SpringBoot笔记(4)
一、请求处理
1.1 常用参数注解使用
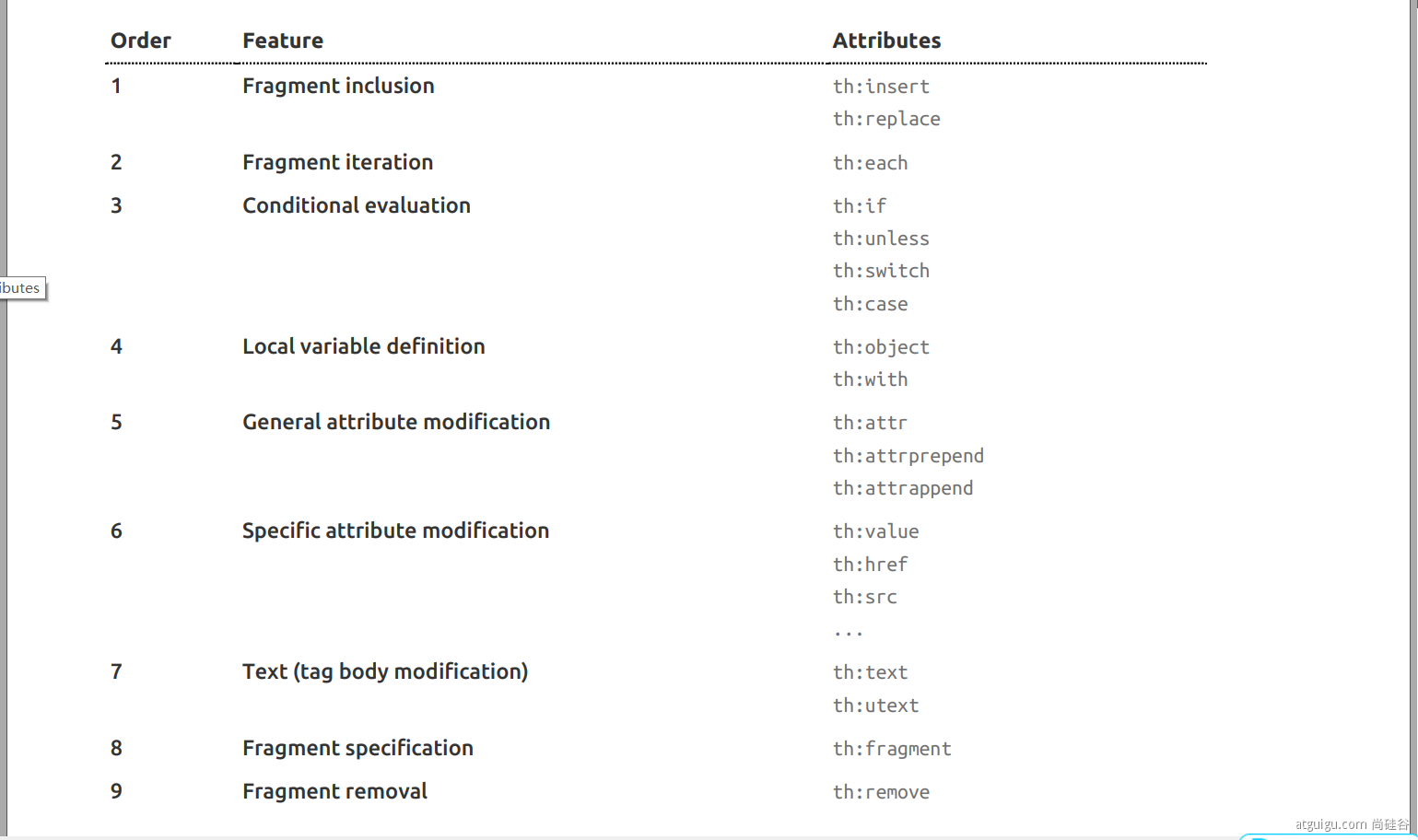
| 注解 | 使用 |
|---|---|
| @PathVariable | 获取URI模板指定请求,并赋值到变量中,不指定可以将所有请求放到map中,但是健值都为String |
| @RequestHeader | 获取指定请求头,不指定可以获取所有到map中 |
| @RequestParam | 用于获取简单数据类型的参数如String、List<Integer>等 |
| @CookieValue | 获取cookie的值,String或Cookie类型 |
| @RequestBody | 获取请求体数据 |
| @ResposeBody | 将对象转换为json格式并写入response的body区中 |
| @RequestAttribute | 相当于request.getAttribute(), 获取请求域中的值 |
矩阵变量:参数之间用;分割
SpringBoot默认不开启矩阵变量, 需要实现或重写webMvcConfigurer,将urlPathHelper的setRemoveSemicolonContent 设置为false
可用于重写url,cookie被禁用时传入jesessionId
参数前面要用{}的路径变量【/cars/{path};low=20;band=zhangsan,lisi】
二、视图解析器与模板引擎
1.模板引擎-Thymeleaf
1、thymeleaf简介
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments, capable of processing HTML, XML, JavaScript, CSS and even plain text.
