[swarthmore cs75] Compiler 1 – Adder
课程回顾
Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业。本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第3次大作业。
- 编译的过程:首先解析(parse)源代码,然后成抽象语法树(AST),再生成汇编代码(asm),最后用asm生成的目标文件(object)和其他库文件链接成一个可执行的二进制文件(binary)。其中从抽象语法树到生成汇编代码这个过程(complier.ml)工作量最大。
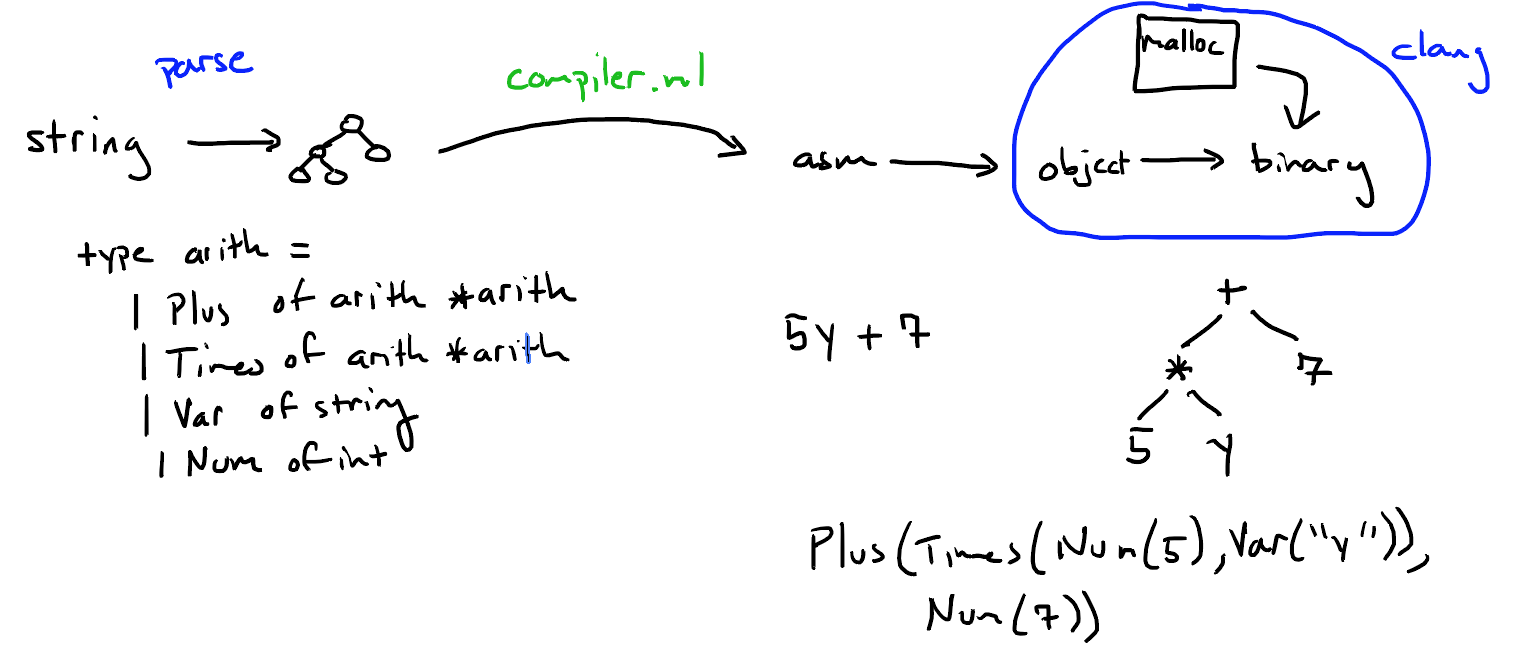
- 具体语法树(Concrete Syntax Tree):programmer写的就是具体语法,下图展示了某具体语法形象的表示。
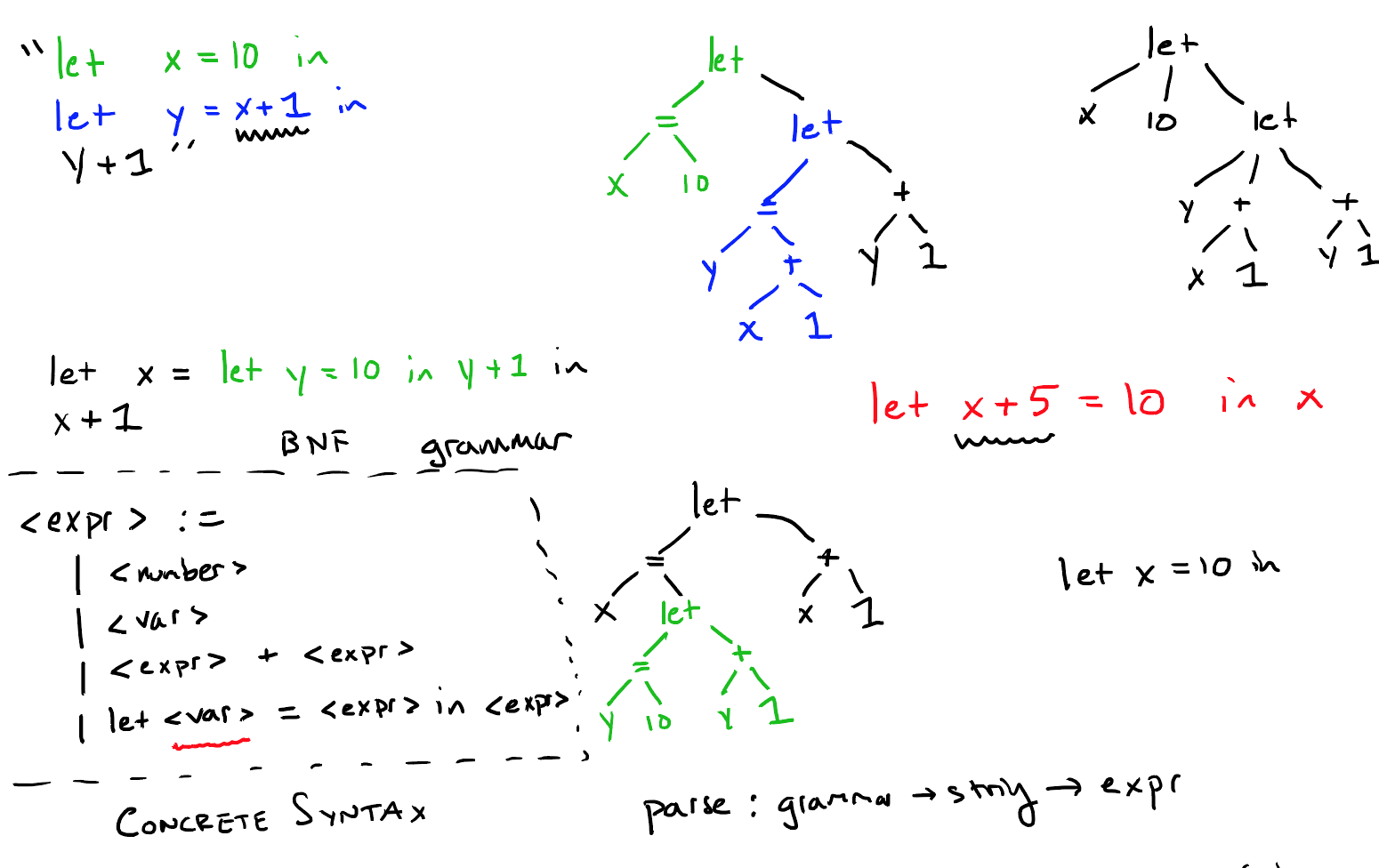
- 抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree):一段具体语法,应该在内存中用何种数据结构来表示。所以根据具体语法的定义,有了抽象语法的概念。比如:let x=6, y=add1(x) in y; 在内存中可以表示为 Let([(x, 6), (Prim1(add1, Id("x")))], Id("y"))
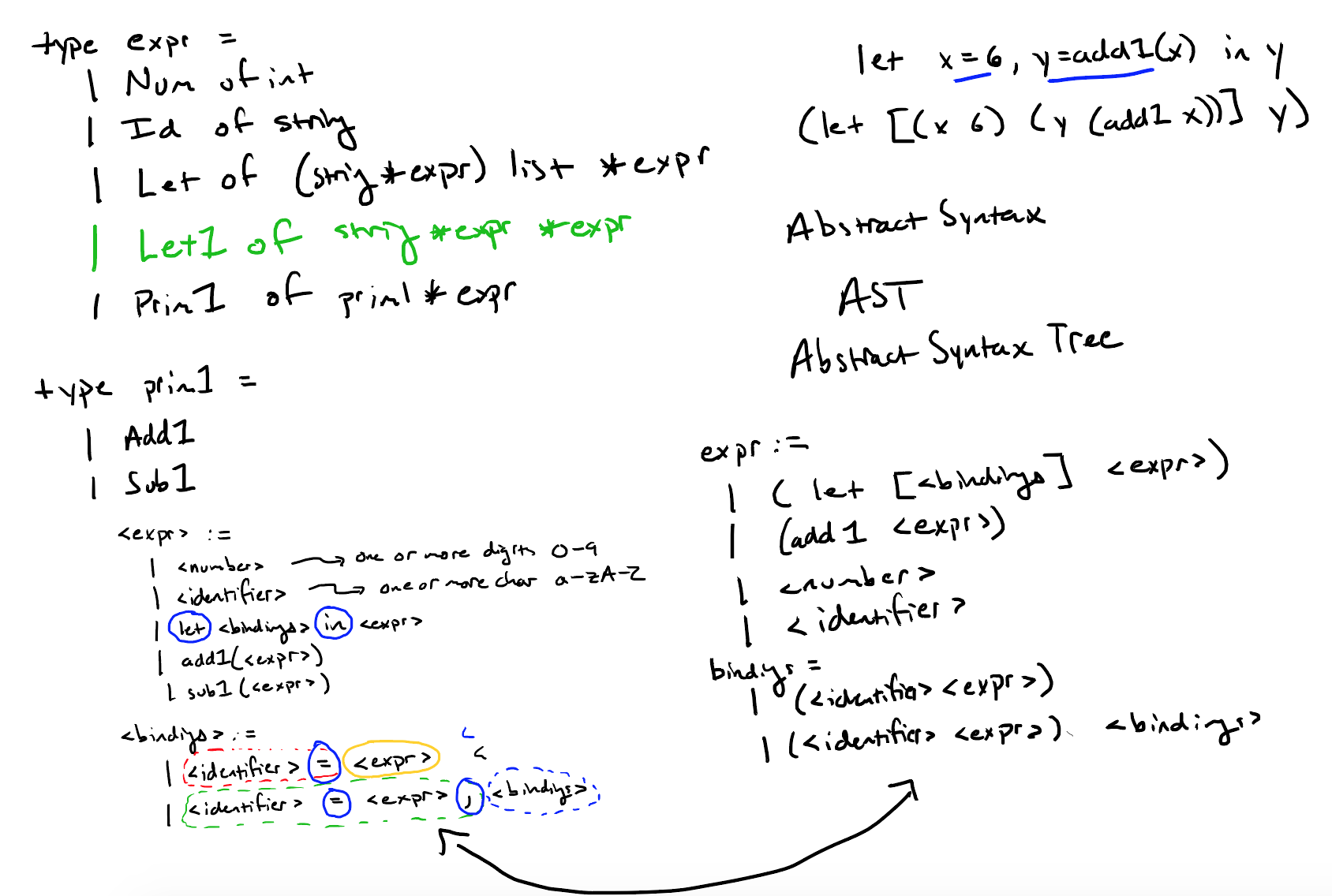
- 汇编代码生成(Add1、Sub1):
- Add1:需要将操作数mov到eax寄存器,然后把eax加1即可,这里操作数可能是一个表达式的计算结果,所以需要递归求值。
- Sub1:同理

- 汇编代码生成(Let、Id):
- Id:检查当前env是否绑定了某变量的地址,如果绑定了,把操作数(esp[地址偏移量])移动到eax寄存器,否则抛出错误。
- Let:为了简化问题,假设let中的binding list只有一个元素,比如要计算:let ex in eb;首先要对ex=(x, value)中的value进行递归求值(参数使用env和si);然后为x绑定一个新地:-4 * si,添加到new_env中,并对eb进行递归求值(参数使用new_env并将si+1)。最后将两个递归所生成的指令拼接到一起。
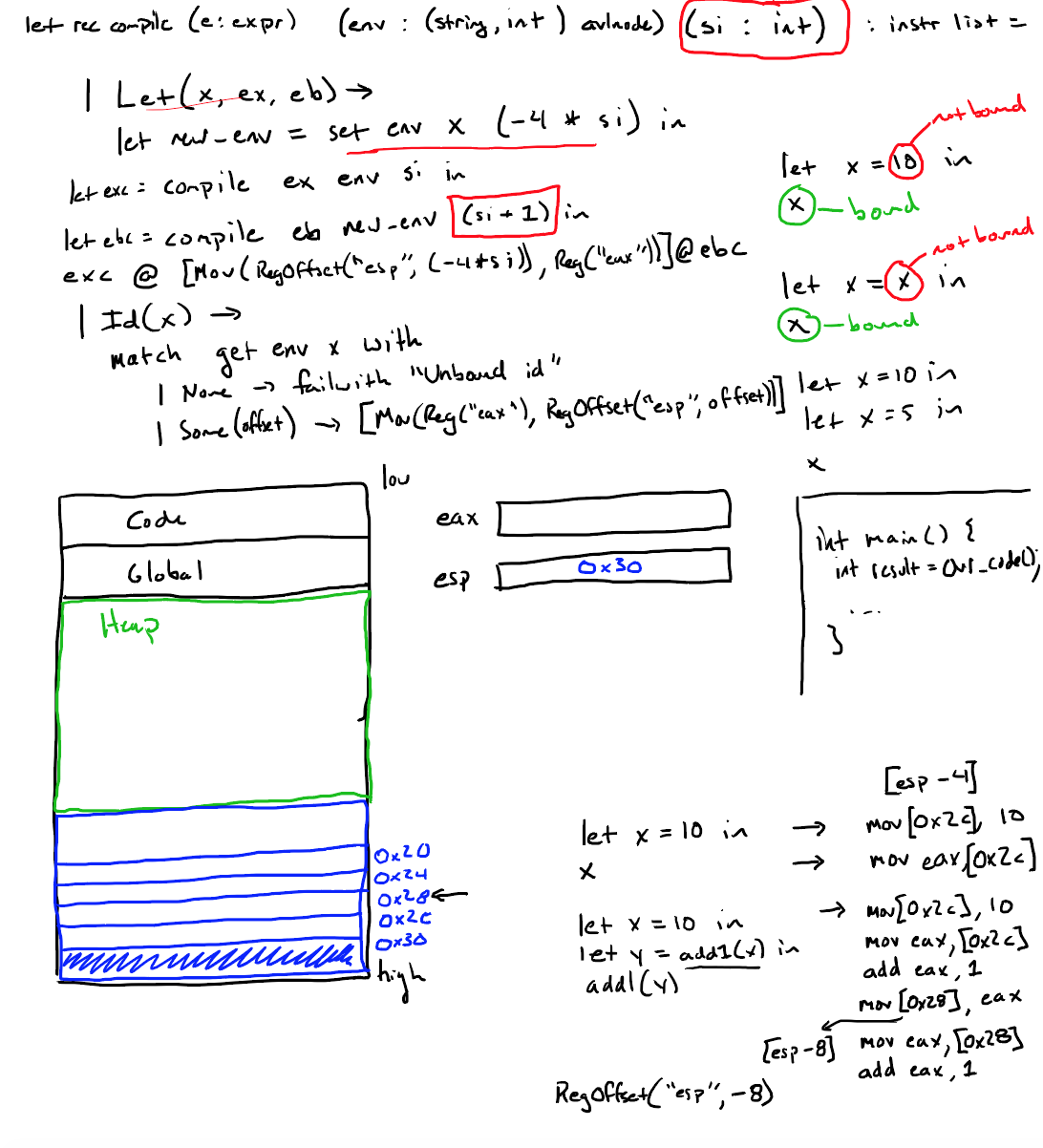
- 汇编代码生成(案例):注意下图第一个例子在对x进行赋值操作的时候,变量x并没有使用一个新的地址:esp-8,而是重复利用了变量y的地址:esp-4。因为变量y在外部无法引用。

编程作业
本次大作业是为Adder编程语言实现一个小型编译器,将Adder程序编译为X86_32汇编。
具体语法:
<expr> :=
| <number>
| <identifier>
