[LeetCode] 723. Candy Crush 糖果粉碎
This question is about implementing a basic elimination algorithm for Candy Crush.
Given a 2D integer array board representing the grid of candy, different positive integers board[i][j] represent different types of candies. A value of board[i][j] = 0 represents that the cell at position (i, j) is empty. The given board represents the state of the game following the player's move. Now, you need to restore the board to a stable state by crushing candies according to the following rules:
- If three or more candies of the same type are adjacent vertically or horizontally, "crush" them all at the same time - these positions become empty.
- After crushing all candies simultaneously, if an empty space on the board has candies on top of itself, then these candies will drop until they hit a candy or bottom at the same time. (No new candies will drop outside the top boundary.)
- After the above steps, there may exist more candies that can be crushed. If so, you need to repeat the above steps.
- If there does not exist more candies that can be crushed (ie. the board is stable), then return the current board.
You need to perform the above rules until the board becomes stable, then return the current board.
Example 1:
Input:
board =
[[110,5,112,113,114],[210,211,5,213,214],[310,311,3,313,314],[410,411,412,5,414],[5,1,512,3,3],[610,4,1,613,614],[710,1,2,713,714],[810,1,2,1,1],[1,1,2,2,2],[4,1,4,4,1014]]
Output:
[[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[110,0,0,0,114],[210,0,0,0,214],[310,0,0,113,314],[410,0,0,213,414],[610,211,112,313,614],[710,311,412,613,714],[810,411,512,713,1014]]
Explanation:
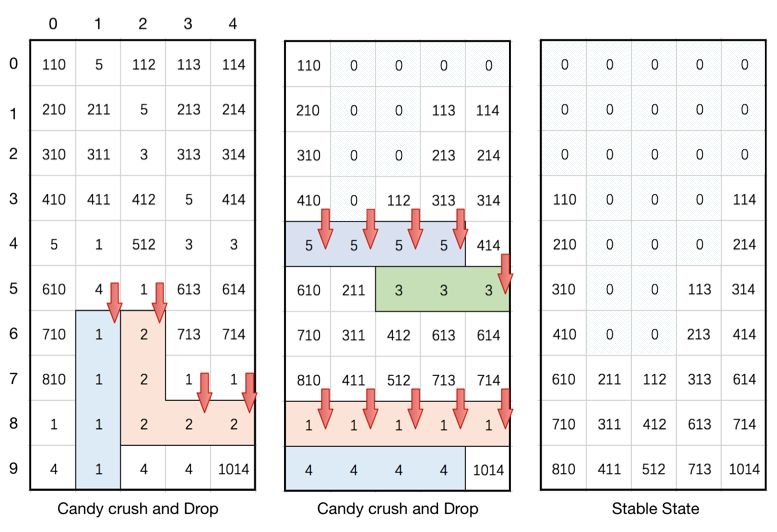
Note:
- The length of
boardwill be in the range [3, 50]. - The length of
board[i]will be in the range [3, 50]. - Each
board[i][j]will initially start as an integer in the range [1, 2000].
一个类似糖果消消乐游戏的题,给一个二维数组board,数组代表糖果,在水平和竖直方向上3个或以上连续相同的数字可以被消除,消除后位于上方的数字会填充空位。注意是所以能消除的糖果消除后然后再落下,进行第二次消除。直到最后没有能消除的了,达到稳定状态。
解法:标记出所有需要被crush的元素,然后去掉这些元素,将上面的数下降,空位变为0。难的地方是如何确定哪些元素需要被crush。
Python:
class Solution(object):
def candyCrush(self, board):
"""
:type board: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
R, C = len(board), len(board[0])
changed = True while changed:
changed = False for r in xrange(R):
for c in xrange(C-2):
if abs(board[r][c]) == abs(board[r][c+1]) == abs(board[r][c+2]) != 0:
board[r][c] = board[r][c+1] = board[r][c+2] = -abs(board[r][c])
changed = True for r in xrange(R-2):
for c in xrange(C):
if abs(board[r][c]) == abs(board[r+1][c]) == abs(board[r+2][c]) != 0:
board[r][c] = board[r+1][c] = board[r+2][c] = -abs(board[r][c])
changed = True for c in xrange(C):
i = R-1
for r in reversed(xrange(R)):
if board[r][c] > 0:
board[i][c] = board[r][c]
i -= 1
for r in reversed(xrange(i+1)):
board[r][c] = 0 return board
C++:
// Time: O((R * C)^2)
// Space: O(1) class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> candyCrush(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
const auto R = board.size(), C = board[0].size();
bool changed = true; while (changed) {
changed = false; for (int r = 0; r < R; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c + 2 < C; ++c) {
auto v = abs(board[r][c]);
if (v != 0 && v == abs(board[r][c + 1]) && v == abs(board[r][c + 2])) {
board[r][c] = board[r][c + 1] = board[r][c + 2] = -v;
changed = true;
}
}
} for (int r = 0; r + 2 < R; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) {
auto v = abs(board[r][c]);
if (v != 0 && v == abs(board[r + 1][c]) && v == abs(board[r + 2][c])) {
board[r][c] = board[r + 1][c] = board[r + 2][c] = -v;
changed = true;
}
}
} for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) {
int empty_r = R - 1;
for (int r = R - 1; r >= 0; --r) {
if (board[r][c] > 0) {
board[empty_r--][c] = board[r][c];
}
}
for (int r = empty_r; r >= 0; --r) {
board[r][c] = 0;
}
}
} return board;
}
};
C++:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> candyCrush(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
while (true) {
vector<pair<int, int>> del;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (board[i][j] == 0) continue;
int x0 = i, x1 = i, y0 = j, y1 = j;
while (x0 >= 0 && x0 > i - 3 && board[x0][j] == board[i][j]) --x0;
