深入了解SpringMVC源码解析
Spring MVC源码解析
Spring MVC的使用原理其实是通过配置一个Servlet来接管所有的请求,所有的请求由这个Servlet来进行分发处理。
我们可以从web.xml里面看出这一点
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
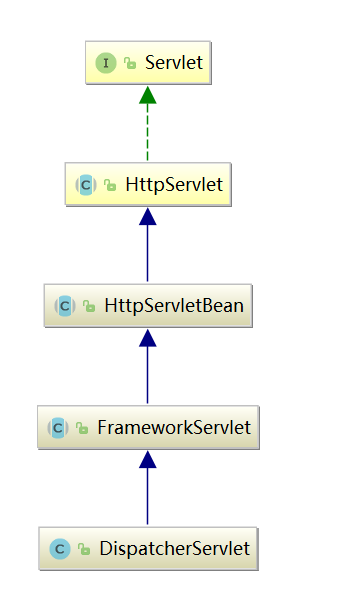
这个Servlet就是Spring MVC提供的DispatcherServlet,它的继承图如下:
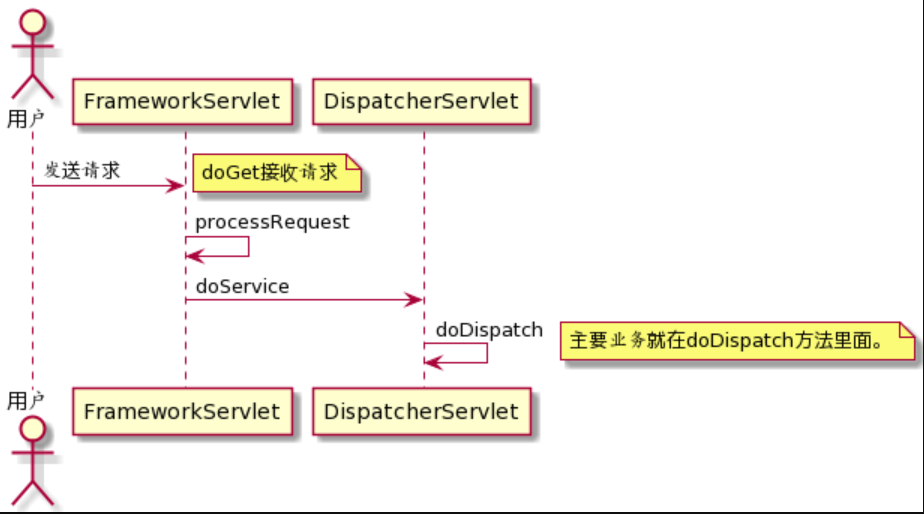
DispatcherServlet大致接收请求的时序图如下:
下面我们先设定几个问题然后再去看源码。
- DispatcherServlet初始化的时机?
我们将断点打在DispatcherServlet中的onRefresh方法上
,然后启动项目。
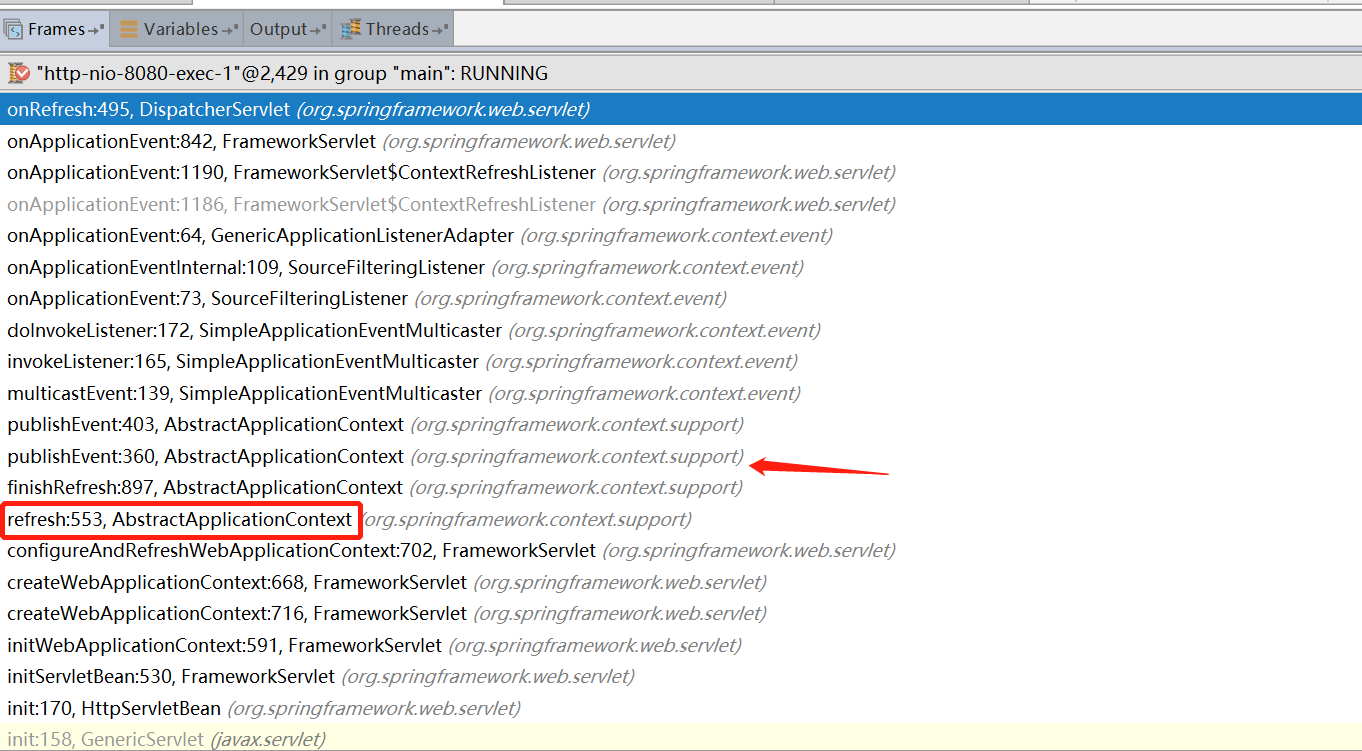
从这个堆栈的图可以看出,最开始是HttpServletBean的init方法执行,然后启动Spring容器,Spring容器初始化的最后一步finishRefresh里面进行了事件通知。
FrameworkServlet里有个内部类ContextRefreshListener,实现了ApplicationListener接口,接收到了上面的事件通知,执行onApplicationEvent方法。
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}
继续跟踪onApplicationEvent方法
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}
发现最终是由onRefresh方法来进行具体处理的,并且这个onRefresh方法在FrameworkServlet里面是个空方法,是由它的子类DispatcherServlet来实现的。
我们来看DispatcherServlet里的onRefresh方法
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这样就把SpringMVC的九大组件给初始化了。
- 我们的@RequestMapping注解在方法上,SpringMVC是怎么根据这个注解就能将对应的请求执行到这个方法上的?
从上面可以看到有个initHandlerMappings方法:
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// 找所有实现了HandlerMapping接口的类
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//默认情况下,我们是使用的这个方法。
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
继续跟踪getDefaultStrategies方法
protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) {
String key = strategyInterface.getName();
String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value);
List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length);
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader());
Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz);
strategies.add((T) strategy);
}
//省略部分代码...
}
return strategies;
}
else {
return new LinkedList<>();
}
}
可以看出对classNames进行了遍历,这里有两个值,
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping和RequestMappingHandlerMapping,我们一般用的是RequestMappingHandlerMapping。
