Digester解析xml原理
Tomcat内部是使用Digester来解析xml文件的,将xml转化为java对象。
digester底层是基于SAX+事件驱动+栈的方式来搭建实现的,SAX主要用来解析xml,事件驱动主要是在解析的过程中加入事件来操作节点元素,栈主要是在节点解析开始和结束时对xml节点元素对应的对象操作入栈或出栈来实现事件的调用。
使用方法
定义一个Department部门类以及一个User用户类,部门中包含许多个用户
@Data
public class Department {
private String departmentName;
private List<User> userList;
public Department() {
userList = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addUser(User user) {
userList.add(user);
}
}@Data
public class User {
private String userName;
private String age;
public void print() {
System.out.println("userName:" + userName + ", age:" + age);
}
}xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<department departmentName="产品技术部">
<user userName="monian" age="25">默念</user>
</department>定义规则解析xml文件
1. ObjectCreateRule规则类
public void addObjectCreate(String pattern, String className, String attributeName) 当匹配到pattern模式节点时会创建对象,当在节点中指定了attributeName属性时,会创建类型为attributeName属性值的对象否则创建类名为className的对象,并将创建的对象push到stack栈顶
2. SetPropertiesRule规则类
public void addSetProperties(String pattern) 当匹配到pattern模式节点时会填充stack栈顶元素对象的属性值
3. CallMethodRule规则类
public void addCallMethod(String pattern, String methodName) (无参)当匹配到pattern模式节点时会调用stack栈顶元素对象的methodName方法
public void addCallMethod(String pattern, String methodName, int paramCount) (有参,指定参数个数与CallParamRule规则配合使用,设置参数值),构建空的参数数组并push到params栈顶
4. CallParamRule规则类
public void addCallParam(String pattern, int paramIndex) 当匹配到pattern模式时,以pattern模式节点的内容填充params栈顶元素参数的值
5. SetNextRule规则类
public void addSetNext(String pattern, String methodName, String paramType) 当匹配到pattern模式时,调用栈顶元素的上一个元素的methodName方法并以栈顶元素作为参数
6. 自定义规则类
public void addRule(String pattern, Rule rule) 当匹配到pattern模式时,执行自定义的规则
public class DigesterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, SAXException {
InputStream resource
= ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.xml");
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
// 创建对象规则
digester.addObjectCreate("department", Department.class.getName());
// 填充属性规则
digester.addSetProperties("department");
digester.addObjectCreate("department/user", User.class.getName());
digester.addSetProperties("department/user");
// 调用方法规则
digester.addCallMethod("department/user", "print");
// 调用栈顶元素上一个元素的指定方法,以栈顶元素作为参数
digester.addSetNext("department/user", "addUser", User.class.getName());
// 解析test.xml文件 获取department对象
Department department = (Department) digester.parse(resource);
System.out.println(department);
}
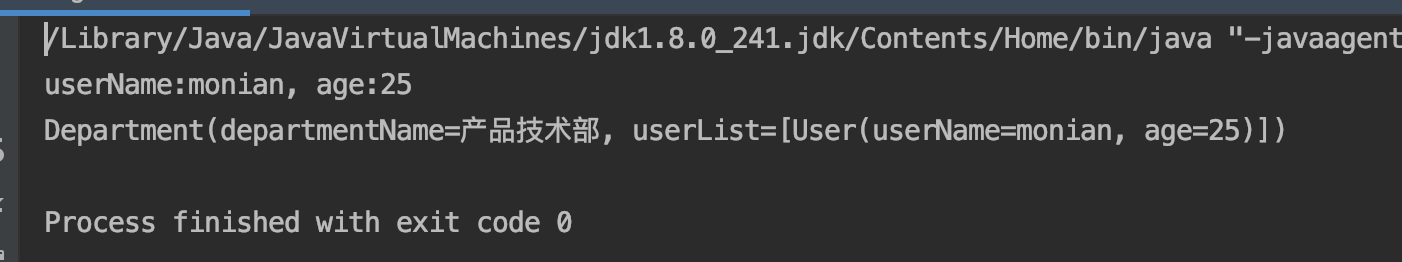
}运行程序可以看到调用digester的parse方法后成功解析获得department对象
原理
上面列出的规则类都继承了Rule这个抽象类,能够在匹配pattern模式时执行相应的事件方法,让我们看看Rule中定义了哪些方法
/**
* Concrete implementations of this class implement actions to be taken when
* a corresponding nested pattern of XML elements has been matched.
