Node笔记(1)
Node.js 是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。
进程
1.process.argv 用于获取当前进程信息0--node.exe的目录
1--js文件的目录
2--第一个参数 process.argv.slice(2) 获取从第一个参数开始的参数
2.process.env 获取当前系统的环境变量 3.process.stdout.write('xxx') console.log('xxx') = process.stdout.write('xxx\n');
4.process.stdin.on('data',function(data){
process.stdout.write(data);
})
//回车时触发
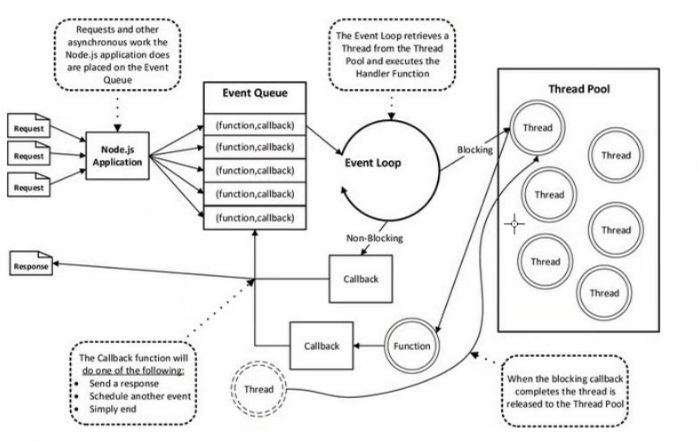
传统的java,.net遇到阻塞io时会创建新的线程来处理。 node内部实现其实也是多线程的,(通过线程池)
//
多线程都是‘假’的,对于一个cpu核心。创建线程需要时间,线程数量有限,cpu在不同线程间切换需要转换上下文,耗费时间
多线程的意义并不大(多核心cpu则可能会提升效率) node的主线程————事件队列与事件循环圈。
模块
exports的实现:
module是定义在.js文件中的对象
xxx.js
console.log(module)
....(打印出module对象)
module中有一个exports对象,可以向内添加属性和方法
(参考 https://www.cnblogs.com/wbxjiayou/p/5767632.html)
写一个require的实现:
function $require(id){
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const filename = path.join(__dirname,id);
$require.cache = $require.cache || {};
if($require.cache[filename]){
return $require.cache[filename].exports;
}
const dirname = path.dirname(filename);
let code = fs.readFileSync(filename,'utf8');
let module = { id:filename,exports:{} };
let exports = module.exports;
code=`
(function($require,module,exports,__dirname,__filename){
${code}
})($require,module,exports,dirname,filename)
;`;
eval(code);
$require.cache[filename] = module;
return module.exports;
}
var m4 = $require('../xx.js');
m4.say();
...
清空require中的缓存机制:
Object.keys(require.cache).forEach((key)=>{delete require.cache[key]});
内置模块:
path:处理文件路径。
fs:操作(CRUD)文件系统。
child_process:新建子线程。
util:提供一系列实用小工具。
http:提供http服务器功能。
url:用于解析URL。
querystring:解析URL中的查询字符串。
crypto:提供加密和解密功能。
..
包(Node package manager):
Buffer
:读取文件时没有指定编码默认读取的是一个Buffer(缓冲区)
缓冲区:内存中操作数据的容器。
为什么要有缓冲区?
早期JS擅长处理字符串,及HTML文档,不会接触到二进制的数据。
而在Node中操作数据,网络通信是完全没法以字符串的方式操作的,所以在Node中引入了一个二进制缓冲区的实现,Buffer
//readfile的方式确实是使用buffer,但是也是一次性读取
Stream:
读一点数据,处理一点点数据(读到有限长的buffer中,然后再读取出来,)
写一个歌词滚动效果的实现:
假定有一个xxx.lrc文件
方法1.用buffer的方式读入fs.readFile(pathxx,callback)
在回调函数中对buffer进行tostring转换,然后split掉'\n',对于数组中的每一行,用正则提取时间,然后settimeout按时间显示出来
(由于对每一行处理需要耗费几毫秒的时间,可以设置begin=new Date().getTime() 然后在后面的settimeout中设置新的new Date.getTime()-begin 减掉这个时间)
方法2.用stream的方式读入 var streamReader = fs.createReadStream(filename);
var data = '';
streamReader.on('data',function(chunk){ data+=chunk.tostring(); });
streamReader.on('end',function(){console.log(data); };
在这里对data进行处理
方法3.使用readline模块,用stream的方式读入 var streamReader = fs.createReadStream(filename);
var rl = readline.createInterface({ input:streamReader });
var begin = new Date().getTime();
rl.on('line',(line)=>{....对line进行处理})
写文件
默认写入是覆盖 ,可以使用append追加
方法1.fs.writeFile(path,callback);
方法2.var streamwriter = fs.createWriteStream(path);
streamwriter.write('xxx',callback) (以流的方式写入,防止在内存中读取过多)
其他文件api
检查文件、删除、重命名..
