Spring-boot:快速搭建微框架服务
前言:
Spring Boot是为了简化Spring应用的创建、运行、调试、部署等而出现的,使用它可以做到专注于Spring应用的开发,而无需过多关注XML的配置。
简单来说,它提供了一堆依赖打包,并已经按照使用习惯解决了依赖问题---习惯大于约定。
Spring Boot默认使用tomcat作为服务器,使用logback提供日志记录。
Spring Boot的主要优点:
- 为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化Web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
技术栈:
- Java 8
- Maven
- Spring-boot
- Mybatis
- Redis
- Lombok
- Swagger2
- Jenkins
- SonarQuber
1、使用Maven构建项目
1.1 通过 SPRING INITIALIZR 工具生产基础项目
通过访问:http://start.spring.io/ 快速创建Spring-boot 的服务框架。

初始化相应信息后,下载压缩包。解压完成后,用IDEA打开项目,项目的目录结构:
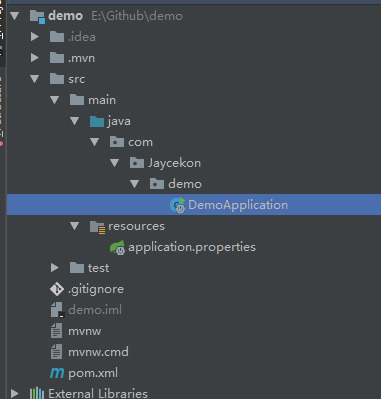
总体流程:
- 访问:
http://start.spring.io/ - 选择构建工具
Maven Project、Spring Boot版本1.3.2以及一些工程基本信息 - 点击
Generate Project下载项目压缩包
解压项目包,并用IDE以Maven项目导入,以IntelliJ IDEA 14为例:
- 菜单中选择
File–>New–>Project from Existing Sources... - 选择解压后的项目文件夹,点击
OK - 点击
Import project from external model并选择Maven,点击Next到底为止。 - 若你的环境有多个版本的JDK,注意到选择
Java SDK的时候请选择Java 7以上的版本
1.2 导入Spring-boot 相关依赖
项目初始化时,相关依赖如下:
- spring-boot-starters:核心模块,包括自动配置支持、日志和YAML
- spring-boot-starter-test:测试模块,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito
- spring-boot-devtools:用于设置热部署
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
这里我们需要引入Web模块,需要添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.3 启动项目
添加首页控制层:
@RestController
public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("index")
public String index() {
return "hello world!";
}
}
运行DemoApplication中的main方法,启动服务:
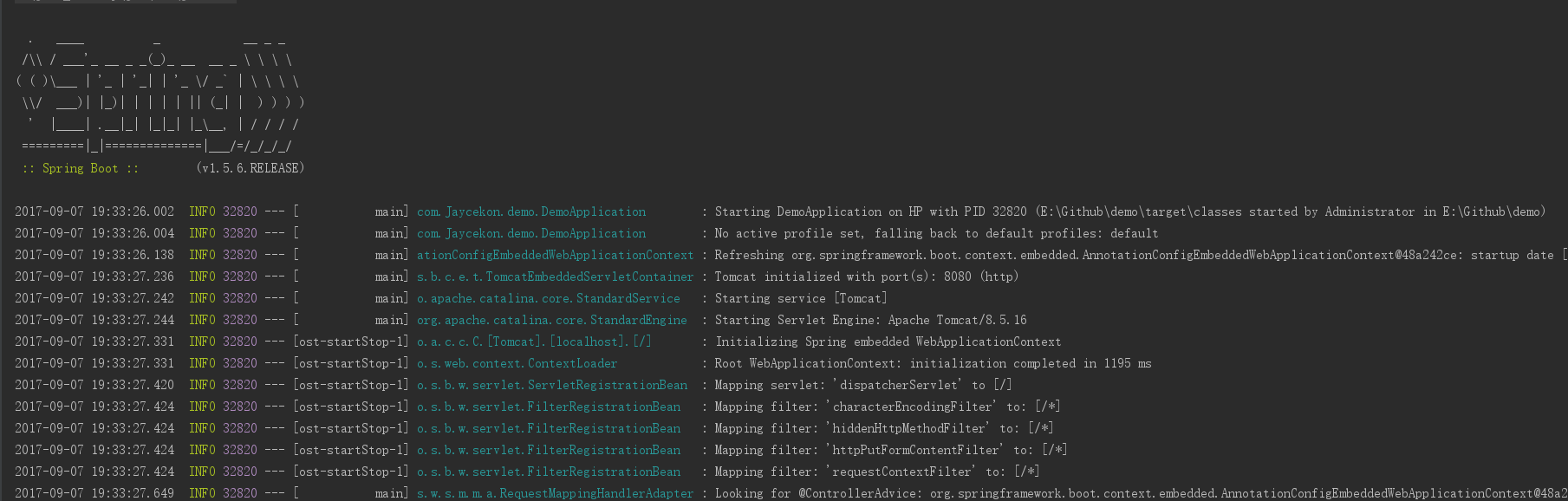
服务启动后, 访问 http://localhost:8080/index ,可以看到页面输出Hello world!。
2、整合Mybatis
2.1 项目依赖
- 引入连接mysql的必要依赖mysql-connector-java
