ML Lecture 0-1: Introduction of Machine Learning
本博客是针对李宏毅教授在Youtube上上传的课程视频《ML Lecture 0-1: Introduction of Machine Learning》的学习笔记。在Github上也po了这个系列学习笔记(MachineLearningCourseNote),觉得写的不错的小伙伴欢迎来给项目点个赞哦~~
Lecture 0-1: Introduction of Machine Learning
What we expect to learn from this course?
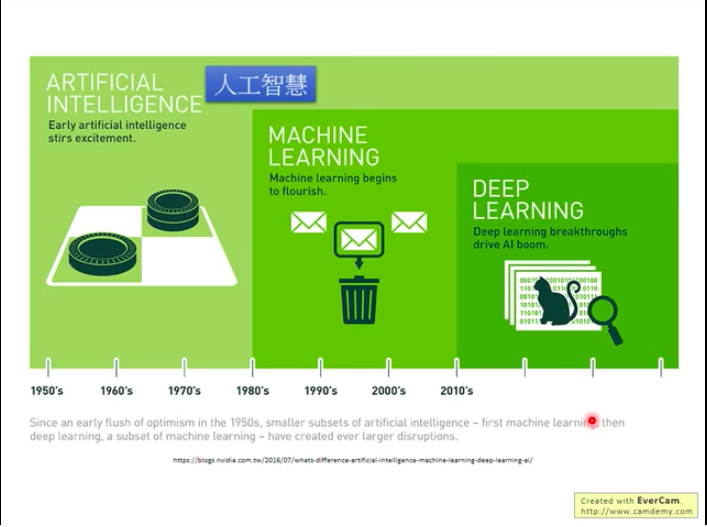
Artificial Intelligence (AI) aims to make machines as smart as human beings. But for long, people don’t know how to do this.
Until 1980s, machine learning (ML) comes into beings. Just like its name, machine learning aims to make machine learn to learn.
Q1: what is the relationship between AI and ML?
A: ML is a potential way to achieve AI.
Q2: what is the relationship between ML and deep learning (DL)?
A: DL is one of methods of ML.
- Extension: Creature’s Instinct: Beaver Build Dam
Beavers are born with the instinct to move stones to build dams as long as they hear the sounds of water flows.

This can be summarized to a rule for beaver: When hear the sounds of water flows, build dam!
Compare it with Human Being’s Instinct

- AI is just some “if”s ?

No, it’s not what we are chasing in the course!
What is Machine Learning ?
- Do Speech Recognition
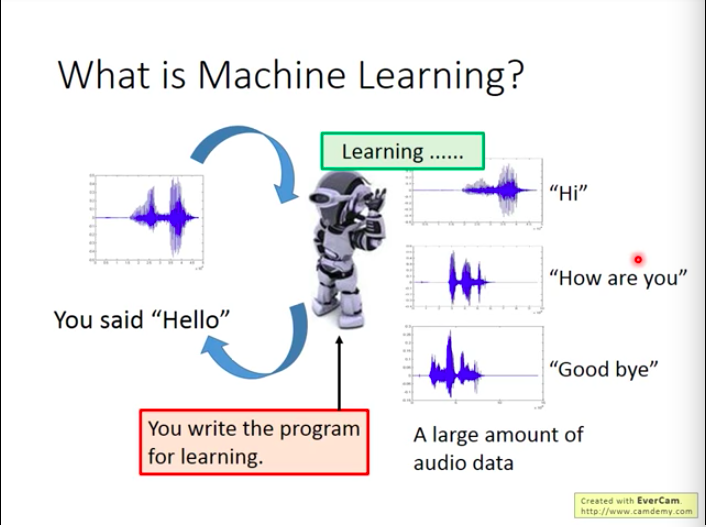
- Do Image Recognition

ML mostly equal to Looking for a Function
True function to do perfect speech recognition is too complex, there are efforts starting from 1960s trying to write enough rules to include all mappings from voice to word, however it’s still not finished yet! So we need machine to help us find out the function From Data.
To simplify, we let machines try to find the true function using training data we give them. After that, machines would give response to new input data we give to them based on rules that they have learned from training.

