C++ spdlog日志管理
【1】spdlog简介
spdlog是一个开源的、快速的、仅有头文件的基于C++11实现的一款C++专用日志管理库。
【2】源码下载
下载地址:https://github.com/gabime/spdlog
【3】工程配置
(1)解压缩源码包
解压后,找到include文件夹。类比本地:
注意:include文件夹里是所需的头文件及源码。
(2)工程配置
2.1 新建一个C++控制台应用程序空项目spdlog
2.2 在项目属性页:VC++目录->包含目录 中添加上述include路径,如下图:
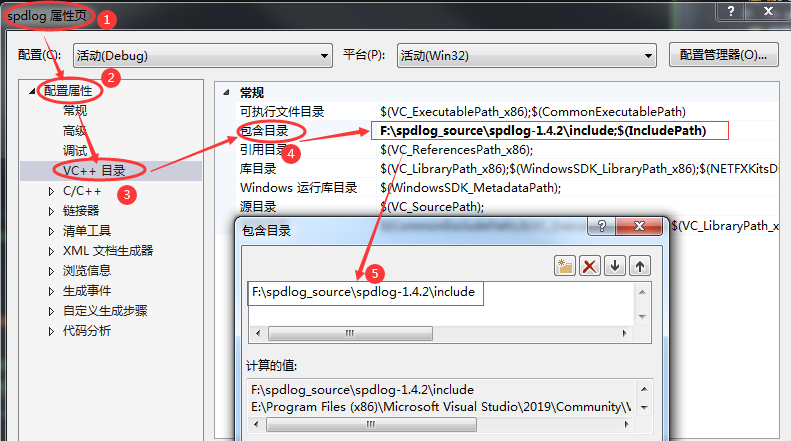
2.3 在项目中添加头文件即可,如下:
#include "spdlog/spdlog.h"
using namespace spdlog;
OK 请尽情享用。是的,没错,就是这么简单,你不用怀疑你自己。。。。
【4】应用示例
为了更权威、更有说服力,遂决定把源码包中的example示例贴出来(加了若干自己理解的信息)
应用示例如下:
//
// Copyright(c) 2015 Gabi Melman.
// Distributed under the MIT License (http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT) // spdlog usage example #include <cstdio> // 标准输出类型
void stdout_logger_example();
// 基本类型:日志文件会一直被写入,不断变大。
void basic_example();
// 滚动类型:日志文件会先写入一个文件,当超出规定大小时,会备份(或删除)当前日志内容,重建文件开始写入。
/* 说明:从函数声明可以看出,参数max_file_size规定了文件数量的最大值,当文件数量超过此值就会把最早的先清空。
参数max_file_size规定了滚动文件的个数。当logger_name存满时,将其名称更改为logger_name.1,再新建一个logger_name文件来存储新的日志。
再次存满时,把logger_name.1改名为logger_name.2,logger_name改名为logger_name.1,再新建一个logger_name来存放新的日志。
以此类推,max_files 数量为几,就可以有几个logger_name文件用来滚动。
*/
void rotating_example();
// 每日类型:每天新建一个日志,新建日志文件时间可以自定义。
void daily_example();
// 异步模式类型
void async_example();
// 二进制类型
void binary_example();
// 追踪类型
void trace_example();
// 多汇入类型
/* 带多接收器的记录器 - 每个接收器都有不同的格式和日志级别
譬如,创建具有 2 个不同日志级别和格式的目标的记录器。
控制台将仅显示警告或错误,而文件将记录所有。
*/
void multi_sink_example();
// 自定义类型
void user_defined_example();
// 错误处理类型
/*
自定义错误处理程序。将在日志失败时触发。
可以全局设置或针对性设置
*/
void err_handler_example();
// 系统类型 (linux/osx/freebsd)
void syslog_example(); // 重点备注:
// 日志实时写入接口:logger->flush();
/*
上述各种日志文件,仅在程序退出时才保存日志。
如果要想在程序运行时也能够实时保存日志,可以在程序中添加如上语句。
具体参见譬如166行的应用示例
*/ #include "spdlog/spdlog.h" int main(int, char* [])
{
spdlog::info("Welcome to spdlog version {}.{}.{} !", SPDLOG_VER_MAJOR, SPDLOG_VER_MINOR, SPDLOG_VER_PATCH);
spdlog::warn("Easy padding in numbers like {:08d}", );
spdlog::critical("Support for int: {0:d}; hex: {0:x}; oct: {0:o}; bin: {0:b}", );
spdlog::info("Support for floats {:03.2f}", 1.23456);
spdlog::info("Positional args are {1} {0}..", "too", "supported");
spdlog::info("{:>8} aligned, {:<8} aligned", "right", "left"); // Runtime log levels
// 支持设置日志级别:低于设置级别的日志将不会被输出。各level排序详见源码,数值越大级别越高:
/*
enum level_enum
{
trace = SPDLOG_LEVEL_TRACE,
debug = SPDLOG_LEVEL_DEBUG,
info = SPDLOG_LEVEL_INFO,
warn = SPDLOG_LEVEL_WARN,
err = SPDLOG_LEVEL_ERROR,
critical = SPDLOG_LEVEL_CRITICAL,
off = SPDLOG_LEVEL_OFF,
};
*/
spdlog::set_level(spdlog::level::info); // Set global log level to info
spdlog::debug("This message should not be displayed!");
spdlog::set_level(spdlog::level::trace); // Set specific logger's log level
spdlog::debug("This message should be displayed.."); // Customize msg format for all loggers
// 支持自定义日志格式
spdlog::set_pattern("[%H:%M:%S %z] [%^%L%$] [thread %t] %v");
spdlog::info("This an info message with custom format");
spdlog::set_pattern("%+"); // back to default format
spdlog::set_level(spdlog::level::info); // 支持回溯分析
// Backtrace support