- 引入整合MyBatis的核心依赖mybatis-spring-boot-starter
- 引入tk.mybatis 依赖,实现对实体类的增删改查的代码
- 引入pagerhelper 依赖,实现分页功能
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.43</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--pagehelper-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
2.2 项目配置
修改resources 下的application.properties文件:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #实体类扫描包
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.jaycekon.demo.model
#Mapper.xml文件扫描目录
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
#驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.mapUnderscoreToCamelCase=true #tkmapper 工具类
mapper.mappers=com.Jaycekon.demo.util.MyMapper
mapper.not-empty=false
mapper.identity=MYSQL
pagehelper.helperDialect=mysql
pagehelper.reasonable=true
pagehelper.supportMethodsArguments=true
pagehelper.params=count=countSql
2.3 单元测试
创建实体类,我们引入Lombok相关依赖,用于避免数据Get Set方法的重复创建:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.18</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
实体类最终的代码如下:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String idCard;
private String phone;
private String password;
}
可以看出,在添加了Lombok 之后,我们的Java 实体类代码简洁了很多。
接下来,我们需要创建UserMapper 数据库处理类。由于MyMapper 已经帮我们实现了基本的CRUD操作,因此我们这里并不需要再重写操作,我可以先一个根据用户名查找的方法:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends MyMapper<User> { @Select("select * from user where username=#{username}")
User selectByName(String username);
}
MyMapper 类位于util 目录下:
public interface MyMapper<T> extends Mapper<T>, MySqlMapper<T> {
}
这里需要注意,MyMapper 与我们的实体类Mapper 不能放在同一个目录。
