RANSAC随机一致性采样算法学习体会
The RANSAC algorithm is a learning technique to estimate parameters of a model by random sampling of observed data. Given a dataset whose data elements contain both inliers and outliers, RANSAC uses the voting scheme to find the optimal fitting result. Data elements in the dataset are used to vote for one or multiple models. The implementation of this voting scheme is based on two assumptions: that the noisy features will not vote consistently for any single model (few outliers) and there are enough features to agree on a good model (few missing data). The RANSAC algorithm is essentially composed of two steps that are iteratively repeated:
- In the first step, a sample subset containing minimal data items is randomly selected from the input dataset. A fitting model and the corresponding model parameters are computed using only the elements of this sample subset. The cardinality of the sample subset is the smallest sufficient to determine the model parameters.首先从输入数据中采集最小数据集,根据这个最小数据集计算相应的fitting模型参数。
- In the second step, the algorithm checks which elements of the entire dataset are consistent with the model instantiated by the estimated model parameters obtained from the first step. A data element will be considered as an outlier if it does not fit the fitting model instantiated by the set of estimated model parameters within some error threshold that defines the maximum deviation attributable to the effect of noise.接着,应用第一步中得到的模型参数,检查整个输入数据集,如果和模型不匹配则视为离群点。通过一定的容错阈值范围限制由于噪声引起的最大误差,
The set of inliers obtained for the fitting model is called consensus set.适用模型的群内点被称为一致集。
The RANSAC algorithm will iteratively repeat the above two steps until the obtained consensus set in certain iteration has enough inliers.算法将重复上面的2个步骤进行迭代,直到通过一定迭代得到的一致集包含足够多的群内点。
The input to the RANSAC algorithm is a set of observed data values, a way of fitting some kind of model to the observations, and some confidence parameters. RANSAC achieves its goal by repeating the following steps:
- Select a random subset of the original data. Call this subset the hypothetical inliers.
- A model is fitted to the set of hypothetical inliers.//计算模型参数
- All other data are then tested against the fitted model. Those points that fit the estimated model well, according to some model-specific loss function, are considered as part of the consensus set.
- The estimated model is reasonably good if sufficiently many points have been classified as part of the consensus set.
- Afterwards, the model may be improved by reestimating it using all members of the consensus set.
This procedure is repeated a fixed number of times, each time producing either a model which is rejected because too few points are part of the consensus set, or a refined model together with a corresponding consensus set size. In the latter case, we keep the refined model if its consensus set is larger than the previously saved model.
关于采样次数的推导
The values of parameters t and d have to be determined from specific requirements related to the application and the data set, possibly based on experimental evaluation. The parameter k (the number of iterations), however, can be determined from a theoretical result. Let p be the probability that the RANSAC algorithm in some iteration selects only inliers from the input data set when it chooses the n points from which the model parameters are estimated. When this happens, the resulting model is likely to be useful so p gives the probability that the algorithm produces a useful result. Let w be the probability of choosing an inlier each time a single point is selected, that is,
- w = number of inliers in data / number of points in data
A common case is that w is not well known beforehand, but some rough value can be given. Assuming that the n points needed for estimating a model are selected independently, 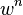 is the probability that all n points are inliers and
is the probability that all n points are inliers and 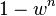 is the probability that at least one of the n points is an outlier, a case which implies that a bad model will be estimated from this point set. That probability to the power of k is the probability that the algorithm never selects a set of n points which all are inliers and this must be the same as
is the probability that at least one of the n points is an outlier, a case which implies that a bad model will be estimated from this point set. That probability to the power of k is the probability that the algorithm never selects a set of n points which all are inliers and this must be the same as 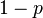 . Consequently,
. Consequently,
which, after taking the logarithm of both sides, leads to
This result assumes that the n data points are selected independently, that is, a point which has been selected once is replaced and can be selected again in the same iteration. This is often not a reasonable approach and the derived value for k should be taken as an upper limit in the case that the points are selected without replacement. For example, in the case of finding a line which fits the data set illustrated in the above figure, the RANSAC algorithm typically chooses two points in each iteration and computes maybe_model as the line between the points and it is then critical that the two points are distinct.
To gain additional confidence, the standard deviation or multiples thereof can be added to k. The standard deviation of k is defined as
RANSAC随机一致性采样算法学习体会的更多相关文章
- 过采样算法之SMOTE
SMOTE(Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique),合成少数类过采样技术.它是基于随机过采样算法的一种改进方案,由于随机过采样采取简单复制样本的策略来增加 ...
- 一致性Hash算法(KetamaHash)的c#实现
Consistent Hashing最大限度地抑制了hash键的重新分布.另外要取得比较好的负载均衡的效果,往往在服务器数量比较少的时候需要增加虚拟节点来保证服务器能均匀的分布在圆环上.因为使用一般的 ...
