android开发_ViewGroup(组视图)-- 五大布局
view组--ViewGroup(组视图)
ViewGroup的作用:在view中添加子控件。ViewGroup的5个子类,就是五大布局:
(1) LinearLayout 线性布局(常用)
(2) RelativeLayout 相对布局(常用)
(3) FrameLayout 帧布局
(4) AbsoluteLayout 绝对布局
(5) TableLayout 表格布局
1 LinearLayout 线性布局:在该布局下包含的子布局列表为 横向 或 纵向 排布
1.1 LinearLayout 默认是横向布局,即:从左到右 布局控件
指定布局方向: android:orientation=“ ”
1 <!-- 指定布局方向的属 性:orientation,
2 属性值:horizontal(横向)
3 vertical(纵向)
4 -->
5
6 <!--横向布局-->
7 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
8 android:layout_width="match_parent"
9 android:layout_height="match_parent"
10 android:orientation="horizontal" >
11
12 <!--纵向布局-->
13 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
14 android:layout_width="match_parent"
15 android:layout_height="match_parent"
16 android:orientation="vertical" >
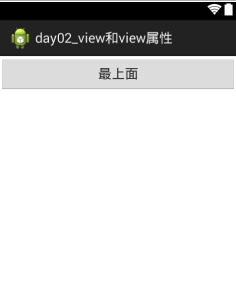
1.2 权重(只有在子控件中才有的属性)
android:layout_weight=" "
例1:没添加权重属性之前:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2
3 <!-- 指定布局方向的属相为:orientation,属性值:horizontal(横向)或vertical(纵向) -->
4 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
5 android:layout_width="match_parent"
6 android:layout_height="match_parent"
7 android:orientation="horizontal" >
8
9 <TextView
10 android:id="@+id/textView1"
11 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
12 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
13 android:text="TextView" />
14
15 <TextView
16 android:id="@+id/textView2"
17 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
19 android:text="TextView" />
20
21 <TextView
22 android:id="@+id/textView3"
23 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
24 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
25 android:text="TextView" />
26
27 </LinearLayout>

添加权重属性 android:layout_weight=" " 之后
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2
3 <!-- 指定布局方向的属相为:orientation,属性值:horizontal(横向)或vertical(纵向) -->
4 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
5 android:layout_width="match_parent"
6 android:layout_height="match_parent"
7 android:orientation="horizontal" >
8
9 <TextView
10 android:id="@+id/textView1"
11 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
12 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
13 android:layout_weight="1"
14 android:text="TextView" />
15
16 <TextView
17 android:id="@+id/textView2"
18 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
19 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
20 android:layout_weight="1"
21 android:text="TextView" />
22
23 <TextView
24 android:id="@+id/textView3"
25 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
26 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
27 android:layout_weight="1"
28 android:text="TextView" />
29
30 </LinearLayout>
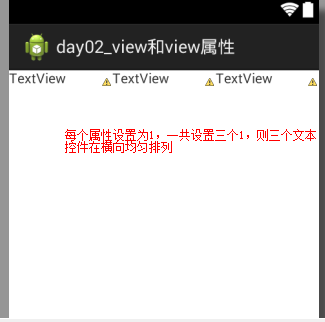
纵向布局同理。
例2:实现下面布局

颜色值忽略
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#F00"> <View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#F00"
/>
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#0F0"
/>
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#00F"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#F00"
/>
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#0F0"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#00F">
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#F00"
/>
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#0F0"
/>
<View
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#00F"
/>
</LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
2 RelativeLayout 相对布局:
2.1相对父控件布局
(1) android:layout_centerHorizontal 横向居中
(2) android:layout_centerVertical 纵向居中
(3) android:layout_centerInParent 横向纵向居中
跟父控件最左边/最右边/顶部/底部对齐
(1) android:layout_alignParentLeft
(2) android:layout_alignParentRight
(3) android:layout_alignParentTop
(4) android:layout_alignParentBottom
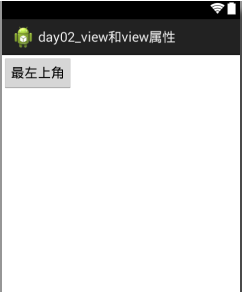
2.1.1位置默认在左上角
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<!--如果没有位置属性,按钮在左上角 --> <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="最左上角" />
</RelativeLayout>
2.1.2属性:android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" 横向中间
android:layout_centerVertical="true" 纵向中间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:text="两种属性定位到中间" /> </RelativeLayout>

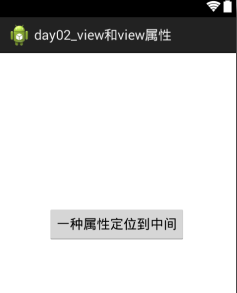
2.1.3属性:android:layout_centerInParent="true" 父窗体中间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="一种属性定位到中间" />
</RelativeLayout>
2.1.4属性:android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" 对齐到父窗口的左面,其中align是“对齐”的意思
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:text="最左面" /> </RelativeLayout>
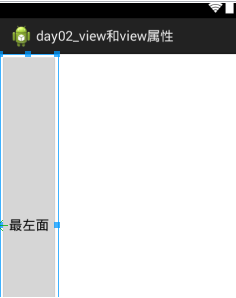
2.1.5属性:android:layout_alignParentRight="true" 对齐到父窗口的右面,其中align是“对齐”的意思
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent" >
5 <Button
6 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
7 android:layout_height="match_parent"
8 android:layout_alignParentRight ="true"
9 android:text="最右面" />
10
11 </RelativeLayout>
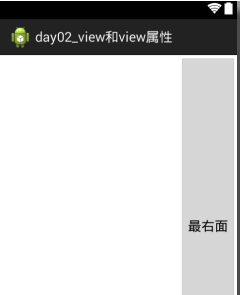
2.1.6属性:android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 对齐到父窗口的右面,其中align是“对齐”的意思
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:text="最上面" />
</RelativeLayout>
2.1.7属性:android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 对齐到父窗口的右面,其中align是“对齐”的意思
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="最下面" /> </RelativeLayout>