测试类:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@MapperScan("com.Jaycekon.demo.mapper")
public class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper mapper; @Test
public void testInset() {
User user = new User(1, "Jaycekon","1234","1234","123");
int i = mapper.insert(user);
Assert.assertNotEquals(0, i);
} @Test
public void testSelect(){
User user = mapper.selectByName("Jaycekon");
Assert.assertNotEquals(null,user);
}
}
3、整合Redis
3.1 相关依赖
Spring Boot提供的数据访问框架Spring Data Redis基于Jedis。可以通过引入 spring-boot-starter-redis 来配置依赖关系。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
3.2 Redis 配置
1、Spring-boot 连接单机版Redis 的配置如下:
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=0
2、Spring-boot 连接Sentinel 哨兵集群配置:
# REDIS (RedisProperties)
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
#spring.redis.host=localhost
# Redis服务器连接端口
#spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=0 #哨兵监听redis server名称
spring.redis.sentinel.master=cn-test-master
#哨兵的配置列表
spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=localhost:26379,localhost:36379,localhost:46379
3.3 Redis 操作工具类
1、StringRedisTemplate 工具类
StringRedisTemplate 工具类可以解决字符串级别的Redis操作。在写好配置后,可以直接通过Autowried 就可以注入对象。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(Application.class)
public class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
// 保存字符串
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("aaa", "111");
Assert.assertEquals("111", stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("aaa"));
}
}
2、RedisTemplate<Object,Object> 工具类
可以处理大部分的序列化操作,在这里我封装了一个简化Redis工具类,后续可以继续优化。
@Component
public class RedisComponent {
@Autowired