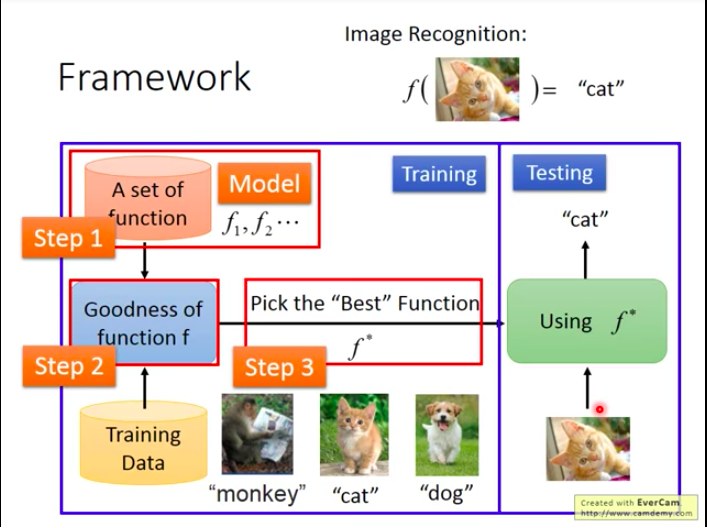
How to find this function: Framework
Example: Image Recognition
First, we have a set of function. (This set is called Model)
Then, we have training data, they consist of some input & output pairs, respectively used as function input and function output. (This method also known as Supervised Learning)
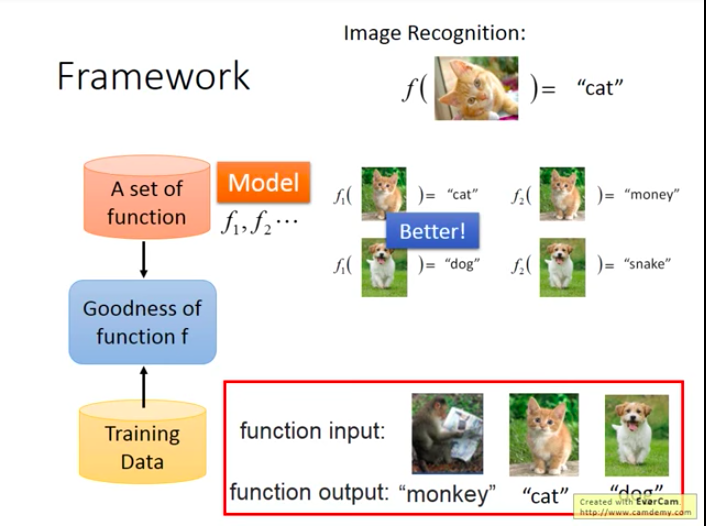
- How to find the true function from the set?
We need a good algorithm to find the best function (f∗" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">f∗f∗function that has greatest goodness).
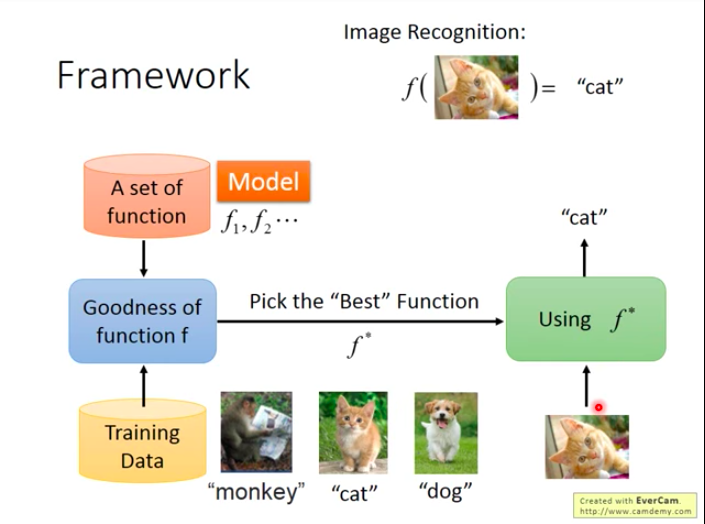
After we find the best function f∗" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">f∗f∗, how can we make sure that a machine can recognize the cat in a picture that it has never seen before? Well, that is exactly one of the most important problem in ML, that is: can machine draw inferences?
