【MySQL】自定义数据库连接池和开源数据库连接池的使用
数据库连接池的概念
数据库连接背景
- 数据库连接是一种关键的、有限的、昂贵的资源,这一点在多用户的网页应用程序中体现得尤为突出。对数据库连接的管理能显著影响到整个应用程序的伸缩性和健壮性,影响到程序的性能指标。数据库连接池正是针对这个问题提出来的。
数据库连接池
- 数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个。这项技术能明显提高对数据库操作的性能。
数据库连接池的原理
没有使用数据库连接池:一个访问创建一个连接,使用完关闭连接。而频繁的创建和关闭连接非常耗时
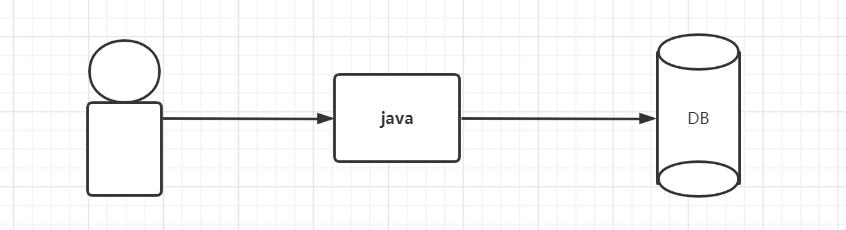
使用数据库连接池之后:提前准备一些数据库连接,使用时从池中取出,用完归还连接池
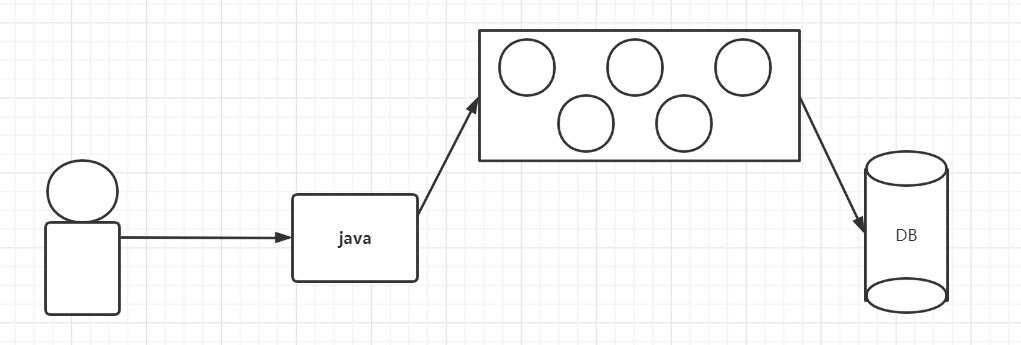
自定义连接池
初探连接池
自定义JDBC工具类
配置文件 config.properties
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://主机名:3306/数据库名
username=用户名
password=密码
JDBCUtils工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
private JDBCUtils() {} //构造函数私有化
private static String driverClass;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
private static Connection con;
static {
try {
InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() { //获取连接对象
try {
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
//关闭连接(有查询结果集)
public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat, ResultSet res) {
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stat != null) {
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (res != null) {
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//关闭连接(无查询结果集)
public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat) {
close(con, stat, null);
}
}
实现连接池类
定义一个连接池类并实现java.sql.DataSource 接口。
Connection getConnection(); //获取数据库连接对象
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{
//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象
//使用Collections 工具类实现集合的线程同步
private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());
//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
pool.add(con);
}
}
//返回连接池的大小
public int getSize() {
return pool.size();
}
//从池中返回一个数据库连接
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
if(pool.size() > 0) {
//从池中获取数据库连接
return pool.remove(0);
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");
}
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
}
自定义连接池的测试
public class MyDataSourceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyDataSource dataSource = new MyDataSource();
System.out.println("使用前连接池数量:" + dataSource.getSize());
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from emp";
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet res = pst.executeQuery();
while (res.next()) {
String ename = res.getString("ename");
String job = res.getString("job");
String hiredate = res.getString("hiredate");
System.out.println("ename:" + ename + "\t job:" + job + "\t hiredate:" + hiredate);
}
res.close();
pst.close();
con.close();
System.out.println("使用后连接池数量:" + dataSource.getSize());
}
}
输出:
使用前连接池数量:10
ename:SMITH job:CLERK hiredate:1980-12-17
ename:ALLEN job:SALESMAN hiredate:1981-02-20
ename:WARD job:SALESMAN hiredate:1981-02-22
ename:JONES job:MANAGER hiredate:1981-04-02
ename:MARTIN job:SALESMAN hiredate:1981-09-28
ename:BLAKE job:MANAGER hiredate:1981-05-01
ename:CLARK job:MANAGER hiredate:1981-06-09
ename:SCOTT job:ANALYST hiredate:1987-04-19
ename:KING job:PRESIDENT hiredate:1981-11-17
ename:TURNER job:SALESMAN hiredate:1981-09-08
ename:ADAMS job:CLERK hiredate:1987-05-23
ename:JAMES job:CLERK hiredate:1981-12-03
ename:FORD job:ANALYST hiredate:1981-12-03
ename:MILLER job:CLERK hiredate:1982-01-23
使用后连接池数量:9
问题:虽然我们自定义了数据库连接池,但是连接关闭以后并没有归还给数据库连接池,还需要改进归还连接的问题
继承方式改进连接池
System.out.println(JDBCUtils.getConnection());
//com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@470e2030
通过输出Connection的地址发现Connection类的实现类是JDBC4Connection,是否能够通过编写一个类继承JDBC4Connection,然后重写close()方法,在关闭连接的同时归还连接?