// Loggers can store in a ring buffer all messages (including debug/trace) for later inspection.
// When needed, call dump_backtrace() to see what happened:
spdlog::enable_backtrace(); // create ring buffer with capacity of 10 messages
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
spdlog::debug("Backtrace message {}", i); // not logged.
}
// e.g. if some error happened:
spdlog::dump_backtrace(); // log them now! try
{
stdout_logger_example();
basic_example();
rotating_example();
daily_example();
async_example();
binary_example();
multi_sink_example();
user_defined_example();
err_handler_example();
trace_example(); // Flush all *registered* loggers using a worker thread every 3 seconds.
// note: registered loggers *must* be thread safe for this to work correctly!
spdlog::flush_every(std::chrono::seconds()); // Apply some function on all registered loggers
spdlog::apply_all([&](std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> l) { l->info("End of example."); }); // Release all spdlog resources, and drop all loggers in the registry.
// This is optional (only mandatory if using windows + async log).
spdlog::shutdown();
} // Exceptions will only be thrown upon failed logger or sink construction (not during logging).
catch (const spdlog::spdlog_ex & ex)
{
std::printf("Log initialization failed: %s\n", ex.what());
return ;
}
} #include "spdlog/sinks/stdout_color_sinks.h"
// or #include "spdlog/sinks/stdout_sinks.h" if no colors needed.
void stdout_logger_example()
{
// Create color multi threaded logger.
auto console = spdlog::stdout_color_mt("console");
// or for stderr:
// auto console = spdlog::stderr_color_mt("error-logger");
} #include "spdlog/sinks/basic_file_sink.h"
void basic_example()
{
// Create basic file logger (not rotated).
auto my_logger = spdlog::basic_logger_mt("file_logger", "logs/basic-log.txt");
} #include "spdlog/sinks/rotating_file_sink.h"
void rotating_example()
{
// Create a file rotating logger with 5mb size max and 3 rotated files.
auto rotating_logger = spdlog::rotating_logger_mt("some_logger_name", "logs/rotating.txt", * , );
int a = , b = ;
rotating_logger->error("error!");
rotating_logger->info("a = {}, b = {}, a/b = {}, a%b = {}", a, b, a / b, a % b);
rotating_logger->flush();
} #include "spdlog/sinks/daily_file_sink.h"
void daily_example()
{
// Create a daily logger - a new file is created every day on 2:30am.
auto daily_logger = spdlog::daily_logger_mt("daily_logger", "logs/daily.txt", , );
} #include "spdlog/async.h"
void async_example()
{
// Default thread pool settings can be modified *before* creating the async logger:
// spdlog::init_thread_pool(32768, 1); // queue with max 32k items 1 backing thread.
auto async_file = spdlog::basic_logger_mt<spdlog::async_factory>("async_file_logger", "logs/async_log.txt");
// alternatively:
// auto async_file = spdlog::create_async<spdlog::sinks::basic_file_sink_mt>("async_file_logger", "logs/async_log.txt"); for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
{
async_file->info("Async message #{}", i);
}
} // Log binary data as hex.