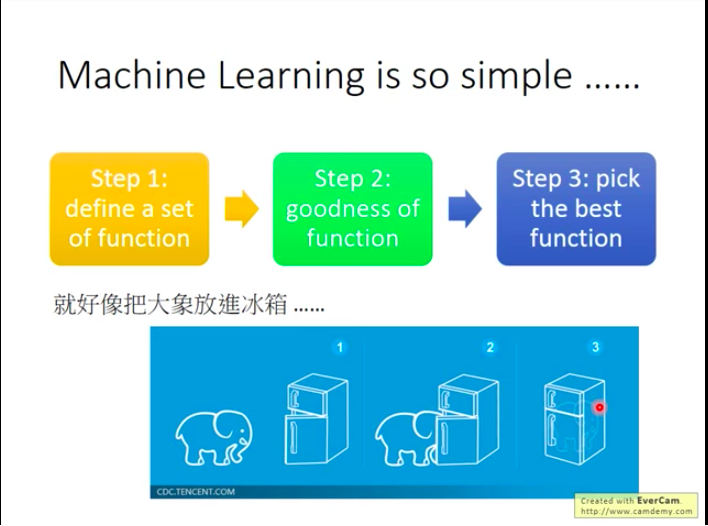
- Three Steps to do ML
1.Determine a function set;
2.Enable machines to measure how good a function is;
3.Give machines an algorithm that can help pick the “best” function.
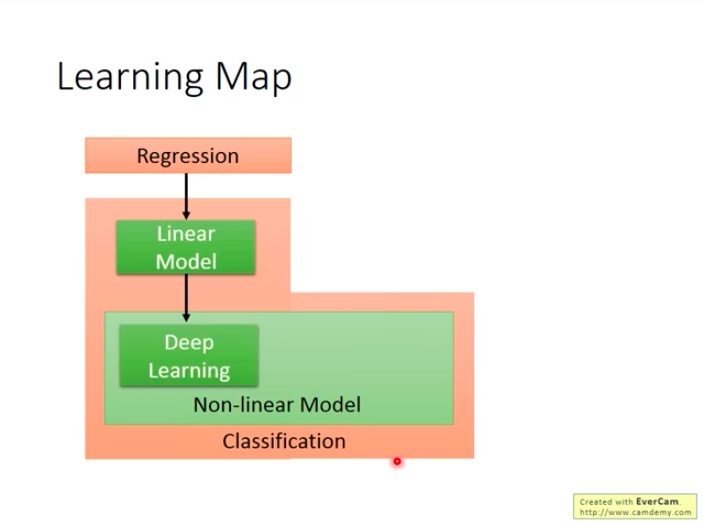
Learning Map
- What ML technics you can learn from this course ?
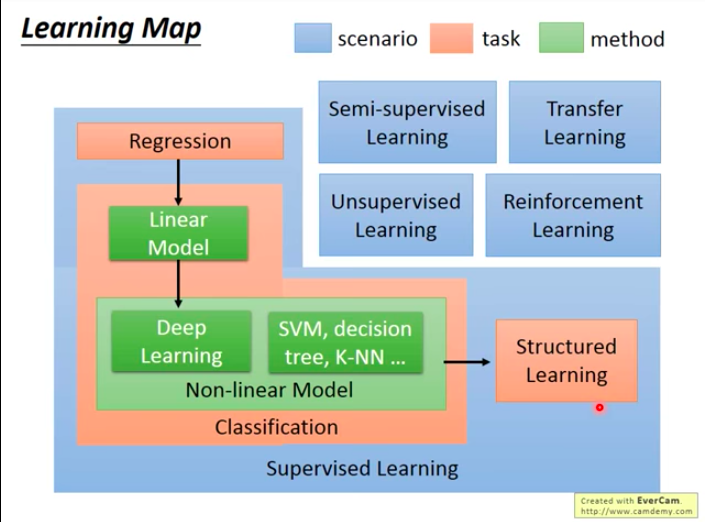
Next, we give a simple introduction to conceptions included in the map.
Regression
Definition: The output of function that machine is trying to learn is a scalar.
