Dubbo系列之 (七)链路层那些事(1)
辅助链接
Dubbo系列之 (一)SPI扩展
Dubbo系列之 (二)Registry注册中心-注册(1)
Dubbo系列之 (三)Registry注册中心-注册(2)
Dubbo系列之 (四)服务订阅(1)
Dubbo系列之 (五)服务订阅(2)
Dubbo系列之 (六)服务订阅(3)
Dubbo系列之 (七)链路层那些事(1)
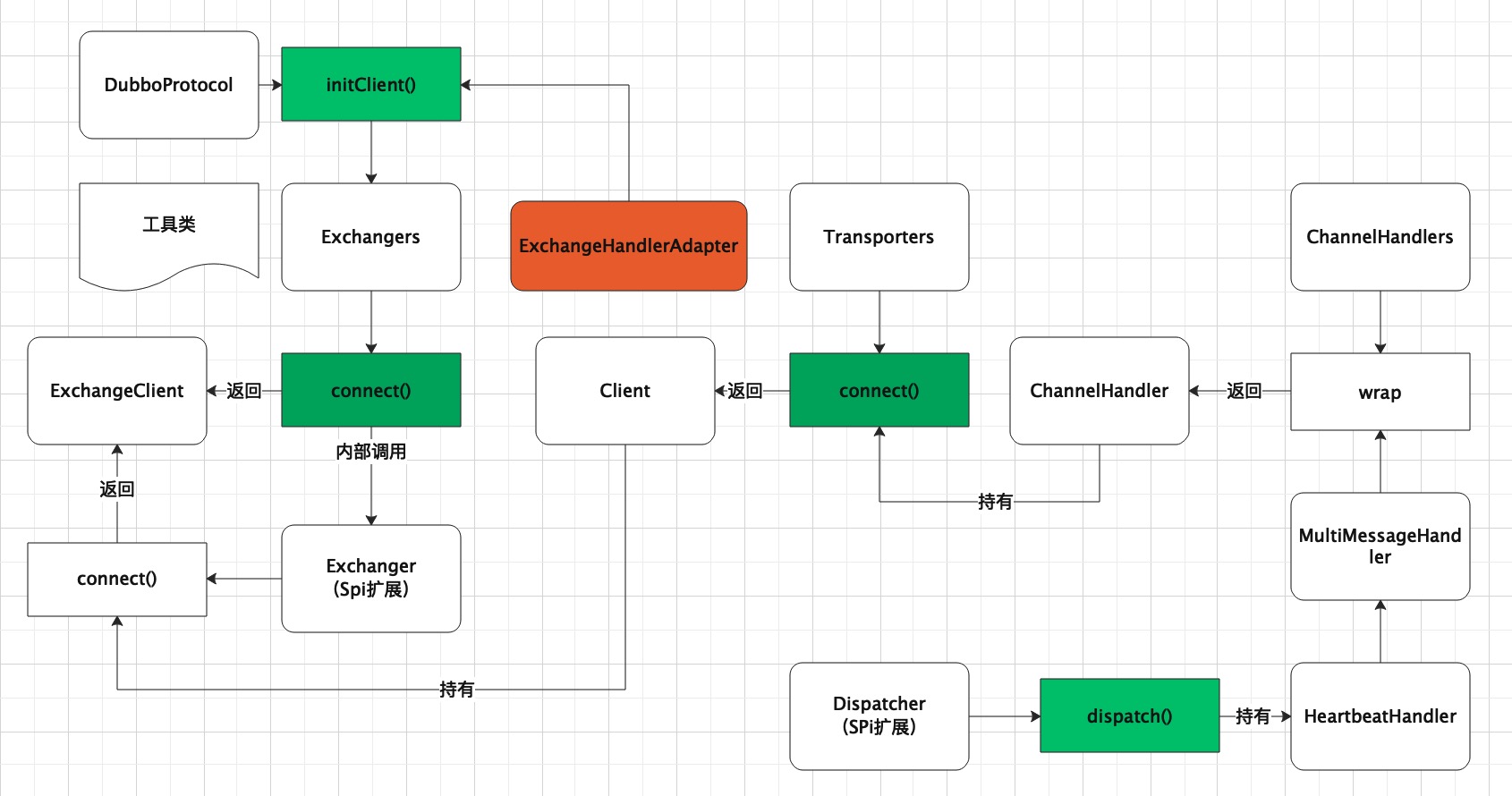
在讲解dubboTCP端的设计时,先了解下一些类的关系图。它们是如何组织在一起的,每个功能又是什么,接着在进一步深入了解其内涵。
类简介
1、Exchangers(交换器工具类) 用来创建TCP服务(bind)和建立客户端连接(connect)辅助类
2、Transporters(数据流传输工具类)用来创建TCP服务(bind)和建立客户端连接(connect)辅助类,Exchangers的底层内容依赖于Transporters,并且Transporters会根据SPI扩展,来适配合适的tcp通讯框架,比如netty,mina等。
3、Exchanger(交换器) 用来创建TCP链接,通过工具类Exchangers完成,该接口是一个SPI扩展,目前唯一仅有就是HeaderExchanger。从名字的含义可以得到,该协议是具有自定义协议头的交换器,所以取名HeaderExchanger。
4、Transporter(数据传输层) 用来创建TCP连接,通过工具类Transporters完成。它也是一个SPI扩展,比如NettyTransporter,MinaTransporter。
5、ExchangeClient (交换器客户端),Exchanger的connect()方法返回,即建立了TCP连接后,返回的客户端,接着就是通过该客户端与服务端通信,实例有HeaderExchangeClient、LazyConnectExchangeClient、ReferenceCountExchangeClient。之后分别讲解这3个,Exchangers工具类建立的连接客户端是HeaderExchangeClient。
6、ExchangeServer (交换器服务端端) Exchanger的bind()方法返回,即服务端监听的服务端实例,它监听这某个具体的tcp端口。默认实现是HeaderExchangeServer。
7、RemotingServer(远程的TCP服务端),ExchangeServer类也实现了该接口,代表其也是一个远程服务器,具体的实现有NettyServer,由Transporter的bind()方法返回,具体的Transporter返回相应的远程服务端。比如NettyTransporter#bind()返回NettyServer。
8、Client(TCP客户端),ExchangeClient类也实现了该接口,代表其也是一个TCP客户端,具体实现有NettyClient,由Transporter的connect()方法返回,具体的Transporter返回相应的TCP客户端。比如NettyTransporter#connect()返回NettyClient。
9、Channel (通信通道) ,每建立一个TCP链接就相应创建一个Channel。比如Netty建立连接后,就有一个Channel。这里的Channel指的是dubbo自己定义的一个channel。它与netty的channel建立关联,通过NettyChannel类,框架操作的是NettyChannel,而NettyChannel内部持有一个netty的channel对象。
10、HeaderExchangeChannel(交换器Channel,ExchangeChannel属于交换器Channel),它被HeaderExchangeClient客户端所持有,客户端就是通过HeaderExchangeChannel进行通信的,HeaderExchangeChannel内部持有一个具体的Channel。
11、ChannelHandler (通道处理器) 用来处理建立连接、发送请求、结束请求等操作的具体抽象。
12、ChannelHandlers(通道处理器工具类) 主要用来包裹封装具体的Channel,它的作用是通过消息类型,根据Dispatcher返回不同的