- DSP算法学习-过采样技术
DSP算法学习-过采样技术 彭会锋 2015-04-27 23:23:47 参考论文: 1 http://wr.lib.tsinghua.edu.cn/sites/default/files/1207 ...
- Javascript经典算法学习1:产生随机数组的辅助类
辅助类 在几个经典排序算法学习部分,为方便统一测试不同算法,新建了一个辅助类,主要功能为:产生指定长度的随机数组,提供打印输出数组,交换两个元素等功能,代码如下: function ArraySort ...
- 分布式缓存技术memcached学习(四)—— 一致性hash算法原理
分布式一致性hash算法简介 当你看到“分布式一致性hash算法”这个词时,第一时间可能会问,什么是分布式,什么是一致性,hash又是什么.在分析分布式一致性hash算法原理之前,我们先来了解一下这几 ...
- 一致性哈希算法学习及JAVA代码实现分析
1,对于待存储的海量数据,如何将它们分配到各个机器中去?---数据分片与路由 当数据量很大时,通过改善单机硬件资源的纵向扩充方式来存储数据变得越来越不适用,而通过增加机器数目来获得水平横向扩展的方式则 ...
- 分布式缓存技术memcached学习系列(四)—— 一致性hash算法原理
分布式一致性hash算法简介 当你看到"分布式一致性hash算法"这个词时,第一时间可能会问,什么是分布式,什么是一致性,hash又是什么.在分析分布式一致性hash算法原理之前, ...
- 机器学习 —— 类不平衡问题与SMOTE过采样算法
在前段时间做本科毕业设计的时候,遇到了各个类别的样本量分布不均的问题——某些类别的样本数量极多,而有些类别的样本数量极少,也就是所谓的类不平衡(class-imbalance)问题. 本篇简述了以下内 ...
- MCMC等采样算法
一.直接采样 直接采样的思想是,通过对均匀分布采样,实现对任意分布的采样.因为均匀分布采样好猜,我们想要的分布采样不好采,那就采取一定的策略通过简单采取求复杂采样. 假设y服从某项分布p(y),其累积 ...
随机推荐
- explicit关键字
C++中,explicit关键字用来修饰类只有一个参数的构造函数,被修饰的构造函数的类,不能发生相应的隐式类型转换,只能以显示的方式进行类型转换. explicit使用注意事项: explicit 关 ...
- php数组操作,删除第一个和最后一个元素
对于一个php数组,该如何删除该数组的第一个元素或者最后一个元素呢?其实这两个过程都可以通过php自带的函数 array_pop 和 array_shift 来完成,下面就具体介绍一下如何来操作. ( ...
- CSS与JavaScript文件的位置
1.CSS 尽量放置在head标签中. 原因: 避免浏览器重新渲染: 避免阻塞JS文件的执行. 注:CSS选择器的解释顺序是 从右向左 的,所以尽量减少选择器的层级. 2.JS 尽量放置在</b ...
- Apache Spark源码走读之10 -- 在YARN上运行SparkPi
y欢迎转载,转载请注明出处,徽沪一郎. 概要 “spark已经比较头痛了,还要将其运行在yarn上,yarn是什么,我一点概念都没有哎,再怎么办啊.不要跟我讲什么原理了,能不能直接告诉我怎么将spar ...
- Nginx 笔记与总结(3)配置虚拟主机
Nginx 重启的另外一种方式,相当于 kill -HUP `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid`: /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s ...
- Linux文件管理命令
cd /home 进入 '/ home' 目录' cd .. 返回上一级目录 cd ../.. 返回上两级目录 cd 进入个人的主目录 cd ~user1 进入个人的主目录 cd - 返回上次所在的目 ...
- ESXi云管理平台
实验室有多台使用ESXi实现虚拟化的服务器,平时管理不便,便通实验室其他同学一起编写了一个基于ESXi的云平台管理系统. 对物理服务器进行管理,实现增加.删除.修改.性能监控. 对虚拟机进行管理,实现 ...
- css伪元素before/after和画三角形的搭配应用
想要实现的效果如下: 第一步:如何用css画出三角形? /* css画三角形 */ .sanjiao{ ; border-top:40px solid red; border-bottom:40px ...
- ext在web工程目录导致myeclipse内存溢出问题
分类: Extjs2013-01-24 00:01 2068人阅读 评论(2) 收藏 举报 当在eclipse中的web工程中增加了extjs4,出现An internal error occurre ...
- JsonCpp 简单使用
[转]自: http://www.cnblogs.com/ytjjyy/archive/2012/04/17/2453348.html JsonCpp 是一个C++用来处理JSON 数据的开发包.下面 ...