/*
自定义Connection类
*/
public class MyConnection1 extends JDBC4Connection {
//声明连接对象和连接池集合对象
private Connection con;
private List<Connection> pool;
//通过构造方法给成员变量赋值
public MyConnection1(String hostToConnectTo, int portToConnectTo, Properties info, String databaseToConnectTo, String url,Connection con,List<Connection> pool) throws SQLException {
super(hostToConnectTo, portToConnectTo, info, databaseToConnectTo, url);
this.con = con;
this.pool = pool;
}
//重写close()方法,将连接归还给池中
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.add(con);
}
}
但是这种方式行不通,通过查看JDBC工具类获取连接的方法我们发现:我们虽然自定义了一个子类,完成了归还连接的操作。但是DriverManager获取的还是JDBC4Connection这个对象,并不是我们的子类对象。而我们又不能整体去修改驱动包中类的功能!
//将之前的连接对象换成自定义的子类对象
private static MyConnection1 con;
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
//等效于:MyConnection1 con = new JDBC4Connection(); 子类引用指向父类对象,语法错误!
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
装饰设计模式改进连接池
自定义Connection类。通过装饰设计模式,实现和mysql驱动包中的Connection实现类相同的功能!
实现步骤:
定义一个类,实现Connection接口
定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量
提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值
在close()方法中,完成连接的归还
剩余方法,只需要调用mysql驱动包的连接对象完成即可
public class MyConnection2 implements Connection {
//2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量
private Connection con;
private List<Connection> pool;
//3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值
public MyConnection2(Connection con,List<Connection> pool) {
this.con = con;
this.pool = pool;
}
//4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.add(con);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement();
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql);
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.nativeSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
con.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return con.getAutoCommit();
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
con.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return con.isClosed();
}
@Override
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return con.getMetaData();
}
@Override
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
con.setReadOnly(readOnly);
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return con.isReadOnly();
}
@Override
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
con.setCatalog(catalog);
}
@Override
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return con.getCatalog();
}
@Override
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
con.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
@Override
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return con.getTransactionIsolation();
}
@Override
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return con.getWarnings();
}
@Override
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
con.clearWarnings();
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return con.getTypeMap();
}
@Override
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
con.setTypeMap(map);
}
@Override
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
con.setHoldability(holdability);
}
@Override
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return con.getHoldability();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint(name);
}
@Override
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.rollback(savepoint);
}
@Override
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);
}
@Override
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createClob();
}
@Override
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return con.createBlob();
}
@Override
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createNClob();
}
@Override
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return con.createSQLXML();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return con.isValid(timeout);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(name,value);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(properties);
}
@Override
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo(name);
}
@Override
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo();
}
@Override
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);
}
@Override
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);
}
@Override
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
con.setSchema(schema);
}
@Override
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return con.getSchema();
}
@Override
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
con.abort(executor);
}
@Override
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);
}
@Override
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return con.getNetworkTimeout();
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
}
自定义连接池类
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{
//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象
private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());
//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
pool.add(con);
}
}
//返回连接池的大小
public int getSize() {
return pool.size();
}
//从池中返回一个数据库连接
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
if(pool.size() > 0) {
//从池中获取数据库连接
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
//通过自定义连接对象进行包装
MyConnection2 mycon = new MyConnection2(con,pool);
//返回包装后的连接对象
return mycon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");
}
}
}
缺点:Connection 接口中要实现的方法太多了,代码繁杂
适配器设计模式改进连接池
提供一个适配器类,实现Connection接口,将所有功能进行实现(除了close()方法),作为中间类。自定义连接类只需要继承这个适配器类,重写需要改进的close()方法即可!