13、Dispatcher(消息派发器)
| 类型 | Dispatcher | Channelhandler | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| All | AllDispatcher | AllChannelHandler | 所有的消息类型全部通过业务线程池处理 |
| Connection | ConnectionOrderedDispatcher | ConnectionOrderedChannelHandler | 连接、断开消息单独通过一个线程池池来处理,其他的读写等消息通过业务线程池处理 |
| Direct | DirectDispatcher | DirectChannelHandler | 所有的消息都通过IO线程池处理,不放到业务线程池中 |
| Execution | ExecutionDispatcher | ExecutionChannelHandler | 请求消息在业务线程池处理,其他消息在IO线程池。 |
| Message | MessageOnlyDispatcher | MessageOnlyChannelHandler | 请求和响应消息在业务线程池处理,其他心跳,连接等消息在IO线程池处理 |
类关系图

试一把,Netty操作--客户端多线程,单链路(TCP)
1、定义传输消息
@Data
@ToString
public class SampleMessage {
private String threadName;
private String id;
private String desc;
}
2、编写编码器
public class SampleEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<SampleMessage> {
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, SampleMessage sampleMessage, ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
String threadName = sampleMessage.getThreadName();
String id = sampleMessage.getId();
String desc = sampleMessage.getDesc();
byteBuf.writeInt(threadName.getBytes().length);
byteBuf.writeBytes(threadName.getBytes());
byteBuf.writeInt(id.getBytes().length);
byteBuf.writeBytes(id.getBytes());
byteBuf.writeInt(desc.getBytes().length);
byteBuf.writeBytes(desc.getBytes());
String str = sampleMessage.getThreadName() + ":" + sampleMessage.getDesc() + ":" + sampleMessage.getId();
System.out.println(str);
}
}
3、编写解码器
public class SampleDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
byteBuf.markReaderIndex();
String threadName = read(byteBuf);
if (threadName == null) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
String id = read(byteBuf);
if (id == null) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
String desc = read(byteBuf);
if (desc == null) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
