IO的详细解释:It's all about buffers: zero-copy, mmap and Java NIO
There are use cases where data need to be read from source to a sink without modification. In code this might look quite simple: for example in Java, you may read data from one InputStream chunk by chunk into a small buffer (typically 8KB), and feed them into the OutputStream, or even better, you could create a PipedInputStream, which is basically just a util that maintains that buffer for you. However, if low latency is crucial to your software, this might be quite expensive from the OS perspective and I shall explain.
What happens under the hood
Well, here’s what happens when the above code is used:
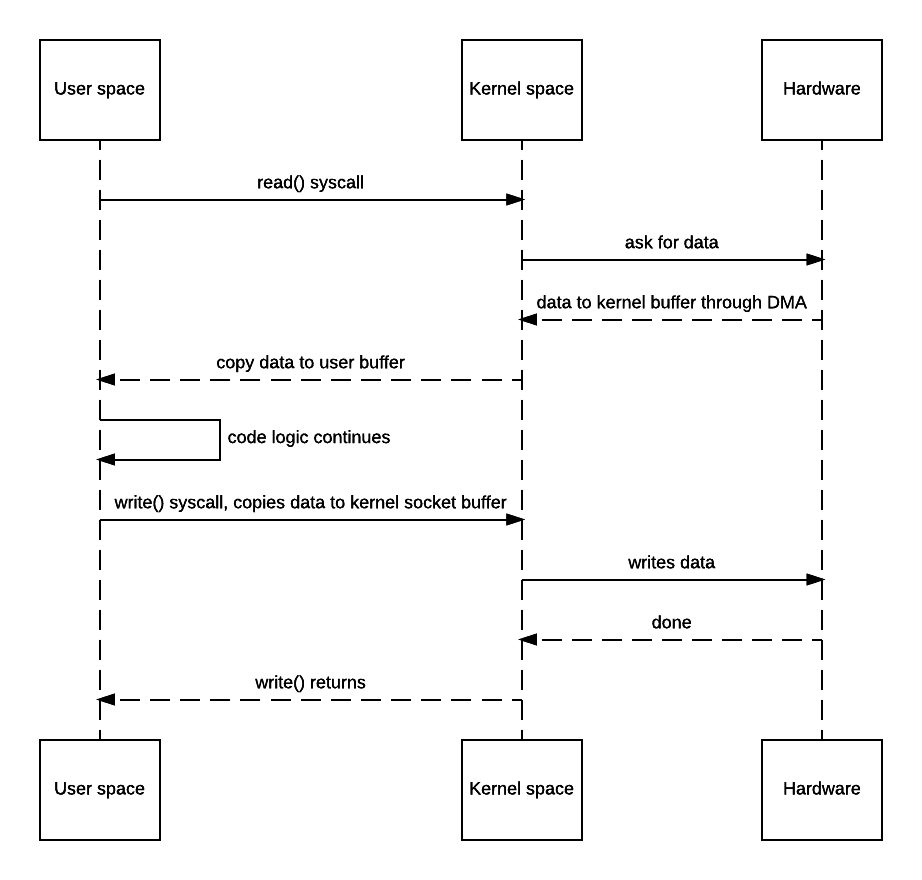
- JVM sends read() syscall.
- OS context switches to kernel mode and reads data into the input socket buffer.
- OS kernel then copies data into user buffer, and context switches back to user mode. read() returns.
- JVM processes code logic and sends write() syscall.
- OS context switches to kernel mode and copies data from user buffer to output socket buffer.
- OS returns to user mode and logic in JVM continues.
This would be fine if latency and throughput aren’t your service’s concern or bottleneck, but it would be annoying if you do care, say for a static asset server. There are 4 context switches and 2 unnecessary copies for the above example.
OS-level zero copy for the rescue
Clearly in this use case, the copy from/to user space memory is totally unnecessary because we didn’t do anything other than dumping data to a different socket. Zero copy can thus be used here to save the 2 extra copies. The actual implementation doesn’t really have a standard and is up to the OS how to achieve that. Typically *nix systems will offer sendfile(). Its man page can be found here. Some say some operating systems have broken versions of that with one of them being OSX link. Honestly with such low-level feature, I wouldn’t trust Apple’s BSD-like system so never tested there.
