Codeforces 711D Directed Roads - 组合数学
ZS the Coder and Chris the Baboon has explored Udayland for quite some time. They realize that it consists of n towns numbered from1 to n.
There are n directed roads in the Udayland. i-th of them goes from town i to some other town ai (ai ≠ i). ZS the Coder can flip the direction of any road in Udayland, i.e. if it goes from town A to town B before the flip, it will go from town B to town A after.
ZS the Coder considers the roads in the Udayland confusing, if there is a sequence of distinct towns A1, A2, ..., Ak (k > 1) such that for every 1 ≤ i < k there is a road from town Ai to town Ai + 1 and another road from town Ak to town A1. In other words, the roads are confusing if some of them form a directed cycle of some towns.
Now ZS the Coder wonders how many sets of roads (there are 2n variants) in initial configuration can he choose to flip such that after flipping each road in the set exactly once, the resulting network will not be confusing.
Note that it is allowed that after the flipping there are more than one directed road from some town and possibly some towns with no roads leading out of it, or multiple roads between any pair of cities.
The first line of the input contains single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of towns in Udayland.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ n, ai ≠ i), ai denotes a road going from town i to town ai.
Print a single integer — the number of ways to flip some set of the roads so that the resulting whole set of all roads is not confusing. Since this number may be too large, print the answer modulo 109 + 7.
3
2 3 1
6
4
2 1 1 1
8
5
2 4 2 5 3
28
Consider the first sample case. There are 3 towns and 3 roads. The towns are numbered from 1 to 3 and the roads are 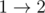 ,
,  ,
,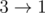 initially. Number the roads 1 to 3 in this order.
initially. Number the roads 1 to 3 in this order.
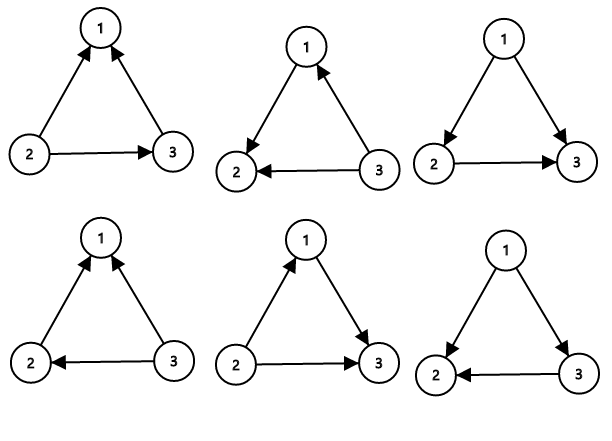
The sets of roads that ZS the Coder can flip (to make them not confusing) are {1}, {2}, {3}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 3}. Note that the empty set is invalid because if no roads are flipped, then towns 1, 2, 3 is form a directed cycle, so it is confusing. Similarly, flipping all roads is confusing too. Thus, there are a total of 6 possible sets ZS the Coder can flip.
The sample image shows all possible ways of orienting the roads from the first sample such that the network is not confusing.
题目大意
给定一个有向图,每个点的出度为1。有一种操作可以将一条边的方向翻转,问有多少种不同的操作方案使得操作后图中不存在点数大于1的强连通分量。
因为图很特殊,所以有比较特殊的计算方法。
容易发现,对于已经存在的强连通分量,只有全部翻转中间的边和什么都不做的量两种方案不可行,其他都可行。
对于不在强连通分量内的边,可翻转也可以不翻转。
然后用dfs找环,用乘法原理乘一乘就好。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#711D
* Accepted
* Time: 62ms
* Memory: 4376k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int M = 1e9 + ; int n;
int cnt = ;
int ric = ;
int *suf;
int *vid;
int *bel; int qpow(int a, int pos) {
int rt = , pa = a;
for (; pos; pos >>= , pa = pa * 1ll * pa % M)
if (pos & )
rt = rt * 1ll * pa % M;
return rt;
} inline void init() {
scanf("%d", &n);
suf = new int[(n + )];
vid = new int[(n + )];
bel = new int[(n + )];
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", suf + i);
memset(vid, , sizeof(int) * (n + ));
memset(bel, , sizeof(int) * (n + ));
} int dfs(int node, int id) {
vid[node] = ++cnt;
bel[node] = id;
int e = suf[node];
if (vid[e])
return (bel[e] == id) ? (vid[node] - vid[e] + ) : ();
return dfs(e, id);
} int ans = ;
inline void solve() {
for (int i = , s; i <= n; i++)
if (!vid[i]) {
s = dfs(i, i);
if(s)
ans = (ans * 1ll * ((qpow(, s) + M - ) % M)) % M;
ric += s;
}
ans = (ans * 1ll * qpow(, n - ric)) % M;
printf("%d\n", ans);
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces 711D Directed Roads - 组合数学的更多相关文章
- codeforces 711D Directed Roads(DFS)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/711/D 思路:由于每个点出度都为1,所以没有复杂的环中带环.DFS遍历,若为环则有2^k-2种,若为链则 ...