适配器类不需要实现close()方法,所以定义为抽象类
public abstract class MyAdapter implements Connection {
// 定义数据库连接对象的变量
private Connection con;
// 通过构造方法赋值
public MyAdapter(Connection con) {
this.con = con;
}
// 所有的方法,均调用mysql的连接对象实现
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement();
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql);
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.nativeSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
con.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return con.getAutoCommit();
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
con.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return con.isClosed();
}
@Override
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return con.getMetaData();
}
@Override
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
con.setReadOnly(readOnly);
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return con.isReadOnly();
}
@Override
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
con.setCatalog(catalog);
}
@Override
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return con.getCatalog();
}
@Override
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
con.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
@Override
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return con.getTransactionIsolation();
}
@Override
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return con.getWarnings();
}
@Override
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
con.clearWarnings();
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return con.getTypeMap();
}
@Override
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
con.setTypeMap(map);
}
@Override
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
con.setHoldability(holdability);
}
@Override
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return con.getHoldability();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint(name);
}
@Override
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.rollback(savepoint);
}
@Override
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);
}
@Override
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createClob();
}
@Override
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return con.createBlob();
}
@Override
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createNClob();
}
@Override
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return con.createSQLXML();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return con.isValid(timeout);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(name,value);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(properties);
}
@Override
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo(name);
}
@Override
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo();
}
@Override
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);
}
@Override
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);
}
@Override
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
con.setSchema(schema);
}
@Override
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return con.getSchema();
}
@Override
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
con.abort(executor);
}
@Override
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);
}
@Override
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return con.getNetworkTimeout();
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
}
自定义连接类
通过适配器设计模式。完成close()方法的重写
定义一个类,继承适配器父类
定义
Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值
在
close()方法中,完成连接的归还
public class MyConnection3 extends MyAdapter {
//2.定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的变量
private Connection con;
private List<Connection> pool;
//3.提供有参构造方法,接收连接对象和连接池对象,对变量赋值
public MyConnection3(Connection con,List<Connection> pool) {
super(con); // 将接收的数据库连接对象给适配器父类传递
this.con = con;
this.pool = pool;
}
//4.在close()方法中,完成连接的归还
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.add(con);
}
}
自定义连接池类
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{
//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象
private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());
//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
pool.add(con);
}
}
//返回连接池的大小
public int getSize() {
return pool.size();
}
//从池中返回一个数据库连接
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
if(pool.size() > 0) {
//从池中获取数据库连接
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
//通过自定义连接对象进行包装
MyConnection3 mycon = new MyConnection3(con,pool);
//返回包装后的连接对象
return mycon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");
}
}
}
缺点:自定义连接类中的方法已经很简洁了。剩余所有的方法已经抽取到了适配器类中。但是适配器这个类还是我们自己编写的,也比较麻烦!所以可以使用动态代理的方式来改进。
动态代理
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{
//定义集合容器,用于保存多个数据库连接对象
private static List<Connection> pool = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<Connection>());
//静态代码块,生成10个数据库连接保存到集合中
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
pool.add(con);
}
}
//返回连接池的大小
public int getSize() {
return pool.size();
}
//动态代理方式
@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
if(pool.size() > 0) {
//从池中获取数据库连接
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