现代化、服务端Java模板引擎
2、基本语法
1、表达式
| 表达式名字 | 语法 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 变量取值 | ${...} | 获取请求域、session域、对象等值 |
| 选择变量 | *{...} | 获取上下文对象值 |
| 消息 | #{...} | 获取国际化等值 |
| 链接 | @{...} | 生成链接 |
| 片段表达式 | ~{...} | jsp:include 作用,引入公共页面片段 |
2、字面量
文本值: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…数字: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…布尔值: true , false
空值: null
变量: one,two,.... 变量不能有空格
3、文本操作
字符串拼接: +
变量替换: |The name is ${name}|
4、数学运算
运算符: + , - , * , / , %
5、布尔运算
运算符: and , or
一元运算: ! , not
**
**
6、比较运算
比较: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )等式: == , != ( eq , ne )
7、条件运算
If-then: (if) ? (then)
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
8、特殊操作
无操作: _
3、设置属性值-th:attr
设置单个值
<form action="subscribe.html" th:attr="action=@{/subscribe}">
<fieldset>
<input type="text" name="email" />
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:attr="value=#{subscribe.submit}"/>
</fieldset>
</form>
设置多个值
<img src="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
以上两个的代替写法 th:xxxx
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe!" th:value="#{subscribe.submit}"/>
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">
所有h5兼容的标签写法
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html#setting-value-to-specific-attributes
4、迭代
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
<tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
5、条件运算
<a href="comments.html"
th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"
th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">view</a>
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
6、属性优先级
2.Thymeleaf的使用
1、引入Starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
SpringBoot已经自动配置好了,
1、所有thymeleaf的配置值都在 ThymeleafProperties
2、配置好了 SpringTemplateEngine
3、配好了 ThymeleafViewResolver
4、我们只需要直接开发页面
放在templates下,后缀为html
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; //xxx.html
5、导入命名空间
2、编写controller层
@Controller
public class ViewTestController {
@RequestMapping("/success")
public String ViewTest(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","郜宇博,你好");
model.addAttribute("link","http://www.baidu.com");
//已经自动配置添加后缀
return "success";
}
}
3、编写页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${msg}">nihao</h1>
<a href="www.hao123.com" th:href="${link}">百度</a>
</body>
</html>
三、 拦截器
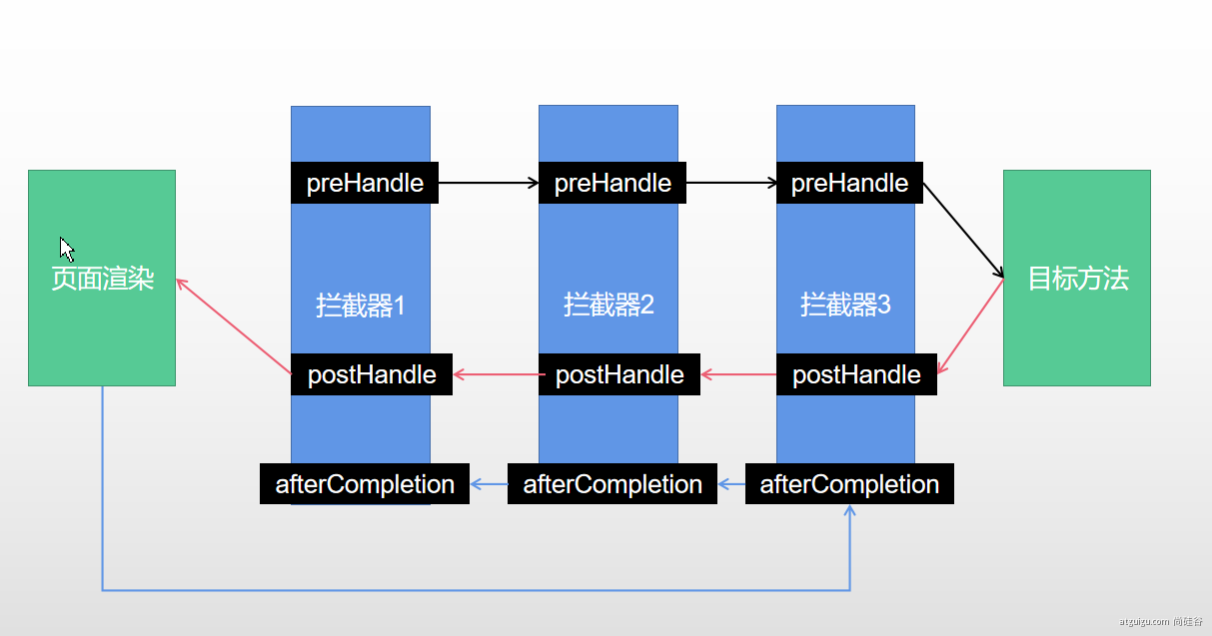
0、拦截器原理
1、根据当前请求,找到HandlerExecutionChain【可以处理请求的handler以及handler的所有 拦截器】
2、先来顺序执行 所有拦截器的 preHandle方法
- 1、如果当前拦截器prehandler返回为true。则执行下一个拦截器的preHandle
- 2、如果当前拦截器返回为false。直接 倒序执行所有已经执行了的拦截器的 afterCompletion;
3、如果任何一个拦截器返回false。直接跳出不执行目标方法
4、所有拦截器都返回True。执行目标方法
5、倒序执行所有拦截器的postHandle方法。
6、前面的步骤有任何异常都会直接倒序触发 afterCompletion
7、页面成功渲染完成以后,也会倒序触发 afterCompletion
