SVM实践
在Ubuntu上使用libsvm(附上官网链接以及安装方法)进行SVM的实践:
1、代码演示:(来自一段文本分类的代码)
# encoding=utf8
__author__ = 'wang'
# set the encoding of input file utf-8
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf-8')
import os
from svmutil import *
import subprocess # get the data in svm format
featureStringCorpusDir = './svmFormatFeatureStringCorpus/'
fileList = os.listdir(featureStringCorpusDir)
# get the number of the files
numFile = len(fileList)
trainX = []
trainY = []
testX = []
testY = []
# enumrate the file
for i in xrange(numFile):
# print i
fileName = fileList[i]
if(fileName.endswith(".libsvm")):
# check the data format
#
checkdata_py = r"./tool/checkdata.py"
# the file name
svm_file = featureStringCorpusDir + fileName
cmd = 'python {0} {1} '.format(checkdata_py, svm_file)
# print ("excute '{}'".format(cmd))
# print('Check Data...')
check_data = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell = True, stdout = subprocess.PIPE)
(stdout, stderr) = check_data.communicate()
returncode = check_data.returncode
if returncode == 1:
print stdout
exit(1) y, x = svm_read_problem(svm_file)
trainX += x[:100]
trainY += y[:100]
testX += x[-1:-6:-1]
testY += y[-1:-6:-1] print testX
# train the c-svm model
m = svm_train(trainY, trainX, '-s 0 -c 4 -t 2 -g 0.1 -e 0.1')
# predict the test data
p_label, p_acc, p_val = svm_predict(testY, testX, m)
# output the result to the file
result_file = open("./result.txt","w")
result_file.write( "testY p_label p_val\n")
for c in xrange(len(p_label)):
result_file.write( str(testY[c]) + " " + str(p_label[c]) + " " + str(p_val[c]) + "\n")
result_file.write( "accuracy: " + str(p_acc) + "\n")
result_file.close()
# print p_val
(1)关于训练数据的格式:
The format of training and testing data file is: <label> <index1>:<value1> <index2>:<value2> ..
.
.
. Each line contains an instance and is ended by a '\n' character. For
classification, <label> is an integer indicating the class label
(multi-class is supported)(如何label是个非数值的,将其转化为数值型). For regression, <label> is
the target value which can be any real number. For one-class SVM, it's not used
so can be any number. The pair <index>:<value> gives a feature (attribute) value:
<index> is an integer starting from 1 and <value> is a real number. The only exception
is the precomputed kernel, where <index> starts from 0; see the section of precomputed kernels.
Indices must be in ASCENDING order(要升序排序). Labels in the testing file are only used to calculate accuracy
or errors. If they are unknown, just fill the first column with any numbers. A sample classification data included in this package is `heart_scale'. To check if your data is
in a correct form, use `tools/checkdata.py' (details in `tools/README'). Type `svm-train heart_scale', and the program will read the training
data and output the model file `heart_scale.model'. If you have a test
set called heart_scale.t, then type `svm-predict heart_scale.t
heart_scale.model output' to see the prediction accuracy. The `output'
file contains the predicted class labels. For classification, if training data are in only one class (i.e., all
labels are the same), then `svm-train' issues a warning message:
`Warning: training data in only one class. See README for details,'
which means the training data is very unbalanced. The label in the
training data is directly returned when testing.
