Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2)
Where do odds begin, and where do they end? Where does hope emerge, and will they ever break?
Given an integer sequence a1, a2, ..., an of length n. Decide whether it is possible to divide it into an odd number of non-empty subsegments, the each of which has an odd length and begins and ends with odd numbers.
A subsegment is a contiguous slice of the whole sequence. For example, {3, 4, 5} and {1} are subsegments of sequence {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, while {1, 2, 4} and {7} are not.
The first line of input contains a non-negative integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the length of the sequence.
The second line contains n space-separated non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100) — the elements of the sequence.
Output "Yes" if it's possible to fulfill the requirements, and "No" otherwise.
You can output each letter in any case (upper or lower).
3
1 3 5
Yes
5
1 0 1 5 1
Yes
3
4 3 1
No
4
3 9 9 3
No
In the first example, divide the sequence into 1 subsegment: {1, 3, 5} and the requirements will be met.
In the second example, divide the sequence into 3 subsegments: {1, 0, 1}, {5}, {1}.
In the third example, one of the subsegments must start with 4 which is an even number, thus the requirements cannot be met.
In the fourth example, the sequence can be divided into 2 subsegments: {3, 9, 9}, {3}, but this is not a valid solution because 2 is an even number.
题意:给定一数组,判断是否可以分成奇数个组,每组个数是奇数,每组的首尾都为奇数。
分析:偶数长度不可能,奇数长度无论怎么分,首尾必须都为奇数,否则不可能,思维题!
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = ; int a[maxn]; int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]); if(n%==) {
if(a[]%==||a[n-]%==)
puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
else {
puts("No");
} return ;
}
Connect the countless points with lines, till we reach the faraway yonder.
There are n points on a coordinate plane, the i-th of which being (i, yi).
Determine whether it's possible to draw two parallel and non-overlapping lines, such that every point in the set lies on exactly one of them, and each of them passes through at least one point in the set.
The first line of input contains a positive integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 1 000) — the number of points.
The second line contains n space-separated integers y1, y2, ..., yn ( - 109 ≤ yi ≤ 109) — the vertical coordinates of each point.
Output "Yes" (without quotes) if it's possible to fulfill the requirements, and "No" otherwise.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
5
7 5 8 6 9
Yes
5
-1 -2 0 0 -5
No
5
5 4 3 2 1
No
5
1000000000 0 0 0 0
Yes
In the first example, there are five points: (1, 7), (2, 5), (3, 8), (4, 6) and (5, 9). It's possible to draw a line that passes through points 1, 3, 5, and another one that passes through points 2, 4 and is parallel to the first one.
In the second example, while it's possible to draw two lines that cover all points, they cannot be made parallel.
In the third example, it's impossible to satisfy both requirements at the same time.
题意:
给定 n 个点的坐标,判断是否所有的点,都在两条不重合的平行线上。
分析:
计算几何很少接触,但是一般CF的计算几何都是考思维,感觉很复杂,情况很多!
看了大牛的思路,确实厉害。
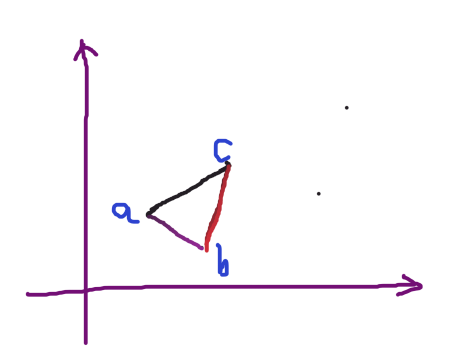
因为只存在两条平行直线,枚举这平行直线,平行直线可以通过ab,bc,ac,另一个点就在另一条平行的直线上。
这样将所有点分为了两个部分,其中另一个部分,要么只有一个点,要么在一条直线上,并且平行。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = ; typedef long long ll;
int n; struct Node {
ll x,y;
} nodes[maxn],pp[maxn]; ll cc(Node a,Node b,Node c) {
return (b.y-a.y)*(c.x-b.x) - (c.y-b.y)*(b.x-a.x);
} bool check() {
int cnt=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
if(cc(nodes[],nodes[],nodes[i])!=)
pp[++cnt]=nodes[i]; for(int i=; i<=cnt; i++)
if(cc(pp[],pp[],pp[i])!=)
return ;
Node ta,tb,tc;
ta.x=nodes[].x-nodes[].x,ta.y=nodes[].y-nodes[].y;
tb.x=pp[].x-pp[].x,tb.y=pp[].y-pp[].y;
tc.x=tc.y=;
return cnt<||cc(tc,ta,tb)==;
} int main() {
scanf("%d",&n); for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%I64d",&nodes[i].y);
nodes[i].x = i;
} int ff = ;
for(int i=; i<=n&&!ff; i++)
if(cc(nodes[i-],nodes[i-],nodes[i])!=)
ff=;
if(!ff) {
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
if(check()) {
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
swap(nodes[],nodes[]);
if(check()) {
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
swap(nodes[],nodes[]);
if(check()) {
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
printf("NO\n");
return ; return ;
}
From beginning till end, this message has been waiting to be conveyed.
For a given unordered multiset of n lowercase English letters ("multi" means that a letter may appear more than once), we treat all letters as strings of length 1, and repeat the following operation n - 1 times:
- Remove any two elements s and t from the set, and add their concatenation s + t to the set.
The cost of such operation is defined to be 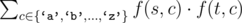 , where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character cappears in string s.
, where f(s, c) denotes the number of times character cappears in string s.
Given a non-negative integer k, construct any valid non-empty set of no more than 100 000 letters, such that the minimum accumulative cost of the whole process is exactly k. It can be shown that a solution always exists.