// Many types of std::container<char> types can be used.
// Iterator ranges are supported too.
// Format flags:
// {:X} - print in uppercase.
// {:s} - don't separate each byte with space.
// {:p} - don't print the position on each line start.
// {:n} - don't split the output to lines. #include "spdlog/fmt/bin_to_hex.h"
void binary_example()
{
std::vector<char> buf;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
buf.push_back(static_cast<char>(i & 0xff));
}
spdlog::info("Binary example: {}", spdlog::to_hex(buf));
spdlog::info("Another binary example:{:n}", spdlog::to_hex(std::begin(buf), std::begin(buf) + ));
// more examples:
// logger->info("uppercase: {:X}", spdlog::to_hex(buf));
// logger->info("uppercase, no delimiters: {:Xs}", spdlog::to_hex(buf));
// logger->info("uppercase, no delimiters, no position info: {:Xsp}", spdlog::to_hex(buf));
} // Compile time log levels.
// define SPDLOG_ACTIVE_LEVEL to required level (e.g. SPDLOG_LEVEL_TRACE)
void trace_example()
{
// trace from default logger
SPDLOG_TRACE("Some trace message.. {} ,{}", , 3.23);
// debug from default logger
SPDLOG_DEBUG("Some debug message.. {} ,{}", , 3.23); // trace from logger object
auto logger = spdlog::get("file_logger");
SPDLOG_LOGGER_TRACE(logger, "another trace message");
} // A logger with multiple sinks (stdout and file) - each with a different format and log level.
void multi_sink_example()
{
auto console_sink = std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::stdout_color_sink_mt>();
console_sink->set_level(spdlog::level::warn);
console_sink->set_pattern("[multi_sink_example] [%^%l%$] %v"); auto file_sink = std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::basic_file_sink_mt>("logs/multisink.txt", true);
file_sink->set_level(spdlog::level::trace); spdlog::logger logger("multi_sink", { console_sink, file_sink });
logger.set_level(spdlog::level::debug);
logger.warn("this should appear in both console and file");
logger.info("this message should not appear in the console, only in the file");
} // User defined types logging by implementing operator<<
#include "spdlog/fmt/ostr.h" // must be included
struct my_type
{
int i;
template<typename OStream>
friend OStream& operator<<(OStream& os, const my_type& c)
{
return os << "[my_type i=" << c.i << "]";
}
}; void user_defined_example()
{
spdlog::info("user defined type: {}", my_type{ });
} // Custom error handler. Will be triggered on log failure.
void err_handler_example()
{
// can be set globally or per logger(logger->set_error_handler(..))
spdlog::set_error_handler([](const std::string& msg) { printf("*** Custom log error handler: %s ***\n", msg.c_str()); });
} // syslog example (linux/osx/freebsd)
#ifndef _WIN32
#include "spdlog/sinks/syslog_sink.h"
void syslog_example()
{
std::string ident = "spdlog-example";
auto syslog_logger = spdlog::syslog_logger_mt("syslog", ident, LOG_PID);
syslog_logger->warn("This is warning that will end up in syslog.");
}
#endif // Android example.
#if defined(__ANDROID__)
#include "spdlog/sinks/android_sink.h"
void android_example()
{
std::string tag = "spdlog-android";
auto android_logger = spdlog::android_logger_mt("android", tag);
android_logger->critical("Use \"adb shell logcat\" to view this message.");
} #endif
good good study, day day up.
顺序 选择 循环 总结
C++ spdlog日志管理的更多相关文章
- 第13章 Linux日志管理
1. 日志管理 (1)简介 在CentOS 6.x中日志服务己经由rsyslogd取代了原先的syslogd服务.rsyslogd日志服务更加先进,功能更多.但是不论该服务的使用,还是日志文件的格式其 ...
- ABP(现代ASP.NET样板开发框架)系列之8、ABP日志管理
点这里进入ABP系列文章总目录 基于DDD的现代ASP.NET开发框架--ABP系列之8.ABP日志管理 ABP是“ASP.NET Boilerplate Project (ASP.NET样板项目)” ...
