python之02数据类型学习
参考链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5782764.html
python的数据类型有:Number、Boolean、String 、List、Tuple、Dictionary、Set、bytes.
一、Number(数字)
int、float
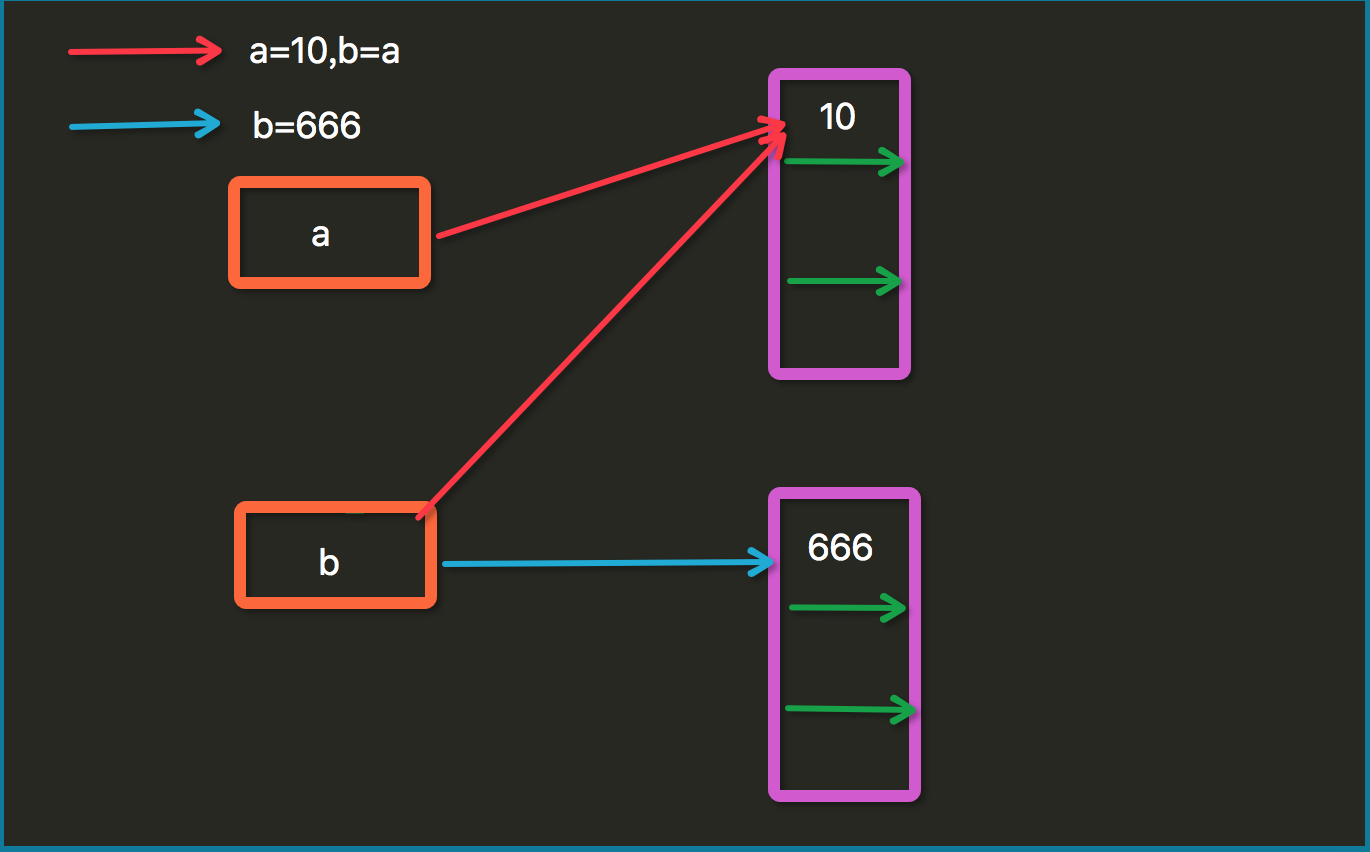
a=
b=a
b= print(a)#
print(b)#
var1=3.14
var2=5
var3=int(var1)
var4=float(var2) print(var3,var4)
abs(x) 返回数字的绝对值,如abs(-10) 返回 10
# ceil(x) 返回数字的上入整数,如math.ceil(4.1) 返回 5
# cmp(x, y) 如果 x < y 返回 -1, 如果 x == y 返回 0, 如果 x > y 返回 1
# exp(x) 返回e的x次幂(ex),如math.exp(1) 返回2.718281828459045
# fabs(x) 返回数字的绝对值,如math.fabs(-10) 返回10.0
# floor(x) 返回数字的下舍整数,如math.floor(4.9)返回 4
# log(x) 如math.log(math.e)返回1.0,math.log(100,10)返回2.0
# log10(x) 返回以10为基数的x的对数,如math.log10(100)返回 2.0
# max(x1, x2,...) 返回给定参数的最大值,参数可以为序列。
# min(x1, x2,...) 返回给定参数的最小值,参数可以为序列。
# modf(x) 返回x的整数部分与小数部分,两部分的数值符号与x相同,整数部分以浮点型表示。
# pow(x, y) x**y 运算后的值。
# round(x [,n]) 返回浮点数x的四舍五入值,如给出n值,则代表舍入到小数点后的位数。
# sqrt(x) 返回数字x的平方根,数字可以为负数,返回类型为实数,如math.sqrt(4)返回 2+0j PY内置数学函数
二、布尔:
只有两种类型True和False。补充:python区分大小写。
三、字符串:
# String的内置方法
# st='hello kitty {name} is {age}'
#
# print(st.count('l')) # 统计元素个数
# print(st.capitalize()) # 首字母大写
# print(st.center(,'#')) # 居中
# print(st.endswith('tty3')) # 判断是否以某个内容结尾
# print(st.startswith('he')) # 判断是否以某个内容开头
# print(st.expandtabs(tabsize=))
# print(st.find('t')) # 查找到第一个元素,并将索引值返回
# print(st.format(name='alex',age=)) # 格式化输出的另一种方式 待定:?:{}
# print(st.format_map({'name':'alex','age':}))
# print(st.index('t'))
# print('asd'.isalnum())
# print(''.isdecimal())
# print('1269999.uuuu'.isnumeric())
# print('abc'.isidentifier())
# print('Abc'.islower())
# print('ABC'.isupper())
# print(' e'.isspace())
# print('My title'.istitle())
# print('My tLtle'.lower())
# print('My tLtle'.upper())
# print('My tLtle'.swapcase())
# print('My tLtle'.ljust(,'*'))
# print('My tLtle'.rjust(,'*'))
# print('\tMy tLtle\n'.strip())
# print('\tMy tLtle\n'.lstrip())
# print('\tMy tLtle\n'.rstrip())
# print('ok')
# print('My title title'.replace('itle','lesson',))
# print('My title title'.rfind('t'))
# print('My title title'.split('i',))
# print('My title title'.title())
#摘一些重要的字符串方法
