Annotate类
在Annotate类中有个Annotator接口,定义如下:
/** A client that has annotations to add registers an annotator,
* the method it will use to add the annotation. There are no
* parameters; any needed data should be captured by the
* Annotator.
*/
public interface Annotator {
void enterAnnotation();
String toString();
}
其中的实现分部在MemberEnter与ClassReader类中,如下:
方法1:
/** Queue processing of an attribute default value. */
void annotateDefaultValueLater(final JCExpression defaultValue,
final Env<AttrContext> localEnv,
final MethodSymbol m) {
annotate.later(new Annotate.Annotator() {
public String toString() {
return "annotate " + m.owner + "." + m + " default " + defaultValue;
}
public void enterAnnotation() {
JavaFileObject prev = log.useSource(localEnv.toplevel.sourcefile);
try {
enterDefaultValue(defaultValue, localEnv, m);
} finally {
log.useSource(prev);
}
}
});
}
/** Enter a default value for an attribute method. */
private void enterDefaultValue(final JCExpression defaultValue,
final Env<AttrContext> localEnv,
final MethodSymbol m) {
m.defaultValue = annotate.enterAttributeValue(m.type.getReturnType(),defaultValue,localEnv);
}
方法2:
/** Queue annotations for later processing. */
void annotateLater(final List<JCAnnotation> annotations,
final Env<AttrContext> localEnv,
final Symbol s) {
if (annotations.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (s.kind != PCK) {
s.attributes_field = null; // mark it incomplete for now
}
annotate.later(new Annotate.Annotator() {
public String toString() {
return "annotate " + annotations + " onto " + s + " in " + s.owner;
}
public void enterAnnotation() {
Assert.check(s.kind == PCK || s.attributes_field == null);
JavaFileObject prev = log.useSource(localEnv.toplevel.sourcefile);
try {
if (s.attributes_field != null &&
s.attributes_field.nonEmpty() &&
annotations.nonEmpty()) {
log.error(annotations.head.pos, "already.annotated", kindName(s), s);
}
enterAnnotations(annotations, localEnv, s);
} finally {
log.useSource(prev);
}
}
});
}
其中调用了enterAnnotations()方法,代码如下:
/** Enter a set of annotations. */
private void enterAnnotations(List<JCAnnotation> annotations,Env<AttrContext> env,Symbol s) {
ListBuffer<Attribute.Compound> buf = new ListBuffer<Attribute.Compound>();
Set<TypeSymbol> annotated = new HashSet<TypeSymbol>();
if (!skipAnnotations) {
for (List<JCAnnotation> al = annotations; al.nonEmpty(); al = al.tail) {
JCAnnotation a = al.head;
Attribute.Compound c = annotate.enterAnnotation(a, syms.annotationType, env);
if (c == null) {
continue;
}
buf.append(c);
// Note: @Deprecated has no effect on local variables and parameters
if (!c.type.isErroneous()
&& s.owner.kind != MTH
&& types.isSameType(c.type, syms.deprecatedType)) {
s.flags_field |= Flags.DEPRECATED;
}
// Internally to java.lang.invoke, a @PolymorphicSignature annotation
// acts like a classfile attribute.
if (!c.type.isErroneous() &&
types.isSameType(c.type, syms.polymorphicSignatureType)) {
if (!target.hasMethodHandles()) {
// Somebody is compiling JDK7 source code to a JDK6 target.
// Make it an error, since it is unlikely but important.
log.error(env.tree.pos(), "wrong.target.for.polymorphic.signature.definition", target.name);
}
// Pull the flag through for better diagnostics, even on a bad target.
s.flags_field |= Flags.POLYMORPHIC_SIGNATURE;
}
if (!annotated.add(a.type.tsym)) {
log.error(a.pos, "duplicate.annotation");
}
}
}
s.attributes_field = buf.toList();
}
方法3:
/** Import statics types of a given name. Non-types are handled in Attr.
* @param pos Position to be used for error reporting.
* @param tsym The class from which the name is imported.
* @param name The (simple) name being imported.
