mybaits源码分析--binding模块(五)
一、binding模块
接下来我们看看在org.apache.ibatis.binding包下提供的Binding模块 ,binding其实在执行sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);获取接口代理的对象时有用到;
发现这个包里面提供的工具比较少,就几个,先来分别了解下他们的作用,然后在串联起来。
1.1 MapperRegistry
这显然是一个注册中心,这个注册中是用来保存MapperProxyFactory对象的,所以这个注册器中提供的功能肯定是围绕MapperProxyFactory的添加和获取操作,来看看具体的代码逻辑
成员变量:
private final Configuration config;
// 记录 Mapper 接口和 MapperProxyFactory 之间的关系
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
addMapper方法
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) { // 检测 type 是否为接口
if (hasMapper(type)) { // 检测是否已经加装过该接口
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// !Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> 存放的是接口类型,和对应的工厂类的关系
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 注册了接口之后,根据接口,开始解析所有方法上的注解,例如 @Select >>
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
getMapper方法
/**
* 获取Mapper接口对应的代理对象
*/
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 获取Mapper接口对应的 MapperProxyFactory 对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
通过这个方法本质上获取的就是Mapper接口的代理对象。
1.2 MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory是一个工厂对象,专门负责创建MapperProxy对象。其中核心字段的含义和功能如下:
/**
* 负责创建 MapperProxy 对象
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { /**
* MapperProxyFactory 可以创建 mapperInterface 接口的代理对象
* 创建的代理对象要实现的接口
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 缓存
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
} public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
} public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
/**
* 创建实现了 mapperInterface 接口的代理对象
*/
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 1:类加载器:2:被代理类实现的接口、3:实现了 InvocationHandler 的触发管理类
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
} }
1.3 MapperProxy
通过MapperProxyFactory创建的MapperProxy是Mapper接口的代理对象,实现了InvocationHandler接口,通过前面讲解的动态代理模式,那么这部分的内容就很简单了。
/**
* Mapper 代理对象
* @author
* @author
*/
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -4724728412955527868L;
private static final int ALLOWED_MODES = MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC;
private static final Constructor<Lookup> lookupConstructor;
private static final Method privateLookupInMethod;
private final SqlSession sqlSession; // 记录关联的 SqlSession对象
private final Class<T> mapperInterface; // Mapper接口对应的Class对象
// 用于缓存MapperMethod对象,key是Mapper接口方法对应的Method对象,value是对应的MapperMethod对象。‘
// MapperMethod对象会完成参数转换以及SQL语句的执行
// 注意:MapperMethod中并不会记录任何状态信息,可以在多线程间共享
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
} static {
Method privateLookupIn;
try {
privateLookupIn = MethodHandles.class.getMethod("privateLookupIn", Class.class, MethodHandles.Lookup.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
privateLookupIn = null;
}
privateLookupInMethod = privateLookupIn; Constructor<Lookup> lookup = null;
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
// JDK 1.8
try {
lookup = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
lookup.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"There is neither 'privateLookupIn(Class, Lookup)' nor 'Lookup(Class, int)' method in java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.",
e);
} catch (Exception e) {
lookup = null;
}
}
lookupConstructor = lookup;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// toString hashCode equals getClass等方法,无需走到执行SQL的流程
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 提升获取 mapperMethod 的效率,到 MapperMethodInvoker(内部接口) 的 invoke
// 普通方法会走到 PlainMethodInvoker(内部类) 的 invoke
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
// Java8 中 Map 的方法,根据 key 获取值,如果值是 null,则把后面Object 的值赋给 key
// 如果获取不到,就创建
// 获取的是 MapperMethodInvoker(接口) 对象,只有一个invoke方法