*/
public abstract class Rule {
// ----------------------------------------------------------- Constructors
/**
* <p>Base constructor.
* Now the digester will be set when the rule is added.</p>
*/
public Rule() {}
// ----------------------------------------------------- Instance Variables
/**
* The Digester with which this Rule is associated.
*/
// 这个规则关联的digester
protected Digester digester = null;
/**
* The namespace URI for which this Rule is relevant, if any.
*/
protected String namespaceURI = null;
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
/**
* Identify the Digester with which this Rule is associated.
*
* @return the Digester with which this Rule is associated.
*/
public Digester getDigester() {
return digester;
}
/**
* Set the <code>Digester</code> with which this <code>Rule</code> is
* associated.
*
* @param digester The digester with which to associate this rule
*/
public void setDigester(Digester digester) {
this.digester = digester;
}
/**
* Return the namespace URI for which this Rule is relevant, if any.
*
* @return The namespace URI for which this rule is relevant or
* <code>null</code> if none.
*/
public String getNamespaceURI() {
return namespaceURI;
}
/**
* Set the namespace URI for which this Rule is relevant, if any.
*
* @param namespaceURI Namespace URI for which this Rule is relevant,
* or <code>null</code> to match independent of namespace.
*/
public void setNamespaceURI(String namespaceURI) {
this.namespaceURI = namespaceURI;
}
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* This method is called when the beginning of a matching XML element
* is encountered. The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param namespace the namespace URI of the matching element, or an
* empty string if the parser is not namespace aware or the
* element has no namespace 节点定义的命名空间
* @param name the local name if the parser is namespace aware, or just
* the element name otherwise 节点名称
* @param attributes The attribute list of this element 节点属性值列表
*
* @throws Exception if an error occurs while processing the event
*/
// 遇到匹配xml元素的开头是调用此方法
public void begin(String namespace, String name, Attributes attributes) throws Exception {
// NO-OP by default.
}
/**
* This method is called when the body of a matching XML element is
* encountered. If the element has no body, this method is not called at
* all. The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param namespace the namespace URI of the matching element, or an empty
* string if the parser is not namespace aware or the
* element has no namespace 节点定义的命名空间
* @param name the local name if the parser is namespace aware, or just the
* element name otherwise 节点名称
* @param text The text of the body of this element 节点文本内容
*
* @throws Exception if an error occurs while processing the event
*/
// 遇到匹配的 XML 元素的主体时调用此方法, 内容为空的话不调用
public void body(String namespace, String name, String text) throws Exception {
// NO-OP by default.
}
/**
* This method is called when the end of a matching XML element
* is encountered. The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param namespace the namespace URI of the matching element, or an empty
* string if the parser is not namespace aware or the
* element has no namespace
* @param name the local name if the parser is namespace aware, or just the
* element name otherwise
*
* @throws Exception if an error occurs while processing the event
*/
// 当遇到匹配的 XML 元素的结尾时调用此方法。
public void end(String namespace, String name) throws Exception {
// NO-OP by default.
}
/**
* This method is called after all parsing methods have been
* called, to allow Rules to remove temporary data.
*
* @throws Exception if an error occurs while processing the event
*/
// 所有解析方法调用后调用此方法,允许规则删除临时产生的数据
public void finish() throws Exception {
// NO-OP by default.