# print(st.count('l'))
# print(st.center(,'#')) # 居中
# print(st.startswith('he')) # 判断是否以某个内容开头
# print(st.find('t'))
# print(st.format(name='alex',age=)) # 格式化输出的另一种方式 待定:?:{}
# print('My tLtle'.lower())
# print('My tLtle'.upper())
# print('\tMy tLtle\n'.strip())
# print('My title title'.replace('itle','lesson',))
# print('My title title'.split('i',))
四、列表:
# 本节所有内容 增 删 改 查 排序 身份判断 # 查
fruits = ["apple", 'pear', 'peach', 'melon', 'orange', 'banana']
# 切片操作
# print(fruits[:]) #从索引1处截到末尾
# print(fruits[:]) #从索引1截到索引4的位置(不包括索引4)
# print(fruits[::])#从索引1的位置到末尾,向右每两个截取一个
# print(fruits[:-])#截取从索引1的位置到倒数第一个(不包括倒数第一个)
# print(fruits[-:-:-])#从倒数第二个到倒数第五个(不包括倒数第五个),向左逐个截取。
# print(fruits.count("apple"))#获取fruits里apple的个数
# print(fruits.__len__())#获取fruits的长度
# ret = fruits.count("apple") # apple出现的次数
# print(ret)
# print(fruits.__len__())
# print(fruits.index("melon"))
# ret = "melon" in fruits
# print(ret) # 改
# fruits[] = ""
# print(fruits) # fruits[:] = [, ]
# print(fruits) # 增
# fruits.append('strawberry')
# print(fruits)
# fruits.insert(, "strawberry")
# print(fruits)
# new_fruits = ['strawberry']
# fruits.extend(new_fruits)
# print(fruits)
# print(new_fruits) # 删 pop remove del
# ret = fruits.pop()
# print(ret)
# print(fruits) # fruits.remove("pear")
# print(fruits) # del fruits[]
# print(fruits) # 其他操作 :排序 和倒转
# print(fruits)
# fruits.reverse()
# print(fruits) # print(fruits)
# fruits.sort()
# print(fruits) # fruits.sort(reverse=True)
# print(fruits) # 身份判断
# print(type(fruits) is list) t = [, , ]
f = tuple(t)
print(t)
print(f)
列表的遍历3种方法,
(1)直接遍历内容
(2)通过下标遍历
(3)通过enumerate方法 遍历下标和内容。
address = [
{(, '上海市'): [{(, '上海市'): [(, '崇明区'), (, '松江区'), (, '徐汇区'), (, '静安区')]}]},
{(, '河南省'): [{(, '周口市'): [(, '太康县'), (, '淮阳县'), (, '鹿邑县')]},
{(, '郑州市'): [(, '中原区'), (, '上街区'), (, '新郑市')]}]},
{(, '江苏省'): [{(, '南京市'): [(, '玄武区'), (, '六合区'), (, '雨花台区')]},
{(, '无锡市'): [(, '宜兴市'), (, '锡山区'), (, '惠山区')]},
{(, '徐州市'): [(, '新沂市'), (, '睢宁县'), (, '铜山区')]}]}
] for i in address:
print(i) # list 里的内容 for i in range(len(address)):
print(i) # 下标
print(address[i]) #list里的内容 for i,v in enumerate(address):
print(i) # 下标
print(v) # list里的内容
五、字典
