Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws
Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws
你能区分异常和错误吗?
我们每天上班,正常情况下可能30分钟就能到达。但是由于车多,人多,道路拥挤,致使我们要花费更多地时间,这就是生活中的异常!
程序和生活一样都会出现异常,先来看个异常:

上面出现的是算数错误的异常。
在java中,除去一些编译上的错误(语法)之外,就有异常和错误!
异常的定义是可自己进行处理后,程序依然可以正常运行下去!错误是Java虚拟机抛出的,终止程序的运行,这就是程序和异常的区别。
一:什么是异常处理?
异常处理机制就像我们对平时可能遇到的意外情况,预先想好了一些处理的办法。也就是说,在程序执行代码的时候,万一发生了异常,程序会按照预定的处理办法对异常进行处理,异常处理完毕后,程序继续运行。
java的异常处理是通过5个关键字来实现的:try、catch、finally、throw、throws。
二:java异常类的层次结构
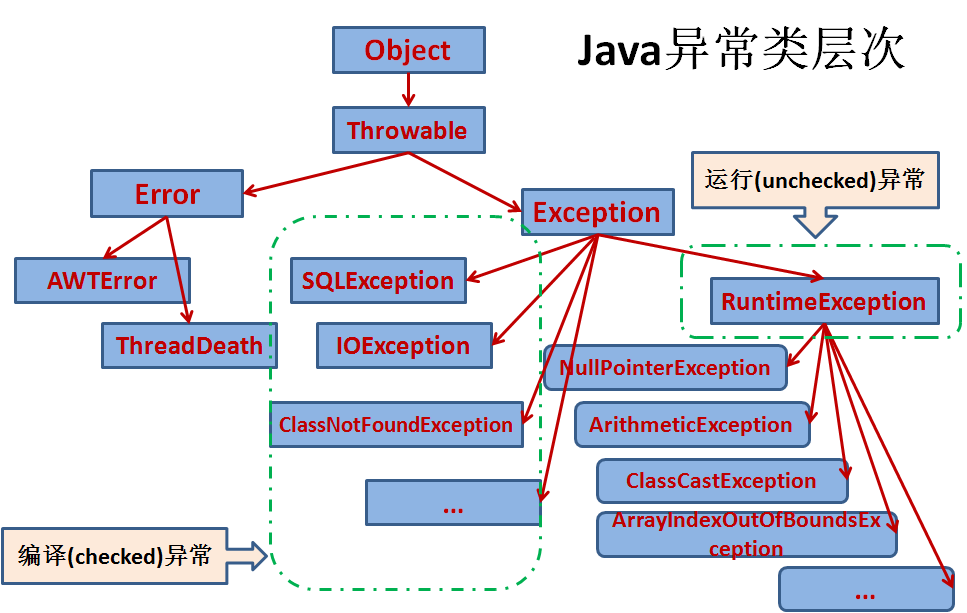
三.常见的异常类型
Exception 异常层次结构的根类
ArithmeticException 算数错误情形
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组下标越界
NullPointerException 尝试访问null对象成员
ClassNotFoundException 不能加载所需的类
InputMismatchException 欲得到的数据类型与实际输入的类型不匹配
IllegalArgumentException 方法接受到非法参数
ClassCastException 对象强制类型转换出错
NumberFormatException 数字格式转换异常
四.具体实例
- try—catch
package Test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
try {
int num1=input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入除数:");
int num2=input.nextInt();
System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
num1, num2, num1 / num2));
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("出现错误:被除数和除数必须是整数,"+
"除数不能为零。");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
运行结果如下:
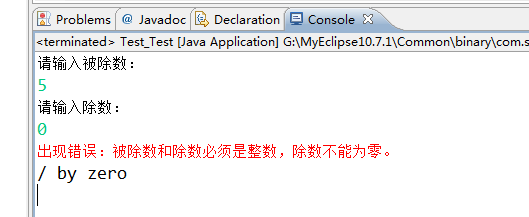
System.err.println();这种输出方式可以输出错误的消息,在控制台呈现红色。
System.out用于正常的输出,也就是程序真正想输出的内容。而System.err用于出错信息的输出,也就是你本来不期待看到的东西。
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
这行的作用是——返回该错误的详细信息的字符串。
- try-catch-finally
package Test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
try {
int num1=input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入除数:");
int num2=input.nextInt();
System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
num1, num2, num1 / num2));
}catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("出现错误:被除数和除数必须是整数,"+
"除数不能为零。");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
finally{
System.out.println("Thanks");
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
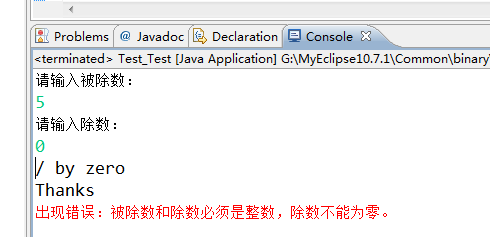