}
}接下来再来看看Digester的几个重要属性和方法
// 继承了SAX的DefaultHandler类,会在解析过程中接受到相应的通知
public class Digester extends DefaultHandler2 {
// 用来解析占位符属性 ${xxx}, 主要从System.getProperty(xxx)获取
protected IntrospectionUtils.PropertySource source[] = new IntrospectionUtils.PropertySource[] {
new SystemPropertySource() };
// 当前正在解析的节点内容
protected StringBuilder bodyText = new StringBuilder();
// 解析过程中产生的节点内容堆栈
protected ArrayStack<StringBuilder> bodyTexts = new ArrayStack<>();
// 解析过程中存储规则列表的堆栈 list中的每个规则有相同的pattern
protected ArrayStack<List<Rule>> matches = new ArrayStack<>(10);
// 嵌套元素处理的当前匹配模式 例如 department 、 department/user
protected String match = "";
// 存储方法参数的堆栈
protected ArrayStack<Object> params = new ArrayStack<>();
// 根节点元素,最后出栈stack的那个元素
protected Object root = null;
// 实现类为RulesBase,拥有cache属性存储了pattern和规则列表的映射,能根据pattern获取规则列表
protected Rules rules = null;
// 存储新创建对象的堆栈
protected ArrayStack<Object> stack = new ArrayStack<>();
// 假属性映射(通常用于对象创建)
protected Map<Class<?>, List<String>> fakeAttributes = null;
// 接收元素内字符数据的通知
@Override
public void characters(char buffer[], int start, int length) throws SAXException {
if (saxLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
saxLog.debug("characters(" + new String(buffer, start, length) + ")");
}
bodyText.append(buffer, start, length);
}
//处理到达 XML 元素开始的通知
@Override
public void startElement(String namespaceURI, String localName, String qName, Attributes list)
throws SAXException {
boolean debug = log.isDebugEnabled();
if (saxLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
saxLog.debug("startElement(" + namespaceURI + "," + localName + "," + qName + ")");
}
// Parse system properties
// 解析系统属性(若有)
list = updateAttributes(list);
// Save the body text accumulated for our surrounding element
bodyTexts.push(bodyText);
bodyText = new StringBuilder();
// the actual element name is either in localName or qName, depending
// on whether the parser is namespace aware
String name = localName;
if ((name == null) || (name.length() < 1)) {
name = qName;
}
// Compute the current matching rule
// 计算当前的pattern规则
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(match);
if (match.length() > 0) {
sb.append('/');
}
sb.append(name);
match = sb.toString();
if (debug) {
log.debug(" New match='" + match + "'");
}
// Fire "begin" events for all relevant rules
// 获取与pattern模式匹配的规则
List<Rule> rules = getRules().match(namespaceURI, match);
// push进matches栈
matches.push(rules);
// 遍历规则执行每个规则的begin方法
if ((rules != null) && (rules.size() > 0)) {
for (int i = 0; i < rules.size(); i++) {
try {
Rule rule = rules.get(i);
if (debug) {
log.debug(" Fire begin() for " + rule);
}
rule.begin(namespaceURI, name, list);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Begin event threw exception", e);
throw createSAXException(e);
} catch (Error e) {
log.error("Begin event threw error", e);
throw e;
}
}
} else {
if (debug) {
log.debug(" No rules found matching '" + match + "'.");
}
}
}
// 接收元素结束的通知
@Override
public void endElement(String namespaceURI, String localName, String qName)
throws SAXException {
boolean debug = log.isDebugEnabled();
if (debug) {
if (saxLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
saxLog.debug("endElement(" + namespaceURI + "," + localName + "," + qName + ")");
}
log.debug(" match='" + match + "'");
log.debug(" bodyText='" + bodyText + "'");
}
// Parse system properties
// 获取节点元素内容
bodyText = updateBodyText(bodyText);
