逐个使用C++11新特性
C++11
auto & decltype
auto:根据变量初始值来推导变量类型,并用右值初始化变量。
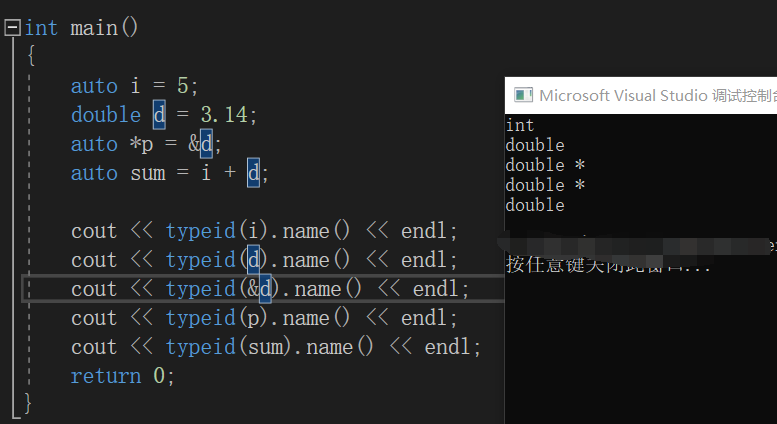
int main()
{
map<string, vector<string>> family;
family.insert(pair<string, vector<string>>("陈", {"澄", "尘"}));
family.insert(pair<string, vector<string>>("朱", {"珠", "茱"}));
for(const auto &mp : family)
{
cout << mp.first << endl;
for(const auto &str : mp.second)
cout << str << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return ;
}

decltype:从表达式推导出类型,并将变量定义为该类型,但不用表达式的值初始化该变量。
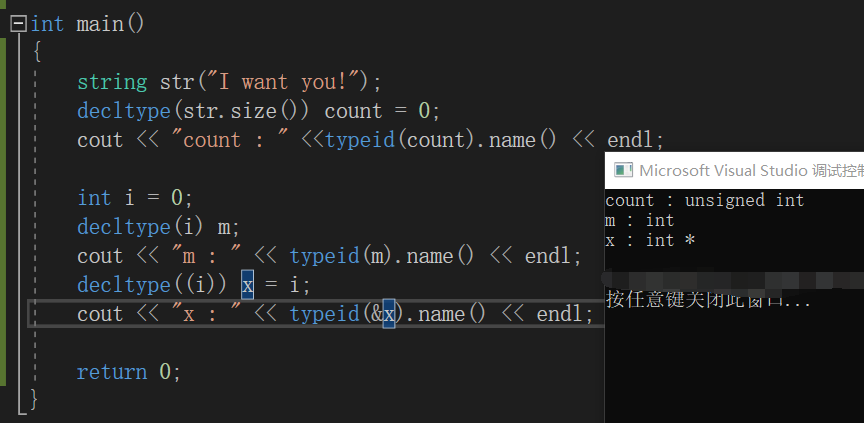
这里要注意下:decltype(i)--是i的类型,而decltype((i))就是引用了。就像上面例子中的x 就是int &x;
右值引用
新标准在拷贝构造函数、拷贝赋值运算符和析构函数之外,还增加了移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符,而这二位就需要右值引用的支持。
1. 延长将亡值的生命。
//右值引用
int a = ;
int &b = a;
int &&bb = ;//右值引用只能绑定将亡值
//int &&bb = a;//错,a是左值(持久值)
a = std::move(bb);//右值引用移动 cout << "引用:" << b << endl;
cout << "右值引用:" << bb << endl;
cout << "移动: " << a << endl;
&&bb = 999;//错,类似左值引用,不可二次赋值
&b = 888;//错

我们居然输出了89,要知道,右值只是临时量,用完就扔的。
2. 用于移动(构造)函数
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; class test
{
public:
test();
~test();
void push(const int& i);
void push(int&& i)
{
bar = std::move(i);//std::move(右值引用)实现移动
}
private:
int bar;
}; int main()
{
int a = ;
test t;
t.push();
//t.push(a);错误无法将右值绑定到左值 return ;
}
范围for循环
统计字符
string str = "No pain, no gain! Everyone need to struggle for himself.";
decltype(str.length()) count = , count1 =;
for (auto i : str)
if (ispunct(i))
++count;
else
++count1;
cout << "字符串长度:" << str.size() << endl;
cout << "标点字符的个数:" << count << endl;
cout << "其他字符的个数:" << count1 << endl;
改写字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; int main()
{
string str("No pain, no gain! Everyone need to struggle for himself.");
cout << str << endl; for (auto &c : str)
c = toupper(c);//小写换大写 cout << str << endl;;
return ;
}

去除字符
//去除标点 1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; int main()
{
string input, res = "";
while (cin >> input)
{
for (auto c : input)
if (!ispunct(c))
res += c;
cout << res << endl;
res = "";
}
}
智能指针
std::weak_ptr & std::shared_ptr
