Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) A , B , C 水,水,拓扑dp
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently Adaltik discovered japanese crosswords. Japanese crossword is a picture, represented as a table sized a × b squares, and each square is colored white or black. There are integers to the left of the rows and to the top of the columns, encrypting the corresponding row or column. The number of integers represents how many groups of black squares there are in corresponding row or column, and the integers themselves represents the number of consecutive black squares in corresponding group (you can find more detailed explanation in Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Japanese_crossword).
Adaltik decided that the general case of japanese crossword is too complicated and drew a row consisting of n squares (e.g. japanese crossword sized 1 × n), which he wants to encrypt in the same way as in japanese crossword.
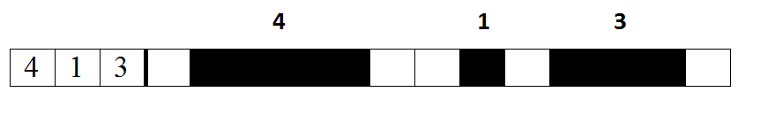 The example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.
The example of encrypting of a single row of japanese crossword.
Help Adaltik find the numbers encrypting the row he drew.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the length of the row. The second line of the input contains a single string consisting of n characters 'B' or 'W', ('B' corresponds to black square, 'W' — to white square in the row that Adaltik drew).
The first line should contain a single integer k — the number of integers encrypting the row, e.g. the number of groups of black squares in the row.
The second line should contain k integers, encrypting the row, e.g. corresponding to sizes of groups of consecutive black squares in the order from left to right.
3
BBW
1
2
5
BWBWB
3
1 1 1
4
WWWW
0
4
BBBB
1
4
13
WBBBBWWBWBBBW
3
4 1 3
The last sample case correspond to the picture in the statement.
题意:输出连续B的个数;
思路:模拟;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
char a[N];
vector<int>ans;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",a);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
int sum=;
if(a[i]=='W')continue;
while(a[i]=='B')
{
sum++;
i++;
}
ans.push_back(sum);
}
cout<<ans.size()<<endl;
for(int i=;i<ans.size();i++)
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Vanya is managed to enter his favourite site Codehorses. Vanya uses n distinct passwords for sites at all, however he can't remember which one exactly he specified during Codehorses registration.
Vanya will enter passwords in order of non-decreasing their lengths, and he will enter passwords of same length in arbitrary order. Just when Vanya will have entered the correct password, he is immediately authorized on the site. Vanya will not enter any password twice.
Entering any passwords takes one second for Vanya. But if Vanya will enter wrong password k times, then he is able to make the next try only 5 seconds after that. Vanya makes each try immediately, that is, at each moment when Vanya is able to enter password, he is doing that.
Determine how many seconds will Vanya need to enter Codehorses in the best case for him (if he spends minimum possible number of second) and in the worst case (if he spends maximum possible amount of seconds).
The first line of the input contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 100) — the number of Vanya's passwords and the number of failed tries, after which the access to the site is blocked for 5 seconds.
The next n lines contains passwords, one per line — pairwise distinct non-empty strings consisting of latin letters and digits. Each password length does not exceed 100 characters.
The last line of the input contains the Vanya's Codehorses password. It is guaranteed that the Vanya's Codehorses password is equal to some of his n passwords.
Print two integers — time (in seconds), Vanya needs to be authorized to Codehorses in the best case for him and in the worst case respectively.
5 2
cba
abc
bb1
abC
ABC
abc
1 15
4 100
11
22
1
2
22
3 4
Consider the first sample case. As soon as all passwords have the same length, Vanya can enter the right password at the first try as well as at the last try. If he enters it at the first try, he spends exactly 1 second. Thus in the best case the answer is 1. If, at the other hand, he enters it at the last try, he enters another 4 passwords before. He spends 2 seconds to enter first 2 passwords, then he waits 5seconds as soon as he made 2 wrong tries. Then he spends 2 more seconds to enter 2 wrong passwords, again waits 5 seconds and, finally, enters the correct password spending 1 more second. In summary in the worst case he is able to be authorized in 15 seconds.
Consider the second sample case. There is no way of entering passwords and get the access to the site blocked. As soon as the required password has length of 2, Vanya enters all passwords of length 1 anyway, spending 2 seconds for that. Then, in the best case, he immediately enters the correct password and the answer for the best case is 3, but in the worst case he enters wrong password of length 2 and only then the right one, spending 4 seconds at all.