// the actual element name is either in localName or qName, depending
// on whether the parser is namespace aware
String name = localName;
if ((name == null) || (name.length() < 1)) {
name = qName;
}
// Fire "body" events for all relevant rules
// 弹出最近元素的规则匹配 遍历调用body方法
List<Rule> rules = matches.pop();
if ((rules != null) && (rules.size() > 0)) {
String bodyText = this.bodyText.toString();
for (int i = 0; i < rules.size(); i++) {
try {
Rule rule = rules.get(i);
if (debug) {
log.debug(" Fire body() for " + rule);
}
rule.body(namespaceURI, name, bodyText);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Body event threw exception", e);
throw createSAXException(e);
} catch (Error e) {
log.error("Body event threw error", e);
throw e;
}
}
} else {
if (debug) {
log.debug(" No rules found matching '" + match + "'.");
}
if (rulesValidation) {
log.warn(" No rules found matching '" + match + "'.");
}
}
// Recover the body text from the surrounding element
bodyText = bodyTexts.pop();
// Fire "end" events for all relevant rules in reverse order
// 遍历规则调用end方法
if (rules != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < rules.size(); i++) {
int j = (rules.size() - i) - 1;
try {
Rule rule = rules.get(j);
if (debug) {
log.debug(" Fire end() for " + rule);
}
rule.end(namespaceURI, name);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("End event threw exception", e);
throw createSAXException(e);
} catch (Error e) {
log.error("End event threw error", e);
throw e;
}
}
}
// Recover the previous match expression
int slash = match.lastIndexOf('/');
if (slash >= 0) {
match = match.substring(0, slash);
} else {
match = "";
}
}
// 处理到达文档开头的通知
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
if (saxLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
saxLog.debug("startDocument()");
}
if (locator instanceof Locator2) {
if (root instanceof DocumentProperties.Charset) {
String enc = ((Locator2) locator).getEncoding();
if (enc != null) {
try {
((DocumentProperties.Charset) root).setCharset(B2CConverter.getCharset(enc));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("disgester.encodingInvalid", enc), e);
}
}
} else if (root instanceof DocumentProperties.Encoding) {
((DocumentProperties.Encoding) root).setEncoding(((Locator2) locator).getEncoding());
}
}
// ensure that the digester is properly configured, as
// the digester could be used as a SAX ContentHandler
// rather than via the parse() methods.
configure();
}
// 处理到达文档末尾的通知
@Override
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
if (saxLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (getCount() > 1) {
saxLog.debug("endDocument(): " + getCount() + " elements left");
} else {
saxLog.debug("endDocument()");
}
}
// 弹出stack中的所有对象
while (getCount() > 1) {
pop();
}
// Fire "finish" events for all defined rules
// 遍历所有的规则 调用finish方法
for (Rule rule : getRules().rules()) {
try {
rule.finish();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Finish event threw exception", e);
throw createSAXException(e);
} catch (Error e) {
log.error("Finish event threw error", e);
throw e;
}
}
// Perform final cleanup
clear();
}
}sax解析xml的过程中无论是处理文档还是节点元素都会有开始解析节点、结束解析节点的通知,会调用子类Digester的相应方法,在方法中用事先定义的规则对节点元素进行事件处理。
接着尝试自定义一个规则来打印节点解析过程中的日志,方便我们更加清晰的明白其处理流程。
自定义规则CustomRule,继承Rule
@Slf4j(topic = "e")
public class CustomRule extends Rule {
@Override
public void begin(String namespace, String name, Attributes attributes) throws Exception {
