linux用户权限管理, chmod, ln
1 /etc/passwd文件
用户名 密码 UID GID Full Name 主目录 默认的shell
asn :x :1000 :1000 :asnjudy@163.com :/home/asn :/bin/bash
sshd :x :116 :65534 : :/var/run/sshd :/usr/sbin/nologin
2 /etc/group文件
adm:x:4:syslog,asn
cdrom:x:24:asn
sudo:x:27:asn
dip:x:30:asn
plugdev:x:46:asn
lpadmin:x:108:asn
asn:x:1000:
sambashare:x:124:asn
docker:x:125:asn
查看 用户asn所属的组:

组名 密码 GID
nogroup:x:65534:
查看sshd所属的组:

3 文件的读、写、执行权限
u 文件所属用户
g 文件所属组
o 其他用户
chmod -R g=rwx testDir
给testDir目录所属的组赋予读、写、执行权限
=============================
chmod - change file mode bits
语法:
chmod [OPTION]... MODE[,MODE]... FILE...
chmod [OPTION]... OCTAL-MODE FILE...
chmod [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...
描述:
chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode,
which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
The format of a symbolic mode is [ugoa...][[+-=][perms...]...], where perms is either zero or more letters from the set rwxXst, or a single letter from the set ugo.
Multiple symbolic modes can be given, separated by commas.
一个符号模式的格式:
A combination of the letters ugoa controls which users' access to the file will be changed:
the user who owns it (u), 文件所有者为 o
other users in the file's group (g), 文件所属组中的其他用户(排除了拥有者) g
other users not in the file's group (o), 不在文件所属组中的其他用户 o
or all users (a). 所有用户
If none of these are given, the effect is as if a were given, but bits that are set in the umask are not affected. 如果未指定,即默认所有用户
The operator + causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file; +号把当前选中的文件模式位增加到每个文件的现有文件模式位
- causes them to be removed;
and = causes them to be added and causes unmentioned bits to be removed except that a directory's unmentioned set user and group ID bits are not affected.
=号,以前的模式位将被移除,除了目录的未提到打用户、组id位不受影响
The letters rwxXst select file mode bits for the affected users:
read (r),
write (w),
execute (or search for directories) (x),
execute/search only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user (X), 仅当文件是一个目录、或该文件对某些用户已经有执行权限
set user or group ID on execution (s),
restricted deletion flag or sticky bit (t).
Instead of one or more of these letters, you can specify exactly one of the letters ugo: 确切地,你能够指定字母ugo中的一个,而不能同时指定多个
the permissions granted to the user who owns the file (u), 权限授予拥有该文件的用户
the permissions granted to other users who are members of the file's group (g), 权限授予文件组成员中的其他用户
and the permissions granted to users that are in neither of the two preceding categories (o). 权限授予不是上面2种情况的用户
A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1. 通过位4、2、1相加得到
Omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and restricted deletion or sticky (1) attributes.
The second digit selects permissions for the user who owns the file: read (4), write (2), and execute (1);
the third selects permissions for other users in the file's group, with the same values; and the fourth for other users not in the file's group, with the same values.
chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links; chmod不能改变符号链接的权限 the chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. 因为符号连接的权限永远不会被使用,所以也无需改变符号连接的权限
However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. 然而对于命令行上列出的每个符号链接,chmod改变的是其指向文件的权限
In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals. 相反,在递归遍历文件的过程中,chmod会忽略遇到的符号连接
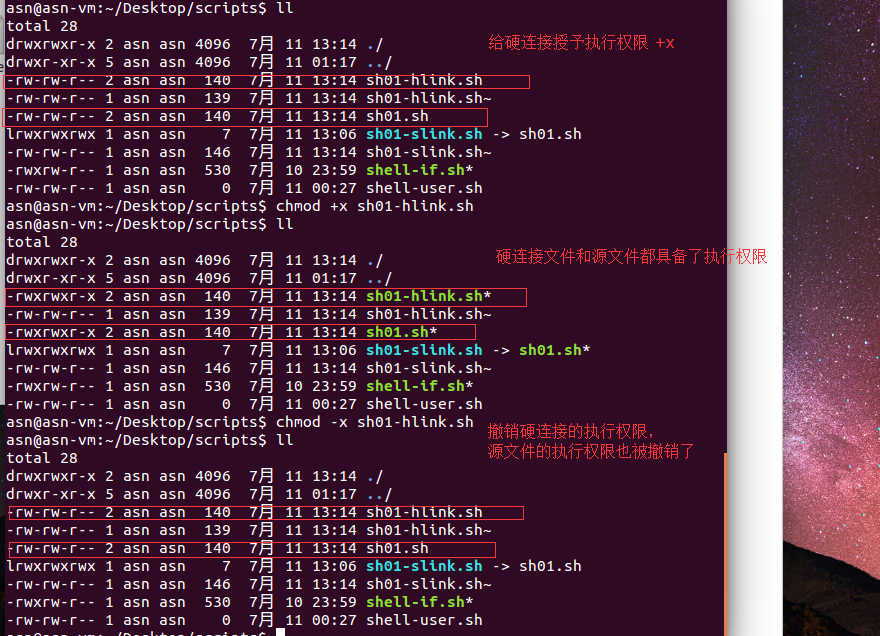
SETUID AND SETGID BITS (setUID 和 setGID位)
chmod clears the set-group-ID bit of a regular file, if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs,
如果文件的组ID与用户的有效组ID(或用户的服务组ID)不匹配,chmod将会清除一个常规文件的组ID设置位;
文件sh01.sh属于用户asn,属于组asn(组asn的ID是文件的组ID)。文件sh01.sh的组ID是文件sh01.sh所属用户的有效组,所以此文件的组ID设置位是有效的
rw- r-- r--, 分别是,用户ID设置位 --
unless the user has appro priate privileges.
举例:
新建组shtestgroup,把文件sh01.sh所属组asn改为shtestgroup
Additional restrictions may cause the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits of MODE or RFILE to be ignored.
This behavior depends on the policy and functionality of the underlying chmod system call. When in doubt, check the underlying system behavior.
chmod preserves a directory's set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits unless you explicitly specify otherwise.
You can set or clear the bits with symbolic modes like u+s and g-s, and you can set (but not clear) the bits with a numeric mode.
RESTRICTED DELETION FLAG OR STICKY BIT (restricted deletion flag or sticky bit)
The restricted deletion flag or sticky bit is a single bit, whose interpretation depends on the file type. 受限删除标志是一个单独的位,它的解释取决于文件的类型
For directories, it prevents unprivileged users from removing or renaming a file in the directory unless they own the file or the directory;
对于目录,该位会能够防止未授权的用户(什么样的用户就是被授权了的)移除或重命名目录中的一个文件,除非该未授权的用户拥有该文件或目录
this is called the restricted deletion flag for the directory, and is commonly found on world-writable directories like /tmp. 这就叫做目录的限制删除标志位,通常在如tmp这种人人可写的目录上发现。
For regular files on some older systems, the bit saves the program's text image on the swap device so it will load more quickly when run; this is called the sticky bit.
对于某些系统上的普通常文件,该位在swap交换区设备上保存了程序的文件镜像,所有运行该程序是能够更快地加载 --- 称为粘结位
OPTIONS
Change the mode of each FILE to MODE. With --reference, change the mode of each FILE to that of RFILE.
-c, --changes
like verbose but report only when a change is made 仅当改变做出时报告
-f, --silent, --quiet
-v, --verbose
output a diagnostic for every file processed
--no-preserve-root
do not treat '/' specially (the default) 不对根目录特别对待
--preserve-root
fail to operate recursively on '/' 使不能再根目录上进行递归操作
--reference=RFILE
use RFILE's mode instead of MODE values
-R, --recursive
change files and directories recursively 递归地改变文件、目录的模式
--help display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exit
Each MODE is of the form '[ugoa]*([-+=]([rwxXst]*|[ugo]))+|[-+=][0-7]+'.