// 根据method 去methodCache中获取 如果返回空 则用第二个参数填充
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
// 接口的默认方法(Java8),只要实现接口都会继承接口的默认方法,例如 List.sort()
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 创建了一个 MapperMethod
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
} private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava9(Method method)
throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return ((Lookup) privateLookupInMethod.invoke(null, declaringClass, MethodHandles.lookup())).findSpecial(
declaringClass, method.getName(), MethodType.methodType(method.getReturnType(), method.getParameterTypes()),
declaringClass);
} private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava8(Method method)
throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return lookupConstructor.newInstance(declaringClass, ALLOWED_MODES).unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass);
} interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
} private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod; public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// SQL执行的真正起点
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
} private static class DefaultMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MethodHandle methodHandle; public DefaultMethodInvoker(MethodHandle methodHandle) {
super();
this.methodHandle = methodHandle;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return methodHandle.bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
}
}
1.4 MapperMethod
MapperMethod中封装了Mapper接口中对应方法的信息,以及SQL语句的信息,可以把MapperMethod看成是配置文件中定义的SQL语句和Mapper接口的桥梁。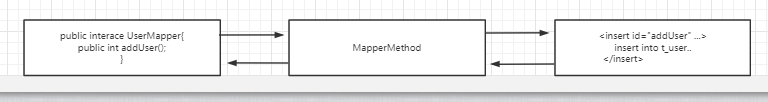
属性和构造方法
// statement id (例如:com.gupaoedu.mapper.BlogMapper.selectBlogById) 和 SQL 类型
private final SqlCommand command;
// 方法签名,主要是返回值的类型
private final MethodSignature method; public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
1.4.1 SqlCommand
SqlCommand是MapperMethod中定义的内部类,记录了SQL语句名称以及对应的类型(UNKNOWN,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,SELECT,FLUSH)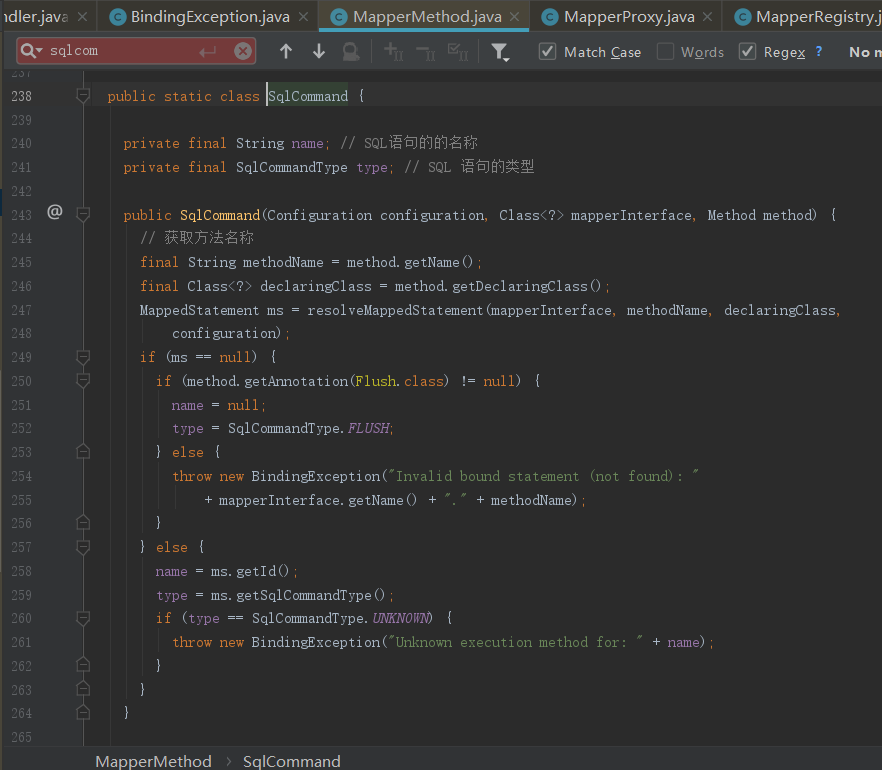
1.4.2 MethodSignature
MethodSignature也是MapperMethod的内部类,在其中封装了Mapper接口中定义的方法相关信息。
private final boolean returnsMany; // 判断返回是否为 Collection类型或者数组类型
private final boolean returnsMap; // 返回值是否为 Map类型
private final boolean returnsVoid; // 返回值类型是否为 void
private final boolean returnsCursor; // 返回值类型是否为 Cursor 类型
private final boolean returnsOptional; // 返回值类型是否为 Optional 类型
private final Class<?> returnType; // 返回值类型
private final String mapKey; // 如果返回值类型为 Map 则 mapKey 记录了作为 key的 列名
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex; // 用来标记该方法参数列表中 ResultHandler 类型参数的位置
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex; // 用来标记该方法参数列表中 rowBounds 类型参数的位置
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver; // 该方法对应的 ParamNameResolver 对象
构造方法中完成了相关信息分初始化操作
/**
* 方法签名
* @param configuration
* @param mapperInterface
* @param method
*/
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 获取接口方法的返回类型
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray();
this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsOptional = Optional.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null;
// getUniqueParamIndex 查找指定类型的参数在 参数列表中的位置
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}
getUniqueParamIndex的主要作用是 查找指定类型的参数在参数列表中的位置
/**
* 查找指定类型的参数在参数列表中的位置
* @param method
* @param paramType
* @return
*/
private Integer getUniqueParamIndex(Method method, Class<?> paramType) {
Integer index = null;
// 获取对应方法的参数列表
final Class<?>[] argTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 遍历
for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) {
// 判断是否是需要查找的类型
if (paramType.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i])) {