log.info("开始解析" + name + "节点");
log.info("节点属性值:");
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
log.info(attributes.getLocalName(i) + "=" + attributes.getValue(i));
}
}
@Override
public void body(String namespace, String name, String text) throws Exception {
log.info("节点元素" + name + "内容:" + text);
}
@Override
public void end(String namespace, String name) throws Exception {
log.info("结束解析" + name + "节点");
}
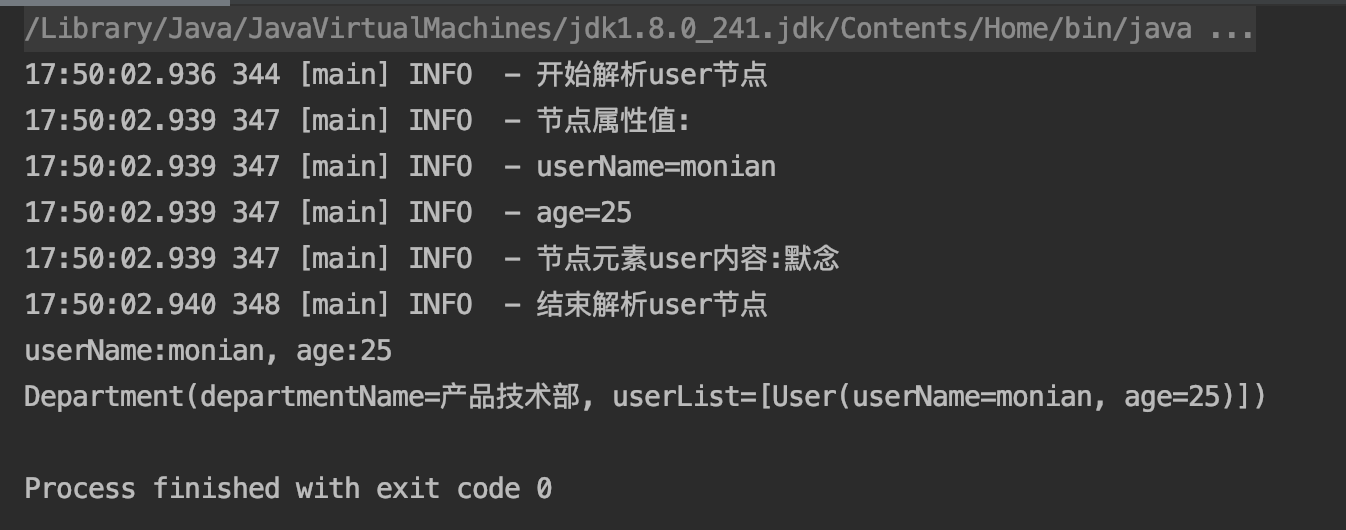
}在测试类中加入一行代码使我们自定义的规则发生作用,digester.addRule("department/user", new CustomRule()); 自定义规则匹配user节点,下图可以看到节点解析过程中调用方法传递的参数等信息
最后附上tomcat中的server.xml解析代码
server.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- Note: A "Server" is not itself a "Container", so you may not
define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/server.html
-->
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" />
<!-- Security listener. Documentation at /docs/config/listeners.html
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.security.SecurityListener" />
-->
<!--APR library loader. Documentation at /docs/apr.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" />
<!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs-->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" />
<!-- Global JNDI resources
Documentation at /docs/jndi-resources-howto.html
-->
<GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- Editable user database that can also be used by
UserDatabaseRealm to authenticate users
-->
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" />
</GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- A "Service" is a collection of one or more "Connectors" that share
a single "Container" Note: A "Service" is not itself a "Container",
so you may not define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/service.html
-->
<Service name="Catalina">
<!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools-->
<!--
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>
-->
<!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are received
and responses are returned. Documentation at :
Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html
Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.html
APR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.html
Define a non-SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8080
-->
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
<!-- A "Connector" using the shared thread pool-->
<!--
<Connector executor="tomcatThreadPool"
port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
-->
<!-- Define an SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443
This connector uses the NIO implementation. The default
SSLImplementation will depend on the presence of the APR/native
library and the useOpenSSL attribute of the
AprLifecycleListener.
Either JSSE or OpenSSL style configuration may be used regardless of
the SSLImplementation selected. JSSE style configuration is used below.
-->
<!--
<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true">
<SSLHostConfig>
<Certificate certificateKeystoreFile="conf/localhost-rsa.jks"
type="RSA" />
</SSLHostConfig>
</Connector>
-->
<!-- Define an SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443 with HTTP/2
This connector uses the APR/native implementation which always uses
OpenSSL for TLS.
Either JSSE or OpenSSL style configuration may be used. OpenSSL style
configuration is used below.
