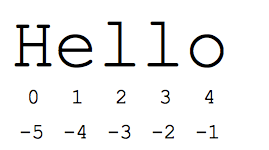Python学习笔记3-string
More on Modules and their Namespaces
Suppose you've got a module "binky.py" which contains a "def foo()". The fully qualified name of that foo function is "binky.foo". In this way, various Python modules can name their functions and variables whatever they
want, and the variable names won't conflict — module1.foo is different from module2.foo. In the Python vocabulary, we'd say that binky, module1, and module2 each have their own "namespaces," which as you can guess are variable name-to-object bindings.
For example, we have the standard "sys" module that contains some standard system facilities, like the argv list, and exit() function. With the statement "import sys" you can then access the definitions in the sys module
and make them available by their fully-qualified name, e.g. sys.exit(). (Yes, 'sys' has a namespace too!)
import sys
# Now can refer to sys.xxx facilities
sys.exit(0)There is another import form that looks like this: "from sys import argv, exit". That makes argv and exit() available by their short names; however, we recommend the original form with the fully-qualified names because it's
a lot easier to determine where a function or attribute came from.
import sys
# Now can refer to sys.xxx facilities
sys.exit(0)
Online help, help(), and dir()
dir(sys)—dir()is
likehelp()but just gives a quick list of its defined symbols, or "attributes"
The "print" operator prints out one or more python items followed by a newline (leave a trailing comma at the end of the items to inhibit the newline).
A "raw" string literal is prefixed by an 'r' and passes all the chars through without special treatment of backslashes, so r'x\nx' evaluates to
the length-4 string 'x\nx'. A 'u' prefix allows you to write a unicode string literal (Python has lots of other unicode support features -- see
the docs below).
raw = r'this\t\n and that'
print raw ## this\t\n and that
multi = """It was the best of times.
It was the worst of times."""String Methods
Here are some of the most common string methods:
- s.lower(), s.upper() -- returns the lowercase or uppercase version of the string
- s.strip() -- returns a string with whitespace removed from the start and end
- s.isalpha()/s.isdigit()/s.isspace()... -- tests if all the string chars are in the various character classes
"s.isalpha()"discriminate the string s whether contains only alphas. example:1. s='dfd24s',s.isalpha() returns false; 2. s='sdufjd',s.isalpha() returns Ture. - s.startswith('other'), s.endswith('other') -- tests if the string starts or ends with the given other string
- s.find('other') -- searches for the given other string (not a regular expression) within s, and returns the first index where it begins or -1 if not found
- s.replace('old', 'new') -- returns a string where all occurrences of 'old' have been replaced by 'new'
- s.split('delim') -- returns a list of substrings separated by the given delimiter. The delimiter is not a regular expression, it's just text. 'aaa,bbb,ccc'.split(',') -> ['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']. As a convenient special
case s.split() (with no arguments) splits on all whitespace chars. - s.join(list) -- opposite of split(), joins the elements in the given list together using the string as the delimiter. e.g. '---'.join(['aaa', 'bbb', 'ccc']) -> aaa---bbb---ccc
String Slices
- s[1:4] is 'ell' -- chars starting at index 1 and extending up to but not including index 4
- s[1:] is 'ello' -- omitting either index defaults to the start or end of the string
- s[:] is 'Hello' -- omitting both always gives us a copy of the whole thing (this is the pythonic way to copy a sequence like a string or list)
- s[1:100] is 'ello' -- an index that is too big is truncated down to the string length
String %
Python has a printf()-like facility to put together a string. The % operator takes a printf-type format string on the left (%d int, %s string, %f/%g floating point), and the matching values in a tuple on the right (a tuple is made of values separated by commas,
typically grouped inside parentheses):
# % operator
text = "%d little pigs come out or I'll %s and %s and %s" % (3, 'huff', 'puff', 'blow down')The above line is kind of long -- suppose you want to break it into separate lines. You cannot just split the line after the '%' as you might
in other languages, since by default Python treats each line as a separate statement (on the plus side, this is why we don't need to type semi-colons on each line). To fix this, enclose the whole expression in an outer set of parenthesis -- then the expression
is allowed to span multiple lines. This code-across-lines technique works with the various grouping constructs detailed below: ( ), [ ], { }.
