hdu 4119 Isabella's Message 模拟题
Isabella's Message
Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4119
Description
The encrypted message is an N * N matrix, and each grid contains a character.
Steve
uses a special mask to work as a key. The mask is N * N(where N is an
even number) matrix with N*N/4 holes of size 1 * 1 on it.
The decrypt process consist of the following steps:
1. Put the mask on the encrypted message matrix
2. Write down the characters you can see through the holes, from top to down, then from left to right.
3. Rotate the mask by 90 degrees clockwise.
4. Go to step 2, unless you have wrote down all the N*N characters in the message matrix.
5. Erase all the redundant white spaces in the message.
For
example, you got a message shown in figure 1, and you have a mask looks
like figure 2. The decryption process is shown in figure 3, and finally
you may get a message "good morning".
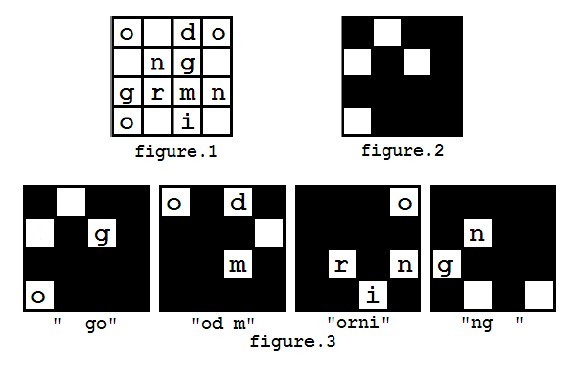
You
can assume that the mask is always carefully chosen that each character
in the encrypted message will appear exactly once during decryption.
However, in the first step of decryption, there are several ways to
put the mask on the message matrix, because the mask can be rotated
(but not flipped). So you may get different results such as "od morning
go" (as showed in figure 4), and you may also get other messages like
"orning good m", "ng good morni".
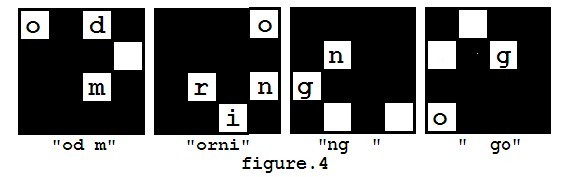
Steve
didn't know which direction of the mask should be chosen at the
beginning, but after he tried all possibilities, he found that the
message "good morning" is the only one he wanted because he couldn't
recognize some words in the other messages. So he will always consider
the message he can understand the correct one. Whether he can understand
a message depends whether he knows all the words in the message. If
there are more than one ways to decrypt the message into an
understandable one, he will choose the lexicographically smallest one.
The way to compare two messages is to compare the words of two messages
one by one, and the first pair of different words in the two messages
will determine the lexicographic order of them.
Isabella sends
letters to Steve almost every day. As decrypting Isabella's message
takes a lot of time, and Steve can wait no longer to know the content of
the message, he asked you for help. Now you are given the message he
received, the mask, and the list of words he already knew, can you write
a program to help him decrypt it?
Input
The first line contains an integer T(1 <= T <= 100), indicating the number of test cases.
Each test case contains several lines.
The first line contains an even integer N(2 <= N <= 50), indicating the size of the matrix.
The
following N lines each contains exactly N characters, reresenting the
message matrix. The message only contains lowercase letters and
periods('.'), where periods represent the white spaces.
You can assume the matrix contains at least one letter.
The
followingN lines each containsN characters, representing the mask
matrix. The asterisk('*') represents a hole, and period('.') otherwise.
The next line contains an integer M(1 <= M <= 100), the number of
words he knew.
Then the following M lines each contains a string
represents a word. The words only contain lowercase letters, and its
length will not exceed 20.
Output
For each test case in the input, print one line: "Case #X: Y", where X is the test case number (starting with 1) and Y is Isabella's message.
If Steve cannot understand the message, just print the Y as "FAIL TO DECRYPT".