Connection proxyCon = (Connection)Proxy.newProxyInstance(con.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Connection.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
/*
执行Connection实现类所有方法都会经过invoke
如果是close方法,则将连接还回池中
如果不是,直接执行实现类的原有方法
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if(method.getName().equals("close")) {
pool.add(con);
return null;
}else {
return method.invoke(con,args);
}
}
});
return proxyCon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");
}
}
//从池中返回一个数据库连接
/*@Override
public Connection getConnection() {
if(pool.size() > 0) {
//从池中获取数据库连接
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
//通过自定义连接对象进行包装
//MyConnection2 mycon = new MyConnection2(con,pool);
MyConnection3 mycon = new MyConnection3(con,pool);
//返回包装后的连接对象
return mycon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接数量已用尽");
}
}*/
}
开源连接池的使用
C3P0连接池
导入jar包


导入配置文件到src目录下
创建c3p0连接池对象
获取数据库连接进行使用
配置文件 c3p0-config.xml 注意该配置文件的名字是固定的不要改,否则无法识别
initialPoolSize:初始化连接数量maxPoolSize:最大连接数量,当连接数量超过初始化连接数量时,会在连接池内继续创建连接,直到达到数据库连接池所能容纳的最大连接数量checkoutTimeout:超过时间。如果使用的连接数量超过最大连接数量,编译器会在checkoutTimeout时间以后报错并终止程序。
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 使用默认的配置读取连接池对象 -->
<default-config>
<!-- 连接参数 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://主机名:3306/数据库名</property>
<property name="user">用户名</property>
<property name="password">密码</property>
<!-- 连接池参数 -->
<!-- 初始化连接数量 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 最大连接数量 -->
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- 超时时间 -->
<property name="checkoutTimeout">3000</property>
</default-config>
<!-- 创建数据库连接池时指定名称-->
<named-config name="otherc3p0">
<!-- 连接参数 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://主机名:3306/数据库名</property>
<property name="user">用户名</property>
<property name="password">密码</property>
<!-- 连接池参数 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">8</property>
<property name="checkoutTimeout">1000</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
C3P0数据库连接池的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//创建c3p0连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
//获取数据库连接进行使用
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
String s = "select *from emp";
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(s);
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
String job = rs.getString("job");
String hiredate = rs.getString("hiredate");
System.out.println("ename:" + ename + " job:" + job + " hiredate:" + hiredate);
}
rs.close();
pst.close();
con.close(); // 将连接对象归还池中
}
Druid连接池
导入jar包

编写配置文件,放在src目录下
通过Properties集合加载配置文件
通过Druid连接池工厂类获取数据库连接池对象
获取数据库连接,进行使用
配置文件druid.properties
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://主机名:3306/数据库名
username:用户名
password:密码
# 初始连接数量
initialSize=5
# 最大连接数量
maxActive=10
# 最长等待时间
maxWait=3000
Druid数据库的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//通过Properties集合加载配置文件
InputStream is = demo01.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(is);
//通过Druid连接池工厂类获取数据库连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//获取数据库连接,进行使用
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement("select *from emp");
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
String job = rs.getString("job");
String hiredate = rs.getString("hiredate");
System.out.println("ename:" + ename + " job:" + job + " hiredate:" + hiredate);
}
rs.close();
pst.close();
con.close();
}
抽取工具类
/*
数据库连接池工具类
*/
public class DataSourceUtils {
//1.私有构造方法
private DataSourceUtils(){}
//2.定义DataSource数据源变量
private static DataSource dataSource;
//3.提供静态代码块,完成配置文件的加载和获取连接池对象
static {
try{
//加载配置文件
InputStream is = DruidDemo1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(is);
//获取数据库连接池对象
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//4.提供获取数据库连接的方法
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection con = null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
//5.提供获取数据库连接池的方法
public static DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
//6.提供释放资源的方法
public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat, ResultSet rs) {
if(con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stat != null) {
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Connection con, Statement stat) {
close(con,stat,null);
}
}
工具类的使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//利用工具类获取DataSoure
DataSource dataSource = DataSourceUtils.getDataSource();
//获取连接,并使用
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
String s = "select *from emp";
PreparedStatement pst = con.prepareStatement(s);
ResultSet rs = pst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
String ename = rs.getString("ename");
String job = rs.getString("job");
String hiredate = rs.getString("hiredate");
System.out.println("ename:" + ename + " job:" + job + " hiredate:" + hiredate);
}
DataSourceUtils.close(con, pst, rs);
}
【MySQL】自定义数据库连接池和开源数据库连接池的使用的更多相关文章
- 开源数据库连接池之Tomcat内置连接池
本篇介绍几种开源数据库连接池,同时重点讲述如何使用Tomcat服务器内置的数据库连接池. 之前的博客已经重点讲述了使用数据库连接池的好处,即是将多次创建连接转变为一次创建而使用长连接模式.这样能减少数 ...
- 开源数据库连接池之C3P0
本篇介绍几种开源数据库连接池,同时重点讲述如何使用C3P0数据库连接池. 之前的博客已经重点讲述了使用数据库连接池的好处,即是将多次创建连接转变为一次创建而使用长连接模式.这样能减少数据库创建连接的消 ...
- 开源数据库连接池之DBCP
本篇介绍几种开源数据库连接池,同时重点讲述如何使用Apache公司的的DBCP数据库连接池. 前面一篇博客已经重点讲述了使用数据库连接池的好处,即是将多次创建连接转变为一次创建而使用长连接模式.这样能 ...
