Android中滑屏初探 ---- scrollTo 以及 scrollBy方法使用说明
今天给大家介绍下Android中滑屏功能的一个基本实现过程以及原理初探,最后给大家重点讲解View视图中scrollTo 与
scrollBy这两个函数的区别 。
首先 ,我们必须明白在Android View视图是没有边界的,Canvas是没有边界的,只不过我们通过绘制特定的View时对
Canvas对象进行了一定的操作,例如 : translate(平移)、clipRect(剪切)等,以便达到我们的对该Canvas对象绘制的要求 ,
我们可以将这种无边界的视图称为“视图坐标”-----它不受物理屏幕限制。通常我们所理解的一个Layout布局文件只是该视
图的显示区域,超过了这个显示区域将不能显示到父视图的区域中 ,对应的,我们可以将这种有边界的视图称为“布局坐标”
------ 父视图给子视图分配的布局(layout)大小。而且, 一个视图的在屏幕的起始坐标位于视图坐标起始处,如下图所示。
这么来说吧 ,世界本是无边无界的,可是我们的眼睛我们的心约束了我们所看到的“世界” 。
如下所示:
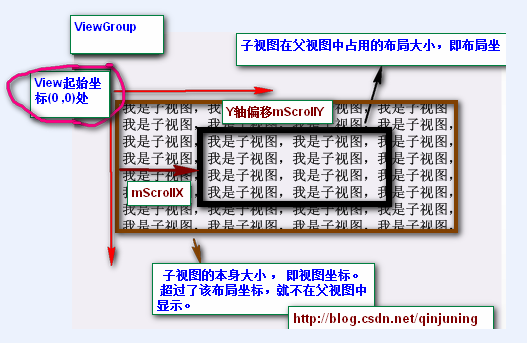
黑色框框表示该子视图的布局坐标, 褐色框框表示该子视图的视图坐标--该坐标是无限的,超过了父视图给子视图
规定的区域后,不再显示该超出内容。
那么下面的问题就是:如何将我们的视图的任意坐标能显示到该视图的中心坐标上呢? 由于该布局位置是只能显示特定的
一块视图内容 ,因此我们需要通过scrollTo()或者scrollBy()方法将我们期望的视图“滚动”至布局坐标上。
在View.java中提供了了如下两个变量以及相应的属性方法去读取滚动值 ,如下: View.java类中
- /**
- * The offset, in pixels, by which the content of this view is scrolled
- * horizontally.
- * {@hide}
- */
- protected int mScrollX; //该视图内容相当于视图起始坐标的偏移量 , X轴 方向
- /**
- * The offset, in pixels, by which the content of this view is scrolled
- * vertically.
- * {@hide}
- */
- protected int mScrollY; //该视图内容相当于视图起始坐标的偏移量 , Y轴方向
- /**
- * Return the scrolled left position of this view. This is the left edge of
- * the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels
- * farther left, since those are outside of the frame of your view on
- * screen.
- *
- * @return The left edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
- */
- public final int getScrollX() {
- return mScrollX;
- }
- /**
- * Return the scrolled top position of this view. This is the top edge of
- * the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels above
- * it, since those are outside of the frame of your view on screen.
- *
- * @return The top edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
- */
- public final int getScrollY() {
- return mScrollY;
- }
/**
* The offset, in pixels, by which the content of this view is scrolled
* horizontally.
* {@hide}
*/
protected int mScrollX; //该视图内容相当于视图起始坐标的偏移量 , X轴 方向
/**
* The offset, in pixels, by which the content of this view is scrolled
* vertically.
* {@hide}
*/
protected int mScrollY; //该视图内容相当于视图起始坐标的偏移量 , Y轴方向 /**
* Return the scrolled left position of this view. This is the left edge of
* the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels
* farther left, since those are outside of the frame of your view on
* screen.