Sample Input
Sample Output
HINT
题意
给你一个n*n的格子,格子里面有字母和空格,然后你拿挡板去截取字母,然后问你是否能够还原。
题解:
最多4种情况,直接模拟搞就好了
我的代码是wa的,我不想再写了= =
代码:
//qscqesze
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
//freopen("D.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("D.out","w",stdout);
#define sspeed ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)
#define maxn 10001
#define mod 10007
#define eps 1e-9
int Num;
char CH[];
//const int inf=0x7fffffff; //нчоч╢С
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
/* inline void P(int x)
{
Num=0;if(!x){putchar('0');puts("");return;}
while(x>0)CH[++Num]=x%10,x/=10;
while(Num)putchar(CH[Num--]+48);
puts("");
}
*/
inline ll read()
{
ll x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
inline void P(int x)
{
Num=;if(!x){putchar('');puts("");return;}
while(x>)CH[++Num]=x%,x/=;
while(Num)putchar(CH[Num--]+);
puts("");
}
//************************************************************************************** string s1[maxn];
string s2[maxn];
string s3[maxn];
int n,m;
string s66[maxn];
int flag;
int cnt;
int deal(string s55)
{
//cout<<s55<<endl;
cnt=;
flag=;
s66[cnt]="";
for(int i=;i<s55.size();i++)
{
if(s55[i]=='.')
continue;
else
{
s66[cnt]+=s55[i];
if(i+>=s55.size()||s55[i+]=='.')
{
int flag2=;
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
if(s66[cnt]==s3[i])
flag2++;
if(!flag2)
flag=;
if(flag==)
break;
cnt++;
s66[cnt]="";
}
}
}
return flag;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("test.txt","r",stdin);
int t=read();
for(int cas=;cas<=t;cas++)
{
//memset(s1,0,sizeof(s1));
//memset(s2,0,sizeof(s2));
//memset(s3,0,sizeof(s3));
n=read();
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>s1[i];
int len=s1[].size();
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>s2[i];
m=read();
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>s3[i];
}
string s11,s22,s33,s44;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
{
if(s2[i][j]=='*')
s11+=s1[i][j];
if(s2[j][n-i-]=='*')
s44+=s1[i][j];
if(s2[n-i-][n-j-]=='*')
s33+=s1[i][j];
if(s2[n-j-][i]=='*')
s22+=s1[i][j];
}
}
string s55=s11+s22+s33+s44;
deal(s55);
if(!flag)
{
printf("Case #%d: ",cas);
for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(i!=cnt-)
cout<<s66[i]<<" ";
else
cout<<s66[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
else
{
s55=s22+s33+s44+s11;
deal(s55);
if(!flag)
{
printf("Case #%d: ",cas);
for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(i!=cnt-)
cout<<s66[i]<<" ";
else
cout<<s66[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
else
{
s55=s33+s44+s11+s22;
deal(s55);
if(!flag)
{
printf("Case #%d: ",cas);
for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(i!=cnt-)
cout<<s66[i]<<" ";
else
cout<<s66[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
else
{
s55=s44+s11+s22+s33;
deal(s55);
if(!flag)
{
printf("Case #%d: ",cas);
for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
if(i!=cnt-)
cout<<s66[i]<<" ";
else
cout<<s66[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
else
{
printf("Case #%d: FAIL TO DECRYPT\n",cas);
}
}
}
}
}
}
hdu 4119 Isabella's Message 模拟题的更多相关文章
- hdu 4119 Isabella's Message
Isabella's Message Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011亚洲北京赛区网络赛)
HDU 4041 Eliminate Witches! (模拟题 ACM ICPC 2011 亚洲北京赛区网络赛题目) Eliminate Witches! Time Limit: 2000/1000 ...