(2)svm训练的参数解释来自官方的github:https://github.com/cjlin1/libsvm
`svm-train' Usage
================= Usage: svm-train [options] training_set_file [model_file]
options:
-s svm_type : set type of SVM (default 0)
0 -- C-SVC (multi-class classification)
1 -- nu-SVC (multi-class classification)
2 -- one-class SVM
3 -- epsilon-SVR (regression)
4 -- nu-SVR (regression)
-t kernel_type : set type of kernel function (default 2)
0 -- linear: u'*v
1 -- polynomial: (gamma*u'*v + coef0)^degree
2 -- radial basis function: exp(-gamma*|u-v|^2)
3 -- sigmoid: tanh(gamma*u'*v + coef0)
4 -- precomputed kernel (kernel values in training_set_file)
-d degree : set degree in kernel function (default 3)
-g gamma : set gamma in kernel function (default 1/num_features)
-r coef0 : set coef0 in kernel function (default 0)
-c cost : set the parameter C of C-SVC, epsilon-SVR, and nu-SVR (default 1)
-n nu : set the parameter nu of nu-SVC, one-class SVM, and nu-SVR (default 0.5)
-p epsilon : set the epsilon in loss function of epsilon-SVR (default 0.1)
-m cachesize : set cache memory size in MB (default 100)
-e epsilon : set tolerance of termination criterion (default 0.001)
-h shrinking : whether to use the shrinking heuristics, 0 or 1 (default 1)
-b probability_estimates : whether to train a SVC or SVR model for probability estimates, 0 or 1 (default 0)
-wi weight : set the parameter C of class i to weight*C, for C-SVC (default 1) (当数据不平衡时,可给不同的类设置不用的惩罚)
-v n: n-fold cross validation mode
-q : quiet mode (no outputs) The k in the -g option means the number of attributes in the input data. option -v randomly splits the data into n parts and calculates cross
validation accuracy/mean squared error on them. See libsvm FAQ for the meaning of outputs. `svm-predict' Usage
=================== Usage: svm-predict [options] test_file model_file output_file
options:
-b probability_estimates: whether to predict probability estimates, 0 or 1 (default 0); for one-class SVM only 0 is supported model_file is the model file generated by svm-train.
test_file is the test data you want to predict.
svm-predict will produce output in the output_file.
注:
nu-SVR: nu回归机。引入能够自动计算epsilon的参数nu。若记错误样本的个数为q ,则nu大于等于q/l,即nu是错误样本的个数所占总样本数的份额的上界;若记支持向量的个数为p,则nu小于等于p/l,即nu是支持向量的个数所占总样本数的份额的下界。首先选择参数nu和C,然后求解最优化问题。
Shrinking: 即参数-h, 优化求解过程中是否采用shrinking. 边界支持向量BSVs(ai=C的SV)在迭代过程中ai不会变化,如果找到这些点,并把它们固定为C,可以减少QP的规模。
2、运行结果展示并分析部分参数的意思:
*
optimization finished, #iter = 119
nu = 0.272950
obj = -122.758206, rho = -1.384603
nSV = 127, nBSV = 21
* ..............(此处省略部分) *
optimization finished, #iter = 129
nu = 0.214275
obj = -89.691907, rho = -1.105131
nSV = 103, nBSV = 8
*
optimization finished, #iter = 77
nu = 0.147922
obj = -67.825431, rho = 0.984237
nSV = 80, nBSV = 10
Total nSV = 1246
Accuracy = 51.4286% (36/70) (classification)
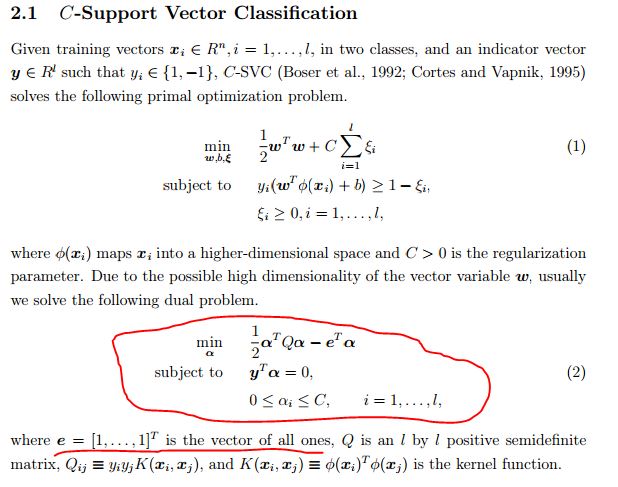
官方解释:obj is the optimal objective value of the dual SVM problem(obj表示SVM最优化问题对偶式的最优目标值,公式如下图的公式(2)). rho is the bias term in the decision function sgn(w^Tx - rho). nSV and nBSV are number of support vectors and bounded support vectors (i.e., alpha_i = C). nu-svm is a somewhat equivalent form of C-SVM where C is replaced by nu. nu simply shows the corresponding parameter. More details are in libsvm document.
SVM实践的更多相关文章
- SVM 实践步骤
主要公式步骤: 原距离问题的函数: 1.将SVM的距离问题转化为拉格朗日函数: 2.原函数问题化成如下问题: 3.对各非拉格朗日参数求偏导来求min值: 4.将上面 令各偏导等于0 的结果带回 拉 ...