RequestMappingHandlerMapping的父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,我们来看看它实现的afterPropertiesSet方法。
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
前面都是一些配置,后面是调用父类的afterPropertiesSet方法,此方法里只有initHandlerMethods一个方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
主要看processCandidateBean方法
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
继续跟踪detectHandlerMethods方法
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//利用工具,取出类里面的方法并组装成map
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));
}
//遍历map,处理里面的方法
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
继续跟踪里面的register方法
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
可以看出mappingLookup、urlLookup、registry都放入了值。这时我也不知道每个的具体作用。我把断点打到这3个属性上。然后前端发起一个get请求。
- 请求匹配的过程?
前端发起请求,断点停在了AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistry#getMappingsByUrl方法上,以前端发起的请求路径,从urlLookup上获取对应的值。

最后看看请求分发的主流程,也是springMVC最核心的代码
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//multipart请求处理
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 获取合适的HandlerExecutionChain
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
//获取合适的HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// handle执行调用(核心)
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//视图解析并渲染到页面
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
总结:
tomcat的Servlet调起Spring容器启动,Spring容器启动完,事件通知到SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet。
这时会扫描所有的bean,将注解了@Controller和@RequestMapping的解析出来。
前端请求发过来,DispatcherServlet接收到(因为它是个servlet,配置在web.xml的),根据上一步处理好的映射关系,找到对应的方法来处理。
如通过/test能找到test方法
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(String name, HttpServletRequest request,Model model){
System.out.println("name");
model.addAttribute("date",new Date());
return "success";
}
- 找到对应的方法后,反射调用
method.invoke(Object obj,Object... args)
- 组装modelAndView渲染视图到前端
深入了解SpringMVC源码解析的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter - ModelFactory(转)
ModelFactory主要是两个职责: 1. 初始化model 2. 处理器执行后将modle中相应参数设置到SessionAttributes中 我们来看看具体的处理逻辑(直接充当分析目录): 1 ...