2.2相对于同等级的控件进行布局
针对已存在的兄弟控件(在某个控件的左边/右边/上面/下面)
(1)android:layout_toLeftOf
(2)android:layout_toRightOf
(3)android:layout_above
(4)android:layout_below
相对于兄弟控件的边对齐
(1)android:layout_alignTop
(2)android:layout_alignBottom
(3) android:layout_alignLeft
(4)android:layout_alignRight
上述属性的值为@id/相对控件的id。如:android:layout_above="@id/center_btn"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/center_btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="中间"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@id/center_btn"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/center_btn"
android:text="相对"/>
/> </RelativeLayout>

3 FrameLayout 帧布局:越写在后面的控件,越展示最前面(最上层)
4 AbsoluteLayout 绝对布局:

5 TableLayout 表格布局:就是一个表格(应用场景:银行表格)
<TableLayout><TableLayout/>表格标签
<TableRow><TableRow/> 行标签

上面代码只给出了身份证那一行的代码
android开发_ViewGroup(组视图)-- 五大布局的更多相关文章
- Android开发之详解五大布局
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-3654213-1-1.html 为了适应各式各样的界面风格,Android系统提供了5种布局,这5种布局分别是: LinearLayo ...
- Android开发之玩转FlexboxLayout布局
在这之前,我曾认真的研究过鸿洋大神的Android 自定义ViewGroup 实战篇 -> 实现FlowLayout,按照大神的思路写出了一个流式布局,所有的东西都是难者不会会者不难,当自己能自 ...
- Android开发之自定义视图
继承View 1.重写onMeasure(int wMeasureSpec,int hMeasureSpec)处理程序,这样可以标明视图尺寸 2.重写onDraw,以便绘制我们自己的自定义视图内 3. ...
- android开发------编写用户界面之相对布局
今天要说的是RelativeLayout.RelativeLayout相对于LinearLayout的主要不同点在于它需要一个参照物. 我们先来看一下官方对这个布局的解释: RelativeLayou ...
- android开发------编写用户界面之线性布局(补充知识)
在前面的文章中 http://www.cnblogs.com/ai-developers/p/android_linearlayout.html 我们看到了布局中有这样一个属性: layout_wei ...
- android开发------编写用户界面之线性布局
一个好的应用程序离不开人性化的用户界面.在学习其他东西之前.理应先学习编写程序的布局(外观) 今天,我们就来学习android的UI布局----LinearLayout. LinearLayout,即 ...
- Android开发:组播(多播)与广播
近期由于需要编写能够使同一局域网中的Android客户端与PC端进行自动匹配通信功能的程序,学习并试验了JAVA组播与广播的内容,记录一些理解如下: 一.组播(多播) 背景知识:组播使用UDP对一定范 ...
- android 开发 RecyclerView 横排列列表布局
1.写一个一竖的自定义布局: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xml ...
- Android 开发日常积累
Android 集合 Android 开源项目分类汇总 扔物线的 HenCoder 高级 Android 教程 hencoder HenCoder:给高级 Android 工程师的进阶手册 Andro ...
随机推荐
- direction: rtl;
这个属性,有点无语,费了点时间. <style type="text/css"> .hao {direction: rtl;}</style> <se ...
- JAR包结构,META-INF/MANIFEST.MF文件详细说明[全部属性][打包][JDK]
转载请注:[https://www.cnblogs.com/applerosa/p/9736729.html] 常见的属性 jar文件的用途 压缩的和未压缩的 jar工具 可执行的JAR 1.创建可执 ...
- ide phpStorm管理远程主机
- php协议流
文件包含漏洞结合php协议流的特性,使得漏洞利用效率更高,下面的内容主要讲解协议流的使用. 0x00 测试环境: php版本: 5.2,5.3,5.5,7.0等web服务: apache2OS系统: ...
- python练习题-day21
1.三级菜单 china_ditie = { "北京": { "一号线": ["四惠", "大望路", "天安 ...
- PyCharm更换sublime类似主题
1. 下载jar主题包 下载地址:https://github.com/spasserby/PyCharm-monokai 2.导入pycharm设置 导入方法:file-->Import Se ...
- LeetCode 5 最长对称串
LeetCode 5 最长对称串 最早时候做这道题的时候还是用Java写的,用的是字符串匹配的思路,一直Time Limit Exceeded.甚至还想过用KMP开优化子串查找. public cla ...
- apache----------在apache环境下安装https支持
1.安装mod_ssl yum install mod_ssl2.修改阿帕奇的配置文件开启3.防火墙要开启443端口4.要把三个证书上传到阿帕奇配置文件下.5.更新 httpd.conf 配置文件 ...
- jquery on()方法重复绑定解决方法
最近再一次项目中发现 不刷新页面的情况下使用on()方法绑定事件会出现重复执行的问题,意思就是说点击一次会绑定一次...点击n次会绑定n次,执行起来是以你绑定的次数为准,绑定了n次就会执行n次 解决办 ...
- 单点登录(SSO)详解
背景 在企业发展初期,企业使用的系统很少,通常一个或者两个,每个系统都有自己的登录模块,运营人员每天用自己的账号登录,很方便.但随着企业的发展,用到的系统随之增多,运营人员在操作不同的系统时,需要多次 ...