Spring框架(二)
Spring反射机制:
1, 通过spring来获取一个对象的实例
<bean id="user" class="com.model.User">
</bean>
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-all.xml");//调用此方法时类已经实例化好了
User u=(User)ac.getBean("user");//拿到实例化的类
2, 通过spring进行属性注入
setter方法注入
<!-- 通过Spring給类注入属性,通过空参构造方法 -->
<property name="username">
<value>hanqi</value>
</property>
<property name="password">
<value>123</value>
</property>
构造器注入
<!--
另一种通过带参构造方法-->
<constructor-arg index="0" value="name1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="pwd1"></constructor-arg>
接口注入
public class ClassA {
private InterfaceB clzB;
public init() {
Ojbect obj =
Class.forName(Config.BImplementation).newInstance();
clzB = (InterfaceB)obj;
}
……
}
上面的代码中,ClassA依赖于InterfaceB的实现,如何获得InterfaceB实现类的实例?传统的方法是在代码中创建InterfaceB实现类的实例,并将起赋予clzB。
而这样一来,ClassA在编译期即依赖于InterfaceB的实现。为了将调用者与实现者在编译期分离,于是有了上面的代码,我们根据预先在配置文件中设定的实现类的类名,动态加载实现类,并通过InterfaceB强制转型后为ClassA所用。
这就是接口注入的一个最原始的雏形。
而对于一个Type1型IOC容器而言,加载接口实现并创建其实例的工作由容器完成,如J2EE开发中常用的Context.lookup(ServletContext.getXXX),都是Type1型IOC的表现形式。
Apache Avalon是一个典型的Type1型IOC容器。
p标记的使用
<bean p:username=""></bean>
<bean id="user" class="com.model.User" p:username="pusername" p:password="ppwd">
</bean>
3, 将一个对象注入到另一个对象<ref bean="...">
用户有一个部门
部门有多个用户
model:
package com.model;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private Dept dept;
public User() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public User(String username, String password, Dept dept) {
super();
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.dept = dept;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", dept=" + dept + "]";
}
}
package com.model;
import java.util.List;
public class Dept {
private int deptid;
private String deptname;
private List<User> users;
public Dept() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public Dept(int deptid, String deptname, List<User> users) {
super();
this.deptid = deptid;
this.deptname = deptname;
this.users = users;
}
public int getDeptid() {
return deptid;
}
public void setDeptid(int deptid) {
this.deptid = deptid;
}
public String getDeptname() {
return deptname;
}
public void setDeptname(String deptname) {
this.deptname = deptname;
}
public List<User> getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(List<User> users) {
this.users = users;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept [deptid=" + deptid + ", deptname=" + deptname + ", users人数=" + users.size() + "]";
}
}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user1" class="com.model.User">
<property name="username" value="苦海"></property>
<property name="password" value="111"></property>
<property name="dept" ref="dept1"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept1" class="com.model.Dept">
<property name="deptid" value="6001"></property>
<property name="deptname" value="部门1"></property>
<property name="users">
<list>
<ref bean="user1"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试:
package com.test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.model.Dept;
import com.model.User;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-all.xml");//调用此方法时类已经实例化好了
User u=(User)ac.getBean("user1");//拿到实例化的类
Dept d=(Dept)ac.getBean("dept1");
System.out.println(u);
System.out.println(d);
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ac).close();
}
}

4, AutoWired(byType, byName)
autowire
自动装载:
byName根据名字自动注入