//操作字符串的template,StringRedisTemplate是RedisTemplate的一个子集
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisComponent.class); @Autowired
// RedisTemplate,可以进行所有的操作
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate; public void set(String key, String value) {
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = this.stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
boolean bExistent = this.stringRedisTemplate.hasKey(key);
if (bExistent) {
logger.info("this key is bExistent!");
} else {
ops.set(key, value);
}
} public String get(String key) {
return this.stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
} public void del(String key) {
this.stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
} public void sentinelSet(String key, Object object) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSON.toJSONString(object));
} public String sentinelGet(String key) {
return String.valueOf(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key));
}
}
4、整合Swagger2
4.1 添加Swagger2 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>
4.2 创建Swagger2 配置类:
在Application.java 同级创建一个Swagger2 的配置类:
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2 { @Bean
public Docket webApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.groupName("DemoAPI接口文档")
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.Jaycekon.demo.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
} /**
swagger2使用说明:
@Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
@ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
@ApiIgnore:使用该注解忽略这个API
@ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
path(用于restful接口)-->请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
body(不常用)
form(不常用)
name:参数名
dataType:参数类型
required:参数是否必须传
value:参数的意思
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
*/
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("Demo使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
.description("微信打卡服务")
.contact(new Contact("Jaycekon", "http://petstore.swagger.io/v2/swagger.json", "jaycekon@163.com"))
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
4.3 在需要生成Api 的接口添加注解:
@Api(tags = "测试用例")
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/users") // 通过这里配置使下面的映射都在/users下,可去除
public class UserController { @ApiOperation(value="获取用户列表", notes="")
@RequestMapping(value={""}, method= RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUserList() {
return new ArrayList<>();
} @ApiOperation(value="创建用户", notes="根据User对象创建用户")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
@RequestMapping(value="", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String postUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return "success";
} @ApiOperation(value="获取用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来获取用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long")
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return new User();
} @ApiOperation(value="更新用户详细信息", notes="根据url的id来指定更新对象,并根据传过来的user信息来更新用户详细信息")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long"),
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "user", value = "用户详细实体user", required = true, dataType = "User")
})
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody User user) {