* @param env The environment containing the named import
* scope to add to.
*/
private void importNamedStatic(final DiagnosticPosition pos,
final TypeSymbol tsym,
final Name name,
final Env<AttrContext> env) {
if (tsym.kind != TYP) {
log.error(DiagnosticFlag.RECOVERABLE, pos, "static.imp.only.classes.and.interfaces");
return;
}
final Scope toScope = env.toplevel.namedImportScope;
final PackageSymbol packge = env.toplevel.packge;
final TypeSymbol origin = tsym;
// enter imported types immediately
new Object() {
Set<Symbol> processed = new HashSet<Symbol>();
void importFrom(TypeSymbol tsym) {
if (tsym == null || !processed.add(tsym)) {
return;
}
// also import inherited names
importFrom(types.supertype(tsym.type).tsym);
for (Type t : types.interfaces(tsym.type)) {
importFrom(t.tsym);
}
for (Scope.Entry e = tsym.members().lookup(name); e.scope != null; e = e.next()) {
Symbol sym = e.sym;
if (sym.isStatic() &&
sym.kind == TYP &&
staticImportAccessible(sym, packge) &&
sym.isMemberOf(origin, types) &&
chk.checkUniqueStaticImport(pos, sym, toScope)) {
toScope.enter(sym, sym.owner.members(), origin.members());
}
}
}
}.importFrom(tsym);
// enter non-types before annotations that might use them
annotate.earlier(new Annotate.Annotator() {
Set<Symbol> processed = new HashSet<Symbol>();
boolean found = false;
public String toString() {
return "import static " + tsym + "." + name;
}
void importFrom(TypeSymbol tsym) {
if (tsym == null || !processed.add(tsym)) {
return;
}
// also import inherited names
importFrom(types.supertype(tsym.type).tsym);
for (Type t : types.interfaces(tsym.type))
importFrom(t.tsym);
for (Scope.Entry e = tsym.members().lookup(name);e.scope != null;e = e.next()) {
Symbol sym = e.sym;
if (sym.isStatic() &&
staticImportAccessible(sym, packge) &&
sym.isMemberOf(origin, types)) {
found = true;
if (sym.kind == MTH ||
sym.kind != TYP && chk.checkUniqueStaticImport(pos, sym, toScope)) {
toScope.enter(sym, sym.owner.members(), origin.members());
}
}
}
}
public void enterAnnotation() {
JavaFileObject prev = log.useSource(env.toplevel.sourcefile);
try {
importFrom(tsym);
if (!found) {
log.error(pos, "cant.resolve.location",
KindName.STATIC,
name, List.<Type>nil(), List.<Type>nil(),
Kinds.typeKindName(tsym.type),
tsym.type);
}
} finally {
log.useSource(prev);
}
}
});
}
方法4:
/** Import all static members of a class or package on demand.
* @param pos Position to be used for error reporting.
* @param tsym The class or package the members of which are imported.
* @param toScope The (import) scope in which imported classes are entered.