- 【图论】Codeforces 711D Directed Roads
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/711/D 题目大意: 给一张N个点N条有向边的图,边可以逆向.问任意逆向若干条边使得这张图无环的方案数( ...
- CodeForces 711D Directed Roads (DFS判环+计数)
题意:给定一个有向图,然后你可能改变某一些边的方向,然后就形成一种新图,让你求最多有多少种无环图. 析:假设这个图中没有环,那么有多少种呢?也就是说每一边都有两种放法,一共有2^x种,x是边数,那么如 ...
- CodeForces 711D Directed Roads
计数,模拟. 首先观察一下给出的图的特点: $1.$一定存在环. $2.$可能存在多个环. 我们对每个环计算方案数,假设环$C$上包含$x$条边,那么把环$C$破坏掉的方案数有${2^x} - 2$种 ...
- CodeForces 711D Directed Roads (DFS找环+组合数)
<题目链接> 题目大意: 给定一个$n$条边,$n$个点的图,每个点只有一条出边(初始状态),现在能够任意对图上的边进行翻转,问你能够使得该有向图不出先环的方案数有多少种. 解题分析: 很 ...
- Code Forces 711D Directed Roads
D. Directed Roads time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- codeforces 711D D. Directed Roads(dfs)
题目链接: D. Directed Roads time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input stan ...
- 【34.40%】【codeforces 711D】Directed Roads
time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes inputstandard input outputstandard o ...
- Directed Roads CodeForces - 711D (基环外向树 )
ZS the Coder and Chris the Baboon has explored Udayland for quite some time. They realize that it co ...
随机推荐
- svn中给个地址,然后把自己建立的项目拖进去
1.首先checkout 那个地址就会得到一个空的文件夹(里面有.svn文件) 2.把你的项目copy一下,粘贴到你chekout的文件夹里面,所有文件都是?,然后选中全部,点击add,然后在comm ...
- 前端获取的数据是undefined
var id = $("id1").val(); var username = $("username1").val(); var password = $(& ...
- C Alyona and Spreadsheet Codeforces Round #401(Div. 2)(思维)
Alyona and Spreadsheet 这就是一道思维的题,谈不上算法什么的,但我当时就是不会,直到别人告诉了我,我才懂了的.唉 为什么总是这么弱呢? [题目链接]Alyona and Spre ...
- lnmp----------lnmp集成环境使用lnmp安装包安装lnmp集成环境的步骤
1.先看下screen -S lnmp 命令是否存在,不存在则安装.这个是个什么东东呢?百度一下( GNU Screen是一款由GNU计划开发的用于命令行终端切换的自由软件.用户可以通过该软件同时连接 ...
- 关于hibernate总是报错 配置factory的id找不到,mapping配置文件Could not parse mapping document from input stream
Caused by: org.hibernate.InvalidMappingException: Could not parse mapping document from input stream ...
- CNN超参数优化和可视化技巧详解
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27905191 在深度学习中,有许多不同的深度网络结构,包括卷积神经网络(CNN或convnet).长短期记忆网络(LSTM)和生成对抗网络 ...
- 如何重置Sitecore CMS中的管理员密码
在Sitecore项目上工作时,有时管理员凭据会丢失或损坏.在这些情况下,重新获得快速访问权限以便不中断开发非常重要. 对Core数据库运行以下查询,您将能够admin/b再次使用以下命令登录Site ...
- Sql日期时间格式转换[zhuan]
sql server2000中使用convert来取得datetime数据类型样式(全) 日期数据格式的处理,两个示例: CONVERT(varchar(16), 时间一, 20) 结果:2007-0 ...
- window下nodejs用nodemon启动koa2项目(用cmd启动不了,要用Git Bash Here 启动才可以)
window下nodejs用nodemon启动koa2项目(用cmd启动不了,要用Git Bash Here 启动才可以)nodemon --watch 'app/**/*' -e ts --exec ...
- C++中set用法详解
1.关于set C++ STL 之所以得到广泛的赞誉,也被很多人使用,不只是提供了像vector, string, list等方便的容器,更重要的是STL封装了许多复杂的数据结构算法和大量常用数据结构 ...