// 记录对应类型在参数列表中的位置
if (index == null) {
index = i;
} else {
// RowBounds 和 ResultHandler 类型的参数只能有一个,不能重复出现
throw new BindingException(method.getName() + " cannot have multiple " + paramType.getSimpleName() + " parameters");
}
}
}
return index;
}
1.4.3 execute方法
最后来看下再MapperMethod中最核心的方法execute方法,这个方法完成了数据库操作
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) { // 根据SQL语句的类型调用SqlSession对应的方法
case INSERT: {
// 通过 ParamNameResolver 处理args[] 数组 将用户传入的实参和指定参数名称关联起来
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param) 调用SqlSession的insert方法
// rowCountResult 方法会根据 method 字段中记录的方法的返回值类型对结果进行转换
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
// 返回值为空 且 ResultSet通过 ResultHandler处理的方法
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 返回值为 单一对象的方法
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 普通 select 语句的执行入口 >>
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
在这个方法中所对应一些分支方法都还是比较简单的,看一下其实就懂,我就不想再往里跟了
1.4.4 核心流程串联
首先在映射文件加载解析的位置,XMLMapperBuilder.parse位置
public void parse() {
// 总体上做了两件事情,对于语句的注册和接口的注册
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 1、具体增删改查标签的解析。
// 一个标签一个MappedStatement。 >>
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 2、把namespace(接口类型)和工厂类绑定起来,放到一个map。
// 一个namespace 一个 MapperProxyFactory >>
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
在bindMapperForNamespace中会完成Mapper接口的注册并调用前面介绍过的addMapper方法然后就是在我们执行
// 4.通过SqlSession中提供的 API方法来操作数据库
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> list = mapper.selectUserList();
这两行代码的内部逻辑,首先看下getMapper方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// mapperRegistry中注册的有Mapper的相关信息 在解析映射文件时 调用过addMapper方法
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
然后就是从MapperRegistry中获取对应的MapperProxyFactory对象。
/**
* 获取Mapper接口对应的代理对象
*/
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 获取Mapper接口对应的 MapperProxyFactory 对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
然后根据MapperProxyFactory对象获取Mapper接口对应的代理对象。
/**
* 创建实现了 mapperInterface 接口的代理对象
*/
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 1:类加载器:2:被代理类实现的接口、3:实现了 InvocationHandler 的触发管理类
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
不清楚可以看前面画的时序图

然后我们再来看下调用代理对象中的方法执行的顺序
List<User> list = mapper.selectUserList();
会进入MapperProxy的Invoker方法中
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// toString hashCode equals getClass等方法,无需走到执行SQL的流程
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 提升获取 mapperMethod 的效率,到 MapperMethodInvoker(内部接口) 的 invoke
// 普通方法会走到 PlainMethodInvoker(内部类) 的 invoke
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
然后进入PlainMethodInvoker中的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// SQL执行的真正起点
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
然后会进入到 MapperMethod的execute方法中
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) { // 根据SQL语句的类型调用SqlSession对应的方法
case INSERT: {
// 通过 ParamNameResolver 处理args[] 数组 将用户传入的实参和指定参数名称关联起来
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param) 调用SqlSession的insert方法
// rowCountResult 方法会根据 method 字段中记录的方法的返回值类型对结果进行转换
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
// 返回值为空 且 ResultSet通过 ResultHandler处理的方法
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 返回值为 单一对象的方法
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 普通 select 语句的执行入口 >>
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
之后就会根据对应的SQL类型而调用SqlSession中对应的方法来执行操作
mybaits源码分析--binding模块(五)的更多相关文章
- mybaits源码分析--缓存模块(六)
一.缓存模块 MyBatis作为一个强大的持久层框架,缓存是其必不可少的功能之一,Mybatis中的缓存分为一级缓存和二级缓存.但本质上是一样的,都是使用Cache接口实现的.缓存位于 org.apa ...
- mybaits源码分析--日志模块(四)
一.日志模块 首先日志在我们开发过程中占据了一个非常重要的地位,是开发和运维管理之间的桥梁,在Java中的日志框架也非常多,Log4j,Log4j2,Apache Commons Log,java.u ...
