[hdu 2604] Queuing 递推 矩阵快速幂
Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
4 7
4 8
2
1
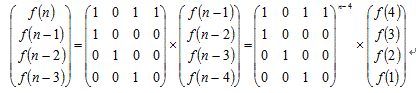
直接递推:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; int L, M; int solve()
{
int a[];
a[] = ; a[] = ;
a[] = ; a[] = ;
for (int i = ; i <= L; i++) {
a[i] = a[i-]+a[i-]+a[i-];
a[i] %= M;
}
return a[L];
} int main()
{
//freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
while (~scanf("%d%d", &L, &M)) {
printf("%d\n", solve());
} return ;
}
矩阵快速幂
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
const int Max = ;
int L, M;
struct Mat
{
LL m[Max][Max]; void clear() {
memset(m, , sizeof(m));
} void Init() {
clear();
for (int i = ; i < Max; i++)
m[i][i] = ;
} }; Mat operator * (Mat a, Mat b)
{
Mat c;
c.clear();
for (int i = ; i < Max; i++)
for (int j = ; j < Max; j++)
for (int k = ; k < Max; k++) {
c.m[i][j] += (a.m[i][k]*b.m[k][j])%M;
c.m[i][j] %= M;
}
return c;
} Mat quickpow(Mat a, int k)
{
Mat ret;
ret.Init();
while (k) {
if (k & )
ret = ret*a;
a = a*a;
k >>= ;
}
return ret;
} int main()
{
//freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
Mat a, b, c;
a.clear(); b.clear(); c.clear();
a.m[][] = ; a.m[][] = ;
a.m[][] = ; a.m[][] = ; b.m[][] = b.m[][] = b.m[][] =
b.m[][] = b.m[][] = b.m[][] = ; while (~scanf("%d%d", &L, &M)) {
LL ret;
if (L == )
ret = ;
else if (L <= )
ret = a.m[-L][]%M;
else {
c = quickpow(b, L-);
c = c*a;
ret = c.m[][]%M;
}
printf("%lld\n", ret);
} return ;
}
[hdu 2604] Queuing 递推 矩阵快速幂的更多相关文章
- HDU 2604 Queuing(递推+矩阵)
Queuing [题目链接]Queuing [题目类型]递推+矩阵 &题解: 这题想是早就想出来了,就坑在初始化那块,只把要用的初始化了没有把其他的赋值为0,调了3,4个小时 = = 本题是可 ...
- HDU 2604 Queuing( 递推关系 + 矩阵快速幂 )
链接:传送门 题意:一个队列是由字母 f 和 m 组成的,队列长度为 L,那么这个队列的排列数为 2^L 现在定义一个E-queue,即队列排列中是不含有 fmf or fff ,然后问长度为L的E- ...
- hdu 2604 Queuing(动态规划—>矩阵快速幂,更通用的模版)
题目 最早不会写,看了网上的分析,然后终于想明白了矩阵是怎么出来的了,哈哈哈哈. 因为边上的项目排列顺序不一样,所以写出来的矩阵形式也可能不一样,但是都是可以的 //愚钝的我不会写这题,然后百度了,照 ...
- HDU Queuing(递推+矩阵快速幂)
Queuing Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- hdu 2604 递推 矩阵快速幂
HDU 2604 Queuing (递推+矩阵快速幂) 这位作者讲的不错,可以看看他的 #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #inclu ...
- HDU 5950 Recursive sequence 【递推+矩阵快速幂】 (2016ACM/ICPC亚洲区沈阳站)
Recursive sequence Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU - 2604 Queuing(递推式+矩阵快速幂)
Queuing Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- HDU 2842 (递推+矩阵快速幂)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2842 题目大意:棒子上套环.第i个环能拿下的条件是:第i-1个环在棒子上,前i-2个环不在棒子上.每个 ...
- Recursive sequence HDU - 5950 (递推 矩阵快速幂优化)
题目链接 F[1] = a, F[2] = b, F[i] = 2 * F[i-2] + F[i-1] + i ^ 4, (i >= 3) 现在要求F[N] 类似于斐波那契数列的递推式子吧, 但 ...
随机推荐
- Poj 2367 Genealogical tree(拓扑排序)
题目:火星人的血缘关系,简单拓扑排序.很久没用邻接表了,这里复习一下. import java.util.Scanner; class edge { int val; edge next; } pub ...
- POJ2230(打印欧拉回路)
Watchcow Time Limit: 3000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 7473 Accepted: 3270 Specia ...
- HDOJ4768(二分区间)
Flyer Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- (转)更改Web.config中对上传文件大小限制
.net上传超过200K的图片的时候,会跳转到404,但是url没有错误,真J8的坑啊. 本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zwffff/archive/2009/04/29/ ...
- 二 Istio设计的核心原则
Istio架构关键目标 最大化透明度:Istio将自身自动注入到服务间所有的网络路径中.Istio使用sidecar代理来捕获流量,并且在尽可能的地方自动编程网络层,通过代理来路由流量,无需改动应用程 ...
- SpringMVC—对Ajax的处理(含 JSON 类型)(2)
这里编写了一个通用的类型转换器: 用来转换形如: firstName=jack&lastName=lily&gender=1&foods=Steak&foods=Piz ...
- showModalDialog()子窗口刷新父窗口
今天再次使用showModalDialog(),发现了两个问题,一是子窗口如何刷新父窗口,二是窗口的参数问题. 1 子窗口刷新父窗口 如果是window.open();问题就好办,直接用window. ...
- 利用Synergy在局域网内让Ubuntu和Windows 7两台机器共用一套键鼠。
一个主机可以连接多个显示器, 方便自己使用, 但是这只是一个系统分屏显示, 如果想用两台不同系统的电脑, 并且还不想老是在两套键鼠之间来回转换, 那么建议你可以用Synergy软件来实现多台电脑之间的 ...
- 类型:Java;问题:eclipse配置maven;结果:eclipse配置maven
eclipse配置maven 下面跟大家分享的是eclipse配置maven的方法. 方法/步骤 安装maven之前,要先安装jdk及配置JAVA_HOME环境变量.JDK1.4以上. 下载maven ...
- 关于android写入SD卡数据的学习代码
String path = "data/data/com.example.qqlogin/login.txt"; FileOutputStream fos = new FileOu ...