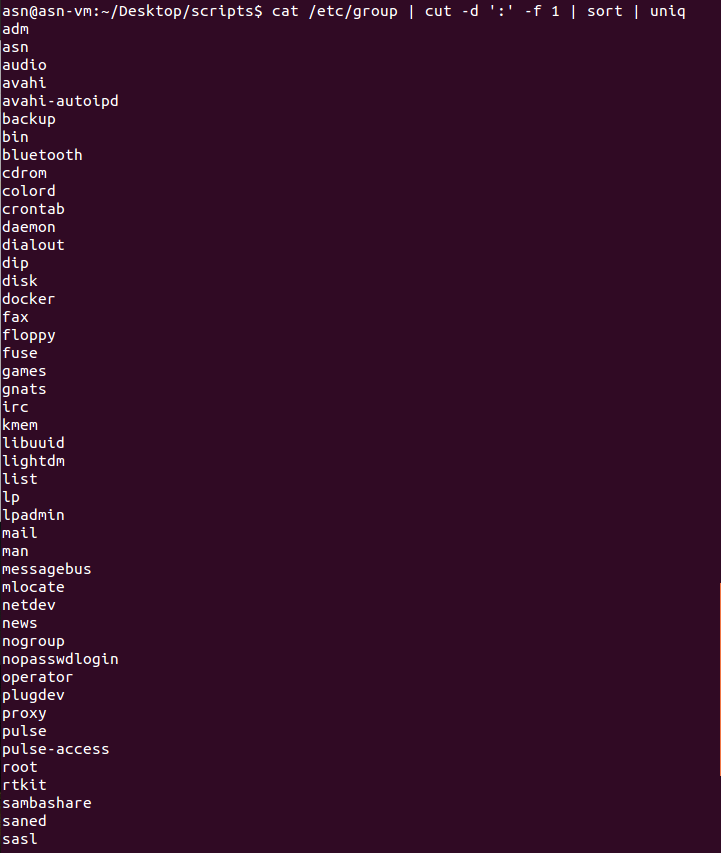
列出系统中的所有组名:
ln是linux中又一个非常重要命令,它的功能是为某一个文件在另外一个位置建立一个链接,这个命令最常用的参数是-s,具体用法是:ln –s 源文件目标文件。
当我们需要在不同的目录,用到相同的文件时,我们不需要在每一个需要的目录下都放一个必须相同的文件,
我们只要在某个固定的目录,放上该文件,然后在其它的目录下用ln命令链接(link)它就可以
例如:ln –s /bin/less /usr/local/bin/less
-s 是代号(symbolic)的意思。
这里有两点要注意:
)ln命令会保持每一处链接文件的同步性,也就是说,不论你改动了哪一处,其它的文件都会发生相同的变化;
)ln的链接分为软链接和硬链接两种, 无论是软链接还是硬链接,文件都保持同步变化
软链接就是ln –s ** **,它只会在你选定的位置上生成一个文件的镜像,不会占用磁盘空间
硬链接ln ** **,没有参数-s,它会在你选定的位置上生成一个和源文件大小相同的文件
如果你用ls察看一个目录时,发现有的文件后面有一个@的符号,那就是一个用ln命令生成的文件,用ls –l命令去察看,就可以看到显示的link的路径了。
指令名称 : ln
使用权限 : 所有使用者
使用方式 : ln [options] source dist
options选项: [-bdfinsvF] [-S backup-suffix] [-V {numbered,existing,simple}] [--help] [--version] [--]
说明 : Linux/Unix 档案系统中,有所谓的连结(link),我们可以将其视为档案的别名,而连结又可分为两种 : 硬连结(hard link)与软连结(symbolic link),
硬连结的意思是一个档案可以有多个名称,而软连结的方式则是产生一个特殊的档案,该档案的内容是指向另一个档案的位置。
硬连结是存在同一个档案系统中,而软连结却可以跨越不同的档案系统。
ln source dist产生一个连接文件dist(连接到source),至于使用硬连结或软链结则由参数决定
不论是硬连结或软链结都不会将原本的档案复制一份,只会占用非常少量的磁碟空间。
