 ...
- python的Web框架,Django的ORM,模型基础,MySQL连接配置及增删改查
Django中的ORM简介 ORM概念:对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM): 用面向对象的方式描述数据库,去操作数据库,甚至可以达到不用编写SQL语句就能够 ...
- JS之BOM、DOM
一.BOM对象 1,window对象 所有浏览器都支持window对象,从概念上讲:一个HTML文档对应一个window对象,从功能上讲:控制浏览器窗口的,从使用上讲:window对象不需要创建对象, ...
- VPS杂谈(一)
1. VPS购买推荐 可参考:http://www.laozuo.org/myvps 2. VPS配置SSH端口号 购买的VPS的主机,一般情况下端口号不是22,被改成了其它的,这个时候为了方便自己的 ...
- 左连接,右连接,内连接(left join ,right join,inner join)
浅谈左连接,右连接,内连接(left join ,right join,inner join) 这个问题一直困扰着我,每次遇到就打擦边球,不正面应对.今天索性把这几个连接搞懂了,写下这篇博客, 让跟我 ...
- 探秘小程序(10):分享功能+webview
场景: 小程序页面用webview嵌入了h5页面,h5页面需要与小程序进行交互,h5页面内容不同,分享的链接也不一样 分享功能: 小程序的分享功能即用户点击小程序右上角,转发功能页面.可以指定分享卡片 ...
