MQ与Webservice的区别
Webservice 和MQ(MessageQueue)都是解决跨平台通信的常用手段,两者有哪些区别呢?
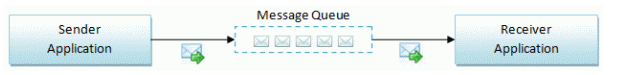
In this article, I will introduce a new and independent Open Source Message Queue system that is entirely built in C# and .NET framework 3.5. DotNetMQ is a message broker that has several features including guaranteed delivering, routing, load balancing, server graphs... so on. I will start by explaining messaging concepts and the need for message brokers. Then I will examine what DotNetMQ is and how to use it.
Messaging is a way of asynchronous communication of applications running on same or different machines with reliable delivery. Programs communicate by sending packets of data called messages to each other [1].
A message may be a string, a byte array, an object... etc. Typically, a sender (producer) program creates a message and pushes it to a message queue and a receiver (consumer) program gets the message from the queue and processes it. The sender and receiver programs don’t have to be running at the same time, since messaging is an asynchronous process. This is called loosely coupled communication.
On the other hand, a Web Service method call (Remote Method Invocation) is a type of tightly coupled andsynchronous communication (both applications have to be running and available during the whole communication; if the Web Service is offline or an error occurs during the method call, the client application gets an exception).

In the figure above, two applications communicate over a message queue in a loosely coupled manner. If the receiver consumes messages slower than the sender produces it, the message count on the queue will increase. Also, the receiver may be offline while the sender is sending messages. In this situation, the receiver gets the messages from the queue when it becomes online (when it starts and joins the queue).
Message Queues are typically provided by Message Brokers. A Message Broker is a standalone application (service) that other applications connect to and send/receive messages. A Message Broker is responsible to store messages until a receiver receives them. A Message Broker can route messages across machines to deliver a message to the destination application and can try delivering the message until the receiver correctly handles it. A Message Broker is sometimes called a Message Oriented Middleware (MOM) or simply Message Queue (MQ).
DotNetMQ is an open source Message Broker that has several features:
- Persistent or non-persistent messaging.
- Guaranteed delivery of persistent messages even in a system crash.
- Automatic and manual routing of messages in a custom machine graph.
- Supports multiple databases (MS SQL Server, MySQL, SQLite, and memory-based storage for now).
- Supports don’t store, direct send style messaging.
- Supports Request/Reply style messaging.
- Easy to use client library to communicate with the DotNetMQ Message Broker.
- Built-in framework to easily construct RMI services upon message queues.
- Supports delivering messages to ASP.NET Web Services.
- GUI-based management and monitoring tool.
- Easy to install, manage, and use.
- Written entirely in C# (using .NET Framework 3.5).
I preferred to name DotNetMQ as MDS (Message Delivery System) when first creating it. Because it is designed not just to be a message queue, but also as a system that delivers messages directly to applications and an environment that provides a framework to build application services. I called it DotNetMQ since it is entirely developed using .NET and the DotNetMQ name is more memorable. So, it’s original name (and internal project name) is MDS and the applications have many classes with the prefix MDS.
First, I will demonstrate a simple situation where a message broker is needed.
In my experiences in business life, I've observed really bad and uncommon asynchronous enterprise application integration solutions. Usually there is an application that runs on a server and performs some tasks and produces data, and then sends the result data to another application on another server. The second application performs other tasks on the data or evaluates the result (the servers are on the same network or connected over the internet). Also, the message data must be persistent. Even if the remote application is not working or the network is not available, themessage must be delivered on the first chance.
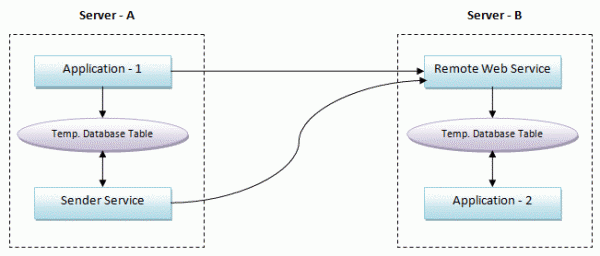
Application - 1 and Application - 2 are executable applications (or Windows services) and Sender Service is a Windows service. Application - 1 performs some task, produces data, and calls a Remote Web Service method onServer - B to transmit data. This Web Service inserts data into a database table. Application - 2 periodically checks the table for new incoming data rows and processes them (and deletes them from the table or marks them as processed to not process the same data again).
If an error occurs during the Web Service call or while processing data in the Web Service, data must not be lost and must be sent later. However, Application - 1 has other tasks to do, so it can not try to send data again and again. It simply inserts data into a database table. Another Windows service (or a thread in Application - 1, if the application always runs) checks this table periodically and tries to send data to the Web Service until data is successfully sent.
This scenario is really reliable (messages are guaranteed to be delivered) but is not an efficient way of communicating between two applications. This solution has some very critical problems:
- It takes a long time to develop (to code).
- Individual coding for all message types (or remote method calls). For a new Web Service method call, you must change all the services, applications, and database tables.