- spring+mybatis+c3p0数据库连接池或druid连接池使用配置整理
在系统性能优化的时候,或者说在进行代码开发的时候,多数人应该都知道一个很基本的原则,那就是保证功能正常良好的情况下,要尽量减少对数据库的操作. 据我所知,原因大概有这样两个: 一个是,一般情况下系统服 ...
- DataSnap数据库连接池,数据集对象池的应用
传统的应用服务器的开发往往是在ServerMethods单元中拖放一堆TDataSet, TDaTaSetProvider控件,这是一个最简单粗暴的开发方向,往往会造成服务端程序文件的臃肿.服务运行期 ...
- Java 学习使用常见的开源连接池
目录 连接池介绍 自定义连接池 JDBC Tomcat Pool DBCP(DataBase Connection Pool) 使用配置文件来设置DBCP C3P0 Druid 连接池介绍 在说连接池 ...
- DBCP、C3P0、Proxool 、 BoneCP开源连接池的比《转》
简介 使用评价 项目主页 DBCP DBCP是一个依赖Jakarta commons-pool对象池机制的数据库连接池.DBCP可以直接的在应用程序用使用 可以设置最大和最小连接,连接等待时 ...
- (转载)DBCP、C3P0、Proxool 、 BoneCP开源连接池的比较
原文链接: http://blog.csdn.net/miclung/article/details/7231553 简介 使用评价 项目主页 DBCP DBCP是一个依赖Jakarta ...
- jdbc(1)(三)DBCP、C3P0、Proxool 、 BoneCP开源连接池的简介
简介 使用评价 项目主页 DBCP DBCP是一个依赖Jakarta commons-pool对象池机制的数据库连接池.DBCP可以直接的在应用程序用使用 可以设置最大和最小连 ...
随机推荐
- PHP利用百度ai实现文本和图片审核
之前做平台内容发布审核都是自己构建一套违禁词库,在代码中利用词库判断用户发布的内容,现在可以使用百度ai api完成这个功能.接下来就简单说下怎么做吧: 首先打开百度ai 开发平台 注册一个账号: 注 ...
- 关于easyswoole实现websocket聊天室的步骤解析
在去年,我们公司内部实现了一个聊天室系统,实现了一个即时在线聊天室功能,可以进行群组,私聊,发图片,文字,语音等功能,那么,这个聊天室是怎么实现的呢?后端又是怎么实现的呢? 后端框架 在后端框架上,我 ...
- NIO 输入输出
NIO 是java14 API 提供的一种新输入输出流,一套用于标准IO的文件读写,一套用于网络编程. 1. NIO 与IO 的区别 IO流以字节流输入输出,一次以一个字节进行数据操作,效率慢: NI ...
- C语言:sizeof判断数据类型长度
#include <stdio.h> int main() { short a = 10; int b = 100; long c=100; int short_length = size ...
- Java基础00-第一个程序2
1. 常用DOS命令 1.1 打开命令提示窗口 按下win+R 输入cmd 按下回车键 得到命令提示窗口 1.2 常用命令 2. Path环境变量的配置 2.1 为什么要配置Path环境变量 2.2 ...
- 给App加上音频编辑功能,让你的用户Show起来
如今短视频当道,BGM无处不在,用户在每个能秀的地方都想要加上个性表达的音频.作为一个开发者,需不断探索和迎合用户的行为喜好,音频编辑功能成为用户在编辑个人信息.内容创作.生活分享等场景下的必需品. ...
- Hive——元数据表含义
Hive--元数据表含义 1.VERSION -- 查询版本信息 Field Type Comment VER_ID bigint(20) ID主键 SCHEMA_VERSION va ...
- 【动态规划DP】[USACO16OPEN]248
题目描述 Bessie likes downloading games to play on her cell phone, even though she doesfind the small to ...
- 第十三天 -- 如何用U盘重装系统Win10以及如何用VMware12安装Win10
U盘制作启动盘 1.在电脑上插入U盘,关闭安全软件杀毒工具,然后打开装机吧U盘启动盘制作工具 2.选择刚插入的U盘,勾选上,点击一键制作启动U盘,制作前U盘数据必须转移备份: 3.选择格式化U盘,记得 ...
- sql注入之类型及提交注入
#参数类型 这里说的参数是源码中存在注入的地方. 其中参数类型有:数字.字符.搜索.json等. 其中sql语句干扰符号有:',",%,),}等,过滤首先考虑闭合这些符号,再进行注入测试. ...