-f 链结时先将与 dist 同档名的档案删除
-d 允许系统管理者硬链结自己的目录
-i 在删除与 dist 同档名的档案时先进行询问
-n 在进行软连结时,将 dist 视为一般的档案
-s 进行软链结(symbolic link)
-v 在连结之前显示其档名
-b 将在链结时会被覆写或删除的档案进行备份
-S SUFFIX 将备份的档案都加上 SUFFIX 的字尾
-V METHOD 指定备份的方式
--help 显示辅助说明
--version 显示版本
范例 :
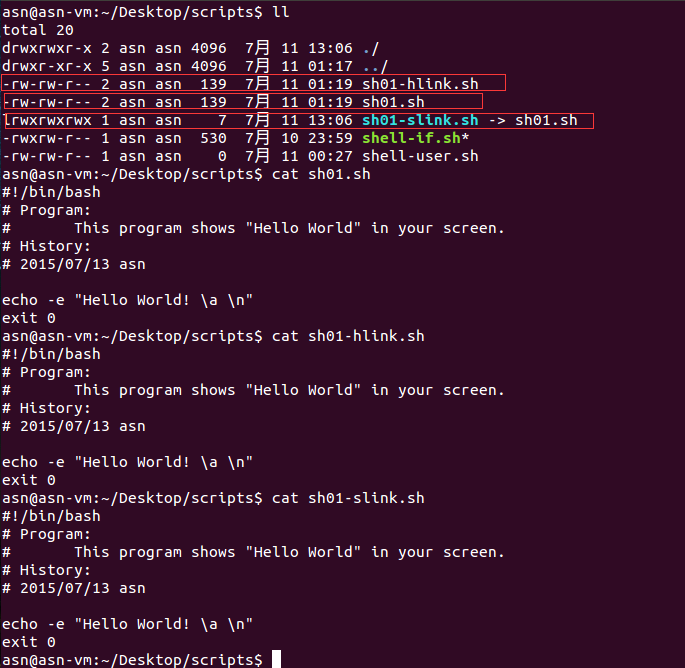
从档案sh01.sh产生一个软连接文件sh01-slink.sh --- 产生的软连接文件(大小为7个字节),
$ ln -s sh01.sh sh01-slink.sh
从档案sh01.sh产生一个硬连接文件sh01-hlink.sh --- 硬连接,拷贝源文件sh01.sh的内容作为新文件sh01-hlink.sh(就是一个普通的文件,与源文件进行了关联
- 内容相互同步更新)的内容
ln sh01.sh sh01-hlink.sh
查看文件:
linux用户权限管理, chmod, ln的更多相关文章
- Linux常用命令之用户权限管理chmod、chown、chgrp、umask命令讲解
这节课我们重点来学习权限管理命令,说到权限大家可能第一时间能想到的就是读.写.执行 rwx 三种权限,在正式讲解权限命令之前,先简单的介绍一下rwx权限对于文件和目录的不同含义. 权限字符 权限 对文 ...
- linux用户管理,linux用户口令管理,linux用户组管理,linux用户权限管理详解
linux用户管理 http://www.qq210.com/shoutu/android 用户账号的添加(新加用户需添加用户口令) :增加用户账号就是在/etc/passwd文件中为新用户增加一条记 ...
- Linux_CentOS用户管理 和 用户权限管理 chmod、ACL、 visudo
一.用户管理 Linux 系统同时可以支持多个用户,每个用户对自己的文件设备有特殊的权利,能够保 证用户之间互不干扰.就像手机开了助手一样,同时登陆多个 qq 账号,当硬件配置非常高 时,每个用户还可 ...