-->
<!--
<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" >
<UpgradeProtocol className="org.apache.coyote.http2.Http2Protocol" />
<SSLHostConfig>
<Certificate certificateKeyFile="conf/localhost-rsa-key.pem"
certificateFile="conf/localhost-rsa-cert.pem"
certificateChainFile="conf/localhost-rsa-chain.pem"
type="RSA" />
</SSLHostConfig>
</Connector>
-->
<!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 -->
<Connector protocol="AJP/1.3"
address="::1"
port="8009"
redirectPort="8443" />
<!-- An Engine represents the entry point (within Catalina) that processes
every request. The Engine implementation for Tomcat stand alone
analyzes the HTTP headers included with the request, and passes them
on to the appropriate Host (virtual host).
Documentation at /docs/config/engine.html -->
<!-- You should set jvmRoute to support load-balancing via AJP ie :
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">
-->
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<!--For clustering, please take a look at documentation at:
/docs/cluster-howto.html (simple how to)
/docs/config/cluster.html (reference documentation) -->
<!--
<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>
-->
<!-- Use the LockOutRealm to prevent attempts to guess user passwords
via a brute-force attack -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<!-- This Realm uses the UserDatabase configured in the global JNDI
resources under the key "UserDatabase". Any edits
that are performed against this UserDatabase are immediately
available for use by the Realm. -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
</Realm>
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<Context path="" docBase="../webapps/zxq/" debug="0"/>
<!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applications
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />
-->
<!-- Access log processes all example.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html
Note: The pattern used is equivalent to using pattern="common" -->
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
</Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina#createStartDigester
/**
* Create and configure the Digester we will be using for startup.
* @return the main digester to parse server.xml
*/
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Initialize the digester
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
Map<Class<?>, List<String>> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<>();
List<String> objectAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
objectAttrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, objectAttrs);
// Ignore attribute added by Eclipse for its internal tracking
List<String> contextAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
contextAttrs.add("source");
fakeAttributes.put(StandardContext.class, contextAttrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setUseContextClassLoader(true);
// Configure the actions we will be using
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/GlobalNamingResources");
digester.addSetNext("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"setGlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
//Executor
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Executor",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Executor");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Executor",
"addExecutor",
"org.apache.catalina.Executor");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new ConnectorCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new SetAllPropertiesRule(new String[]{"executor", "sslImplementationName"}));
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector",
"addConnector",
"org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfig");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig",
"addSslHostConfig",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfig");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
new CertificateCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
new SetAllPropertiesRule(new String[]{"type"}));
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
"addCertificate",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfigCertificate");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConf");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf",
"setOpenSslConf",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConf");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd",
"addCmd",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol",
"addUpgradeProtocol",
"org.apache.coyote.UpgradeProtocol");
// Add RuleSets for nested elements
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/GlobalNamingResources/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Host/Cluster/");
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
// When the 'engine' is found, set the parentClassLoader.
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(parentClassLoader));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Cluster/");
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Digester for server.xml created " + ( t2-t1 ));
}
return (digester);
}Digester解析xml原理的更多相关文章
- digester解析xml文件
在我们的项目中或多或少会采用xml来做配置文件,你可以采用Java原生支持的sax.DOM或者第三方的dom4j等.虽然提供了各式各样的解析方式,但是解析一个复杂的xml所编写的Java代码是非常麻烦 ...
- Dom4j工具j解析XML原理和示例代码
import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; i ...
- 用JAXP的dom方式解析XML文件
用JAXP的dom方式解析XML文件,实现增删改查操作 dom方式解析XML原理 XML文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8 ...
- java 中解析xml的技术
最初,XML 语言仅仅是意图用来作为 HTML 语言的替代品而出现的,但是随着该语言的不断发展和完善,人们越来越发现它所具有的优点:例如标记语言可扩展,严格的语法规定,可使用有意义的标记,内容存储和表 ...
- apache.commoms.digester3 解析xml文件
Technorati 标签: java,xml,digester,xmlrule,FromXmlRulesModule 1 简介 java解析xml,就个人所知有3种方法DOM.SAX和Digeste ...
