Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) E. Berland Local Positioning System 构造
E. Berland Local Positioning System
Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://codeforces.com/contest/534/problem/E
Description
In Berland a bus travels along the main street of the capital. The street begins from the main square and looks like a very long segment. There are n bus stops located along the street, the i-th of them is located at the distance ai from the central square, all distances are distinct, the stops are numbered in the order of increasing distance from the square, that is, ai < ai + 1 for all i from 1 to n - 1. The bus starts its journey from the first stop, it passes stops 2, 3 and so on. It reaches the stop number n, turns around and goes in the opposite direction to stop 1, passing all the intermediate stops in the reverse order. After that, it again starts to move towards stop n. During the day, the bus runs non-stop on this route.
The bus is equipped with the Berland local positioning system. When the bus passes a stop, the system notes down its number.
One of the key features of the system is that it can respond to the queries about the distance covered by the bus for the parts of its path between some pair of stops. A special module of the system takes the input with the information about a set of stops on a segment of the path, a stop number occurs in the set as many times as the bus drove past it. This module returns the length of the traveled segment of the path (or -1 if it is impossible to determine the length uniquely). The operation of the module is complicated by the fact that stop numbers occur in the request not in the order they were visited but in the non-decreasing order.
For example, if the number of stops is 6, and the part of the bus path starts at the bus stop number 5, ends at the stop number 3 and passes the stops as follows: 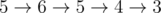 , then the request about this segment of the path will have form: 3, 4, 5, 5, 6. If the bus on the segment of the path from stop 5 to stop 3 has time to drive past the 1-th stop (i.e., if we consider a segment that ends with the second visit to stop 3 on the way from 5), then the request will have form: 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6.
, then the request about this segment of the path will have form: 3, 4, 5, 5, 6. If the bus on the segment of the path from stop 5 to stop 3 has time to drive past the 1-th stop (i.e., if we consider a segment that ends with the second visit to stop 3 on the way from 5), then the request will have form: 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6.
You will have to repeat the Berland programmers achievement and implement this function.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of stops.
The second line contains n integers (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the distance from the i-th stop to the central square. The numbers in the second line go in the increasing order.
The third line contains integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 4·105) — the number of stops the bus visited on some segment of the path.
The fourth line contains m integers (1 ≤ bi ≤ n) — the sorted list of numbers of the stops visited by the bus on the segment of the path. The number of a stop occurs as many times as it was visited by a bus.
It is guaranteed that the query corresponds to some segment of the path.
Output
Sample Input
6
2 3 5 7 11 13
5
3 4 5 5 6
6
2 3 5 7 11 13
9
1 2 2 3 3 4 5 5 6
3
10 200 300
4
1 2 2 3
3
1 2 3
4
1 2 2 3
Sample Output
10
16
-1
3
HINT
The first test from the statement demonstrates the first example shown in the statement of the problem.
The second test from the statement demonstrates the second example shown in the statement of the problem.
In the third sample there are two possible paths that have distinct lengths, consequently, the sought length of the segment isn't defined uniquely.
In the fourth sample, even though two distinct paths correspond to the query, they have the same lengths, so the sought length of the segment is defined uniquely.