| let <bindings> in <expr>
| add1(<expr>)
| sub1(<expr>) <bindings> :=
| <identifier> = <expr>
| <identifier> = <expr>, <bindings>
抽象语法:
type prim1 =
| Add1
| Sub1 type expr =
| Number of int
| Prim1 of prim1 * expr
| Let of (string * expr) list * expr
| Id of string
程序例子:
Concrete Syntax Abstract Syntax Answer 5 Number(5) 5 let x=(let y=10 in y) in x Let(["x", Let(["y", 10], Id("y"))], Id("x")) 10 let x=100 in let x=1 in x Let(["x", Number(100), Let(["x", 1], Id("x"))]) 1 let x = 5 in add1(x) Let([("x", Number(5))], Prim1(Add1, Id("x"))) 6 let x=1 in let y=add1(x) in y Let(["x", 1], Let(["y", Prim1(Add1, Id("x"))], Id("y"))) 2 sub1(add1(sub1(5))) Prim1(Sub1, Prim1(Add1, Prim1(Sub1, Number(5)))) 4 let x=10 in let y=add1(x) in add1(y) Let(["x", 10], Let(["y", Prime1(Add1, Id("x"))], Prime1(Add1, Id("y")))) 12 let x = 5, y = sub1(x) in sub1(y) Let([("x", Number(5)), ("y", Prim1(Sub1, Id("x")))], Prim1(Sub1, Id("y"))) 3 let x=1 in let x=add1(let x=6 in add1(x)) in x Let(["x", 1], Let(["x", Prim1(Add1, Let(["x", 6], Prim1(Add1, Id("x"))))], Id("x"))) 8 let y=sub1(add1(sub1(let x=5 in x))) in add1(add1(add1(y))) Let(["y", Prim1(Sub1, Prim1(Add1, Prim1(Sub1, Let(["x", Number(5)], Id("x")))))], Prim1(Add1, Prim1(Add1, Prim1(Add1, Id("y"))))) 7
| let x=1 in y|
-