Example: Predicting PM2.5

Classification
Two types:
- Binary Classification: output Yes or No
- Multi-class Classification: output i (i∈" role="presentation" style="position: relative;">∈∈{1,2,3,..,N})
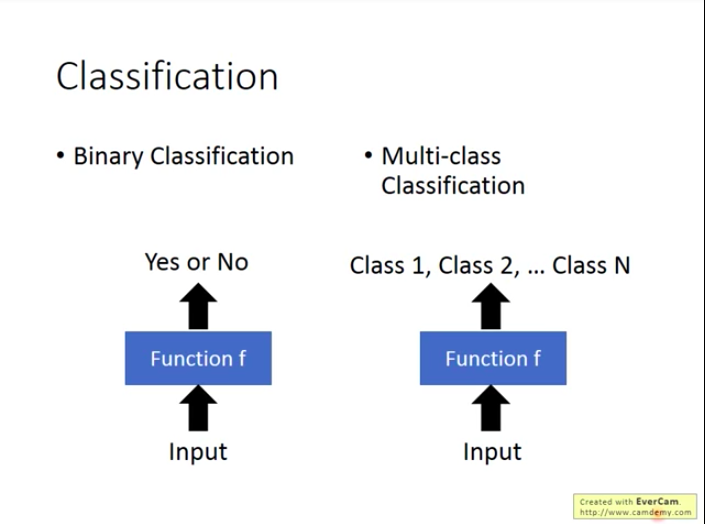
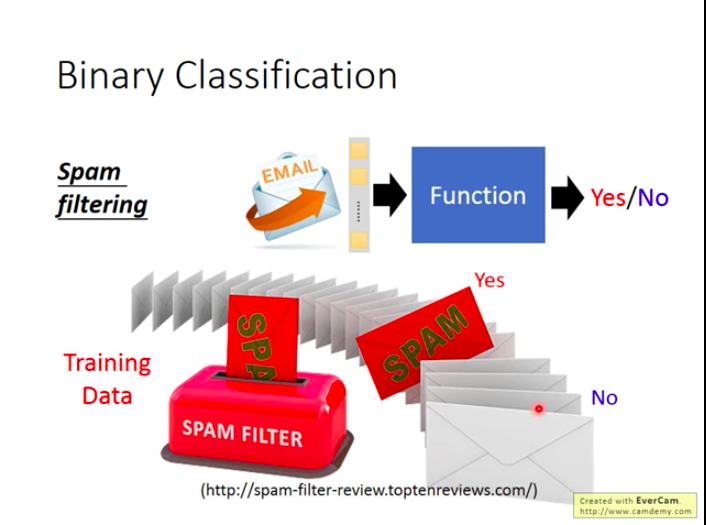
Example for binary classification: Gmail filter Spams
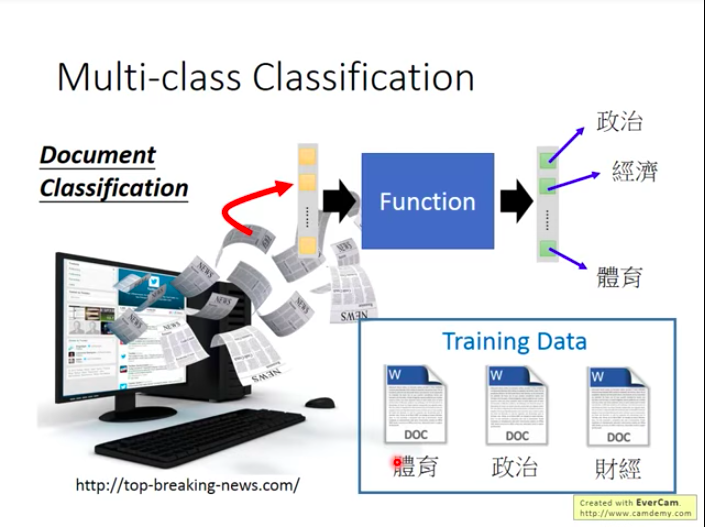
Example for multi-class classification: Document Classification
Model
Different model = Different set of functions -> Different Performance of machine
Linear Model
Non-linear Model
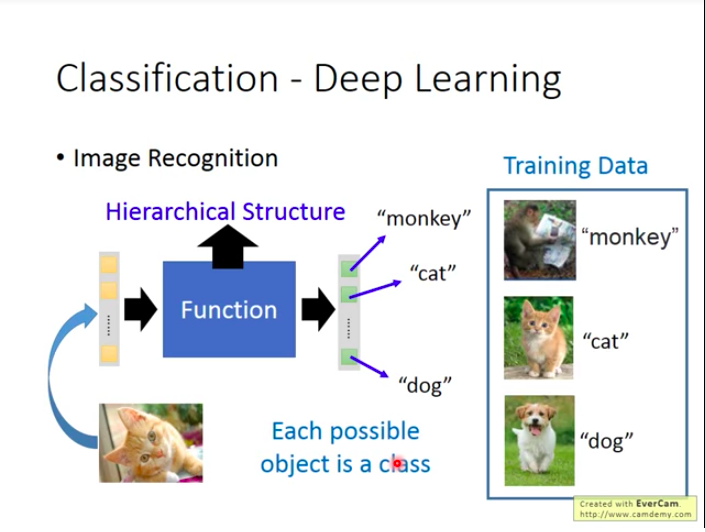