SampleMessage sampleMessage = new SampleMessage();
sampleMessage.setId(id);
sampleMessage.setThreadName(threadName);
sampleMessage.setDesc(desc);
list.add(sampleMessage);
}
private String read(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
if (canReadInt(byteBuf)) {
int readInt = byteBuf.readInt();
if (canReadN(byteBuf, readInt)) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[readInt];
byteBuf.readBytes(bytes);
return new String(bytes);
}
}
return null;
}
private boolean canReadInt(ByteBuf byteBuf) {
return canReadN(byteBuf, 4);
}
private boolean canReadN(ByteBuf byteBuf, int n) {
if (!byteBuf.isReadable()) {
return false;
}
return byteBuf.readableBytes() >= n;
}
}
4、编写消息处理器
public class PrintChannelHandlers extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
if (msg instanceof SampleMessage) {
SampleMessage sampleMessage = (SampleMessage) msg;
System.out.println(sampleMessage.getThreadName() + ":" + sampleMessage.getId() + ":" + sampleMessage.getDesc());
}
}
}
5、编写服务端
public class NettyServerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(1), new NioEventLoopGroup(12))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()
// .addLast("log",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.addLast("decoder", new SampleDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", new SampleEncoder())
.addLast("handler", new PrintChannelHandlers());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8888);
channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
System.out.println("链接前");
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
System.out.println("链接后");
}
}
6、编写客户端
public class NettyClientMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NettyClientMain nettyClientMain = new NettyClientMain();
nettyClientMain.open();
}
public void open() {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(10))