- Almost same software and structures must be developed (or copied and modified) for every similar service.
- Testing and maintenance of too many services/applications/databases after coding.
- Some applications and services periodically check the database even if there is no new message (if the database is not well indexed and optimized, this may consume serious system resources).
Message Brokers do all this job and takes all the responsibility to deliver messages to the remote application in the most efficient way. The same application integration using DotNetMQ is shown in the figure below.

MQ与Webservice的区别的更多相关文章
- MQ与webservice的区别,MQ的区别
Webservice 和MQ(MessageQueue)都是解决跨平台通信的常用手段,两者有哪些区别呢? 个人认为最本质的区别在于 Webservice近乎实时通信,而MQ却通常是延时通信. 什么意思 ...
- WebAPI和WebService的区别
WebAPI和WebService的区别 WebAPI用的是http协议,WebService用的是soap协议 WebAPI无状态,相对WebService更轻量级.WebAPI支持如get,pos ...
- RPC和WebService的区别
最近分析的这个系统,逻辑架构中有一层是RPC interface.之前对RPC不熟悉,就上网搜索了一下资料,在此总结一下: RPC是Remote Procedure Calling,远程过程调用的缩写 ...
- WCF与WebService的区别
1.WebService:严格来说是行业标准,不是技术,使用XML扩展标记语言来表示数据(这个是夸语言和平台的关键).微软的Web服务实现称为ASP.NET Web Service.它使用Soap简单 ...
- Remoting和Webservice的区别
其实现的原理并没有本质的区别,在应用开发层面上有以下区别:1.Remoting可以灵活的定义其所基于的协议,如果定义为HTTP,则与Web Service就没有什么区别了,一般都喜欢定义为TCP,这样 ...
- 大名鼎鼎的RPC和MQ到底有啥区别和联系
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)远程过程调用,主要解决远程通信间的问题,不需要了解底层网络的通信机制. RPC框架 知名度较高的有Thrift(FB的).dubbo(阿里的). R ...
- http和webservice接口区别
httpservice通过post和get得到你想要的东西webservice就是使用soap协议得到你想要的东西,相比httpservice能处理些更加复杂的数据类型 http协议传输的都是字符 ...
- HttpClient和WebService的区别和介绍
1. HTTP 协议可能是现在 Internet 上使用得最多.最重要的协议了,越来越多的 Java 应用程序需要直接通过 HTTP 协议来访问网络资源. HttpClient用来调用服务,它是模拟 ...
- WebAPI 和 WebService的区别
webapi用的是http协议,webservice用的是soap协议 webapi无状态,相对webservice更轻量级.webapi支持如get,post等http操作 http soap关系 ...
随机推荐
- 978. Longest Turbulent Subarray
A subarray A[i], A[i+1], ..., A[j] of A is said to be turbulent if and only if: For i <= k < j ...
- django url 路由设置技巧
Django的url使用方法 利用Django开发站点.能够设计出很优美的url规则,假设url的匹配规则(包括正則表達式)组织得比較好,view的结构就会比較清晰.比較easy维护. 最简单的形式 ...
- django 实现全局支持跨域请求
Django 实现允许跨域请求 1.安装django-cors-headers pip install django-cors-headers 2.配置settings.py文件 INSTALLED_ ...
- Xshell多版本被曝存在后门,了解紧急响应修复预案
近日,Xshell远程终端工具被爆出多个版本存在后门,无疑是安全圈的一个大新闻.恶意攻击者利用该后门可以收集到用户名密码等主机敏感信息,并将之传回攻击者的机器,导致服务器信息泄露,进一步可致使整个服务 ...
- 一个自动换行,不可以滚动的 textview
 主要效果有几点 只显示一行文字 输入文字过长时,自动换行 上下不可以滑动 删除时,自动显示上一行文字. 如何做到 只显示一行 textView.heightAnchor.constraint(eq ...
- Swift 使用 #warning
swift 中没法使用#Warning来提示警告, 可以通过给TODO: FIXME:加上警告, 实现类似的效果. Build Phases ---> Run Script ---> ad ...
- spring中的context:include-filter和context:exclude-filter的区别
在Spring 的配置文件中有: <context:component-scan base-package="njupt.dao,njupt.service"> < ...
- Flowable BPMN 简单使用
1.Flowable是什么? Flowable是一个使用Java编写的轻量级业务流程引擎.Flowable流程引擎可用于部署BPMN 2.0流程定义(用于定义流程的行业XML标准), 创建这些流程定义 ...
- Linux实用指令
Linux实用指令 Rpm&Yum 一种用于互联网下载包的打包和安装工具,它包含某些Linux分发版中,它生产具有 .rpm 扩展名的文件.RPM 是 RedHat Package Man ...
- (转)解锁MySQL备份恢复的4种正确姿势
本文根据DBAplus社群第104期线上分享整理而成. 原文:http://dbaplus.cn/news-11-1267-1.html 讲师介绍 冯帅 点融网高级DBA 获有Oracle OCM ...