lambda表达式·λ
先看它怎么用
例1
//惯用法
//[捕获外部变量](参数列表)->返回类型{ 函数体(别忘记";")}
auto str = "I want you!";
auto f = [](string str)->int { return str.size(); };
cout << f(str) << endl; int m = ;
//捕获参数---值捕获
auto getValue = [m] {cout << m << endl; };
getValue();
//捕获参数---引用捕获
auto getValue1 = [&m] {cout << m << endl; };
getValue1(); //捕获参数---隐式值捕获
auto getValue2 = [=] {cout << m << endl; };
getValue2(); //捕获参数---隐式引用捕获
auto getValue3 = [&] {
cout << m << endl;
cout << "修改:" << ++m << endl;
};
getValue3(); int num[] = { , , , , };
sort(num, num + , [](const int a, const int b) ->bool {return a > b; }); for (auto i : num)
cout << i << " ";

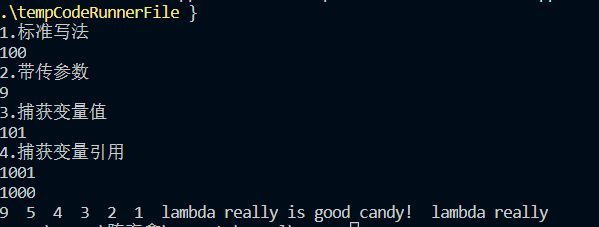
例子补充:
int main()
{
//lambda表达式
//1.标准写法[捕获函数内局部变量列表] (传入参数列表) ->return type {function body;} ;
auto fc = []()->int {
return ;
};
cout << "1.标准写法\n" << fc() << endl; //2.带传参数
auto f = [](int a, int b) {
return a + b;
};
cout << "2.带传参数\n" << f(, ) << endl; //3.捕获变量值
int param = ;
auto ff = [param](int b){
return param + b;
};
cout << "3.捕获变量值\n" << ff() << endl; //4.捕获变量引用
int param2 = ;
auto ff2 = [¶m2](int b){
param2 += ;
return param2 + b;
};
cout << "4.捕获变量引用\n" <<ff2() << endl;
cout << param2 << endl; //4.当作算法函数谓词,例修改sort排序降序
vector<int> vec = {, , , , , };
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a, int b){ return a > b;});
for(auto i : vec)
cout << i << " "; //隐式引用捕获:即默认局部变量都是引用类型,可以在λ体内修改,也可以在参数捕获列表中指定某些参数只是值捕获,否则全部默认引用捕获
string str = "lambda";
string str2 = " is good candy!";
auto addStr = [&]{
str = "lambda really";
return str + str2;
};
cout << addStr() << " " << str << endl;
return ;
}
它的优势在哪里?又或者说为什么要用它呢?
再看一个例子
例2
//多线程
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i)
{
std::thread t([i] { cout << i << endl; });//<thread>
t.detach();
}
从上面的多个例子看来,我们可以很方便的实现“函数内的函数定义和使用”,即函数嵌套【例1】,这样一来就不用再在外部定义函数,然后才能使用【例2】。甚至,它连函数名都可以不要,就像上面的sort函数中的用法一样。极大的简化了我们的代码,可读性也增强了许多,不用再回到定义处推敲了。
逐个使用C++11新特性的更多相关文章
- C++ 11学习和掌握 ——《深入理解C++ 11:C++11新特性解析和应用》读书笔记(一)
因为偶然的机会,在图书馆看到<深入理解C++ 11:C++11新特性解析和应用>这本书,大致扫下,受益匪浅,就果断借出来,对于其中的部分内容进行详读并亲自编程测试相关代码,也就有了整理写出 ...