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 3000);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
.addLast("decoder", new SampleDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", new SampleEncoder());
//.addLast("handler", new PrintChannelHandlers());
}
});
SocketAddress socketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888);
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(socketAddress);
boolean ret = future.awaitUninterruptibly(3000, MILLISECONDS);
if (ret && future.isSuccess()) {
Channel newChannel = future.channel();
doProcess(newChannel);
}
}
private void doProcess(Channel channel) {
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong();
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
final char ch = (char) (i + 65);
final String id = "id" + i;
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
SampleMessage sampleMessage = new SampleMessage();
sampleMessage.setThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName());
sampleMessage.setDesc(getdes(ch));
sampleMessage.setId("id" + sampleMessage.getDesc().length() + "-" + atomicLong.getAndIncrement());
channel.writeAndFlush(sampleMessage);
}
}
});
t.start();
}
}
private String getdes(char a) {
Random random = new Random();
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < random.nextInt(500) + 1; i++) {
buffer.append(a);
}
return buffer.toString();
}
}
7、测试结果
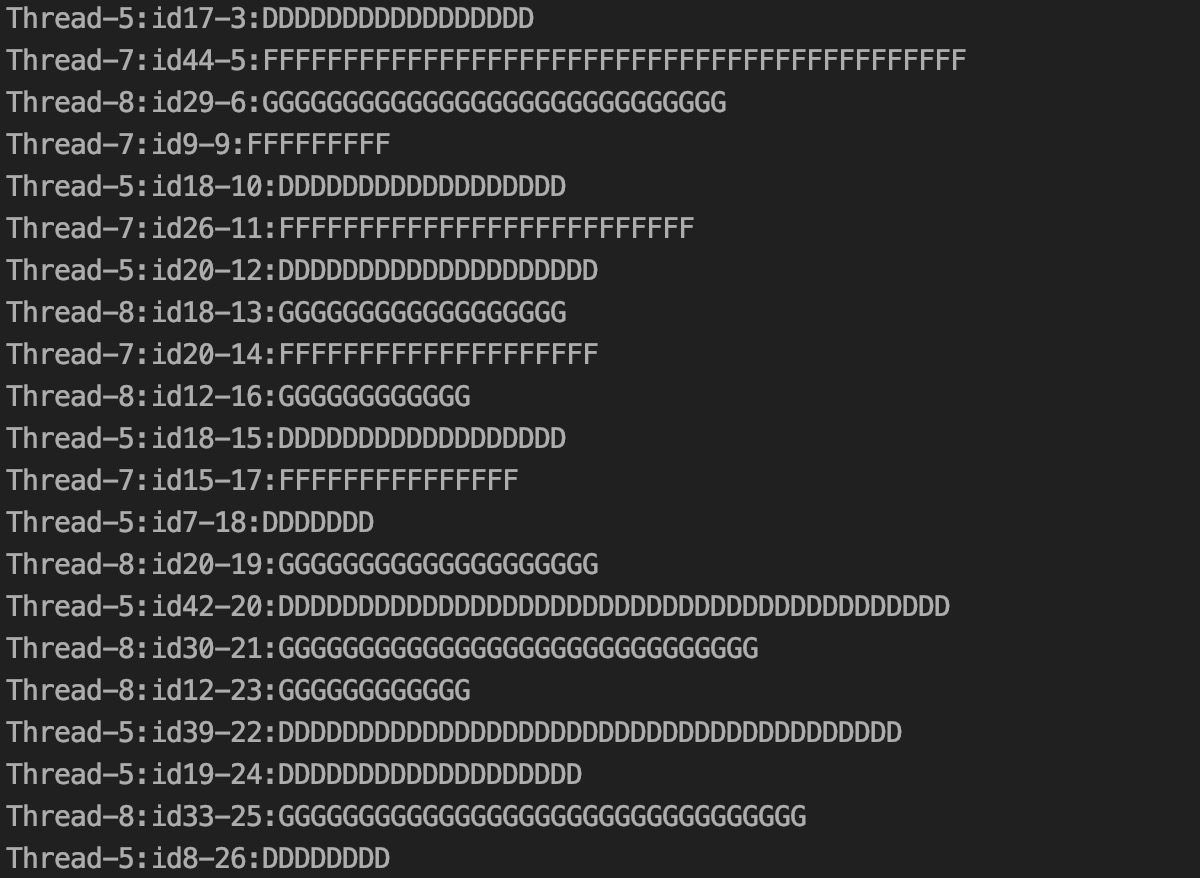
结果符合预期,dubbo 也是通过服务底层公用一条TCP链接,多线程进行调用该链路channel。
Dubbo系列之 (七)链路层那些事(1)的更多相关文章
- Dubbo系列之 (七)网络层那些事(2)
辅助链接 Dubbo系列之 (一)SPI扩展 Dubbo系列之 (二)Registry注册中心-注册(1) Dubbo系列之 (三)Registry注册中心-注册(2) Dubbo系列之 (四)服务订 ...
- dubbo系列十一、dubbo transport层记录
前言 在dubbo接口方法重载且入参未显式指定序列化id导致ClassCastException分析时候用到了dubbo的通信层和编解码,dubbo有个transport层,默认使用netty4进行网 ...
- Android网络编程系列 一 TCP/IP协议族之链路层
这篇借鉴的文章主要是用于后续文章知识点的扩散,在此特作备份和扩散学习交流. 数据链路层有三个目的: 为IP模块发送和 接收IP数据报. 为ARP模块发送ARP请求和接收ARP应答. 为RARP发送RA ...