user1的bean中并没有dept属性,但是还是打印出了这个属性,因为它会找到这个类,然后在配置文件中找到和该属性同名的id,并自动注入
1 <bean id="user1" class="com.model.User" autowire="byName"> 2 <property name="username" value="苦海"></property> 3 <property name="password" value="111"></property> 4 </bean> 5 6 <bean id="dept" lazy-init="true" class="com.model.Dept" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" > 7 <property name="deptid" value="6001"></property> 8 <property name="deptname" value="部门1"></property> 9 <property name="users"> 10 <list> 11 <ref bean="user1"/> 12 </list> 13 </property> 14 </bean>
1 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-all.xml");//调用此方法时类已经实例化好了
2 User u=(User)ac.getBean("user1");//拿到实例化的类
3 System.out.println(u);
4 ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ac).close();
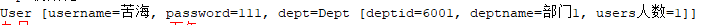
byType根据类型自动装载,用法一致
需要注意,如果根据类型自动装载,应只有一个该类型,否则会无发找到,报错
autowire默认default,指的是根据<beans>声明中得来选择方法
5, scope, lazy-init, init-method, destroy-method(相当的不重要)
scope="singleton(单例) / prototype(原型)"
默认情况下Spring中定义的Bean是以单例模式创建的。
在GoF中的单例模式是指一个ClassLoader中只存在类一个实例。
而在Spring中的单例实际上更确切的说应该是:
1.每个Spring Container中定义的Bean只存在一个实例
2.每个Bean定义只存在一个实例。
<bean id="user1" class="com.model.User" scope="singleton">
<property name="username" value="苦海"></property>
<property name="password" value="111"></property>
</bean>
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-all.xml");//调用此方法时类已经实例化好了
User u=(User)ac.getBean("user1");//拿到实例化的类
User u2=(User)ac.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(u==u2);
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ac).close();

<bean id="user1" class="com.model.User" scope="prototype">
<property name="username" value="苦海"></property>
<property name="password" value="111"></property>
</bean>
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Spring-all.xml");
User u=(User)ac.getBean("user1");
User u2=(User)ac.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(u==u2);
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)ac).close();

lazy-init="true" // 延迟加载,未生效
<bean id="dept1" lazy-init="true" class="com.model.Dept" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" >
写在beans中,设置全局延迟加载
default-lazy-init="true"
lazy-init (一开始不初始化,用到的时候才初始化)
init-method="init" destory-method="destory" 不要和prototype一起使用
类被初始化的时候调用init,被消亡的时候调用destory
正常运行的结果只有一个init和destroy,虽然两个service实例化,但是默认是单例,加了scope=prototype就运行不正常了,结果两个init,没有destroy,原因未知。
首先我们应该知道:一、spring Bean的作用域:scope=singleton(默认,单例,生成一个实例)
二、spring Bean的作用域:scope=prototype(多线程, 生成多个实例)
三、单例模式,默认在程序初始化的时候实例化(lazy-init=”false”)
四、prototype,getBean的时候才是实例化
五、lazy-init 只对单例模式起作用,对 prototype 不起作用(因为 prototype 默认就不是程序初始化的时候实例化的)
Spring框架(二)的更多相关文章
- [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结二:Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发.
前言: 在上一篇中: [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结一. 中 我们已经知道了一个Spring AOP程序是如何开发的, 在这里呢我们将基于AspectJ来进行AOP 的总结和学习 ...
- Spring框架系列(二)之Bean的注解管理
微信公众号:compassblog 欢迎关注.转发,互相学习,共同进步! 有任何问题,请后台留言联系! 1.Spring中的两种容器 在系列(一)中我们已经知道,Spring 是管理对象的容器,其中有 ...
- [ SSH框架 ] Spring框架学习之二(Bean的管理和AOP思想)
一.Spring的Bean管理(注解方式) 1.1 什么是注解 要使用注解方式实现Spring的Bean管理,首先要明白什么是注解.通俗地讲,注解就是代码里的特殊标记,使用注解可以完成相应功能. 注解 ...
- 跟着刚哥学习Spring框架--Spring容器(二)
Spring容器 启动Spring容器(实例化容器) -- IOC容器读取Bean配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化(加载启动),这样才可以从容器中获取Bean的实例并使用. Bean是S ...