try-catch-finally 程序块的流程大致分为两种情况:
- 如果try块中所有语句正常执行完毕,那么finally块就会被执行。
- 如果try语句在执行过程中碰到异常,无论这种异常能否被catch块捕获到,都将执行finally块中的代码。
try-catch-finally结构中try块是必须有的,catch和finally块为可选,但两者至少必须出现其中之一。
- try—catch-catch-finally(多重catch块)
package Test; import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入被除数:");
try {
int num1=input.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入除数:");
int num2=input.nextInt();
System.out.println(String.format("%d / %d = %d",
num1, num2, num1 / num2));
}catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.err.println("被除数和除数必须是整数。");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为零。");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("其他未知异常。");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
finally{
System.out.println("Thanks");
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
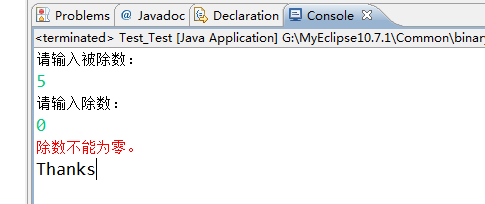
所以,在写异常处理的时候,一定要把异常范围小的放在前面,范围大的放在后面,Exception这个异常的根类一定要刚在最后一个catch里面,如果放在前面或者中间,任何异常都会和Exception匹配的,就会报已捕获到...异常的错误。
下面是try-catch-finally中包含return的情况:
- 情况一:try{} catch(){}finally{} return;
正常按程序顺序执行即可。
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 1;
try
{
x++;
System.out.println("我有用!");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("我没用!");
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("我也有用!");
}
return 2;
}
}
运行结果如下:
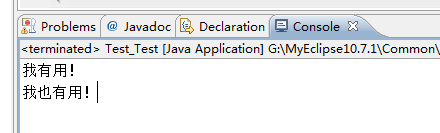
- 情况2:try{ return; }catch(){} finally{} return;
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,最后执行try中return;
finally块之后的语句return,因为程序在try中已经return所以不再执行。
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 1;
try
{
x++;
System.out.println("我有用!");
return 6;
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("我没用!");
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("我也有用!");
}
return 2;
}
}
运行结果如下:
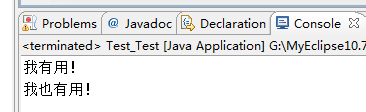
- 情况3:try{} catch(){return;} finally{} return;
程序先执行try,如果遇到异常执行catch块,
有异常:则执行catch中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码,再执行finally语句中全部代码,
最后执行catch块中return. finally之后也就是4处的代码不再执行。
无异常:执行完try再finally再return.