- 二十八、linux下权限管理chmod
(1)查看权限 终端下需要查看文件或文件夹的权限时,可以使用ll查看当前目录的各文件权限. 如图,r代表读取权限,w代表写入权限,x代表执行权限:-代表普通文件,d代表文件夹.使用命令chmod可以修 ...
- Linux用户权限管理
Linux操作系统: 多用户多任务的操作系统 用户类型分为: 管理员用户 : root 普通用户分为:系统用户/程序用户 用户相关的文件: /etc/passwd 用 ...
- linux 用户管理,用户权限管理,用户组管理
linux 用户管理,用户权限管理,用户组管理 一:ls -l 命令 解释 第个d表示是目录,如果是文件是-,如果是连接是l 第2到4个 rwx 表示创建者的操作权限 r 读,w 写,x 执行 第5到 ...
- chmod g+s 、chmod o+t 、chmod u+s:Linux高级权限管理
关于linux下权限操作chmod的一些说明!比rxw高级内容! 转载自http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26642180-id-3378119.html Set uid, ...
- Linux 服务器用户权限管理改造方案与实施项目
Linux 服务器用户权限管理改造方案与实施项目 在了解公司业务流程后,提出权限整改方案改进公司超级权限root泛滥的现状. 我首先撰写方案后,给boss看,取得boss的支持后,召集大家开会讨论. ...
- Linux下安装SVN,仓库创建,用户权限管理
Exported from Notepad++ Linux下安装SVN,仓库创建,用户权限管理 1.SVN安装 Ubuntu系统下安装:sudoapt-getinstallsubv ...
随机推荐
- PHP 学习1.0
1.简单一个class 类: 获取表单提交的值 采用post方式 <html><head><title>PHP TEST</title></hea ...
- scala的插值器
Scala 为我们提供了三种字符串插值的方式,分别是 s, f 和 raw.它们都是定义在 StringContext 中的方法. s 字符串插值器 val a = 2println(s"小 ...
- python实现贝叶斯网络的概率推导(Probabilistic Inference)
写在前面 这是HIT2019人工智能实验三,由于时间紧张,代码没有进行任何优化,实验算法仅供参考. 实验要求 实现贝叶斯网络的概率推导(Probabilistic Inference) 具体实验指导书 ...
- 关于PHP学习--摘自知乎
主要是学框架(其实也没啥可学的).数据库.服务器.linux. 所以我推荐apache/nginx文档,框架的文档,mysql的文档,linux使用说明,等等等等. PHP: PHP 手册MySQL ...
- SpringBoot Cloud eureka 注册中心
SpringBoot Cloud是什么 Spring Cloud是一个分布式的整体解决方案. Spring Cloud 为开发者提供了在分布式系统(配置管理,服务发现,熔断,路由,微代理,控制总线,一 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十八章:立方体贴图
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十八章:立方体贴图 代码工程地址: https://github.c ...
- 解决VS+Qt不生成moc文件问题
使用VS的Qt插件进行Qt开发时,有时候会遇到不能生成moc文件的问题. 1.在工程中可以看到这个Generated files目录下是有一个看似moc文件的文件,双击打开的话: 如果能正常打开,文件 ...
- Codeforces 425B
点击打开题目链接 题意:给定一个n×m的0,1矩阵,做多可以对矩阵做k次变换,每次变换只可以将矩阵的某一个元素由0变成1,或从1变成0. 求最小的变换次数使得得到的矩阵满足:每一个连通块都是一个“实心 ...
- pycharm 永久注册
pycharm 使用又到期了,找到了破解版亲测(到期日期2099/12/31),绝对简单好用,直接使用步骤: 一,下载pycharm(windows版): https://www.jetbrains ...
- TZOJ 4359: Partition the beans (二分)
描述 Given an N x N square grid (2 <= N <= 15) and each grid has some beans in it. You want to w ...