- 【Java EE 学习 76 下】【数据采集系统第八天】【通过AOP实现日志管理】【日志管理功能分析和初步实现】
一.日志管理相关分析 1.日志管理是一种典型的系统级别的应用,非常适合使用spring AOP实现. 2.使用日志管理的目的:对系统修改的动作进行记录,比如对权限.角色.用户的写操作.修改操作.删除操 ...
- ElasticSearch+NLog+Elmah实现Asp.Net分布式日志管理
本文将介绍使用NLOG.Elmah结合ElasticSearch实现分布式日志管理. 一.ElasticSearch简介 ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器.它提供了一个分布 ...
- Apache 日志管理,获取客户端端口号
日志管理分类 日志文件是用户管理和监控 Apache 安全的非常好的第一手资料,它清晰地记录了客户端访问 Apache 服务器资源的每一条记录,以及在访问中出现的错误信息,可以这样说,Apache 可 ...
- linux 学习 14 日志管理
第十四讲 日志管理 14.1 日志管理-简介 .日志服务 在CentOS .x中日志服务已经由rsyslogd取代了原先的syslogd服务.rsyslogd日志服务更加先进,功能更多.但是不论该服 ...
- SQL Server中的事务日志管理(7/9):处理日志过度增长
当一切正常时,没有必要特别留意什么是事务日志,它是如何工作的.你只要确保每个数据库都有正确的备份.当出现问题时,事务日志的理解对于采取修正操作是重要的,尤其在需要紧急恢复数据库到指定点时.这系列文章会 ...
- SQL Server中的事务日志管理(9/9):监控事务日志
当一切正常时,没有必要特别留意什么是事务日志,它是如何工作的.你只要确保每个数据库都有正确的备份.当出现问题时,事务日志的理解对于采取修正操作是重要的,尤其在需要紧急恢复数据库到指定点时.这系列文章会 ...
- 基于吉日嘎底层架构的Web端权限管理操作演示-日志管理
权限管理要实现的效果是对“ 谁”可以访问“什么内容”,可以进行“哪些操作” 一系列权限的精细化控制.衡量一个软件好坏的重要标准是:它的权限体系是否足够细致.是否可以立体勾勒出信息对象的访问控制.前面4 ...
随机推荐
- 吴裕雄 Bootstrap 前端框架开发——Bootstrap 字体图标(Glyphicons):glyphicon glyphicon-time
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- HTTP和HTTPS的区别及HTTPS加密算法
一.HTTP和HTTPS的概念 HTTP:是互联网上应用最为广泛的一种网络协议,是一个客户端和服务器端请求和应答的标准(TCP),用于从WWW服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传 ...
- Oracle SQL存储过程结构、异常处理示例
-- 存储过程结结构. -- EXCeption不是存储过程必须部分,可以用作本存储过程的异常处理,但如果没有异常处理,出了异常将会终止程序 CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_na ...
- 爬虫(十七):Scrapy框架(四) 对接selenium爬取京东商品数据
1. Scrapy对接Selenium Scrapy抓取页面的方式和requests库类似,都是直接模拟HTTP请求,而Scrapy也不能抓取JavaScript动态谊染的页面.在前面的博客中抓取Ja ...
- 033-PHP取1-100的随机数
<?php // 生成一个随机数 // 从1到100中取得随机数 for ($index = 0; $index < 100; $index++) { $number = (rand() ...
- vzray服务端配置
打开securecrt登陆服务器 输入命令:bash <(curl -s -L https://git.io/vzray.sh)1 回车tcp 回车端口 回车默认 回车
- msf中arp_sweep使用报错:usbmon1:ERROR while getting interface flags:no such device
在许多的工具使用中,会出现很多的错误,要养成先思考再去寻找帮助的习惯 在用use命令使用arp_sweep模块的时候爆出错误:usbmon1:ERROR while getting interface ...
- 吴裕雄 Bootstrap 前端框架开发——Bootstrap 字体图标(Glyphicons):glyphicon glyphicon-bold
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- hdu 3308 线段树,单点更新 求最长连续上升序列长度
LCIS Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- DRF源码-fields.py
https://www.cnblogs.com/pyspark/p/8607801.html https://www.cnblogs.com/LYliangying/articles/9896548. ...