With that, the diagram would be like this:
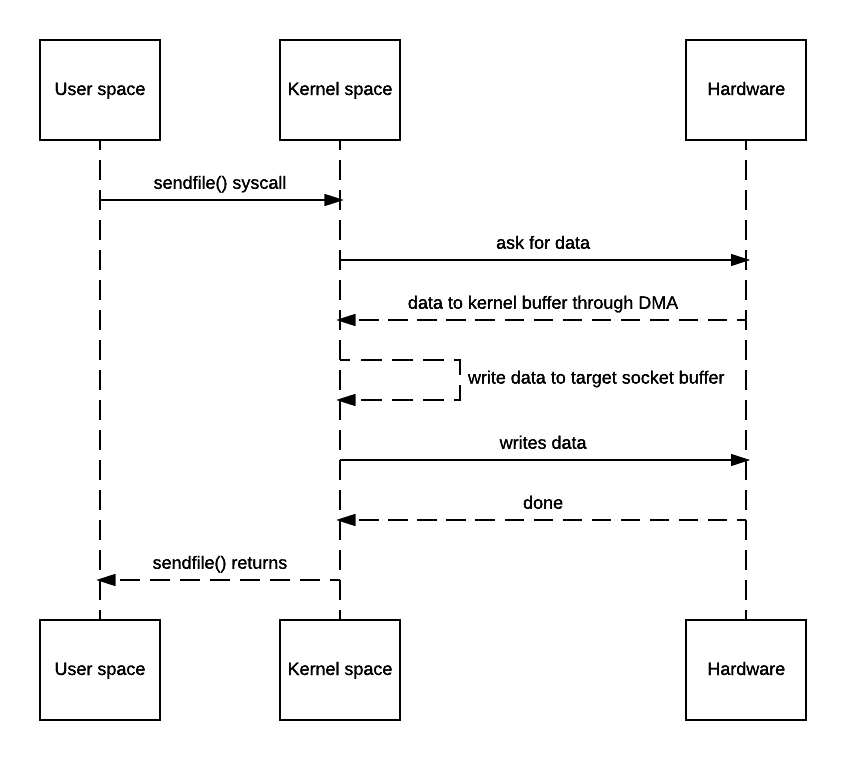
You may say OS still has to make a copy of the data in kernel memory space. Yes but from OS’s perspective this is already zero-copy because there’s no data copied from kernel space to user space. The reason why kernel needs to make a copy is because general hardware DMA access expects consecutive memory space (and hence the buffer). However this is avoidable if the hardware supports scatter-n-gather:
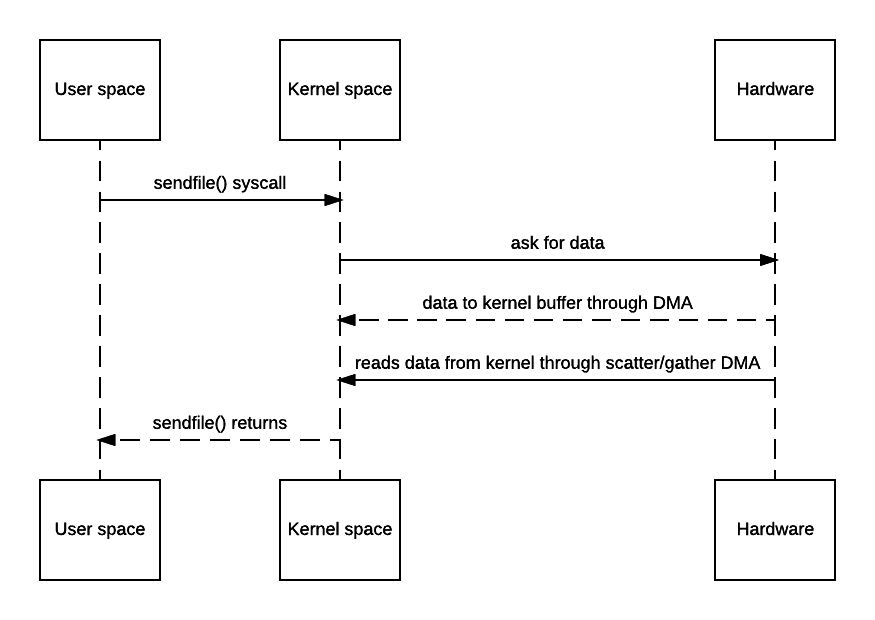
A lot of web servers do support zero-copy such as Tomcat and Apache. For example apache’s related doc can be found here but by default it’s off.
Note: Java’s NIO offers this through transferTo (doc).
mmap
The problem with the above zero-copy approach is that because there’s no user mode actually involved, code cannot do anything other than piping the stream. However, there’s a more expensive yet more useful approach - mmap, short for memory-map.
