【CSS】Sticky Footer 布局
什么是 Sticky Footer 布局?
Sticky Footer 布局是一种将 footer 吸附在底部的CSS布局。
footer 可以是任意的元素,该布局会形成一种当内容不足,footer 会定位在视口的最低部,当内容充足,footer 会紧跟在内容后面的效果。
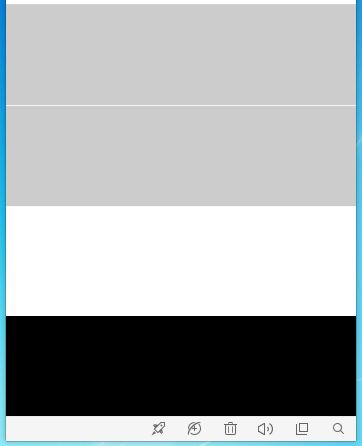
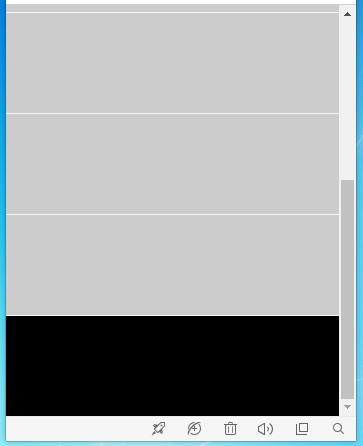
position实现 效果1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
position: relative; /*border-box: 为元素指定的任何 padding 和 border 都将在已设定的宽度和高度内进行绘制
这里的作用是浏览器视口被当成了 border ,如果不设置该属性则无法将 footer 置于浏览器视口的底部*/
box-sizing: border-box; /*这里的作用是将 .wrapper 的高度撑满整个浏览器的视口,当内容不足的时候,也能保证 .wrapper 的高度是浏览器视口的高度*/
min-height: 100%; /*这里的作用是为 .footer 预留空间,防止 .wrapper 的内容被 .footer 遮盖到,值是 .footer 的高度*/
padding-bottom: 100px;
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
position实现 效果2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
/*border-box: 为元素指定的任何 padding 和 border 都将在已设定的宽度和高度内进行绘制
这里的作用是浏览器视口被当成了 border ,如果不设置该属性则无法将 footer 置于浏览器视口的底部*/
box-sizing: border-box; /*这里的作用是将 .wrapper 的高度撑满整个浏览器的视口,当内容不足的时候,也能保证 .wrapper 的高度是浏览器视口的高度*/
min-height: 100%; /*这里的作用是为 .footer 预留空间,防止 .wrapper 的内容被 .footer 遮盖到,值是 .footer 的高度*/
padding-bottom: 100px;
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
flex实现 效果1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
/*使用 flex 布局 子元素列排布*/
display: flex;
flex-direction: column; /*这里的作用是将 .wrapper 的高度撑满整个浏览器的视口,当内容不足的时候,也能保证 .wrapper 的高度是浏览器视口的高度*/
min-height: 100%;
}
.content {
/*因为父元素使用了 flex 布局,这里设置使 .content 的高度是 .wrapper 的高度减去 .footer 的高度*/
flex: 1;
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
flex实现 效果2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
/*使用 flex 布局 子元素列排布*/
display: flex;
flex-direction: column; /*这里的作用是将 .wrapper 的高度撑满整个浏览器的视口,当内容不足的时候,也能保证 .wrapper 的高度是浏览器视口的高度*/
min-height: 100%;
}
.content {
/*因为父元素使用了 flex 布局,这里设置使 .content 的高度是 .wrapper 的高度减去 .footer 的高度*/
flex: 1;
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
calc实现 效果1
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
/*使用 calc 需要显示的设置 height ,如果使用 min-height 则会是跟随的效果*/
min-height: 100%;
}
.content {
/*min-height 是CSS的计算函数*/
min-height: calc(100% - 100px);
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
calc实现 效果2
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Sticky Footer 布局</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
html, body {
height: 100%;
}
.wrapper {
height: 100%;
}
.content {
/*min-height 是CSS的计算函数*/
min-height: calc(100% - 100px);
}
.content ul {
list-style: none;
}
.content ul li {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccc;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f6f6f6;
}
.footer {
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: #000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
【CSS】Sticky Footer 布局的更多相关文章
- css sticky footer 布局 手机端
什么是css sticky footer 布局? 通常在手机端写页面 会遇到如下情况 页面长度很短不足以撑起一屏,此时希望页脚在页面的底部 而当页面超过一屏时候,页脚会在文章的底部 ,网上有许多办法, ...