1、 HandlerInterceptor接口
/**
* 登录检查
* 1、配置好拦截器要拦截哪些请求
* 2、把这些配置放在容器中
*/
@Slf4j
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
/**
* 目标方法执行之前
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("preHandle拦截的请求路径是{}",requestURI);
//登录检查逻辑
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser");
if(loginUser != null){
//放行
return true;
}
//拦截住。未登录。跳转到登录页
request.setAttribute("msg","请先登录");
// re.sendRedirect("/");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request,response);
return false;
}
/**
* 目标方法执行完成以后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
log.info("postHandle执行{}",modelAndView);
}
/**
* 页面渲染以后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param ex
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
log.info("afterCompletion执行异常{}",ex);
}
}
2. 配置拦截器
/**
* 1、编写一个拦截器实现HandlerInterceptor接口
* 2、拦截器注册到容器中(实现WebMvcConfigurer的addInterceptors)
* 3、指定拦截规则【如果是拦截所有,静态资源也会被拦截】
*/
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns("/**") //所有请求都被拦截包括静态资源
.excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**"); //放行的请求
}
}
四、文件上传
1、页面表单
<form method="post" action="/upload" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file"><br>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
2、文件上传代码
/**
* MultipartFile 自动封装上传过来的文件
* @param email
* @param username
* @param headerImg
* @param photos
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("email") String email,
@RequestParam("username") String username,
@RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headerImg,
@RequestPart("photos") MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException {
log.info("上传的信息:email={},username={},headerImg={},photos={}",
email,username,headerImg.getSize(),photos.length);
if(!headerImg.isEmpty()){
//保存到文件服务器,OSS服务器
String originalFilename = headerImg.getOriginalFilename();
headerImg.transferTo(new File("H:\\cache\\"+originalFilename));
}
if(photos.length > 0){
for (MultipartFile photo : photos) {
if(!photo.isEmpty()){
String originalFilename = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("H:\\cache\\"+originalFilename));
}
}
}
return "main";
}
五、异常处理
1、默认规则
默认情况下,Spring Boot提供
/error处理所有错误的映射对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据

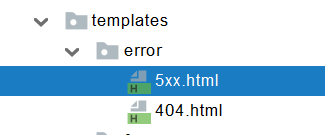
error/下的4xx,5xx页面会被自动解析;
SpringBoot笔记(4)的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot笔记十六:ElasticSearch
目录 ElasticSearch官方文档 ElasticSearch安装 ElasticSearch简介 ElasticSearch操作数据,RESTful风格 存储 检查是否存在 删除 查询 更新 ...
- SpringBoot笔记一
1 开始 1.1 spring介绍 Spring Boot使开发独立的,产品级别的基于Spring的应用变得非常简单,你只需"just run". 我们为Spring平台及第三方库 ...
- 【SpringBoot笔记】SpringBoot整合Druid数据连接池
废话少说,按SpringBoot的老套路来. [step1]:添加依赖 <!-- 数据库连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alib ...