- OSGI企业应用开发(五)使用Blueprint整合Spring框架(二)
上篇文章中,我们开发了一个自定义的Bundle,接着从网络中下载到Spring和Blueprint的Bundle,然后复制到DynamicRuntime项目下. 需要注意的是,这些Bundle并不能在 ...
- Spring框架学习之IOC(二)
Spring框架学习之IOC(二) 接着上一篇的内容,下面开始IOC基于注解装配相关的内容 在 classpath 中扫描组件 <context:component-scan> 特定组件包 ...
- 深入学习Spring框架(二)- 注解配置
1.为什么要学习Spring的注解配置? 基于注解配置的方式也已经逐渐代替xml.所以我们必须要掌握使用注解的方式配置Spring. 关于实际的开发中到底使用xml还是注解,每家公司有着不同的使用习惯 ...
- spring框架学习(二)依赖注入
spring框架为我们提供了三种注入方式,分别是set注入,构造方法注入,接口注入.接口注入不作要求,下面介绍前两种方式. 1,set注入 采用属性的set方法进行初始化,就成为set注入. 1)给普 ...
- Spring框架学习(二)
一.依赖注入的三种注入方式 Spring框架为我们提供了三种注入方式:set注入.构造方法注入和接口注入. 1.set注入 规律:无论给什么赋值,配置文件中<property>标签的nam ...
- Spring 框架 详解 (二)
Spring的入门的程序: 1.1.1 下载Spring的开发包: spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE-dist.zip ---Spring开发包 * docs :sprin ...
随机推荐
- CAD快捷键命令
符号键(CTRL开头) CTRL+1 PROPCLOSEOROPEN 对象特性管理器 CTRL+2或4 ADCENTER 设计中心 CTRL+3 CTOOLPALETTES 工具选项板 CTRL+8或 ...
- TensorFlow框架(4)之CNN卷积神经网络
1. 卷积神经网络 1.1 多层前馈神经网络 多层前馈神经网络是指在多层的神经网络中,每层神经元与下一层神经元完全互连,神经元之间不存在同层连接,也不存在跨层连接的情况,如图 11所示. 图 11 对 ...
- Java入门(5)——类和对象还有构造方法
类 类和对象的概念: 类是对一群具有相同属性.行为的事物的统称. 类是抽象的. 人以类聚 物以群分 对象: 对象是现实生活中的1个具体存在. 看得 ...
- STL中set的用法
set,顾名思义,就是数学上的集合——每个元素最多只出现一次,并且set中的元素已经从小到大排好序. 头文件:#include<set> 常用的函数: begin() 返回set容 ...
- hdu4336 Card Collector
Problem Description In your childhood, do you crazy for collecting the beautiful cards in the snacks ...
- QQ无法通过ISA2006&TMG2010代理收发图片问题解决
近期公司有业务需求通过TMG访问QQ,但配置多次均无法通过QQ收发图片,文字输入正常. 目前已解决,供参考: 这个问题是SSL端口默认使用了443,但QQ的离线文件不使用这个端口.所以ISA会把QQ的 ...
- XWPFRun属性详解
XWPFRun是XWPFDocument中的一段文本对象(就是一段文字) 创建文档对象 XWPFDocument docxDocument = new XWPFDocument(); 创建段落对象 X ...
- Spring详解(五)------AspectJ 实现AOP
上一篇博客我们引出了 AOP 的概念,以及 AOP 的具体实现方式.但是为什么要这样实现?以及提出的切入点表达式到底该怎么理解? 这篇博客我们通过对 AspectJ 框架的介绍来详细了解. 1.什么是 ...
- mqtt实现自动监听服务器消息
本示例借助meteor的一个环境跑,和我们平时用的node自己搭的环境或java,php的环境本质一样,在此不多讨论. 首先需求是:多系统对接进行消息实时传递. 安装好mqtt: npm insta ...
- JTemplates 的使用
注意事项:一定要放在Jquery的页面加载完成事件内 : $(function{}); <script src="~/Js/jquery-2.1.0.js">< ...