题意:给你一个n个字符串,从长度小的到大的输入,每k次会等待五秒,求最坏和最好的情况;
思路:模拟;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
#define eps 1e-14
const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
char ch[][];
char pass[N];
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%s",&ch[i]);
int flag=,k=;
scanf("%s",pass);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(strlen(ch[i])<strlen(pass))
flag++;
if(strcmp(ch[i],pass)==)
k++;
if(strlen(ch[i])>strlen(pass))
k++;
}
n=n-k+;
int ans=;
while(n)
{
ans+=min(n,m);
n-=min(n,m);
if(n==)
break;
ans+=;
}
printf("%d %d\n",flag++(flag/m)*,ans);
return ;
}
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently Irina arrived to one of the most famous cities of Berland — the Berlatov city. There are n showplaces in the city, numbered from1 to n, and some of them are connected by one-directional roads. The roads in Berlatov are designed in a way such that there are nocyclic routes between showplaces.
Initially Irina stands at the showplace 1, and the endpoint of her journey is the showplace n. Naturally, Irina wants to visit as much showplaces as she can during her journey. However, Irina's stay in Berlatov is limited and she can't be there for more than T time units.
Help Irina determine how many showplaces she may visit during her journey from showplace 1 to showplace n within a time not exceeding T. It is guaranteed that there is at least one route from showplace 1 to showplace n such that Irina will spend no more than Ttime units passing it.
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and T (2 ≤ n ≤ 5000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 5000, 1 ≤ T ≤ 109) — the number of showplaces, the number of roads between them and the time of Irina's stay in Berlatov respectively.
The next m lines describes roads in Berlatov. i-th of them contains 3 integers ui, vi, ti (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi, 1 ≤ ti ≤ 109), meaning that there is a road starting from showplace ui and leading to showplace vi, and Irina spends ti time units to pass it. It is guaranteed that the roads do not form cyclic routes.
It is guaranteed, that there is at most one road between each pair of showplaces.
Print the single integer k (2 ≤ k ≤ n) — the maximum number of showplaces that Irina can visit during her journey from showplace 1 to showplace n within time not exceeding T, in the first line.
Print k distinct integers in the second line — indices of showplaces that Irina will visit on her route, in the order of encountering them.
If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
4 3 13
1 2 5
2 3 7
2 4 8
3
1 2 4
6 6 7
1 2 2
1 3 3
3 6 3
2 4 2
4 6 2
6 5 1
4
1 2 4 6
5 5 6
1 3 3
3 5 3
1 2 2
2 4 3
4 5 2
3
1 3 5
题意:给你一个图,n个点,m条边,总时间T;求在T时间内能走过最多的点从1-n;
思路:拓扑dp;dp[i][j]表示从1-i经过j个点花费的时间;
坑点:有无关的点;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define pi (4*atan(1.0))
const int N=2e5+,M=4e6+,inf=1e9+,mod=1e9+;
const ll INF=1e18+;
int dp[][];
int du[N];
struct is
{
int v,w;
int next;
}edge1[N],edge2[N] ;
int jiedge1,jiedge2;
int head1[N],head2[N];
int flag[N];
int n,m,T;
void init()
{
memset(du,,sizeof(du));
memset(head1,,sizeof(head1));
memset(head2,,sizeof(head2));
memset(flag,,sizeof(flag));
jiedge1=;
jiedge2=;
}
void add1(int u,int v,int w)
{
++jiedge1;
edge1[jiedge1].v=v;
edge1[jiedge1].w=w;
edge1[jiedge1].next=head1[u];
head1[u]=jiedge1;
}
void add2(int u,int v,int w)
{
++jiedge2;
edge2[jiedge2].v=v;
edge2[jiedge2].w=w;
edge2[jiedge2].next=head2[u];
head2[u]=jiedge2;
}
void bfs(int u)
{
queue<int>q;
q.push(u);
dp[][]=;
while(!q.empty())
{
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head1[u];i;i=edge1[i].next)
{
int v=edge1[i].v;
int w=edge1[i].w;
for(int t=;t<=n;t++)
{
if(dp[u][t-]+w<=T)
{
dp[v][t]=min(dp[v][t],dp[u][t-]+w);
}
}
if(--du[v]==&&!flag[v])q.push(v);
}
}
}
int ans[N];
void getans(int u,int x)
{
printf("%d\n",x);
int flag=x;
while(u!=)
{
for(int i=head2[u];i;i=edge2[i].next)
{
int v=edge2[i].v;
int w=edge2[i].w;
if(w+dp[v][x-]==dp[u][x])
{
ans[x]=v;
x--;
u=v;
break;
}
}
}
for(int i=;i<=flag;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
printf("%d\n",n);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&T);
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
{
int u,v,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
add1(u,v,w);
add2(v,u,w);
du[v]++;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)for(int t=;t<=n;t++)dp[i][t]=inf;
queue<int>q;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(du[i]==)
q.push(i),flag[i]=;
while(!q.empty())
{
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head1[u];i;i=edge1[i].next)
{
int v=edge1[i].v;
du[v]--;
if(du[v]==&&v!=)
q.push(v),flag[v]=;
}
}
bfs();
for(int i=n;i>=;i--)
if(dp[n][i]<inf)
{
getans(n,i);
break;
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) A , B , C 水,水,拓扑dp的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) A. One-dimensional Japanese Crosswor 水题