- TCP/IP中最高大上的链路层简介(二)
引言 对于程序猿来讲,似乎越接近底层,就越显得高大上.这也算是程序猿们的共同认知吧,虽然不是所有人.今天LZ就和各位一起探讨一下TCP/IP中最高大上的一层,也就是最底层的链路层. 这一层LZ了解的还 ...
- CRL快速开发框架系列教程七(使用事务)
本系列目录 CRL快速开发框架系列教程一(Code First数据表不需再关心) CRL快速开发框架系列教程二(基于Lambda表达式查询) CRL快速开发框架系列教程三(更新数据) CRL快速开发框 ...
- TCP/IP协议学习(六) 链路层详解
学习知识很简单,但坚持不懈却又是如此的困难,即使一直对自己说"努力,不能停下"的我也慢慢懈怠了... 闲话不多说,本篇将讲述TCP/IP协议栈的链路层.在本系列第一篇我讲到,TCP ...
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13 原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7497260 更多请看专栏,地址 ...
- tcp/ip 卷一 读书笔记(2)物理层和链路层网络
物理层和链路层网络 术语 链路 是一对相邻结点间的物理线路,中间没有任何其他的交换结点. 数据链路 除了物理线路外,还必须有通信协议来控制这些数据的传输. 帧 数据链路层的协议数据单元(PDU) 串行 ...
- [HTTP] tcp/ip详解 链路层 网络层 传输层 应用层
1.可以把七层协议简化成四层协议链路层 网络层 传输层 应用层 2.通过路由器连接的两个网络网络层ip提供的是一个逐跳协议,提供了一种不可靠的服务,中间有可能会丢传输层tcp在ip的基础上提供了可靠的 ...
随机推荐
- Android 开发学习进程0.19 webview 的使用
Android 中的webview android 中的webview是可以在app内部打开HTML等的网页,不必再打开浏览器,有两种实现方法,即webviewclient webChromeclie ...
- span和input布局时对不齐
如图 在span和input的css里各添加一行代码: vertical-align:top; (span和input在同一个盒子里)
- python设计模式之外观模式
python设计模式之外观模式 系统会随着演化变得非常复杂,最终形成大量的(并且有时是令人迷惑的)类和交互,这种情况并不少见.许多情况下,我们并不想把这种复杂性暴露给客户端.外观设计模式有助于隐藏系统 ...
- DB2根据报错代码查看表与字段信息
select * from syscat.tables where tbspaceid='?' and tableid='?' select * from syscat.columns where t ...
- 很挫的 SHFileOperation 用法 2011-07-18 11:42
今天编写一个局域网文件拷贝的demo .其中有一个 SHFileOperation 的用法,这个函数有个参数SHFILEOPSTRUCT.查看msdn有如下解释: pFromAddress of a ...
- html表格、表单
知识点一:表格 1.表格标签 table 2.表格的组成 行 tr 单元格 td 3.建立表格步骤 1.建立表格, 2.判断行数和列数 3.用行去包含单元格 4.在每个单元格中去添加内容 4. ...
- 手机APP无法抓包(无法连接服务器)
一. 把证书放到系统信任区 前提:手机已root 详细步骤 计算证书名 openssl x509 -subject_hash_old -in charles-ssl-proxying-certific ...
- Nginx进程模型
多进程模式 在开始介绍Nginx的进程模型之前先说明下:Nginx也支持Single Master单进程模式,但是这个模式效率较低,一般只用在开发环境.所以不是本文介绍的重点. Nginx默认采用多进 ...
- 易盛信息9.0外盘期货行情数据API接口公共授权开发包例子代码
易盛信息9.0外盘期货行情数据API接口公共授权开发包例子代码 怎么才能获取到外盘期货行情数据API接口呢?不少朋友就会考虑到易盛9.0行情API接口,本身易盛就是一个软件提供商,提供行 ...
- 仿京东BOE官网 JavaScript代码
let items = document.getElementsByClassName('item'); let points = document.getElementsByClassName('p ...