字典的特点是:无序、键唯一,并且字典的键类型是不可变类型(整型、字符串、元祖)
创建
# 创建
dic = {"name": "cydong", "age": , "sex": "female", "avocation": {"sports": "basketball,football"}}
print(type(dic))
print(dic)
dic = dict([['name', 'carol'], ["age", ]])
print(type(dic))
print(dic)
dic = dict((['name', 'carol'], ["age", ]))
print(type(dic))
print(dic) ret = dic.setdefault("name", "cydong") # setdefault方法是设置字典的方法,当字典中存在key值时,返回已经存在的value值不覆盖。当字典中不存在key值时,增加key和value。
print(ret)
print(dic)
查询
通过键值查询
# 查
print(list(dic.keys()))
print(list(dic.values()))
print(list(dic.items()))
更新
# 更新
dic["age"] =
print(dic) dic1 = {"name": "cydong", "age": }
dic2 = {"name": "carol", "sex": "male"}
dic1.update(dic2)
print(dic1)
print(dic2)
删除
dic2 = {"name": "carol", "age": , "sex": "male"}
# # dic2.clear()
# print(dic2)
# # del dic2["name"]
# print(dic2.pop("age")) # 返回改键对应的值
# print(dic2)
# ret = dic2.popitem() # 随机删除某组键值对,并以元祖方式返回值
# print(ret, dic2)
del dic2 # 删除整个字典
其他操作
# 其他操作以及涉及到的方法 # dic6=dict.fromkeys(['host1','host2','host3'],'test')
# print(dic6)#{'host3': 'test', 'host1': 'test', 'host2': 'test'}
#
# dic6['host2']='abc'
# print(dic6) # dic6=dict.fromkeys(['host1','host2','host3'],['test1','tets2'])
# print(dic6)#{'host2': ['test1', 'tets2'], 'host3': ['test1', 'tets2'], 'host1': ['test1', 'tets2']}
#
# dic6['host2'][]='test3'
# print(dic6)#{'host3': ['test1', 'test3'], 'host2': ['test1', 'test3'], 'host1': ['test1', 'test3']}
dic5 = {"name": "carol", "age": 27, "sex": "male"}
for i in dic5:
print(i)
# name
# age
# sex
for i, v in dic5.items():
print(i, v)
# name carol
# age 27
# sex male
for item in dic5.items():
print(item)
# ('name', 'carol')
# ('age', 27)
# ('sex', 'male')
dic5 = {"name": "carol", "age": 27, "sex": "male"}
print(dic5)
print(sorted(dic5)) # 返回一个有序的包含字典所有key的列表
#['age', 'name', 'sex']
六、元祖
元祖是用一对小括号括起来的数据。其中“元祖是不能修改的”是分情况的:
(1,2,3)这个是不能修改的,而
(['iphone6s', 5800], ['mac book', 9000], ['coffee', 32], ['python book', 80], ['bicycle', 1500]) 可以针对里面的列表修改。
总之,引用别人的话“老子是不能修改的,孙子是可能被修改的”
python之02数据类型学习的更多相关文章
- python之02数据类型学习-作业练习
题目: 购物车程序 salary = 5000 1. iphone6s 5800 2. mac book 9000 3. coffee 32 4. python book 80 5. bicyle 1 ...