*/
private void importStaticAll(int pos,
final TypeSymbol tsym,
Env<AttrContext> env) {
final JavaFileObject sourcefile = env.toplevel.sourcefile;
final Scope toScope = env.toplevel.starImportScope;
final PackageSymbol packge = env.toplevel.packge;
final TypeSymbol origin = tsym;
// enter imported types immediately
new Object() {
Set<Symbol> processed = new HashSet<Symbol>();
void importFrom(TypeSymbol tsym) {
if (tsym == null || !processed.add(tsym)) {
return;
}
// also import inherited names
importFrom(types.supertype(tsym.type).tsym);
for (Type t : types.interfaces(tsym.type)) {
importFrom(t.tsym);
}
final Scope fromScope = tsym.members();
for (Scope.Entry e = fromScope.elems; e != null; e = e.sibling) {
Symbol sym = e.sym;
if (sym.kind == TYP &&
(sym.flags() & STATIC) != 0 &&
staticImportAccessible(sym, packge) &&
sym.isMemberOf(origin, types) &&
!toScope.includes(sym)
){
toScope.enter(sym, fromScope, origin.members());
}
}
}
}.importFrom(tsym);
// enter non-types before annotations that might use them
annotate.earlier(new Annotate.Annotator() {
Set<Symbol> processed = new HashSet<Symbol>();
public String toString() {
return "import static " + tsym + ".*" + " in " + sourcefile;
}
void importFrom(TypeSymbol tsym) {
if (tsym == null || !processed.add(tsym)) {
return;
}
// also import inherited names
importFrom(types.supertype(tsym.type).tsym);
for (Type t : types.interfaces(tsym.type)) {
importFrom(t.tsym);
}
final Scope fromScope = tsym.members();
for (Scope.Entry e = fromScope.elems; e != null; e = e.sibling) {
Symbol sym = e.sym;
if (sym.isStatic() && sym.kind != TYP &&
staticImportAccessible(sym, packge) &&
!toScope.includes(sym) &&
sym.isMemberOf(origin, types)) {
toScope.enter(sym, fromScope, origin.members());
}
}
}
public void enterAnnotation() {
importFrom(tsym);
}
});
}

继承体系如下图:
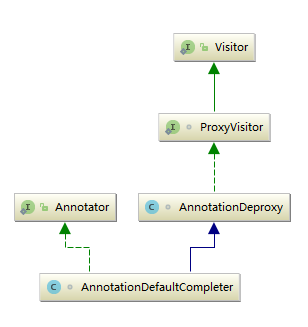

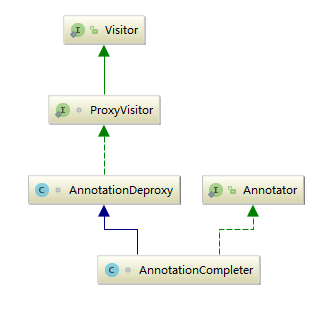
类1:
class AnnotationCompleter extends AnnotationDeproxy implements Annotate.Annotator {
final Symbol sym;
final List<CompoundAnnotationProxy> l;
final JavaFileObject classFile;
@Override
public String toString() {
return " ClassReader annotate " + sym.owner + "." + sym + " with " + l;
}
AnnotationCompleter(Symbol sym, List<CompoundAnnotationProxy> l) {
this.sym = sym;
this.l = l;
this.classFile = currentClassFile;
}
// implement Annotate.Annotator.enterAnnotation()
public void enterAnnotation() {
JavaFileObject previousClassFile = currentClassFile;
try {
currentClassFile = classFile;
List<Attribute.Compound> newList = deproxyCompoundList(l);
sym.attributes_field = ((sym.attributes_field == null)
? newList
: newList.prependList(sym.attributes_field));
} finally {
currentClassFile = previousClassFile;
}
}
}
类2:
class AnnotationDefaultCompleter extends AnnotationDeproxy implements Annotate.Annotator {
final MethodSymbol sym;
final Attribute value;
final JavaFileObject classFile = currentClassFile;
@Override
public String toString() {
return " ClassReader store default for " + sym.owner + "." + sym + " is " + value;
}
AnnotationDefaultCompleter(MethodSymbol sym, Attribute value) {
this.sym = sym;
this.value = value;
}
// implement Annotate.Annotator.enterAnnotation()
public void enterAnnotation() {
JavaFileObject previousClassFile = currentClassFile;
try {
currentClassFile = classFile;
sym.defaultValue = deproxy(sym.type.getReturnType(), value);
} finally {
currentClassFile = previousClassFile;
}
}
}
Annotate类的更多相关文章
- Java类的继承与多态特性-入门笔记
相信对于继承和多态的概念性我就不在怎么解释啦!不管你是.Net还是Java面向对象编程都是比不缺少一堂课~~Net如此Java亦也有同样的思想成分包含其中. 继承,多态,封装是Java面向对象的3大特 ...
- Matplotlib外观和基本配置笔记
title: matplotlib 外观和基本配置笔记 notebook: Python tags:matplotlib --- 参考资料,如何使用matplotlib绘制出数据图形,参考另一篇mat ...