*
* @return The left edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
*/
public final int getScrollX() {
return mScrollX;
} /**
* Return the scrolled top position of this view. This is the top edge of
* the displayed part of your view. You do not need to draw any pixels above
* it, since those are outside of the frame of your view on screen.
*
* @return The top edge of the displayed part of your view, in pixels.
*/
public final int getScrollY() {
return mScrollY;
}
注意,所谓的“by which the content of this view is scrolled”表示该偏移量只针对于该View中onDraw()方法里的
具体内容实现,而不针对绘制背景图片等 。具体原因可参考<Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析>
提示:下文中提到的当前视图内容是在绘制在布局坐标处的内容。
public void scrollTo(int x, int y)
说明:在当前视图内容偏移至(x , y)坐标处,即显示(可视)区域位于(x , y)坐标处。
方法原型为: View.java类中
- /**
- * Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
- * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
- * invalidated.
- * @param x the x position to scroll to
- * @param y the y position to scroll to
- */
- public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
- //偏移位置发生了改变
- if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) {
- int oldX = mScrollX;
- int oldY = mScrollY;
- mScrollX = x; //赋新值,保存当前便宜量
- mScrollY = y;
- //回调onScrollChanged方法
- onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY);
- if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
- invalidate(); //一般都引起重绘
- }
- }
- }
/**
* Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the x position to scroll to
* @param y the y position to scroll to
*/
public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
//偏移位置发生了改变
if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) {
int oldX = mScrollX;
int oldY = mScrollY;
mScrollX = x; //赋新值,保存当前便宜量
mScrollY = y;
//回调onScrollChanged方法
onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY);
if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
invalidate(); //一般都引起重绘
}
}
}
public void scrollBy(int x, int y)
说明:在当前视图内容继续偏移(x , y)个单位,显示(可视)区域也跟着偏移(x,y)个单位。
方法原型为: View.java类中
- /**
- * Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
- * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
- * invalidated.
- * @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally
- * @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically
- */
- // 看出原因了吧 。。 mScrollX 与 mScrollY 代表我们当前偏移的位置 , 在当前位置继续偏移(x ,y)个单位
- public void scrollBy(int x, int y) {
- scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
- }
/**
* Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally
* @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically
*/
// 看出原因了吧 。。 mScrollX 与 mScrollY 代表我们当前偏移的位置 , 在当前位置继续偏移(x ,y)个单位
public void scrollBy(int x, int y) {
scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
}
第一个小Demo非常简单 ,大家重点理解与掌握scrollTo() 与 scrollBy()函数的用法和区别。
第二个小Demo则有了Launcher的模样,能够左右切换屏幕 。实现功能如下: 采用了一个自定义ViewGroup,该ViewGroup
对象包含了3个LinearLayout子视图,并且以一定的布局坐标(由layout()方法指定)显示在ViewGroup上。 接下来,即可调用该
ViewGroup对象的scrollTo或者scrollBy()方法切换指定视图内容了,即切换屏幕。 呵呵 ,挺好玩的吧 。
如果对View绘制流程不懂的,可以参考我的这篇博客<Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析> 。
截图如下:

自定义ViewGroup如下:
- //自定义ViewGroup , 包含了三个LinearLayout控件,存放在不同的布局位置,通过scrollBy或者scrollTo方法切换
- public class MultiViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
- private Context mContext;
- private static String TAG = "MultiViewGroup";
- public MultiViewGroup(Context context) {
- super(context);
- mContext = context;
- init();
- }
- public MultiViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(context, attrs);
- mContext = context;
- init();
- }
- private void init() {
- // 初始化3个 LinearLayout控件
- LinearLayout oneLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
- oneLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
- addView(oneLL);
- LinearLayout twoLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
- twoLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.YELLOW);
- addView(twoLL);
- LinearLayout threeLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
- threeLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