题意
给你过车站的顺序,然后让你输出车走的距离,如果这个距离不是唯一的,直接输出-1
题解:
输出-1的情况只有一种,就是路过所有点的次数都相等(除了首部和尾部),且,每条边的长度有一种不相等
代码:
//qscqesze
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
//freopen("D.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("D.out","w",stdout);
#define sspeed ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)
#define maxn 200001
#define mod 10007
#define eps 1e-9
//const int inf=0x7fffffff; //无限大
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
/*
inline ll read()
{
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int buf[10];
inline void write(int i) {
int p = 0;if(i == 0) p++;
else while(i) {buf[p++] = i % 10;i /= 10;}
for(int j = p-1; j >=0; j--) putchar('0' + buf[j]);
printf("\n");
}
*/
//************************************************************************************** ll a[maxn];
ll b[maxn];
int main()
{
ll mx=,mi=inf;
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int m;
cin>>m;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
b[x]++;
if(x==||x==n)
b[x]++;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
mx=max(mx,b[i]);
mi=min(mi,b[i]);
}
//cout<<mi<<" "<<mx<<endl;
if(mi==mx)
{
int flag=;
for(int i=;i<=n-;i++)
{
if(a[i+]-a[i]!=a[i+]-a[i+])
{
flag=;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
puts("-1");
else
printf("%lld",(a[n]-a[])*mi-(a[]-a[]));
}
else
{
ll ans=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
ans+=(a[i]-a[i-])*min(b[i],b[i-]);
//cout<<ans<<endl;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
} }
Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) E. Berland Local Positioning System 构造的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) A、B、C题
题目链接:Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) A. Exam An exam for n students will take place in a long and nar ...
- 构造 Codeforces Round #Pi (Div. 2) B. Berland National Library
题目传送门 /* 题意:给出一系列读者出行的记录,+表示一个读者进入,-表示一个读者离开,可能之前已经有读者在图书馆 构造:now记录当前图书馆人数,sz记录最小的容量,in数组标记进去的读者,分情况 ...
- Codeforces Round #Pi (Div. 2) B. Berland National Library set
B. Berland National LibraryTime Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest ...
- Codeforces Round #Pi (Div. 2) B. Berland National Library 模拟
B. Berland National LibraryTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contes ...
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) D. Handshakes 构造
D. Handshakes Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/534/problem ...
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) C. Polycarpus' Dice 数学
C. Polycarpus' Dice Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/534/p ...
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) B. Covered Path 物理题/暴力枚举
B. Covered Path Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/534/probl ...
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2) A. Exam 构造
A. Exam Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/534/problem/A Des ...
- Codeforces Round #298 (Div. 2)A B C D
A. Exam time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output ...
随机推荐
- 【读书笔记::深入理解linux内核】内存寻址【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/likeyiyy/p/3837272.html 我对linux高端内存的错误理解都是从这篇文章得来的,这篇文章里讲的 物理地址 = 逻辑地址 – 0 ...
- java系统的优化
1.tomcat.jboss.jetty的jvm内存,增大 2.数据库的优化,如MySQL的innodb_buffer_pool_size等参数,增大
- 25 个常用的 Linux iptables 规则【转】
转自 25 个常用的 Linux iptables 规则 - 文章 - 伯乐在线http://blog.jobbole.com/108468/ # 1. 删除所有现有规则 iptables -F # ...
- xshell5 优化方案
有道云笔记链接-> grep: 过滤 过滤的速度是最快的(相对于另外两个) -v -n -o 显示grep匹配到了什么 grep . -o -i --ignore-case -E == ...
- Ubuntu下使用Nginx+uWSGI+Flask(初体验)
Ubuntu 18.04,Nginx 1.14.0, uWSGI 2.0.17.1,Flask, 前言 Windows不支持uWSGI!为了上线自己的项目,只能选择Linux. 自己前面开发了一个Fl ...
- handlermethodargumentresolver
http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/springMVC-request-param-analysis.html http://www.cnblogs.com/f ...
- collection.toArray(new String[0])中new String[0]的作用
new string[0]的作用 比如:String[] result = set.toArray(new String[0]); Collection的公有方法中,toArray()是比较重要的一个 ...
- No.11 selenium学习之路之加载浏览器插件for Firefox
打开帮助 —— 故障排除信息
- ubuntu12.04安装ruby2.3
为了搭建github-pages博客,而github-pages后端依赖于ruby,且对版本有严格要求,自己尝试了各种姿势升级ruby2.3无果,最终在查阅了各种资料之后找到一个可行方案. icebu ...
- NYOJ 石子合并(一)(区间DP)
题目链接:http://acm.nyist.edu.cn/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=737 题目大意: 有N堆石子排成一排,每堆石子有一定的数量.现要将N堆石子并成为一堆 ...