1.有异常的情况:
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
int num=x / 0;
System.out.println(num);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
return 6;
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
}
return 2;
}
}
运行结果如下:
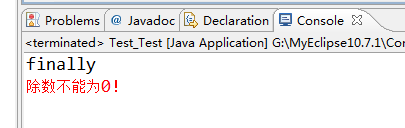
2.无异常的情况:
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
System.out.println("try");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
return 6;
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
}
return 2;
}
}
运行结果如下:
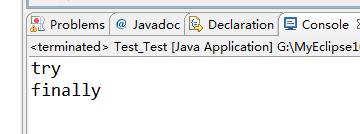
- 情况4:try{ return; }catch(){} finally{return;}
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
int num = x / 0;
System.out.println("try");
return 3;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
return 2;
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
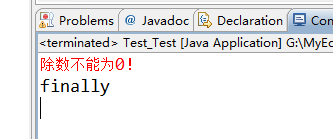
- 情况5:try{} catch(){return;}finally{return;}
程序执行catch块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
int num = x / 0;
System.out.println("try");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
return 4;
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
return 2;
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
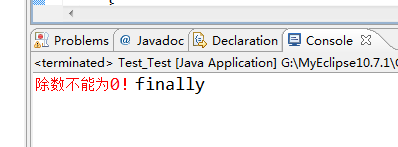
- 情况6:try{ return;}catch(){return;} finally{return;}
程序执行try块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
有异常:执行catch块中return之前(包括return语句中的表达式运算)代码;
则再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
无异常:则再执行finally块,因为finally块中有return所以提前退出。
1.有异常
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
int num = x / 0;
System.out.println("try");
return 4;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
return 4;
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
return 2;
}
}
}
运行结果如下:

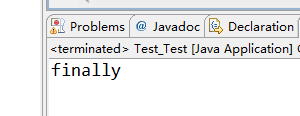
2.无异常
package Test;
public class Test_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1();
}
public static int Test1(){
int x = 5;
try
{
// int num = x / 0;
// System.out.println("try");
return 4;
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.err.println("除数不能为0!");
return 4;
}
finally
{
++x;
System.out.println("finally");
return 2;
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
最终结论:任何执行try 或者catch中的return语句之前,都会先执行finally语句,如果finally存在的话。
如果finally中有return语句,那么程序就return了,所以finally中的return是一定会被return的,
编译器把finally中的return实现为一个warning。
- throw——抛出异常
抛出异常有三种形式,一是throw,一个throws,还有一种系统自动抛异常。
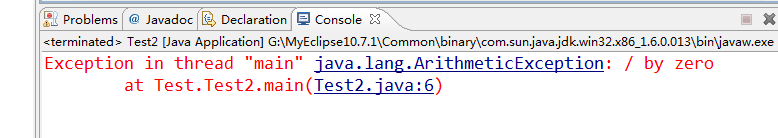
系统抛出异常:
package Test;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5, b =0;
System.out.println(5/b);
}
}
运行结果如下:
throw抛出异常:
throw是语句抛出一个异常。
语法:throw (异常对象);
package Test;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc";
if(s.equals("abc")) {
throw new NumberFormatException();
} else {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
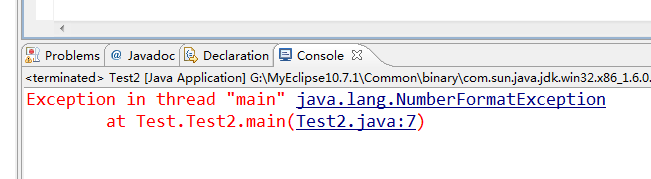
- throws——声明异常
throws是方法可能抛出异常的声明。(用在声明方法时,表示该方法可能要抛出异常)
语法:[(修饰符)](返回值类型)(方法名)([参数列表])[throws(异常类)]{......}
package Test;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Test3();
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.err.println("非数据类型不能转换。");
}
}
public static void Test3() throws NumberFormatException{
String s = "abc";
System.out.println(Double.parseDouble(s));
}
}
运行结果如下:
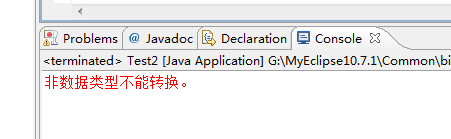
如果在一个方法体中抛出了异常,那么我们就可以通过throws——声明异常来通知调用者,非常方便。
throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常;throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常对象。
最后说一句,try-catch-finally虽好用,但是如果是滥用,这样只是会让程序的可读性变的很糟糕,当程序报错,就无法快速准确的定位了,物尽其用 人尽其才嘛!
