算法:Rate of Growth
Rate of growth describes how an algorithm’s complexity changes as the input size grows. This is commonly represented using Big-O notation. Big-O notation uses a capital O (“order”) and a formula that expresses the complexity of the algorithm. The formula may have a variable, n, which represents the size of the input. The following are some common order functions we will see in this book but this list is by no means complete.
Constant – O(1)
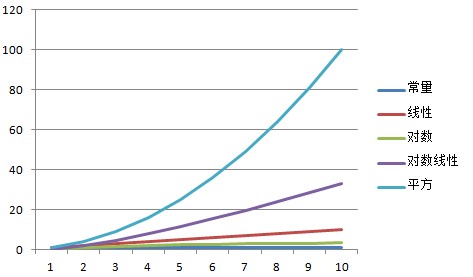
An O(1) algorithm is one whose complexity is constant regardless of how large the input size is. The 1 does not mean that there is only one operation or that the operation takes a small amount of time. It might take 1 microsecond or it might take 1 hour. The point is that the size of the input does not influence the time the operation takes.
public int GetCount(int[] items)
{
return items.Length;
}
Linear – O(n)
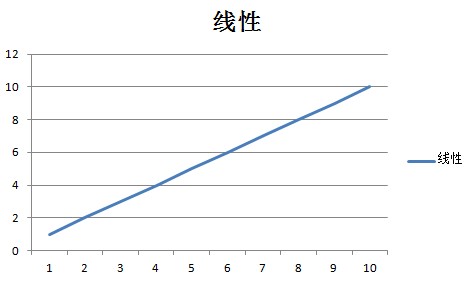
An O(n) algorithm is one whose complexity grows linearly with the size of the input. It is reasonable to expect that if an input size of 1 takes 5 milliseconds, an input with one thousand items will take 5 seconds.You can often recognize an O(n) algorithm by looking for a looping mechanism that accesses each member.
public long GetSum(int[] items)
{
long sum = ;
foreach (int i in items)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
Logarithmic – O(log n)
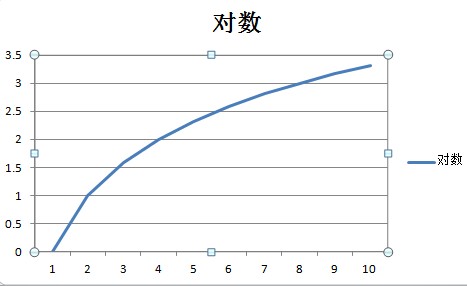
An O(log n) algorithm is one whose complexity is logarithmic to its size. Many divide and conquer algorithms fall into this bucket. The binary search tree Contains method implements an O(log n) algorithm.
Linearithmic – O(n log n)

A linearithmic algorithm, or loglinear, is an algorithm that has a complexity of O(n log n). Some divide and conquer algorithms fall into this bucket. We will see two examples when we look at merge sort and quick sort.
An O(n2)
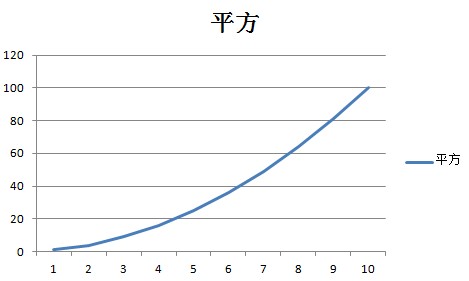
An O(n2) algorithm is one whose complexity is quadratic to its size. While not always avoidable, using a quadratic algorithm is a potential sign that you need to reconsider your algorithm or data structure choice. Quadratic algorithms do not scale well as the input size grows. For example, an array with 1000 integers would require 1,000,000 operations to complete. An input with one million items would take one trillion (1,000,000,000,000) operations. To put this into perspective, if each operation takes one millisecond to complete, an O(n2) algorithm that receives an input of one million items will take nearly 32 years to complete. Making that algorithm 100 times faster would still take 84 days.
We will see an example of a quadratic algorithm when we look at bubble sort.
Best, Average, and Worst Case
When we say an algorithm is O(n), what are we really saying? Are we saying that the algorithm is O(n) on average? Or are we describing the best or worst case scenario?
We typically mean the worst case scenario unless the common case and worst case are vastly different. For example, we will see examples in this book where an algorithm is O(1) on average, but periodically becomes O(n) (see ArrayList.Add). In these cases I will describe the algorithm as O(1) on average and then explain when the complexity changes.
The key point is that saying O(n) does not mean that it is always n operations. It might be less, but it should not be more.
What are we Measuring?
When we are measuring algorithms and data structures, we are usually talking about one of two things: the amount of time the operation takes to complete (operational complexity), or the amount of resources (memory) an algorithm uses (resource complexity).
An algorithm that runs ten times faster but uses ten times as much memory might be perfectly acceptable in a server environment with vast amounts of available memory, but may not be appropriate in an embedded environment where available memory is severely limited.
In this book I will focus primarily on operational complexity, but in the Sorting Algorithms chapter we will see some examples of resource complexity.
Some specific examples of things we might measure include:
- Comparison operations (greater than, less than, equal to).
- Assignments and data swapping.
- Memory allocations.
The context of the operation being performed will typically tell you what type of measurement is being made.
For example, when discussing the complexity of an algorithm that searches for an item within a data structure, we are almost certainly talking about comparison operations. Search is generally a read-only operation so there should not be any need to perform assignments or allocate memory.