- python就业班-淘宝-目录.txt
卷 TOSHIBA EXT 的文件夹 PATH 列表卷序列号为 AE86-8E8DF:.│ python就业班-淘宝-目录.txt│ ├─01 网络编程│ ├─01-基本概念│ │ 01-网络通信概述 ...
- 机器学习算法与Python实践之(四)支持向量机(SVM)实现
机器学习算法与Python实践之(四)支持向量机(SVM)实现 机器学习算法与Python实践之(四)支持向量机(SVM)实现 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- 机器学习算法与Python实践之(三)支持向量机(SVM)进阶
机器学习算法与Python实践之(三)支持向量机(SVM)进阶 机器学习算法与Python实践之(三)支持向量机(SVM)进阶 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- 机器学习算法与Python实践之(二)支持向量机(SVM)初级
机器学习算法与Python实践之(二)支持向量机(SVM)初级 机器学习算法与Python实践之(二)支持向量机(SVM)初级 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- LibLinear(SVM包)使用说明之(三)实践
LibLinear(SVM包)使用说明之(三)实践 LibLinear(SVM包)使用说明之(三)实践 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 我们在U ...
- 机器学习算法实践:Platt SMO 和遗传算法优化 SVM
机器学习算法实践:Platt SMO 和遗传算法优化 SVM 之前实现了简单的SMO算法来优化SVM的对偶问题,其中在选取α的时候使用的是两重循环通过完全随机的方式选取,具体的实现参考<机器学习 ...
- 4、2支持向量机SVM算法实践
支持向量机SVM算法实践 利用Python构建一个完整的SVM分类器,包含SVM分类器的训练和利用SVM分类器对未知数据的分类, 一.训练SVM模型 首先构建SVM模型相关的类 class SVM: ...
- 机器学习(四):通俗理解支持向量机SVM及代码实践
上一篇文章我们介绍了使用逻辑回归来处理分类问题,本文我们讲一个更强大的分类模型.本文依旧侧重代码实践,你会发现我们解决问题的手段越来越丰富,问题处理起来越来越简单. 支持向量机(Support Vec ...
随机推荐
- 《CMake实践》笔记三:构建静态库(.a) 与 动态库(.so) 及 如何使用外部共享库和头文件
<CMake实践>笔记一:PROJECT/MESSAGE/ADD_EXECUTABLE <CMake实践>笔记二:INSTALL/CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX &l ...
- jquery解析php通过ajax传过来的json二维数组对象
ajax获得php传过来的json二维数组对象,jquery解析 php代码: <?php $news = array( '武汉'=>array(1,2,3), '广州'=>arra ...
- php实战开发之自我整理(学习笔记)
PHP没有创建变量的命令,变量会在首次赋值时进行创建. 简单样例 1 <?php $word="My first choice"; $x=5; echo $x; echo & ...
- JavaScript深入浅出6-函数和作用域
慕课网教程视频地址:Javascript深入浅出 函数的概念:定义一次可调用多次的javascript代码段 创建函数:声明 function fuc(){} 声明前置 表达式 var fuc= ...
- AngularJS 分页
前端源码: <div> <h1>列表页33</h1> <table> <thead> <tr><td>CandiID ...
- Javascript 执行环境及作用域
执行环境是javascript中最为重要的一个概念. 执行环境定义了变量或函数有权访问的其他数据,决定了他们各自的行为. 每个执行环境都有一个与之关联的变量对象(variable object),环境 ...
- jquery 控件赋值
input 文本框赋值$("#id").attr("赋值"); input 文本框清空$("#id").attr("") ...
- 解决IE8 内置JSON.stringify,中文变unicode的问题
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/919074/blog/191131 项目中出现在IE下出现把json对象转为json串中文变成unicode的问题,最后经过排查,发现是IE8内 ...
- error LNK2019:unresolved external symbol
error LNK2019:unresolved external symbol 这个错误是指程序不认识函数.具体的说就是.h文件中定义并没有实现,这就是库出现了问题. 遇到这个问题,第一步就要看是哪 ...
- Linux搭建JDK、Tomcat安装及配置
一.JDK安装及配置 1.JKD下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i5NpImx 2.查看安装: rpm -qa | grep jdk 3.卸载:rpm -e --nodeps ...