Java异常之try,catch,finally,throw,throws的更多相关文章
- 顺平讲try catch finally throw throws(精华)
try catch finally 有点像if else语句 还有像javascript的服务器执行成功后的回调函数,success:function(){ 进行处理 }; throws的意思是将异 ...
- 基础知识《十》java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗?
本文转载自 java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗? 前言:java 中的异常处理机制你真的理解了吗?掌握了吗?catch 体里遇到 return 是怎么处理 ...
- java:异常机制(try,catch,finally,throw,throws,自定义异常)
* String类中的格式化字符串的方法: * public static String format(String format, Object... args):使用指定的格式字符串和参数返回一个 ...
- Java异常机制关键字总结,及throws 和 throw 的区别
在Java的异常机制中,时常出现五个关键字:try , catch , throw , throws , finally. 下面将总结各个关键字的用法,以及throw和throws的区别: (1) t ...
- Java基础-异常处理机制 及异常处理的五个关键字:try/catch/finally/throw /throws
笔记: /** 异常处理机制: 抓抛模型 * 1."抛", 一旦抛出,程序终止! printStackTrace()显示异常路径! * 2."抓", 抓住异常 ...
- java 异常捕捉 ( try catch finally ) 你真的掌握了吗?
掌握下面几条原则就可以完全解决“当try.catch.finally遭遇return”的问题. 原则:1.finally语句块中的代码是一定会执行的,而catch块中的代码只有发生异常时才会执行. 2 ...
- Java异常01——捕获和抛出异常
捕获和抛出异常 异常处理五个关键字 try , catch , finally , throw , throws try catch finally(快捷键:选中要要监控的代码语句 快捷键: ctrl ...
- 菜鸡的Java笔记 第三十 - java 异常的捕获及处理
异常的捕获及处理 1.异常的产生分析以及所带来的影响 2.异常的处理的基本格式 3.异常的处理流程 4.异常的处理模式 5.自定义 ...
- java异常——Exception、RuntimException
一.Exception和RuntimeException的区别 Exception是RuntimeException的父类,使用了 Exception 的类都必须对异常进行处理(try / throw ...
随机推荐
- 关于如何设置reduce的个数
在默认情况下,一个MapReduce Job如果不设置Reducer的个数,那么Reducer的个数为1.具体,可以通过JobConf.setNumReduceTasks(int numOfReduc ...
- poj 2778 DNA Sequence AC自动机
DNA Sequence Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 11860 Accepted: 4527 Des ...
- 实现pushViewController:animated:的不同页面转换特效
1. 首先要明确的是,不使用pushViewController的默认动画,所以在调用这个函数时,要将animated设置为NO.2. 使用普通的来CATransition实现转换效果,代码如下:CA ...
- Activity 怎样获得另一个xml布局文件的控件
两个布局文件,一个main.xml,一个main2.xml,一个MActivity,在MActivity的onCreate()里设置的是setContentView(R.layout.main).现在 ...
- Delphi中禁止WebBrowser右键的方法
uses MSHtml; //在控件标签additional中找到TApplicationEvents控件,拖到窗体上.在TApplicationEvents的OnMessage事件中加入以下代码: ...
- git reset到之前的某一个commit或者恢复之前删除的某一个分支
一.使用了git reset之后,想要找回某一个commit 1.git log -g 这个命令只能显示少部分的commit 推荐使用git reflog 找到想要恢复的那个commit的hash, ...
- HDU 5912 Fraction 【模拟】 (2016中国大学生程序设计竞赛(长春))
Fraction Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- HDU-2576 Tug of War
http://poj.org/problem?id=2576 二维数组01背包的变形. Tug of War Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Tot ...
- 使用VisualStudio进行单元测试之四 顺序测试
前文中所提到的测试都是针对一个方法进行的独立测试,即使是同事测试多个方法,他们之间也没有影响.但是在实际的生产过程中,更多的情况是方法与方法之间是存在相互的逻辑关系的,所以也就有了今天要介绍的顺序测试 ...
- supesite 模板相关文档记录
文件说明:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/69c07820af45b307e87197ac.html 开发文档:http://wenku.baidu.com/view/35f6 ...