- 手机自动化测试:appium源码分析之bootstrap五
手机自动化测试:appium源码分析之bootstrap五 poptest是国内唯一一家培养测试开发工程师的培训机构,以学员能胜任自动化测试,性能测试,测试工具开发等工作为目标.poptest测试 ...
- ABP源码分析四十五:ABP ZERO中的EntityFramework模块
AbpZeroDbContext:配置ABP.Zero中定义的entity的Dbset EntityFrameworkModelBuilderExtensions:给PrimitiveProperty ...
- mybaits源码分析(一)
一.源码下载 1.手动编译源码 为了方便在看源码的过程中能够方便的添加注释,可以从官网下载源码编译生成对应的Jar包,然后上传到本地maven仓库,再引用这个Jar. 首先需要编译打包parent项目 ...
- nginx源码分析之模块初始化
在nginx启动过程中,模块的初始化是整个启动过程中的重要部分,而且了解了模块初始化的过程对应后面具体分析各个模块会有事半功倍的效果.在我看来,分析源码来了解模块的初始化是最直接不过的了,所以下面主要 ...
- ABP源码分析二十五:EventBus
IEventData/EventData: 封装了EventData信息,触发event的源对象和时间 IEventBus/EventBus: 定义和实现了了一系列注册,注销和触发事件处理函数的方法. ...
- ABP源码分析三十五:ABP中动态WebAPI原理解析
动态WebAPI应该算是ABP中最Magic的功能之一了吧.开发人员无须定义继承自ApiController的类,只须重用Application Service中的类就可以对外提供WebAPI的功能, ...
- [Abp vNext 源码分析] - 2. 模块系统的变化
一.简要说明 本篇文章主要分析 Abp vNext 当中的模块系统,从类型构造层面上来看,Abp vNext 当中不再只是单纯的通过 AbpModuleManager 来管理其他的模块,它现在则是 I ...
随机推荐
- Tom_No_01 IDEA tomcat 源码环境搭建
1.下载源码 apache-tomcat-8.5.50-src 2.下载源码 放D盘,解压后根目录新建pom.xml和catalina-home pom.xml文件中内容为 <?xml vers ...
- Jenkins(8080)未授权访问
下载地址http://mirrors.jenkins.io/debian/ 测试 浏览器访问http://localhost:8080/manage可以直接访问 点击脚本命令行 println &qu ...
- 用QT写的简单Todo记事本-附源码(浮动窗口)
去年边学边写了搞了很久, 已经好久没继续开发了, 先放出来供大家参考吧. 发现自己的学习能力还是不错的. 技术点: 使用QT, QML技术 代码参考: https://github.com/cnscu ...
- 组合数取模(lukas)板子
求 C(n,m)%mo #include<bits/stdc++.h>#define re register int#define mo 10007#define ll long long ...
- 自学linux——16.LAMP项目上线流程
LAMP项目上线流程 一.编译安装与卸载Nginx(web服务器软件,类似于Apache) 1.安装nginx ① 下载nginx 网页下载https://nginx.org/en/downlo ...
- 从事 Android应用开发4年有余,现在工资7500。很不爽!怎么办?
最近到某论坛看到一个帖子: 坐标北京,在一个公司从事android应用开发4年有余(毕业至今没换过公司).公司利润越来越大,工资却每年长1000,如今才到7500.琢磨着换工作,又不想扔下这四年来逐步 ...
- Tomcat服务器种的HttpServletRequest类
HttpServletRequest 类有什么作用: 每次只要有请求进入 Tomcat 服务器,Tomcat 服务器就会把请求过来的 HTTP 协议信息解析好封装到 Reque ...
- Google Breakpad · 基础介绍
Google breakpad是一个跨平台的崩溃转储和分析框架和工具集合. 三个主要组件 ◆ client 以library的形式内置在你的应用中,当崩溃发生时写 minidump文件 ◆ symbo ...
- 关于下载远程文件为未知文件.txt的解决方法
本地下载文件后缀正常,服务器下载文件后缀都为.txt的解决方法: 后缀为 未知文件.txt 的原因为前端无权限获取Content-Disposition中的文件名 response.setHeader ...
- noip模拟44[我想我以后会碰见计数题就溜走的]
noip模拟44 solutions 这一场抱零的也忒多了,我也只有45pts 据说好像是把几套题里面最难的收拾出来让我们考得 好惨烈啊,这次的考试我只有第一题骗了40pts,其他都抱零了 T1 Em ...