- css sticky footer 布局
方法一:footer 上用负的 margin-top 在内容外面需要额外包一层元素(wrap)来让它产生对应的 padding-bottom.是为了防止负 margin 导致 footer 覆盖任何实 ...
- css sticky footer布局
Sticky footers设计是最古老和最常见的效果之一,大多数人都曾经经历过.它可以概括如下:如果页面内容不够长的时候,页脚块粘贴在视窗底部:如果内容足够长时,页脚块会被内容向下推送.套路为:内容 ...
- 【css技能提升】完美的 Sticky Footer 布局
在总结之前所做的项目时,遇到过下面这种情况. 在主体内容不足够多或者未完全加载出来之前,就会导致出现左边的这种情况,原因是因为没有足够的垂直空间使得页脚推到浏览器窗口最底部.但是,我们期望的效果是页脚 ...
- CSS Sticky Footer
----CSS Sticky Footer 当正文内容很少时,底部位于窗口最下面.当改变窗口高度时,不会出现重叠问题. ----另一个解决方法是使用:flexBox布局 http://www.w3c ...
- 两种最常用的Sticky footer布局方式
Sticky footer布局是什么? 我们所见到的大部分网站页面,都会把一个页面分为头部区块.内容区块和页脚区块,当头部区块和内容区块内容较少时,页脚能固定在屏幕的底部,而非随着文档流排布.当页面内 ...
- 前端经典布局:Sticky footer 布局
什么是Sticky footer布局?前端开发中大部分网站,都会把一个页面分为头部区块.内容区块.页脚区块,这也是比较.往往底部都要求能固定在屏幕的底部,而非随着文档流排布.要实现的样式可以概括如下: ...
- CSS Sticky Footer: 完美的CSS绝对底部
CSS的简单在于它易学,CSS的困难在于寻找更好的解决方案.在CSS的世界里,似乎没有完美这种说法.所以,现在介绍的CSS绝对底部,只是目前个人见过的方案中比较完美的吧. 先说我们为什么会使用到这个C ...
- sticky footer布局,定位底部footer
其作用就是当内容区域比较少时,让footer也能正常定位到底部,以前我们使用js来达到这种效果,其实用css也是完全可以的 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=&q ...
随机推荐
- html5编写软件哪个好?八款html5编写软件推荐
随着各大浏览器对HTML5技术支持的不断完善,未来HTML5必将改变我们创建Web应用程序的方式.而很多html5的初学者都想找一款好用的编写软件,这里主机吧就给大家推荐七款好用的html5编写软件. ...
- 在chrome console中添加jQuery
由于现有seajs等封装,jQuery等已不在全局暴露,即使网站中已使用jQuery,在console也使用不了. 在chrome中可以用以下代码加入jQuery: fetch('http://cod ...
- Django基础回顾与补充(79-80)
Django框架之回顾与补充(d79-80)一 HTTP协议:(重点) 1 请求 -请求首行 -GET /index HTTP/1.1 -请求头部(在django框架中,可以从META ...
- django rest framework serializer中获取request中user方法
views.py serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data, context={'request': request}) seriali ...
- 灰熊:在这6个信息流和DSP平台投放后,我总结了这些血泪经验!
笔者有幸参与公司的一款重度游戏的推广,推广以来市面上主流的信息流和DSP 平台都投过一番,今天就零零碎碎地讲讲各个平台的特点以及用户质量. 需要提前说明的是,文章的观点仅限于各个平台的 iOS 流量, ...
- Linux查看和修改时间、日期
1.查看时间.日期 # date Fri Jan 11 14:04:10 CST 2019 2.修改时间 语法:date -s "时:分:秒" # date -s "17 ...
- Monkey测试简介
1.Monkey测试简介monkey是安卓命令行工具,它向系统发送伪随机的用户事件,例如:按键的输入.触摸屏的输入.手势输入等操作来对设备上的程序进行压力测试,检测程序多久的时间会发生异常.因此,mo ...
- maven repository pom
场景: 如果maven setting.xml 中没指定国内的镜像 可以通过在项目中的pom中指定 指定repository : <properties> <java.version ...
- 如何用jquery获取form表单的值
$(function(){ $('.btn').click(function(){ alert($('#form').serialize()); }) }) 这样就获取到了 #form的值.
- Springboot 使用thymeleaf模板layout布局
使用layout布局前应该在pom文件中导入thymeleaf(dialect)依赖:如下 <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding> ...