while (x1 < m && x1 < i + 3 && board[x1][j] == board[i][j]) ++x1;
while (y0 >= 0 && y0 > j - 3 && board[i][y0] == board[i][j]) --y0;
while (y1 < n && y1 < j + 3 && board[i][y1] == board[i][j]) ++y1;
if (x1 - x0 > 3 || y1 - y0 > 3) del.push_back({i, j});
}
}
if (del.empty()) break;
for (auto a : del) board[a.first][a.second] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int t = m - 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (board[i][j]) swap(board[t--][j], board[i][j]);
}
}
}
return board;
}
};
C++:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> candyCrush(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
bool toBeContinued = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { // horizontal crushing
for (int j = 0; j + 2 < n; ++j) {
int& v1 = board[i][j];
int& v2 = board[i][j+1];
int& v3 = board[i][j+2];
int v0 = std::abs(v1);
if (v0 && v0 == std::abs(v2) && v0 == std::abs(v3)) {
v1 = v2 = v3 = - v0;
toBeContinued = true;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i + 2 < m; ++i) { // vertical crushing
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int& v1 = board[i][j];
int& v2 = board[i+1][j];
int& v3 = board[i+2][j];
int v0 = std::abs(v1);
if (v0 && v0 == std::abs(v2) && v0 == std::abs(v3)) {
v1 = v2 = v3 = -v0;
toBeContinued = true;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { // gravity step
int dropTo = m - 1;
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (board[i][j] >= 0) {
board[dropTo--][j] = board[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = dropTo; i >= 0; i--) {
board[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return toBeContinued ? candyCrush(board) : board;
}
};
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总
[LeetCode] 723. Candy Crush 糖果粉碎的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 723. Candy Crush 糖果消消乐
This question is about implementing a basic elimination algorithm for Candy Crush. Given a 2D intege ...
- LeetCode 723. Candy Crush
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/candy-crush/ 题目: This question is about implementing a basic e ...
- [LeetCode] Candy Crush 糖果消消乐
This question is about implementing a basic elimination algorithm for Candy Crush. Given a 2D intege ...
- 【LeetCode】723. Candy Crush 解题报告 (C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 暴力 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode ...
- [LeetCode] Candy (分糖果),时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度为O(1),且只需遍历一次的实现
[LeetCode] Candy (分糖果),时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度为O(1),且只需遍历一次的实现 原题: There are N children standing in a line. ...
- LeetCode:135. 分发糖果
LeetCode:135. 分发糖果 老师想给孩子们分发糖果,有 N 个孩子站成了一条直线,老师会根据每个孩子的表现,预先给他们评分. 你需要按照以下要求,帮助老师给这些孩子分发糖果: 每个孩子至少分 ...
- [LeetCode] Candy 分糖果问题
There are N children standing in a line. Each child is assigned a rating value. You are giving candi ...
- LeetCode OJ:Candy(糖果问题)
There are N children standing in a line. Each child is assigned a rating value. You are giving candi ...
- LeetCode.888-公平的糖果交换(Fair Candy Swap)
这是悦乐书的第339次更新,第363篇原创 01 看题和准备 今天介绍的是LeetCode算法题中Easy级别的第208题(顺位题号是888).Alice和Bob有不同大小的糖果棒:A[i]是Alic ...
随机推荐
- JVM JDK1.8 以后的新特性 VisualVM的安装使用
一.JVM在新版本的改进更新以及相关知识 1.JVM在新版本的改进更新 图中可以看到运行时常量池是放在方法区的 1.1对比: JDK 1.6 及以往的 JDK 版本中,Java 类信息.常量池.静态变 ...
- websocket简单样例
服务端 var server = require('ws').Server; }); serv.on('connection',function(socket){ socket.send('hello ...
- php生成pdf,php+tcpdf生成pdf, php pdf插件
插件例子:https://tcpdf.org/examples/ 下载tcpdf插件: demo // Include the main TCPDF library (search for insta ...
- LeetCode 731. My Calendar II
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/my-calendar-ii/ 题目: Implement a MyCalendarTwo class to store y ...
- 使用 DML 自定义调试器输出
调试器标记语言 (DML) 提供了一种机制增强来自调试器和扩展的输出. 与 HTML 类似,调试器的标记支持允许将输出包括显示指令和额外非显示的标记窗体中的信息. 调试器用户界面,WinDbg 等中分 ...
- SQL必知必会收集学习
1.按查询列位置排序:如按第一列 降序排序 desc
- 浏览器事件循环 & nodejs事件循环
第1篇:如何理解EventLoop——宏任务和微任务篇 宏任务(MacroTask)引入 在 JS 中,大部分的任务都是在主线程上执行,常见的任务有: 渲染事件 用户交互事件 js脚本执行 网络请求. ...
- 【后缀数组】【SP1811】 LCS - Longest Common Substring
题目链接 题意翻译 输入2 个长度不大于250000的字符串,输出这2 个字符串的最长公共子串.如果没有公共子串则输出0 . 思路 求两个串的最长公共子串 代码 #include<iostrea ...
- 微信小程序前端promise封装
config.js const config = { base_url_api : "https://douban.uieee.com/v2/movie/", } export { ...
- sublime 添加到右键菜单