|An identifier is unbound (there is no surrounding let binding for y)|
| let x=10, y=20, x=5, y=30, x=40 in x|
-
|There is a binding list containing two or more bindings with the same name|
实现一(Let使用尾递归):
分别实现Let、Id、Prim1的代码生成逻辑。因为Adder语法规定,不允许在一个binding list绑定两个相同的变量,所以这里简单的实现了一个has_unique_key方法,判断binding list的长度和去重后的长度是否相同。let rec compile_env
(p : expr)
(stack_index : int)
(env : (string * int) list)
: instruction list =
match p with
| Number(n) ->
[
IMov(Reg(EAX), Const(n))
]
| Let(binds, body) ->
let rec helper xs si env =
match xs with
| [] -> compile_env body (si + 1) env
| (id, expr)::rest ->
let new_env = (id, (-4) * si)::env in
(compile_env expr si env) @ [IMov(RegOffset((-4) * si, ESP), Reg(EAX))] @ helper rest (si + 1) new_env
in
if has_unique_key binds then
helper binds stack_index env
else
failwith "There is a binding list containing two or more bindings with the same name."
| Id(x) ->
[
match (find env x) with
| Some(n) -> IMov(Reg(EAX), RegOffset(n, ESP))
| None -> failwith ("An identifier is unbound (there is no surrounding let binding for " ^ x ^ " )")
]
| Prim1(op, e) ->
match op with
| Add1 -> (compile_env e stack_index env) @ [IAdd(Reg(EAX), Const(1))]
| Sub1 -> (compile_env e stack_index env) @ [ISub(Reg(EAX), Const(1))]
实现二(Let使用迭代):