# add parens to make the long-line work:
text = ("%d little pigs come out or I'll %s and %s and %s" %
(3, 'huff', 'puff', 'blow down'))在python中是没有&&及||这两个运算符的,取而代之的是英文and和or
reference:
https://developers.google.com/edu/python/
Python学习笔记3-string的更多相关文章
- Python学习笔记:String类型所有方法汇总
# 按字母表熟悉下string中的方法# A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z# 标红的为常用重点的方法!! str = " ...
- python学习笔记(五岁以下儿童)深深浅浅的副本复印件,文件和文件夹
python学习笔记(五岁以下儿童) 深拷贝-浅拷贝 浅拷贝就是对引用的拷贝(仅仅拷贝父对象) 深拷贝就是对对象的资源拷贝 普通的复制,仅仅是添加了一个指向同一个地址空间的"标签" ...
- Python学习笔记(十一)
Python学习笔记(十一): 生成器,迭代器回顾 模块 作业-计算器 1. 生成器,迭代器回顾 1. 列表生成式:[x for x in range(10)] 2. 生成器 (generator o ...
- Python学习笔记(十)
Python学习笔记(十): 装饰器的应用 列表生成式 生成器 迭代器 模块:time,random 1. 装饰器的应用-登陆练习 login_status = False # 定义登陆状态 def ...
- Python学习笔记,day5
Python学习笔记,day5 一.time & datetime模块 import本质为将要导入的模块,先解释一遍 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_ __author__ = 'Ale ...
- python学习笔记目录
人生苦短,我学python学习笔记目录: week1 python入门week2 python基础week3 python进阶week4 python模块week5 python高阶week6 数据结 ...
- Python学习笔记_Python对象
Python学习笔记_Python对象 Python对象 标准类型 其它内建类型 类型对象和type类型对象 Python的Null对象None 标准类型操作符 对象值的比較 对象身份比較 布尔类型 ...
- Python学习笔记之异常处理
1.概念 Python 使用异常对象来表示异常状态,并在遇到错误时引发异常.异常对象未被捕获时,程序将终止并显示一条错误信息 >>> 1/0 # Traceback (most re ...
- Python学习笔记之类与对象
这篇文章介绍有关 Python 类中一些常被大家忽略的知识点,帮助大家更全面的掌握 Python 中类的使用技巧 1.与类和对象相关的内置方法 issubclass(class, classinfo) ...
- Python学习笔记之函数
这篇文章介绍有关 Python 函数中一些常被大家忽略的知识点,帮助大家更全面的掌握 Python 中函数的使用技巧 1.函数文档 给函数添加注释,可以在 def 语句后面添加独立字符串,这样的注释被 ...
随机推荐
- PyCharm2017破解步骤
前段时间买了一套python的学习视频,附带一个Pycharm的安装包和注册码,现在注册码被JetBrains封杀了,不得已在网上找了一下破解的教程,在这里记录一下: 先找到破解补丁无需使用注册码,下 ...
- C# 选项卡控件
选项卡控件,它提供一系列操作按钮,单击不同的按钮可以在各个页面之间进行切换. 在Windows Form应用程序中,选项卡控件即“TebPage”控件,它公开“TebPage”属性,表示一个由“Tab ...
- limit小结
1. Limit接受一个或两个数字参数.参数必须是一个整数常量.如果给定两个参数,第一个参数指定第一个返回记录行的偏移量,第二个参数指定返回记录行的最大数目. 2. 初始记录行的偏移量是 0(而不是 ...
- php 获取ip地址的5种方法,插入用户登录日志实例
php 获取ip地址的5种方法,插入用户登录日志实例,推荐使用第二种方法 <?php //方法1: $ip = $_SERVER["REMOTE_ADDR"]; echo $ ...
- Lucene 个人领悟 (一)
在上学的时候就对搜索有着极大地兴趣,图书馆也借了好多的书看过,也用过Python写过爬虫. 有好多人在初步学习Lucene的时候都以为他是一个搜索引擎,或者搜索工具. 在此我要特别强调一下,Lucen ...
- myeclipse项目导入IDEA
1.import project from external model (不需要删除myeclipse多余文件) https://blog.csdn.net/d276031034/artic ...
- MySQL SELECT练习题*28
-- (1)用子查询查询员工“张小娟”所做的订单信息. SELECT * FROM order_master WHERE saler_no = ( SELECT employee_no FROM em ...
- redis-3.2.7安装脚本
redis-3.2.7 安装脚本 for CentOS 6.5 #!/bin/bash #Filename: inst_for_redis.sh #Version: 1.1 #Lastdate: 20 ...
- php stomp.dll 下载地址
http://pecl.php.net/package/stomp/1.0.9/windows 查看方法,打开phpinfo
- Golang对文件读写操作
package main import ( "bufio" "fmt" "io" "os" ) //写 func Wri ...