However, when we are talking about data sorting it might be logical to assume that we could be talking about comparisons, assignments, or allocations. In cases where there may be ambiguity, I will indicate which type of measurement the complexity is actually referring to.
算法:Rate of Growth的更多相关文章
- 算法中的增长率(Rate of Growth)是什么意思?
一个函数或算法的代码块花费的时间随输入增长的速率称为增长率. 假设你去买一辆小车和一辆自行车.如果你朋友刚好看到,问你在买什么,我们一般都会说:买小车.因为买小车比买自行车花费高多了. [总花费=小车 ...
- 关联规则算法之FP growth算法
FP树构造 FP Growth算法利用了巧妙的数据结构,大大降低了Aproir挖掘算法的代价,他不需要不断得生成候选项目队列和不断得扫描整个数据库进行比对.为了达到这样的效果,它采用了一种简洁的数据结 ...
- 机器学习(十五)— Apriori算法、FP Growth算法
1.Apriori算法 Apriori算法是常用的用于挖掘出数据关联规则的算法,它用来找出数据值中频繁出现的数据集合,找出这些集合的模式有助于我们做一些决策. Apriori算法采用了迭代的方法,先搜 ...
- FBOSS: Building Switch Software at Scale
BOSS: 大规模环境下交换机软件构建 本文为SIGCOMM 2018 论文,由Facebook提供. 本文翻译了论文的关键内容. 摘要: 在网络设备(例如交换机和路由器)上运行的传统软件,通常是由供 ...
- News common vocabulary
英语新闻常用词汇与短语 经济篇 accumulated deficit 累计赤字 active trade balance 贸易顺差 adverse trade balance 贸易逆差 aid 援助 ...
- [IT学习]微软如何做网站内容治理
How Microsoft does SharePoint Governance for their internal platform english sources from:http://www ...
- RFC 2616
Network Working Group R. Fielding Request for Comments: 2616 UC Irvine Obsoletes: 2068 J. Gettys Cat ...
- 自然数e这家伙怎么蹦跶出来的?
自然数e这家伙怎么蹦跶出来的? 之前看过一篇中文介绍自然数e的blog,引起了我的兴趣 原文是阮一峰大牛(我认为必须很有必要尊敬的称,大牛)嚼烂了吐出来的哈哈,只是我认为还是自己去看原文比較好 感觉非 ...
- 美国政府关于Google公司2013年度的财务报表红头文件
请管理员移至新闻版块,谢谢! 来源:http://www.sec.gov/ 财务报表下载↓ 此文仅作参考分析. 10-K 1 goog2013123110-k.htm FORM 10-K UNIT ...
随机推荐
- OpenCV持久化(一)
在OpenCV中,采用FileStorage类进行数据持久化,可以采用XML或YAML格式存储数据. 将数据写入XML或YAML文件,可采用以下步骤: 1.创建FileStorage对象.可以调用构造 ...
- Spark(七)Spark内存调优
一.概述 Spark 作为一个基于内存的分布式计算引擎,其内存管理模块在整个系统中扮演着非常重要的角色.理解 Spark 内存管理的基本原理,有助于更好地开发 Spark 应用程序和进行性能调优.本文 ...
- Ionic Tabs
Ionic 默认的 Tabs 模板 ,Android的在上方,IOS的在下方.在www/js/app.js修改配置,添加一个变量,再修改相应属性: .config(function($statePro ...
- 轻松实现Ecshop商城多语言切换
很多人都想让自己的ECSHOP商城实现多语言支持(能够方便的在首页切换多语言).其实实现起来也挺简单的. 效果图如下: 下面就说一下修改方法. 1).首先打开 includds/init.php 文 ...
- Effective C++ —— 模板与泛型编程(七)
C++ templates的最初发展动机很直接:让我们得以建立“类型安全”的容器如vector,list和map.然而当愈多人用上templates,他们发现templates有能力完成愈多可能的变化 ...
- 前端安全系列之二:如何防止CSRF攻击?
背景 随着互联网的高速发展,信息安全问题已经成为企业最为关注的焦点之一,而前端又是引发企业安全问题的高危据点.在移动互联网时代,前端人员除了传统的 XSS.CSRF 等安全问题之外,又时常遭遇网络劫持 ...
- SERVLET API中forward()与redirect()的区别?
前者仅是容器中控制权的转向,在客户端浏览器地址栏中不会显示出转向后的地址:后者则是完全的跳转,浏览器将会得到跳转的地址,并重新发送请求链接.这样,从浏览器的地址栏中可以看到跳转后的链接地址.所以,前者 ...
- iOS 9应用开发教程之使用开关滑块控件以及滚动部署视图
iOS 9应用开发教程之使用开关滑块控件以及滚动部署视图 使用ios9中的开关.滑块控件 开关和滑块也是用于和用户进行交互的控件.本节将主要讲解这两种控件. ios9开关 开关控件常用来控制某个功能的 ...
- 机器学习之路:python线性回归分类器 LogisticRegression SGDClassifier 进行良恶性肿瘤分类预测
使用python3 学习了线性回归的api 分别使用逻辑斯蒂回归 和 随机参数估计回归 对良恶性肿瘤进行预测 我把数据集下载到了本地,可以来我的git下载源代码和数据集:https://gith ...
- s3c2440地址分配
mini2440的地址怎么分配.mini2440处理器的地址怎么分配. S3C2440处理器可以使用的物理地址空间可以达到4GB,其中前1GB的地址为连接外设的地址空间.>1G的地址空间 分配给 ...