- HDU 4452 Running Rabbits (模拟题)
题意: 有两只兔子,一只在左上角,一只在右上角,两只兔子有自己的移动速度(每小时),和初始移动方向. 现在有3种可能让他们转向:撞墙:移动过程中撞墙,掉头走未完成的路. 相碰: 两只兔子在K点整(即处 ...
- HDU 2414 Chessboard Dance(模拟题,仅此纪念我的堕落)
题目 模拟题也各种wa,我最近真的堕落了,,,,,智商越来越为负数了!!!!!!!! #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include ...
- HDU 4925 Apple Tree(模拟题)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4925 解题报告:给你n*m的土地,现在对每一块土地有两种操作,最多只能在每块土地上进行两种操作,第一种 ...
- HDU 4364——Matrix operation——————【模拟题】
Matrix operation Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 1861 游船出租(模拟题,,水)
题意: 现有公园游船租赁处请你编写一个租船管理系统. 当游客租船时,管理员输入船号并按下S键,系统开始计时:当游客还船时,管理员输入船号并按下E键,系统结束计时. 船号为不超过100的正整数.当管理员 ...
- hdu 5641 King's Phone(暴力模拟题)
Problem Description In a military parade, the King sees lots of new things, including an Andriod Pho ...
- HDU 1262 寻找素数对 模拟题
题目描述:输入一个偶数,判断这个偶数可以由哪两个差值最小的素数相加,输出这两个素数. 题目分析:模拟题,注意的是为了提高效率,在逐个进行判断时,只要从2判断到n/2就可以了,并且最好用打表法判断素数. ...
随机推荐
- 31 - gogs安装-git基础
目录 1 Gogs安装 2 Git介绍 3 使用Github仓库 3.1 Git配置 3.2 远程仓库 4 Git基本使用 4.1 创建版本库 4.2 查看工作区状态 4.3 查看修改内容 4.4 查 ...
- 【会装】kylin的安装(填坑)和简单使用
1.简介 kylin的设计思想是空间换时间,将hive上的大表的维度全部排列组合计算也将度量提前计算然后存入HBase库,这个步骤在kylin中称之为build cube. 在查询的时候已经建立cu ...
- Zabbix3.0 API调用
Zabbix API 是什么? API简单来说是服务对外开放的一个接口,用户通过该接口传递请求,完成操作.API的背后是一组方法的集合,这些方法实现了服务对应的不同功能,调用API实际上就是换了一种方 ...
- PHP--- JSON和数组的转换
一.json_encode() <?php $arr =array ('a'=>1,'b'=>2,'c'=>3,'d'=>4,'e'=>5); echo json_ ...
- TCP可靠传输和拥塞控制
1.TCP的可靠传输 tcp的可靠传输主要靠 来自接收方的确认报文 和 超时重传. 发出报文,计时器开始计时,在规定超时时间内未收到确认报文则重新发送. 注意:发送报文都留一个副本,如果收到确认报文就 ...
- CSU 1351 Tree Counting
原题链接:http://acm.csu.edu.cn/OnlineJudge/problem.php?id=1351 DP题,毫无疑问.由于动态规划题目做得少.不熟悉,刚开始自己用f[i]表示用 i ...
- MINIBASE源代码阅读笔记之heapfile
Heapfile 用来管理heap file里的dir page们 成员 _firstDirPageId:这个文件的第一个dir page _ftype:文件类型 _file_deleted:删除的时 ...
- GUC-5 CountDownLatch闭锁
/* * CountDownLatch :闭锁,在完成某些运算是,只有其他所有线程的运算全部完成,当前运算才继续执行 */ public class TestCountDownLatch { publ ...
- 第七章 用户输入和while语句
大多数编程都旨在解决最终用户的问题,为此通常需要从用户那里获取一些信息.例如,假设有人要判断自己是否到了投票的年龄,要编写回答这个问题的程序,就需要知道用户的年龄,这样才能给出答案.因此,这种程序需要 ...
- java EE : tomacat 基础
tomacat 目录结构 conf 配置文件 server.xml