- addView(threeLL);
- }
- // measure过程
- @Override
- protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
- Log.i(TAG, "--- start onMeasure --");
- // 设置该ViewGroup的大小
- int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
- int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
- setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
- int childCount = getChildCount();
- Log.i(TAG, "--- onMeasure childCount is -->" + childCount);
- for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
- View child = getChildAt(i);
- // 设置每个子视图的大小 , 即全屏
- child.measure(MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth, MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
- }
- }
- // layout过程
- @Override
- protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.i(TAG, "--- start onLayout --");
- int startLeft = 0; // 每个子视图的起始布局坐标
- int startTop = 10; // 间距设置为10px 相当于 android:marginTop= "10px"
- int childCount = getChildCount();
- Log.i(TAG, "--- onLayout childCount is -->" + childCount);
- for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
- View child = getChildAt(i);
- child.layout(startLeft, startTop,
- startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth,
- startTop + MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
- startLeft = startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth ; //校准每个子View的起始布局位置
- //三个子视图的在屏幕中的分布如下 [0 , 320] / [320,640] / [640,960]
- }
- }
- }
//自定义ViewGroup , 包含了三个LinearLayout控件,存放在不同的布局位置,通过scrollBy或者scrollTo方法切换
public class MultiViewGroup extends ViewGroup { private Context mContext; private static String TAG = "MultiViewGroup"; public MultiViewGroup(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
init();
} public MultiViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mContext = context;
init();
} private void init() {
// 初始化3个 LinearLayout控件
LinearLayout oneLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
oneLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.RED);
addView(oneLL); LinearLayout twoLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
twoLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.YELLOW);
addView(twoLL); LinearLayout threeLL = new LinearLayout(mContext);
threeLL.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
addView(threeLL);
} // measure过程
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { Log.i(TAG, "--- start onMeasure --"); // 设置该ViewGroup的大小
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, height); int childCount = getChildCount();
Log.i(TAG, "--- onMeasure childCount is -->" + childCount);
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 设置每个子视图的大小 , 即全屏
child.measure(MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth, MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
}
} // layout过程
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i(TAG, "--- start onLayout --");
int startLeft = 0; // 每个子视图的起始布局坐标
int startTop = 10; // 间距设置为10px 相当于 android:marginTop= "10px"
int childCount = getChildCount();
Log.i(TAG, "--- onLayout childCount is -->" + childCount);
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
child.layout(startLeft, startTop,
startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth,
startTop + MultiScreenActivity.scrrenHeight);
startLeft = startLeft + MultiScreenActivity.screenWidth ; //校准每个子View的起始布局位置
//三个子视图的在屏幕中的分布如下 [0 , 320] / [320,640] / [640,960]
}
} }
PS :大家可以分别给这几个LinearLayout试着添加几个子View,例如TextView, Button等。
至于Launcher上滑屏功能的实现,我尝试着去掌握,可能天资愚钝吧,对Scoller类很是感冒,现今还没有掌握好,不过在此
给大家推荐几个不错的学习资源 。 以后有需要的话,还是采用拿来主义吧。 囧
1、 Scoller类介绍:android 中文 api (64) —— Scroller
2、相关资源汇总:http://blog.csdn.net/dellheng/article/details/7164275
示例源代码位于: http://download.csdn.net/detail/qinjuning/4054840
Android中滑屏初探 ---- scrollTo 以及 scrollBy方法使用说明的更多相关文章
- android 布局之滑动探究 scrollTo 和 scrollBy 方法使用说明
涉及到滑动,就涉及到VIEW,大家都知道,Android的UI界面都是由一个一个的View以及View的派生类组成,View作为基类,而常用的布局里面的各种布局就是它派生出来的ViewGroup的子类 ...
- Android中滑屏实现----手把手教你如何实现触摸滑屏以及Scroller类详解
前言: 虽然本文标题的有点标题党的感觉,但无论如何,通过这篇文章的学习以及你自己的实践认知,写个简单的滑屏小 Demo还是just so so的. 友情提示: 在继续往下面读之前,希望您对以下知识点 ...