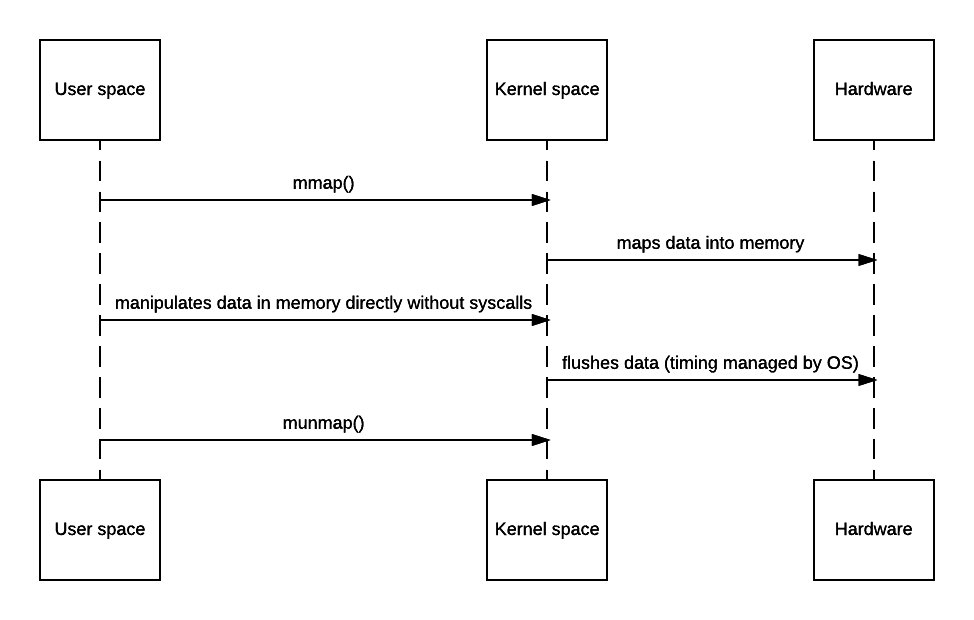
Mmap allows code to map file to kernel memory and access that directly as if it were in the application user space, thus avoiding the unnecessary copy. As a tradeoff, that will still involve 4 context switches. But since OS maps certain chunk of file into memory, you get all benefits from OS virtual memory management - hot content can be intelligently cached efficiently, and all data are page-aligned thus no buffer copying is needed to write stuff back.
However, nothing comes for free - while mmap does avoid that extra copy, it doesn’t guarantee the code will always be faster - depending on the OS implementation, there may be quite a bit of setup and teardown overhead (since it needs to find the space and maintain it in the TLB and make sure to flush it after unmapping) and page fault gets much more expensive since kernel now needs to read from hardware (like disk) to update the memory space and TLB. Hence, if performance is this critical, benchmark is always needed as abusing mmap() may yield worse performance than simply doing the copy.
The corresponding class in Java is MappedByteBuffer from NIO package. It’s actually a variation of DirectByteBuffer though there’s no direct relationship between classes. The actual usage is out of scope of this post.
NIO DirectByteBuffer
Java NIO introduces ByteBuffer which represents the buffer area used for channels. There are 3 main implementations of ByteBuffer:
HeapByteBufferThis is used when
ByteBuffer.allocate()is called. It’s called heap because it’s maintained in JVM’s heap space and hence you get all benefits like GC support and caching optimization. However, it’s not page aligned, which means if you need to talk to native code through JNI, JVM would have to make a copy to the aligned buffer space.DirectByteBufferUsed when
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()is called. JVM will allocate memory space outside the heap space usingmalloc(). Because it’s not managed by JVM, your memory space is page-aligned and not subject to GC, which makes it perfect candidate for working with native code (e.g. when writing OpenGL stuff). However, you are then “deteriorated” to C programmer as you’ll have to allocate and deallocate memory yourself to prevent memory leak.MappedByteBufferUsed when
FileChannel.map()is called. Similar toDirectByteBufferthis is also outside of JVM heap. It essentially functions as a wrapper around OS mmap() system call in order for code to directly manipulate mapped physical memory data.
Conclusion
sendfile() and mmap() offer efficient, low-latency low-level solutions to data manipulation across sockets. Again, no code should assume these are silver bullets as real world scenarios may be complex and it might not be worth the effort to switch code to them if this is not the true bottleneck. For software engineering to get the most ROI, in most cases, it’s better to “make it right” and then “make it fast”. Without the guardrails offered by JVM, it’s easy to make software much more vulnerable to crashing (I literally mean crashing, not exceptions) when it comes to complicated logic.
https://xunnanxu.github.io/2016/09/10/It-s-all-about-buffers-zero-copy-mmap-and-Java-NIO/
IO的详细解释:It's all about buffers: zero-copy, mmap and Java NIO的更多相关文章
- Java NIO和IO的区别(转)
原文链接:Java NIO和IO的区别 下表总结了Java NIO和IO之间的主要差别,我会更详细地描述表中每部分的差异. 复制代码代码如下: IO NIO面向流 ...