- C++11新特性总结 (二)
1. 范围for语句 C++11 引入了一种更为简单的for语句,这种for语句可以很方便的遍历容器或其他序列的所有元素 vector<int> vec = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; ...
- C++11新特性总结 (一)
1. 概述 最近在看C++ Primer5 刚好看到一半,总结一下C++11里面确实加了很多新东西,如果没有任何了解,别说自己写了,看别人写的代码估计都会有些吃力.C++ Primer5是学习C++1 ...
- C++ 11 新特性
C++11新特性: 1.auto 2.nullptr 3.for 4.lambda表达式 5.override ...
- [转载] C++11新特性
C++11标准发布已有一段时间了, 维基百科上有对C++11新标准的变化和C++11新特性介绍的文章. 我是一名C++程序员,非常想了解一下C++11. 英文版的维基百科看起来非常费劲,而中文版维基百 ...
- 在C++98基础上学习C++11新特性
自己一直用的是C++98规范来编程,对于C++11只闻其名却没用过其特性.近期因为工作的需要,需要掌握C++11的一些特性,所以查阅了一些C++11资料.因为自己有C++98的基础,所以从C++98过 ...
- C++11新特性——range for
很多编程语言都有range for语法功能,自C++11起,终于将这个重要功能加入C++标准中.range for语句,可以方便的遍历给定序列中的每个元素并对其执行某种操作. 1.基本语法 for(d ...
- C++11新特性——大括号初始化
C++11之前,C++主要有以下几种初始化方式: //小括号初始化 string str("hello"); //等号初始化 string str="hello" ...
- C++11新特性之六——元编程
C++11新特性之六——元编程
随机推荐
- SpringCloud学习系列之四-----配置中心(Config)使用详解
前言 本篇主要介绍的是SpringCloud中的分布式配置中心(SpringCloud Config)的相关使用教程. SpringCloud Config Config 介绍 Spring Clou ...
- Docker最全教程之使用Docker搭建Java开发环境(十七)
前言 Java是一门面向对象的优秀编程语言,市场占有率极高,但是在容器化实践过程中,发现官方支持并不友好,同时与其他编程语言的基础镜像相比(具体见各语言镜像比较),确实是非常臃肿. 本篇仅作探索,希望 ...
- Android使用google breakpad捕获分析native cash
Android 开发高手课 课后练习(1) 一.Chapter01 崩溃 https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/70602 https://github.c ...
- oppo5.0以上系统怎么样不Root激活Xposed框架的经验
在非常多单位的引流或者业务操作中,基本上都需要使用安卓的黑高科技术Xposed框架,前几天我们单位购来了一批新的oppo5.0以上系统,基本上都都是基于7.0以上版本,基本上都不能够获取root超级权 ...
- ORA-39127: 调用 "WMSYS"."LT_EXPORT_PKG"."SCHEMA_INFO_EXP" 时发生意外错误
expdp 告警提示: Export: Release 11.2.0.4.0 - Production on 星期日 4月 28 12:14:51 2019....ORA-39127: 调用 &quo ...
- Maven配置ojdbc14-10.2.0.4.0.jar
对于oralce的jdbc驱动,在maven上搜索到把pom配置复制到pom.xml里进行引用的时候出现下面这种情况 <dependency> <groupId>com.ora ...
- [原创] 分享我们自己搭建的微信小程序开发框架——wframe及设计思想详解
wframe不是控件库,也不是UI库,她是一个微信小程序面向对象编程框架,代码只有几百行.她的主要功能是规范小程序项目的文件结构.规范应用程序初始化.规范页面加载及授权管理的框架,当然,wframe也 ...
- JS的常用正则表达式 验证密码(转载自用)
JS的正则表达式 强:字母+数字+特殊字符 ^(?![a-zA-z]+$)(?!\d+$)(?![!@#$%^&*]+$)(?![a-zA-z\d]+$)(?