本实现仅改写了Let的模式匹配逻辑,其他类型的pattern mathcing和上述代码一样。let new_env = List.mapi (fun si (x, _) -> x, (-4) * (stack_index + si)) binds @ env in
let f si (_, e) -> (compile_env e stack_index new_env) @ [IMov(RegOffset((-4) * (stack_index + si), ESP), Reg(EAX))] in
let exc = List.flatten (List.mapi f binds) in
let exb = compile_env body (stack_index + 1) (new_env) in
exc @ exb
有一个地方需要注意一下,比如在对表达式:
let x=10, y=sub1(x) in y
进行求值的时候,会执行上述代码并会返回:
new_env = [("x", -4); ("y", -8)]
exc = List.flatten (List.mapi f [("x", Number(10)), ("y", Prim1(Sub1, Id("x")))])在函数f中,使用的是new_env作为compile_env递归调用的参数。实际上:
- 在计算Number(10)的时候,compile_env只需要传入env,而不是 [("x", -4); ("y", -8)] @ env
- 在计算Prim1(Sub1, Id("x")))的时候,compile_env只需要传入("x", -4)::env,而不是 [("x", -4); ("y", -8)] @ env
- ...以此类推。
因为Adder语言不支持binding list出现重名的变量,所以这里直接传入new_env不会出现问题。当然要是改进可以用切片操作或使用实现一中的尾递归,这里就不详述了。
测试时可能出现的错误:
Error: This expression has type bytes but an expression was expected of type string
⤇ export OCAMLPARAM="safe-string=0,_"
参考资料
starter-adder
safe-string-error
[swarthmore cs75] Compiler 1 – Adder的更多相关文章
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 6 – Garbage Snake
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第9次大作业. 赋值的副作用:循环元组 下面的代码展示了Python3是如何处理循环列表(pri ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 6 – Fer-de-lance