写一个目录树显示的实现:
思路:通过使用fs.readdirSync
网络框架
Express框架的核心是对http模块的再包装
var http = require("http");
var app = http.createServer(function(request, response) {
response.writeHead(200, {"Content-Type": "text/plain"});
response.end("Hello world!");
});
app.listen(3000, "localhost");
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello world!');
});
app.listen(3000);
中间件(middleware)是处理HTTP请求的函数。
app.use("/home", function(request, response, next) {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
response.end("Welcome to the homepage!\n");
});
app.use("/about", function(request, response, next) {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
response.end("Welcome to the about page!\n");
});
app.use(function(request, response) {
response.writeHead(404, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
response.end("404 error!\n");
});
http.createServer(app).listen(1337);
还可以这样写(*是指所有的请求都要先通过这个中间件)app.all("*", function(request, response, next) {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "text/plain" });
next();
});
app.get("/", function(request, response) {
response.end("Welcome to the homepage!");
});
app.get("/about", function(request, response) {
response.end("Welcome to the about page!");
});
app.get("*", function(request, response) {
response.end("404!");
});
Node笔记(1)的更多相关文章
- node笔记——gulp修改静态文件的名字
cmd小技巧: 1.换到下级或同等级目录 D: 2.换到上级目录 cd.. node 包管理器小技巧[以gulp为例] npm install --save-dev gulp gulp-concat ...
- Node笔记五-进程、线程
进程 -每一个正在运行的应用程序都称之为进程 -每一个应用程序都至少有一个进程 -进程是用来给应用程序提供一个运行的环境 -进程是操作系统为应用程序分配资源的一个单位线程 -用来执行应用程序中的代码 ...
- Node笔记四
异步操作 -Node采用chrome v8 引擎处理javascript脚本 --v8最大特点就是单线程运行,一次只能运行一个任务 -Node大量采用异步操作 --任务不是马上执行,而是插在任务队列的 ...
- Node笔记三
global --类似与客户端javascript运行环境中的window process --用于获取当前node进程信息,一般用于获取环境变量之类的信息 console --node中内置的con ...
- Node笔记二
### 安装包的方式安装 - 安装包下载链接: + Mac OSX: [darwin](http://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node/v5.7.0/node-v5.7.0.pk ...
- Node笔记一
什么是javascript? --脚本语言 --运行在浏览器中 --一般用来做客户端页面的交互 javascript运行环境 --运行在浏览器内核中的JS引擎 浏览器这种javascript可以做什么 ...
- node笔记
基础入门可参考: <一起学 Node.js>—— https://github.com/nswbmw/N-blog 核心模块使用前需要引入 let fs=require('fs'); ...
- node笔记汇总
项目依赖分两种,一个就是普通的项目依赖比如bootstrap,还用一种只是开发阶段需要用的,这种属于开发依赖比如gulp,开发依赖最终记录在devDependencies节点里面 - ...
- Node笔记 - process.cwd() 和 __dirname 的区别
process.cwd() 返回工作目录 __dirname 返回脚本所在的目录位置 单看概念觉得都差不多,有种似懂非懂的感觉,那么接下用一个简单易懂的例子来理解下这两者的区别,在此之前先看一个方法 ...
随机推荐
- orcale单行函数之字符函数
- 0209利用innobackupex进行简单数据库的备份
利用innobackupex进行简单数据库的备份yum install perl-DBIyum install perl-DBD-MySQLyum install perl-Time-HiResyum ...
- JAVA反映机制A
以下这个URL讲得不错,可以把概念和用途结合起来, 练练手: http://blog.csdn.net/xiaohai798/article/details/11640427 import java. ...
- CSS艺术之---负margin之美
CSS中负边距(nagative margin)是布局中常常使用的一个技巧.仅仅要运用得当时常会产生奇异的效果.勘称CSS中的奇淫巧计,非常多CSS布局方法都依赖于负边距.掌握它对于前端童鞋来说还是非 ...
- hihoCoder-1829 2018亚洲区预选赛北京赛站网络赛 B.Tomb Raider 暴力 字符串
题面 题意:给你n个串,每个串都可以选择它的一个长度为n的环形子串(比如abcdf的就有abcdf,bcdfa,cdfab,dfabc,fabcd),求这个n个串的这些子串的最长公共子序列(每个串按顺 ...
- python里使用reduce()函数
reduce()函数在库functools里,如果要使用它,要从这个库里导入.reduce函数与map函数有不一样地方,map操作是并行操作,reduce函数是把多个参数合并的操作,也就是从多个条件简 ...
- BZOJ 1196 二分+Kruskal
思路: 二分答案 判一下能不能加 //By SirisuRen #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algori ...
- Hadoop MapReduce编程 API入门系列之网页流量版本1(二十一)
不多说,直接上代码. 对流量原始日志进行流量统计,将不同省份的用户统计结果输出到不同文件. 代码 package zhouls.bigdata.myMapReduce.areapartition; i ...
- Npgsql使用入门(一)【搭建环境】
首先去官网下载最新数据库安装包 postgresql-9.6.1-1-windows-x64 将postgreSQL9.6注册为windows服务 注意:大小写要正确 D:\Worksoftware\ ...
- 最小环 hdu1599 poj1734
最小环用floyd改编. hdu1599特殊一些.要求至少有三个不同的点,并且除了起点与终点重合外,中间不能有环.有点很奇怪,最大值不能为0x3f3f3f3f. poj1374就没那么讲究. //hd ...