return "success";
} @ApiOperation(value="删除用户", notes="根据url的id来指定删除对象")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "用户ID", required = true, dataType = "Long")
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
return "success";
} }
完成上述代码添加上,启动Spring Boot程序,访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
。就能看到前文所展示的RESTful API的页面。我们可以再点开具体的API请求,以POST类型的/users请求为例,可找到上述代码中我们配置的Notes信息以及参数user的描述信息,如下图所示。
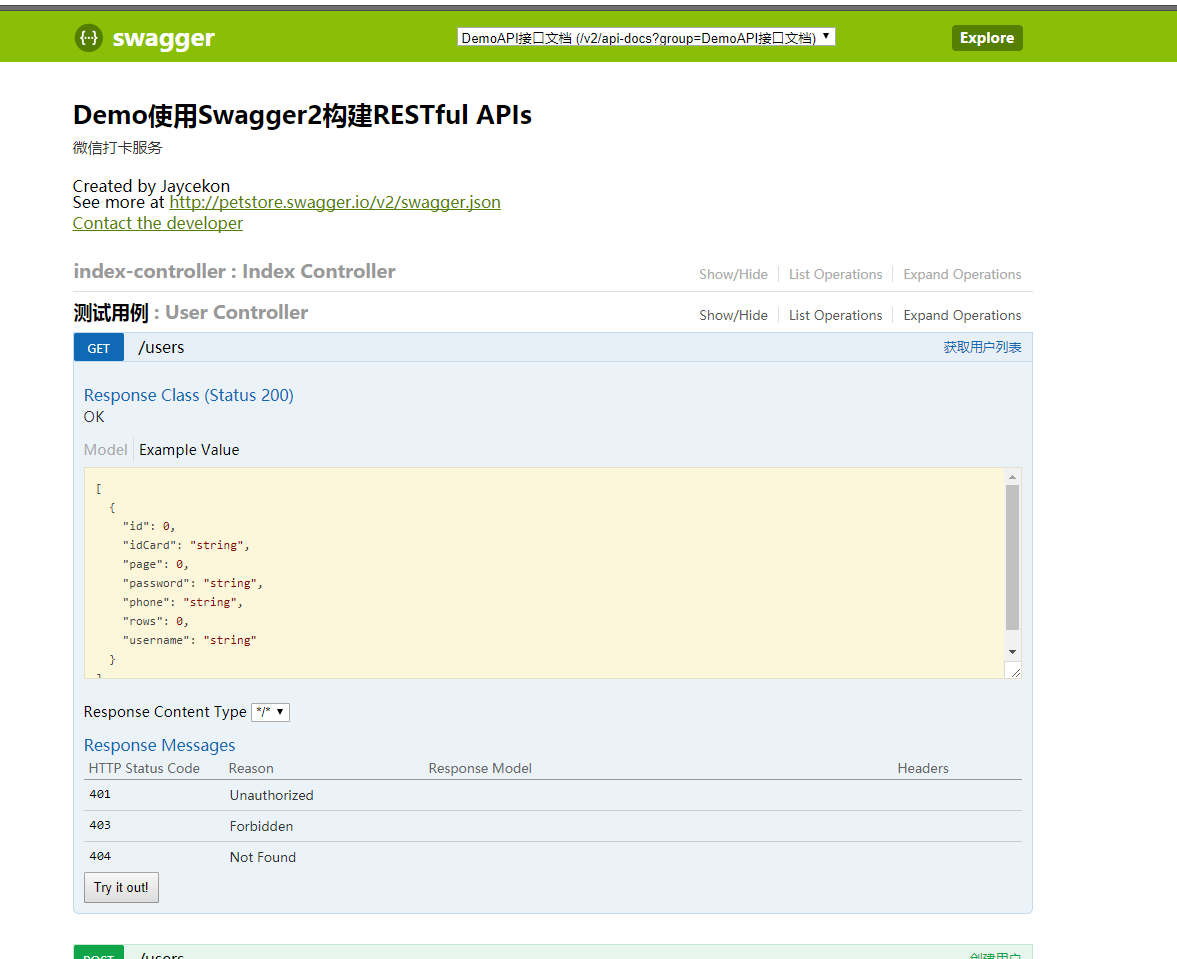
4、接入Jenkins&SonarQube
项目框架搭建好后,我们可以通Jenkins 进行项目的自动发版,以及SonarQube 进行代码质量检测。在接入钱,我们需要将项目打包成war包,需要进行以下修改:
1、修改项目打包类型:
<groupId>com.Jaycekon</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
2、修改Application.java 文件:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer { @Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(DemoApplication.class);
} public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
在我的上一篇博客,哆啦A梦的传送门,已经讲解了一些基本配置方法,这里为大家讲解一下,接入SonarQube 进行代码质量检测的配置(需要本地安装SonarQube服务)。
首先需要在MetaData 中,加入SonarQube 的项目名(新建的命名):
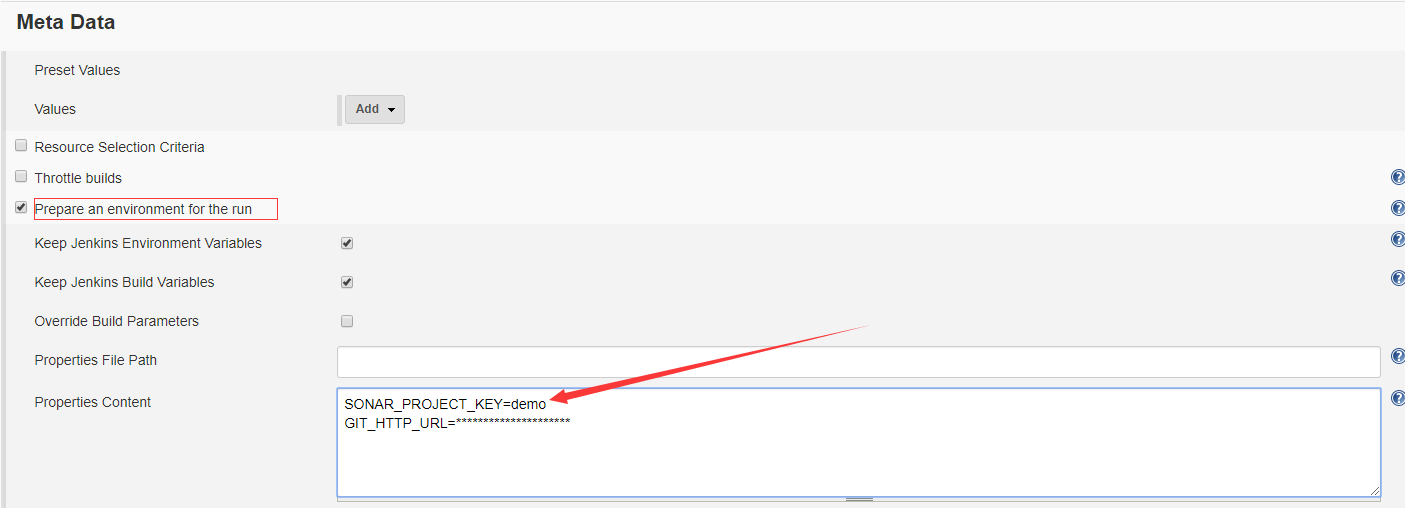
然后在Post Steps 中选择添加 Execute SonarQube Scanner:
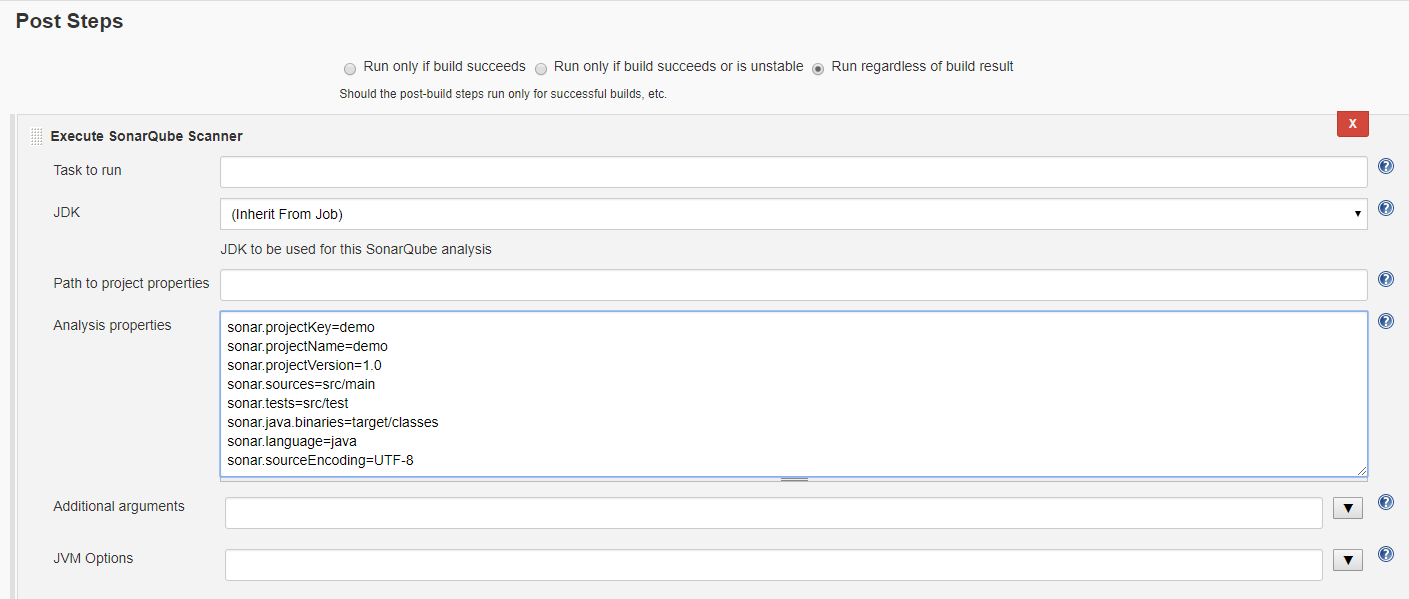
在配置好这两项后,Jenkins 在编译文件时,就会执行SonarQube 代码质量检测。
最后,我们可以设置项目在编译完后,执行shell 脚本,进行项目的自动发版:
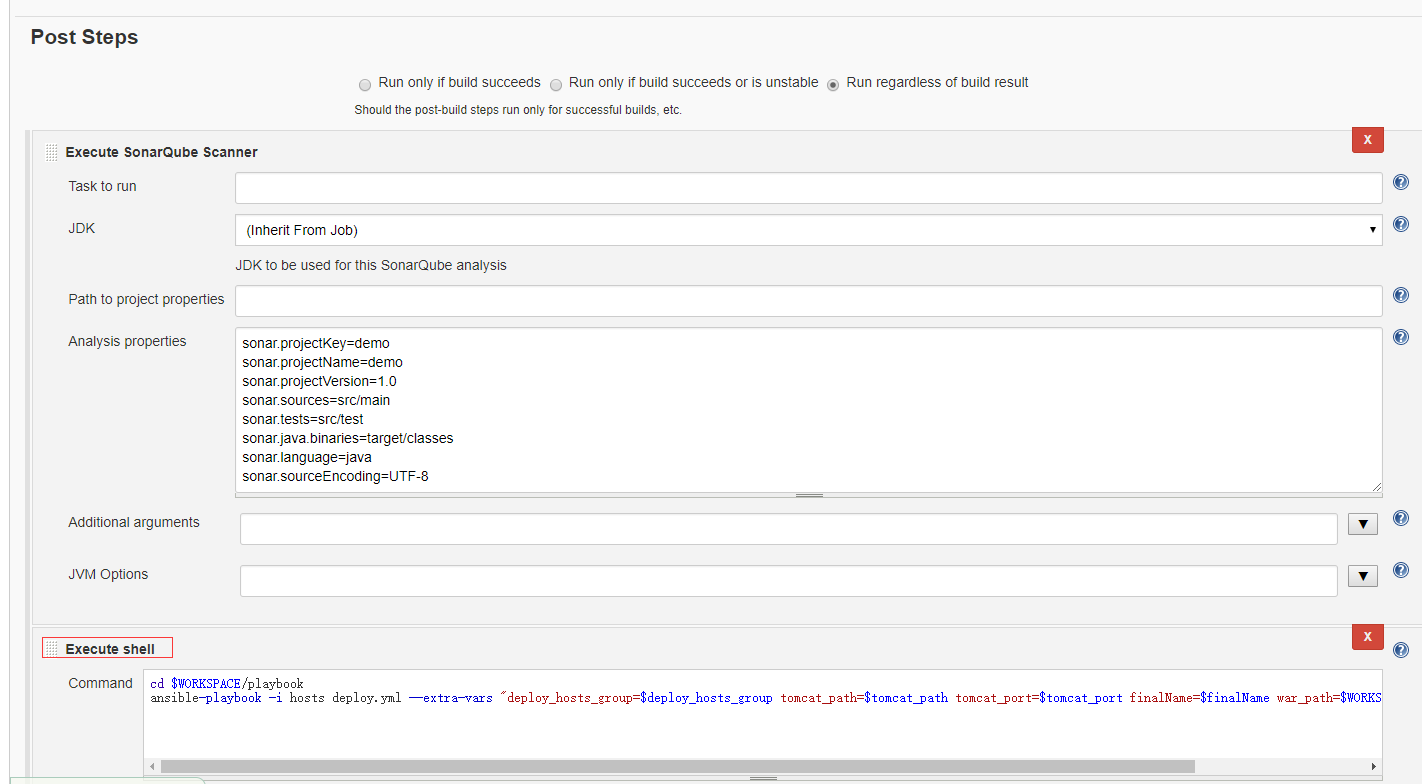
项目编译完后,会找到项目下的playbook,执行里面的脚本,将我们的项目部署到设定的服务器中。
总结 :
本篇文章为大家带来了Spring-boot 的架构搭建,主要使用到了目前较为流行的技术。
源码地址:https://github.com/jaycekon/SpringBootDemo
Spring-boot:快速搭建微框架服务的更多相关文章
- 寻找写代码感觉(一)之使用 Spring Boot 快速搭建项目
写在前面 现在已经是八月份了,我已经荒废了半年居多,不得不说谈恋爱确实是个麻烦的事,谈好了皆大欢喜,分手了就是萎靡不振,需要很长一段时间才能缓过来. 人还是要有梦想的,至于实现只不过是一个契机,但凡不 ...