- .htaccess语法之RewriteCond与RewriteRule指令格式详细解释
htaccess语法之RewriteCond与RewriteRule指令格式详细解释 (2012-11-09 18:09:08) 转载▼ 标签: htaccess it 分类: 网络 上文htacc ...
- cookie的详细解释
突然看到网页上中英文切换的效果,不明白怎么弄得查了查 查到了cookie 并且附有详细解释 就copy留作 以后温习 http://blog.csdn.net/xidor/article/detail ...
- tar命令的详细解释
tar命令的详细解释 标签: linuxfileoutputbashinputshell 2010-05-04 12:11 235881人阅读 评论(12) 收藏 举报 分类: linux/unix ...
- Linux学习笔记15——GDB 命令详细解释【转】
GDB 命令详细解释 Linux中包含有一个很有用的调试工具--gdb(GNU Debuger),它可以用来调试C和C++程序,功能不亚于Windows下的许多图形界面的调试工具. 和所有常用的调试工 ...
- C语言 - 结构体(struct)比特字段(:) 详细解释
结构体(struct)比特字段(:) 详细解释 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/26722511 结构体(struc ...
- 姿势体系结构的详细解释 -- C
我基本上总结出以下4部分: 1.问题的足迹大小. 2.字节对齐问题. 3.特别保留位0. 4.这种结构被存储在存储器中的位置. #include <stdio.h> #include &l ...
- Java - 面向对象(object oriented)计划 详细解释
面向对象(object oriented)计划 详细解释 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/24058107 程序包括 ...
- 设计模式 - 迭代模式(iterator pattern) Java 迭代器(Iterator) 详细解释
迭代模式(iterator pattern) Java 迭代器(Iterator) 详细解释 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy 參考迭代器模式(ite ...
随机推荐
- springMVC_10拦截器
一,简介 拦截器概念和struts概念一致 实现拦截器 实现HandlerInterceptor接口 配置拦截器 <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:intercepto ...
- Spring核心——Bean的定义与控制
在Sring核心与设计模式的文章中,分别介绍了Ioc容器和Bean的依赖关系.如果阅读过前2文就会知道,Spring的整个运转机制就是围绕着IoC容器以及Bean展开的.IoC就是一个篮子,所有的Be ...
- fork/join 全面剖析
fork/join作为一个并发框架在jdk7的时候就加入到了我们的java并发包java.util.concurrent中,并且在java 8 的lambda并行流中充当着底层框架的角色.这样一个优秀 ...
- java通过Access_JDBC30读取access数据库时无法获取最新插入的记录
1.编写了一个循环程序,每几秒钟读取一次,数据库中最新一行数据 连接access数据库的方法和查询的信息.之后开一个定时去掉用. package javacommon.util; import jav ...
- 异常: Recieved SHUTDOWN signal from Resourcemanager ,Registration of NodeManager failed, Message from ResourceManager: NodeManager from localhost doesn't satisfy minimum allocations, Sending SHUTDOWN s
异常: Recieved SHUTDOWN signal from Resourcemanager ,Registration of NodeManager failed, Message from ...
- RNP项目遇到的坑
1.nginx问题 和前端约定了在header中存放登录态k-v,选择的key是带下划线的. nginx 默认会丢弃带下划线的 header. 设置 underscores_in_headers on ...
- 汇编语言--微机CPU的指令系统(五)(移位操作指令)
(5) 移位操作指令 移位操作指令是一组经常使用的指令,它包括算术移位.逻辑移位.双精度移位.循环移位和带进位的循环移位等五大类. 移位指令都有指定移动二进制位数的操作数,该操作数可以是立即数或CL的 ...
- 查看linux 服务器还剩多少空间
df -hl 或者 df -m
- 微信wx.request
官方 wx.request 代码,Post 没成功过,使用Get 方式成功了. wx.request({ url: 'test.php', //仅为示例,并非真实的接口地址 data: { x: '' ...
- 洛谷P4768 [NOI2018]归程(Kruskal重构树)
题意 直接看题目吧,不好描述 Sol 考虑暴力做法 首先预处理出从$1$到每个节点的最短路, 对于每次询问,暴力的从这个点BFS,从能走到的点里面取$min$ 考虑如何优化,这里要用到Kruskal重 ...