- python之02数据类型学习-作业练习2
引用博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/5782764.html 作业描述: 省 市 县的三层数据通过字典 元祖 列表 保存起来执行程序后 ...
- python学习第九讲,python中的数据类型,字符串的使用与介绍
目录 python学习第九讲,python中的数据类型,字符串的使用与介绍 一丶字符串 1.字符串的定义 2.字符串的常见操作 3.字符串操作 len count index操作 4.判断空白字符,判 ...
- python学习第八讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之字典使用与介绍
目录 python学习第八讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之字典使用与介绍.md 一丶字典 1.字典的定义 2.字典的使用. 3.字典的常用方法. python学习第八讲,python ...
- python学习第七讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之元祖使用与介绍
目录 python学习第七讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之元祖使用与介绍 一丶元祖 1.元祖简介 2.元祖变量的定义 3.元祖变量的常用操作. 4.元祖的遍历 5.元祖的应用场景 p ...
- python学习第六讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之列表使用与介绍
目录 python学习第六讲,python中的数据类型,列表,元祖,字典,之列表使用与介绍. 二丶列表,其它语言称为数组 1.列表的定义,以及语法 2.列表的使用,以及常用方法. 3.列表的常用操作 ...
- python基本数据类型学习
python是极其简洁的一门高级语言,在python里面没有真正意义上的常量,只是用大写的标定表示常量(python中的常量是可以修改的),单行注释用#开始,.并且python不用定义数据类型,因为p ...
- Python学习之路【第二篇】-pyc简介、Python常用的数据类型及其用法和常用运算符
1.pyc简介 python程序在运行时也有编译过程,编译后会产生.pyc文件.这是一种由python虚拟机执行的二进制文件(字节码),用于保存内存中PyCodeObject,以便加快程序的加载运行. ...
- python学习笔记03:python的核心数据类型
从根本上讲,Python是一种面向对象的语言.它的类模块支持多态,操作符重载和多重继承等高级概念,并且以Python特有的简洁的语法和类型,OOP十分易于使用.Python的语法简单,容易上手. Py ...
随机推荐
- Appium-xpath详解
一.xpath简介 XPath就是XML 路径,练习XPath的使用可以直接使用火狐浏览器 火狐浏览器下载 free bug和free path两个插件. 手机xpath可以自己写,路径关键字选cla ...
- 超链接向servlet传参数
超链接传参数方式如下: <a href=xxxServlet?flag=1 target=“XX”></a> 注意:target=“XX”是用来指定在什么窗体打开.xx为该窗 ...
- 尴尬的app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways" 配合NavigationDrawer
昨天想到了NavigationDrawer中Item点击的问题. 点击Drawer中的一个Item需要到一个新的页面,你是应该打开一个新的Activity呢还是直接用fragment呢? 如果打开新的 ...
- WC2010 BZOJ1758 重建计划_长链剖分
题目大意: 求长度$\in [L,U]$的路径的最大边权和平均值. 题解 首先二分就不用说了,分数规划大家都懂. 这题有非常显然的点分治做法,但还是借着这个题学一波长链剖分. 其长链剖分本身也没啥,就 ...
- 【整理】如何选取后缀数组&&后缀自动机
后缀家族已知成员 后缀树 后缀数组 后缀自动机 后缀仙人掌 后缀预言 后缀Splay ? 后缀树是后缀数 ...
- LOJ2305 「NOI2017」游戏
「NOI2017」游戏 题目背景 狂野飙车是小 L 最喜欢的游戏.与其他业余玩家不同的是,小 L 在玩游戏之余,还精于研究游戏的设计,因此他有着与众不同的游戏策略. 题目描述 小 L 计划进行$n$场 ...
- Oracle 12c 多租户 CDB 与 PDB之 shared undo 与 Local undo 切换
undo 在12C R1版本中只支持Global Shared Undo模式, 所有container共享一个UNDO表空间, 目前保留这种模式只是为了升级过渡, 在12C R2引入了PDB Loca ...
- html事件绑定总结以及window.onload和document.body.onload事件
//1 document.onkeydown如果多次监听同样的事件,那么前面的监听函数都会被最后一次的监听函数所覆盖. //如下所示: document.onkeydown = function(ev ...
- HDOJ1495(倒水BFS)
非常可乐 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- 人物-IT-任正非:任正非
ylbtech-人物-IT-任正非:任正非 任正非,祖籍浙江省浦江县,1944年10月25日出生于贵州省安顺市镇宁县.华为技术有限公司主要创始人兼总裁. 1963年就读于重庆建筑工程学院(现已并入重庆 ...