A. One-dimensional Japanese Crossword 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/A Description ...
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 模拟 dp+dfs 优先队列
A. One-dimensional Japanese Crossword time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabyt ...
- Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie 水题
Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2)A. Vitaliy and Pie Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: xxx ...
- Codeforces Round #285 (Div. 2) A B C 模拟 stl 拓扑排序
A. Contest time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 trick dp 并查集
A. Mahmoud and Longest Uncommon Subsequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 ...
- 拓扑序+dp Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) C
http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/C 题目大意:给你有向路,每条路都有一个权值t,你从1走到n,最多花费不能超过T,问在T时间内最多能访问多少城市? ...
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) D. Maxim and Array 贪心
D. Maxim and Array 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/D Description Recently Maxim has ...
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) C. Journey DP
C. Journey 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/C Description Recently Irina arrived to o ...
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) B. Passwords 贪心
B. Passwords 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/721/problem/B Description Vanya is managed to enter ...
- Codeforces Round #374 (Div. 2) D. Maxim and Array —— 贪心
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/721/D D. Maxim and Array time limit per test 2 seconds ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ1820】[JSOI2010]Express Service 快递服务 暴力DP
[BZOJ1820][JSOI2010]Express Service 快递服务 Description 「飞奔」快递公司成立之后,已经分别与市内许多中小企业公司签订邮件收送服务契约.由于有些公司是在 ...
- 《从零开始学Swift》学习笔记(Day4)——用Playground工具编写Swift
Swift 2.0学习笔记(Day4)——用Playground工具编写Swift 原创文章,欢迎转载.转载请注明:关东升的博客 用Playground编写Swift代码目的是为了学习.测试算法.验证 ...
- 新手之使用git
本篇博客针对不会Git的小童鞋,大神们可以绕过,错误之处谢谢指正: 关于GitHub的强大此处不在说明,知道GitHub也有一段时间了,但是一直苦于不会使用. 本篇文章介绍的是如何将工程代码托管到上面 ...
- SSL逐渐演变到TLS
w https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/超文本传输安全协议
- <2013 08 27> 雅思阅读相关
1.雅思阅读的总体难度不大,但是时间较紧,三段较长的阅读材料和40个题目,总耗时60min.基本上前两个材料可以花15~20min,最后一个材料至少花20min完成. 2.阅读的技巧在于三点:其一,先 ...
- Docker介绍及优缺点对比分析
1.什么是Docker Docker最初是dotCloud公司创始人Solomon Hykes在法国期间发起的一个公司内部项目,于2013年3月以Apache 2.0授权协议开源,主要项目代码在Git ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android中adb install 安装错误常见列表
adb的安装过程分为传输与安装两步. 在出错后,adb会报告错误信息,但是信息可能只是一个代号,需要自己定位分析出错的原因. 下面是从网上找到的几种常见的错误及解决方法: 1.INSTALL_FAIL ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>修改Android签名证书keystore的密码、别名alias以及别名密码
转载于:http://blog.k-res.net/archives/1229.html 和 http://blog.k-res.net/archives/1671.html ADT允许自定义调试用 ...
- Linux中的awk命令
awk '条件1{动作1} 条件2{动作2} ...' 文件名 条件: BEGIN 在处理文件里的第一行数据之前执行 END 在处理完文件里的最后一行数据 ...
- MongoDB学习笔记—常用命令
这里记录一下MongoDB常用的命令 数据库相关 创建数据库 use DATABASE_NAME 如果数据库不存在,则创建数据库,否则切换到指定数据库. 删除数据库:切换到要删除的数据库下,执行命令即 ...