The first and only line of input contains a non-negative integer k (0 ≤ k ≤ 100 000) — the required minimum cost.
Output a non-empty string of no more than 100 000 lowercase English letters — any multiset satisfying the requirements, concatenated to be a string.
Note that the printed string doesn't need to be the final concatenated string. It only needs to represent an unordered multiset of letters.
12
abababab
3
codeforces
For the multiset {'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'b'}, one of the ways to complete the process is as follows:
- {"ab", "a", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"aba", "b", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "a", "b", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "ab", "a", "b"}, with a cost of 0;
- {"abab", "aba", "b"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abab", "abab"}, with a cost of 1;
- {"abababab"}, with a cost of 8.
The total cost is 12, and it can be proved to be the minimum cost of the process.
题意:给定一个整数 k ,求构造一个字符串,字符串由单个多重集合的字母拼起来,每次连接两个字符串,都有代价,总代价题目中有。
分析:
策略是:全部都与单字符拼起来。接近答案时,换一个字符重头来。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main()
{ int n;
scanf("%d",&n); string s = "";
if(n==) {
cout<<"a"<<endl;
}
else {
char c = 'a';
while(n) {
int sum = ;
int i = ;
for(i = ; sum <=n; i++) {
sum +=i;
} n -=(sum-i+);
for(int j = ; j<i-;j++) {
s +=c;
}
c++; }
cout<<s<<endl;
} return ;
}
总的来说,感觉思维上和大佬们还是有很大的差距,要继续努力才行~~~
Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 1)
A. From Y to Y time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2) C. From Y to Y
题目: C. From Y to Y time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2) C
From beginning till end, this message has been waiting to be conveyed. For a given unordered multise ...
- 【Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 1) D.Shake It!】
·最小割和组合数放在了一起,产生了这道题目. 英文题,述大意: 一张初始化为仅有一个起点0,一个终点1和一条边的图.输入n,m表示n次操作(1<=n,m<=50),每次操作是任选一 ...
- 【Codeforces Round 431 (Div. 2) A B C D E五个题】
先给出比赛地址啦,感觉这场比赛思维考察非常灵活而美妙. A. Odds and Ends ·述大意: 输入n(n<=100)表示长度为n的序列,接下来输入这个序列.询问是否可以将序列划 ...
- Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2) B. Tell Your World
B. Tell Your World time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- 【推导】【分类讨论】Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 1) B. Rooter's Song
给你一个这样的图,那些点是舞者,他们每个人会在原地待ti时间之后,以每秒1m的速度向前移动,到边界以后停止.只不过有时候会碰撞,碰撞之后的转向是这样哒: 让你输出每个人的停止位置坐标. ①将x轴上初始 ...
- 【推导】【贪心】Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 1) A. From Y to Y
题意:让你构造一个只包含小写字母的可重集,每次可以取两个元素,将它们合并,合并的代价是这两个元素各自的从‘a’到‘z’出现的次数之积的和. 给你K,你构造的可重集必须满足将所有元素合而为一以后,所消耗 ...
- Codeforces Round #431 (Div. 2) B
Connect the countless points with lines, till we reach the faraway yonder. There are n points on a c ...
随机推荐
- Nginx + Lua搭建文件上传下载服务
收录待用,修改转载已取得腾讯云授权 最新腾讯云技术公开课直播,提问腾讯W3C代表,如何从小白成为技术专家?点击了解活动详情 作者 | 庄进发 编辑 | 迷鹿 庄进发,信息安全部后台开发工程师,主要负责 ...
- Vue PDF文件预览vue-pdf
最近做项目,遇到预览PDF这个功能,在网上找了找,大多推荐的是pdf.js,不过在Vue中还是想偷懒直接npm组件,最后找到了一个还不错的Vue-pdf 组件,GitHub地址:https:// ...
- mysql explain工具使用
explain工具可以确认执行计划是否良好,查询是否走了合理的索引.查询的执行计划,随着数据的变化也可能会有变化.调用方式:explain + [sql语句]. 另外,explain是有局限性的:1. ...
- 将libFM模型变换成tensorflow可serving的形式
fm_model是libFM生成的模型 model.ckpt是可以tensorflow serving的模型结构 亲测输出正确. 代码: import tensorflow as tf # libFM ...
- NFS 优化及详解
一, 启动过程: 所以启动的时候一定一定要先启用——————rpcbind———————————————— 启动 rpcbind ------>/etc/init.d/rpcbind rest ...
- Android 中判断网络状态
首先在AndroidManifest.xml添加权限 <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_ ...
- underscore javascript工具库支持seajs模块化
underscore是一个很有用的js工具库,但是好像默认不支持seajs模块化 新建一个文件例如叫做xx.js 谈后,键入 define(function(require,exports,modul ...
- ASP.NET MVC 生命周期
本文的目的旨在详细描述ASP.NET MVC请求从开始到结束的每一个过程.我希望能理解在浏览器输入URL并敲击回车来请求一个ASP.NET MVC网站的页面之后发生的任何事情. 为什么需要关心这些?有 ...
- Java Mail邮件发送的简单实现
1.什么是java mail JAVA MAIL是利用现有的邮件账户发送邮件的工具,通过JAVA Mail的操控,让程序自动的使用设置的邮箱发送邮件. 这一机制被广泛的用在注册激活和垃圾邮件的发送等方 ...
- git打补丁、还原补丁
打补丁.还原补丁 1.两个commit间的修改(包含两个commit,<r1>.<r2>表示两个提交的版本号,<r1>是最近提交) git format-patch ...