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第8次大作业. First-class function: It treats function ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 5 – Egg-eater
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第7次大作业. 抽象语法: 存储方式: 栈中的数据如果最后三位(tag bits)是001表示元 ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 4 – Diamondback
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第6次大作业. 函数声明 增加函数声明.函数调用的抽象语法:在转换成anf之前还要检查函数声明和 ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 3 – Cobra
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第5次大作业. 增加了bool数据表示和比较运算符的支持,具体语法参考下图: 第一种int和bo ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Compiler 2 – Boa
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第4次大作业. A-Normal Form 在80年代,函数式语言编译器主要使用Continua ...
- [swarthmore cs75] inlab1 — Tiny Compiler
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了inlab1的实践过程. tiny compiler 这个迷你的编译器可以将一个源文件,编译成可执行的二进制代码. ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Lab 1 — OCaml Tree Programming
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第2大次作业. 比较两个lists的逻辑: let rec cmp l ll = match ( ...
- [swarthmore cs75] Lab 0 Warmup & Basic OCaml
课程回顾 Swarthmore学院16年开的编译系统课,总共10次大作业.本随笔记录了相关的课堂笔记以及第1次大作业. 什么是编译 编译就是执行Program->Program'转换的过程,如下 ...
随机推荐
- position:fixed失效情况
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- CHD 5.15 安装 Kylin
这里主要参考官网安装单机案例,并写入到脚本中.具体请看如下: 1.说明 这里采用的是root用户安装,但是运行时需要改一些配置,不然没有权限 2.安装 ...
- file常用功能
构造方法 File(String pathname):将指定的路径名转换成一个File对象 File f = new File("D:\\a\\b.txt"); File(Stri ...
- Nancy.Net之旅-探索模块
探索Nancy模块 模块是任何Nancy应用程序中的主角,因为它是您定义应用程序行为的地方,所以无法避免使用它. 事实上,在任何的Nancy应用程序中,声明模块是最基本的要求. 通过继承NancyMo ...
- NET(C#):关于正确读取中文编码文件
https://blog.csdn.net/ma_jiang/article/details/53213442 首先如果读者对编码或者BOM还不熟悉的话,推荐先读这篇文章:.NET(C#):字符编码( ...
- poj3250(单调栈模板题)
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3250 题意:求序列中每个点右边第一个>=自身的点的下标. 思路:简单介绍单调栈,主要用来求向左/右第一个小于/大于自身 ...
- 网络通信实验(1)STM32F4 以太网简介
STM32F4 以太网简介 STM32F407 芯片自带以太网模块,该模块包括带专用 DMA 控制器的 MAC 802.3(介质访问控制)控制器,支持介质独立接口 (MII) 和简化介质独立接口 (R ...
- django xadmin查找当前用户所在组
self.request.user:获取当前登录用户用户名 qs = Group.objects.get(user=self.request.user)获取当前登录用户所在组qs.name 获取当前登 ...
- selenium之 chromedriver与chrome版本映射表(更新至v2.46)
chromedriver版本 支持的Chrome版本 v2.46 v71-73 v2.45 v70-72 v2.44 v69-71 v2.43 v69-71 v2.42 v68-70 v2.41 v6 ...
- 【Thread】CountdownEvent任务并行[z]
System.Threading.CountdownEvent 是一个同步基元,它在收到一定次数的信号之后,将会解除对其等待线程的锁定. CountdownEvent 专门用于以下情况:您必须使用 ...