- Spring Boot快速搭建Spring框架
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作Expert One-On-One J2EE Development a ...
- Spring Boot快速搭建Web工程
先想一下,正常我们想要创建一个web服务,首先需要下载tomcat,创建web工程,配置各种web.xml,引入spring的配置,各种配置文件一顿倒腾.....下载有了spring boot,你创建 ...
- Spring Boot 快速搭建的三种方式
方式一:http://start.spring.io/ 打开浏览器,在地址栏中输入http://start.spring.io/ 如下图: 点击generate project 然后就会有一个zip ...
- Spring Boot 快速入门(IDEA)
从字面理解,Boot是引导的意思,因此SpringBoot帮助开发者快速搭建Spring框架:SpringBoot帮助开发者快速启动一个Web容器:SpringBoot继承了原有Spring框架的优秀 ...
- Spring Boot 快速入门 史上最简单
1.Spring Boot 概述 Spring Boot 是所有基于 Spring 开发的项目的起点.Spring Boot 的设计是为了让你尽可能快的跑起来 Spring 应用程序并且尽可能减少你的 ...
- 笔记61 Spring Boot快速入门(一)
IDEA+Spring Boot快速搭建 一.IDEA创建项目 略 项目创建成功后在resources包下,属性文件application.properties中,把数据库连接属性加上,同时可以设置服 ...
- Spring boot项目搭建及简单实例
Spring boot项目搭建 Spring Boot 概述 Build Anything with Spring Boot:Spring Boot is the starting point for ...
- Spring-boot:快速搭建微服务框架
前言: Spring Boot是为了简化Spring应用的创建.运行.调试.部署等而出现的,使用它可以做到专注于Spring应用的开发,而无需过多关注XML的配置. 简单来说,它提供了一堆依赖打包,并 ...
随机推荐
- 【Luogu4723】线性递推(常系数齐次线性递推)
[Luogu4723]线性递推(常系数齐次线性递推) 题面 洛谷 题解 板子题QwQ,注意多项式除法那里每个多项式的系数,调了一天. #include<iostream> #include ...
- [算法进阶0x10]基本数据结构A作业总结
在线题目\(oj\)评测地址:https://xoj.red/contests/show/1237 T1-Editor(hdu4699) 题目描述 维护一个整数序列的编辑器,有以下5种操作,操作总数不 ...
- 【转】C语言字符串与数字相互转换
在C/C++语言中没有专门的字符串变量,通常用字符数组来存放字符串.字符串是以“\0”作为结束符.C/C++提供了丰富的字符串处理函数,下面列出了几个最常用的函数. ● 字符串输出函数puts. ● ...
- Android: 待机时如何让程序继续运行 extends Service
接触Android没几天,不太了解. 本来写好的一个应用在无意中发现,待机的时候,应用中的一个线程停止了运行. 这个线程是每隔一分钟上传一个数据到服务器上. 我当时测试的时候,没想过待机(接开关键)下 ...
- XML模块(二十四)
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟json差不多,但json使用起来更简单,不过,古时候,在json还没诞生的黑暗年代, 大家只能选择用xml呀,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统 ...
- struct字节对齐原则
原则1:windows下,k字节基本类型以k字节倍数偏移量对齐,自定义结构体则以结构体中最高p字节基本类型的p字节倍数偏移量对齐,Linux下则以2或4字节对齐; 原则2:整体对齐原则,例如数组结构体 ...
- CSS的显示模式
div与span div与span有什么区别 div单独占一行,span不会单独占一行 div是容器级的标签,而span是一个文本级的标签 容器级的标签有:div , h , ul , ol , dl ...
- jenkins ansible 附zabbix_agent批量安装示例
插件:Ansible plugin 一.ansible ad-hoc command 二.ansible-playbook 批量部署zabbix-agent示例: playbook 目录及文件组成 [ ...
- nginx的location、root、alias指令用法和区别
nginx指定文件路径有两种方式root和alias,指令的使用方法和作用域: [root] 语法:root path 默认值:root html 配置段:http.server.location.i ...
- 学习windows编程 day3 之窗口绘画一:点线绘制
#include <windows.h> #include <math.h> LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, ...