- Swift 3.0 令人兴奋,但Objective-C也有小改进--Objective-C的类属性
由于Swift 3.0 出了太多令人兴奋的新特性,人们很容易忽略 Objective-C中的小改动.或许你会觉得苹果提及Objective-C 很可能是为了提高和Swift互操作性(译者注:互操作性主 ...
- 分享一个关于jackson的Json工具类
直接贴代码: import org.codehaus.jackson.map.DeserializationConfig.Feature; import org.codehaus.jackson.ma ...
- MyBatis里json型字段到Java类的映射
一.简介 我们在用MyBatis里,很多时间有这样一个需求:bean里有个属性是非基本数据类型,在DB存储时我们想存的是json格式的字符串,从DB拿出来时想直接映射成目标类型,也即json格式的字符 ...
- Java 最常用类(前1000名) 来自GitHub 3000个项目
这篇文章主要介绍了最常用的1000个Java类(附代码示例),需要的朋友可以参考下 分析Github 3000个开源项目,粗略统计如下.括号内的数字是使用频率 0-3000. 下面的列表显示不全,完整 ...
- (译)Objective-C 类属性
翻译自:Objective-C Class Properties 译者:Haley_Wong 由于Swift 3.0 出了太多令人兴奋的新特性,人们很容易忽略 Objective-C中的小改动.苹果展 ...
- Django 数据聚合函数 annotate
统计各个分类下的文章数 2 周,3 日前 字数 3818 阅读 546 评论 21 在我们的博客侧边栏有分类列表,显示博客已有的全部文章分类.现在想在分类名后显示该分类下有多少篇文章,该怎么做呢?最优 ...
- jackson工具类 对象转字符串 -- 字符串转对象
这个一个json的工具类.用的是jackson,当然还有谷歌的gosn,阿里的fastjson ,但是jackson的感觉还是最成熟(网上大神说的...) 实现的功能很简单,对象转字符串 字符串转简 ...
随机推荐
- python实现base64算法加密
python本身有base64加密的模块,不过是用C写的,封装成了.so文件,无法查看源码,本着学习的心态,自己实现了一遍,算法 原理参考 浅谈Base64编码算法. 代码如下: # coding:u ...
- n&&m and n||m 的区别
今天写一道题老是WA最后才发现问题出在了这个地方, 题目说的是当输入的n和m 都为0的时候,结束输入. 于是乎,条件我就写成了while(n&&m),其实这句话的意思是:只有m和n都不 ...
- hdu 4974 贪心
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4974 n个人进行选秀,有一个人做裁判,每次有两人进行对决,裁判可以选择为两人打分,可以同时加上1分,或者单独为一 ...
- Python学习-38.Python中的正则表达式(二)
在Python中,正则表达式还有较其他编程语言有特色的地方.那就是支持松散正则表达式了. 在某些情况,正则表达式会写得十分的长,这时候,维护就成问题了.而松散正则表达式就是解决这一问题的办法. 用上一 ...
- Golang Tcp粘包处理(转)
在用golang开发人工客服系统的时候碰到了粘包问题,那么什么是粘包呢?例如我们和客户端约定数据交互格式是一个json格式的字符串: {"Id":1,"Name" ...
- LeetCode151:Reverse Words in a String
题目: Given an input string, reverse the string word by word. For example, Given s = "the sk ...
- 蚂蚁男孩.缓存组件(Framework.Mayiboy.Caching)
它能做什么? 主要是用来方便使用缓存而诞生,该组件封装了RunTimeCache.Memcached.Redis的使用,通过简单配置就能高效快速使用起来. 使用说明 一. 下载源码,自己手动编译 ...
- window10下Docker安装
首先window版本必须是10,如果是win7那么安装方法有所不同,win10是官方支持安装的.笔者安装的是Community社区版,版本信息如下: 1.去docker官网下载win10安装包: ht ...
- Nigix配置
- 【新题】ocp 062 2019年考试新题-3
3.A database is open read write and the instance has multiple sessions some of which have active tra ...