- Android中滑屏实现----触摸滑屏以及Scroller类详解 .
转:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning/article/details/7419207 知识点一: 关于scrollTo()和scrollBy()以及偏移坐标的设置/取值问 ...
- [学习总结]1、View的scrollTo 和 scrollBy 方法使用说明和区别
参考资料:http://blog.csdn.net/vipzjyno1/article/details/24577023 非常感谢这个兄弟! 先查看这2个方法的源码: scrollTo: 1 /** ...
- 【Android 基础】Android中全屏或者取消标题栏
先介绍去掉标题栏的方法: 第一种:也一般入门的时候经常使用的一种方法 requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);//去掉标题栏 注意这句一定要写在se ...
- Android 中Activity生命周期分析:Android中横竖屏切换时的生命周期过程
最近在面试Android,今天出了一个这样的题目,即如题: 我当时以为生命周期是这样的: onCreate --> onStart -- ---> onResume ---> onP ...
- Android中全屏 取消标题栏,TabHost中设置NoTitleBar的三种方法(转)
Android中全屏 取消标题栏,TabHost中设置NoTitleBar的三种方法http://www.cnblogs.com/zdz8207/archive/2013/02/27/android- ...
- Android逆向之旅---Android中锁屏密码算法解析以及破解方案
一.前言 最近玩王者荣耀,下载了一个辅助样本,结果被锁机了,当然破解它很简单,这个后面会详细分析这个样本,但是因为这个样本引发出的欲望就是解析Android中锁屏密码算法,然后用一种高效的方式制作锁机 ...
- android中实现view可以滑动的六种方法
在android开发中,经常会遇到一个view需要它能够支持滑动的需求.今天就来总结实现其滑动的六种方法.其实每一种方法的 思路都是一样的,即:监听手势触摸的坐标来实现view坐标的变化,从而实现vi ...
随机推荐
- 李洪强漫谈iOS开发[C语言-016]-变量的作用域
- cocos-html5 Json 灵活 遍历方式 不同方式的缺陷,优点总结
1,四种解析Json的方式:Part 1 var list1 = [1,3,4]; alert(list1[1]); var list2 = [{"name":"leam ...
- easyui源码翻译1.32--ComboGrid(数据表格下拉框)
前言 扩展自$.fn.combo.defaults和$.fn.datagrid.defaults.使用$.fn.combogrid.defaults重写默认值对象.下载该插件翻译源码 数据表格下拉框结 ...
- *[codility]ArrayInversionCount
http://codility.com/demo/take-sample-test/arrayinversioncount 求逆序对数,归并排序并记录逆序次数. // you can also use ...
- 奇怪的JS
有的时候发现JS是一门很高深的语言,不是我等俗人可以学会,没有private,没有public不说,居然连Class都没有,这个世界就是这样,有的东西你不一定非要想通,也不一定非要剖根问底,有的时候你 ...
- webstore+nodejs
新建一个普通的project. 编写如下代码: var http=require('http'); http.createServer(function(req,res){ res.writeHead ...
- [译]GotW #6b Const-Correctness, Part 2
const和mutable对于书写安全代码来说是个很有利的工具,坚持使用它们. Problem Guru Question 在下面代码中,在只要合适的情况下,对const进行增加和删除(包括 ...
- Linux 启动参数介绍
Linux 启动参数介绍 取自2.6.18 kernel Documentation/i386/boot.txt 文件中介绍 vga= 这里的不是一个整数(在C语言表示法中,应是十进制,八进制或者十六 ...
- SSH框架应用中常用Jar包用途介绍
struts2需要的几个jar包:1)xwork-core-2.1.62)struts2-core-2.1.83)ognl-2.7.34)freemarker-2.3.155)commons-io-1 ...
- bzoj3165 1568
1568是3165的弱化版,发的代码是3165的这道题完全没想出来,是看wyl大神的题解http://hi.baidu.com/wyl8899/item/2deafd3a376ef2d46d15e99 ...