- Tomcat解析XML和反射创建对象原理
Tomcat解析XML和反射创建对象原理 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Me ...
- XML的四种解析器原理及性能比较
转自zsq 1.DOM DOM 是用与平台和语言无关的方式表示 XML 文档的官方 W3C 标准.DOM 是以层次结构组织的节点或信息片断的集合.这个层次结构允许开发人员在树中寻找特定信息.分 ...
- Android之DOM解析XML
一.DOM解析方法介绍 DOM是基于树形结构的节点或信息片段的集合,允许开发人员使用DOM API遍历XML树,检索所需数据.分析该结构通常需要加载整个文档和构造树形结构,然后才可以检索和更新节点信息 ...
- DuiLib 源码分析之解析xml类CMarkup & CMarkupNode 头文件
xml使用的还是比较多的,duilib界面也是通过xml配置实现的 duilib提供了CMarkkup和CMarkupNode类解析xml,使用起来也是比较方便的,比较好奇它是怎么实现的,如果自己来写 ...
随机推荐
- ML第5周学习小结
本周收获 总结一下本周学习内容: 1.学习了<深入浅出Pandas>的第五章:Pandas高级操作的两个内容 数据迭代 函数应用 我的博客链接: pandas:数据迭代.函数应用 2.&l ...
- python实现对简单的运算型验证码的识别【不使用OpenCV】
最近在写我们学校的教务系统的手机版,在前端用户执行绑定操作后,服务器将执行登录,但在登录过程中,教务系统中有个运算型的验证码,大致是这个样子的: 下面我们开始实现这个验证码的识别. 1.图片读取 从网 ...
- 使用 .NET MAUI 创建移动应用——Get Start
大家好,我是张飞洪,感谢您的阅读,我会不定期和你分享学习心得,希望我的文章能成为你成长路上的垫脚石,让我们一起精进. 1.IDE下载安装 如果你还没安装Visual Studio 2022 预览版 你 ...
- JS:函数的形参与实参
形参: 函数显式参数在函数定义时列出. 函数调用未传参时,参数会默认设置为: undefined. function fn(a,b,c){ //a,b,c为形参 //此时有一个隐式操作:var a,v ...
- 跟着Vam一起学习Typescript(第一期)
一.安装环境与配置1.命令行安装 npm i -g typescript 2.快捷打开Vs Code编辑器 创建一个项目文件夹,在该文件夹下打开命令行工具,使用code .命令快速打开编辑器(如果计算 ...
- React与Koa一起打造一个功能丰富的全栈个人博客(业务篇)
前言 豆哥的个人博客又改版了,本版主要技术栈是前台用的React,后台用的Koa.博客改版的初衷是自己可以练练React(公司的项目部分要用React,我也没法啊,再说早晚得学).本文主要介绍博客的业 ...
- Elasticsearch学习系列四(聚合搜索)
聚合分析 聚合分析是数据库中重要的功能特性,完成对一个查询的集中数据的聚合计算.如:最大值.最小值.求和.平均值等等.对一个数据集求和,算最大最小值等等,在ES中称为指标聚合,而对数据做类似关系型数据 ...
- RabbitMD大揭秘
RabbitMD大揭秘 欢迎关注H寻梦人公众号 通过SpringBoot整合RabbitMQ的案例来说明,RabbitMQ相关的各个属性以及使用方式:并通过相关源码深刻理解. Queue(消息队列) ...
- JavaScript扩展原型链浅析
前言 上文对原型和原型链做了一些简单的概念介绍和解析,本文将浅析一些原型链的扩展. javaScript原型和原型链 http://lewyon.xyz/prototype.html 扩展原型链 使用 ...
- 【Nim 游戏】 学习笔记
前言 没脑子选手随便一道博弈论都不会 -- 正文 Nim 游戏引入 这里给出最简单的 \(Nim\) 游戏的题目描述: \(Nim\) 游戏 有两个顶尖聪明的人在玩游戏,游戏规则是这样的: 有\(n\ ...