- SpringBoot笔记十七:热部署
目录 什么是热部署 Devtools热部署 什么是热部署 热部署,就是在应用正在运行的时候升级软件,却不需要重新启动应用. 举个例子,王者荣耀的更新有时候就是热部署,热更新,就是他提示你更新,更新40 ...
- SpringBoot笔记十四:消息队列
目录 什么是消息队列 消息队列的作用 异步通信 应用解耦 流量削峰 RabbitMQ RabbitMQ流程简介 RabbitMQ的三种模式 安装RabbitMQ RabbitMQ交换器路由和队列的创建 ...
- SpringBoot笔记十三:引入webjar资源和国际化处理
目录 什么是webjar 怎么使用webjar 国际化 新建国际化配置文件 配置配置文件 使用配置文件 我们先来看一个html,带有css的,我们就以这个为准来讲解. 资源可以去我网盘下载 链接:ht ...
- springboot笔记1(转载于puresmile)
构建微服务:Spring boot 入门篇 什么是spring boot Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框 ...
- SpringBoot笔记
官网: http://springboot.fun/ 收集到一个比较全的: https://blog.csdn.net/xiaoyu411502/article/details/52474037 Id ...
- springboot笔记05——profile多环境配置切换
前言 一个应用程序从开发到上线,往往需要经历几个阶段,例如开发.测试.上线.每个阶段所用到的环境的配置可能都是不一样的,Springboot 应用可以很方便地在各个环境中对配置进行切换.所以,今天主要 ...
- springboot笔记09——使用aop
什么是AOP? aop(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,是OOP(Object-Oriented Programing,面向对象编程)的补充和完善.OOP引入封装 ...
随机推荐
- 数据库开发之ETL概念
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/jianzhang11/article/details/104240047/ ETL基础概念 - 背景随着企业的发展,各业务线.产品线.部门都会承 ...
- 解决proto文件转换时提示“Note that enum values use C++ scoping rules, meaning that enum values are siblings of their type, not children of it. ”
前言: 想将.proto文件转换成.pb文件时一直报错,一开始以为是文件编码格式的问题,后来将文件改成windows下的utf-8格式后,又出现了新的报错(见下图).百度了很久,才找到解决方法. &q ...
- 谷粒商城--分布式高级篇P102~P128
谷粒商城--分布式高级篇P102~P128 由于学习的时间也比较少,只有周六周末才有时间出来学习总结,所以一篇一篇慢慢更新吧,本次总结内容为Elasticsearch(相关内容:kibana,es,n ...
- 论文笔记:(ICML2020)On Learning Sets of Symmetric Elements
目录 摘要 一.引言 二.先前的工作 三.基础 3.1 符号和基本定义 3.2 G-不变网络 3.3 描述等变层 3.4 Deep sets 四.DSS层 4.1 对称元素集合 4.2 等变层的表征 ...
- netty系列之:中国加油
目录 简介 场景规划 启动Server 启动客户端 消息处理 消息处理中的陷阱 总结 简介 之前的系列文章中我们学到了netty的基本结构和工作原理,各位小伙伴一定按捺不住心中的喜悦,想要开始手写代码 ...
- Tensorflow2对GPU内存的分配策略
一.问题源起 从以下的异常堆栈可以看到是BLAS程序集初始化失败,可以看到是执行MatMul的时候发生的异常,基本可以断定可能数据集太大导致memory不够用了. 2021-08-10 16:38:0 ...
- 文件上传之WAF绕过及相安全防护
文件上传在数据包中可修改的地方 Content-Disposition:一般可更改 name:表单参数值,不能更改 filename:文件名,可以更改 Content-Type:文件 MIME,视情况 ...
- 一份热乎的字节跳动客户端面经,已拿Offer
字节面试过程: 4月4号进行内推,7天的简历评估,11号接到电话面试,尽管猝不及防回答仓促,但好在前期准备充分,通过.14号现场面试,次日收到通知,通过,二面.三面都很顺利.20号进行HR面,26号收 ...
- 解决win10快速访问不能取消固定
最近发现win10的快速访问不能取消固定,比如ftp和smb之类的都不能取消固定 最后百度了一下发现一个简易的方法: 在文件资源管理器地址栏输入:%APPDATA%\Microsoft\Windows ...
- 一台服务器上部署多个Terracotta的方法
在window server 2003 下,利用apache2.2.11+tomcat6+terracotta 群集不能复制session(http://forums.terracotta.org/f ...