- springMVC源码解析--ViewResolver视图解析器执行(三)
之前两篇博客springMVC源码分析--ViewResolver视图解析器(一)和springMVC源码解析--ViewResolverComposite视图解析器集合(二)中我们已经简单介绍了一些 ...
- SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter - ModelFactory
ModelFactory主要是两个职责: 1. 初始化model 2. 处理器执行后将modle中相应参数设置到SessionAttributes中 我们来看看具体的处理逻辑(直接充当分析目录): 1 ...
- springMVC源码解析--ViewResolverComposite视图解析器集合(二)
上一篇博客springMVC源码分析--ViewResolver视图解析器(一)中我们介绍了一些springMVC提供的很多视图解析器ViewResolver,在开发的一套springMVC系统中是可 ...
- springMVC源码解析--HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite参数解析器集合(二)
上一篇博客springMVC源码分析--HandlerMethodArgumentResolver参数解析器(一)中我们已经介绍了参数解析相关的东西,并且也提到了HandlerMethodArgume ...
- springmvc源码解析MvcNamespaceHandler之<mvc:view-resolvers>
说在前面 本次主要介绍springmvc配置解析. springmvc配置解析 本次介绍MvcNamespaceHandler. 进入到这个方法org.springframework.web.serv ...
- SpringMVC源码解析
一:springmvc运行过程: 1. dispatcherServlet 通过 HandlerMapping 找到controller2. controller经过后台逻辑处理得到结果集modela ...
- SpringMVC源码解析- HandlerAdapter初始化
HandlerAdapter初始化时,主要是进行注解解析器初始化注册;返回值处理类初始化;全局注解@ControllerAdvice内容读取并缓存. 目录: 注解解析器初始化注册:@ModelAttr ...
- springmvc源码解析-初始化
1. 概述 对于Web开发者,MVC模型是大家再熟悉不过的了,SpringMVC中,满足条件的请求进入到负责请求分发的DispatcherServlet,DispatcherServlet根 ...
随机推荐
- Fiddler抓包一键生成代码
首先我们的需求场景是 用Fiddler抓到某个接口调用后,用代码来模拟调用,一般我们写代码会有3个步骤: 1设置http请求相关的参数:header,method,url,cookie等 2设置pos ...
- 超详细的Ribbon源码解析
Ribbon简介 什么是Ribbon? Ribbon是springcloud下的客户端负载均衡器,消费者在通过服务别名调用服务时,需要通过Ribbon做负载均衡获取实际的服务调用地址,然后通过http ...
- Vim合并行
日常常用到多行合并的功能,记录如下: 第一种, 多行合并成一行,即: AAAAABBBBBCCCCC 合并为:AAAAA BBBBB CCCCC 方法1: normal状态下 3J 其中的3是范围,可 ...
- 3.3 Execution Flow of a DDD Based Application 基于DDD的应用程序执行流程
3.3 Execution Flow of a DDD Based Application 基于DDD的应用程序执行流程 The figure below shows a typical reques ...
- MySQL:提高笔记-5
MySQL:提高笔记-5 学完基础的语法后,进一步对 MySQL 进行学习,前几篇为: MySQL:提高笔记-1 MySQL:提高笔记-2 MySQL:提高笔记-3 MySQL:提高笔记-4 MySQ ...
- 【二食堂】Beta - Scrum Meeting 1
Scrum Meeting 1 例会时间:5.13 18:30~18:50 进度情况 组员 当前进度 今日任务 李健 1. 查阅资料,解决划词勾选和右键菜单的问题issue2. 修复了Alpha阶段的 ...
- Noip模拟43 2021.8.18
T1 地一体 可以树形$dp$,但考场没写出来,只打了没正确性的贪心水了$30$ 然后讲题的时候B哥讲了如何正确的贪心,喜出望外的学习了一下 不难发现 每次士兵都会直接冲到叶子节点 从深的点再返回到另 ...
- Xpath语法学习记录
高级参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wudaoshihun/article/details/82226122 举例: 1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <ht ...
- 全志Tina_dolphin播放音视频裸流(h264,pcm)验证
最近在验证tina对裸流音视频的支持,主要指h264视频裸流及pcm音频裸流. 在原始sdk中有针对很多video和audio类型的parser,但就是没有找到pcm和h264的parser,所以需要 ...
- dhcpd:bad subnet number/mask combination. subnet
今天在调试wifi热点启动hdcpd服务时出现报错"bad subnet number/mask combination. subnet 192.168.1.1", Interne ...