Deep Learning is one of Non-linear models. When doing deep learning, it usually means that the goal function is very very complex, and therefore it can also complete complex tasks such as image recognition, playing GO!
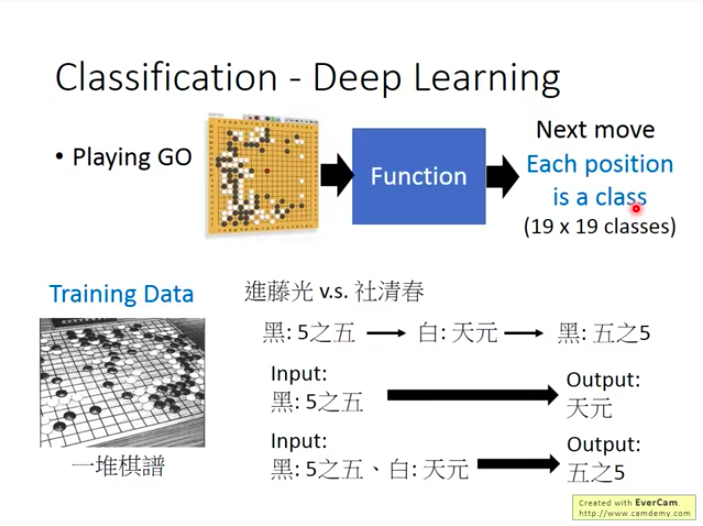
All technics mentioned above belong to field of Supervised Learning, it usually comes with great quantities of training data. These training data are some input/output pairs of target function, and normally the output need to be manually labelled, so the function output is also called label.
Then, how to collect a large amount of labelled data?
A: Semi-supervised Learning.
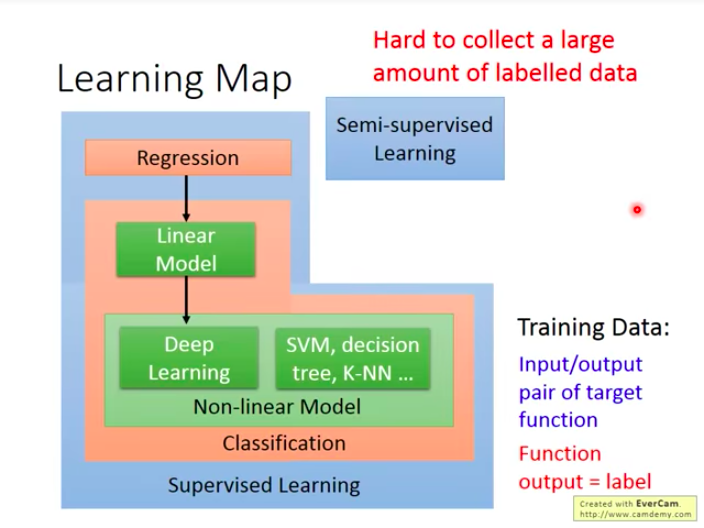
Semi-supervised Learning
Unlabelled data can also help machine learning!
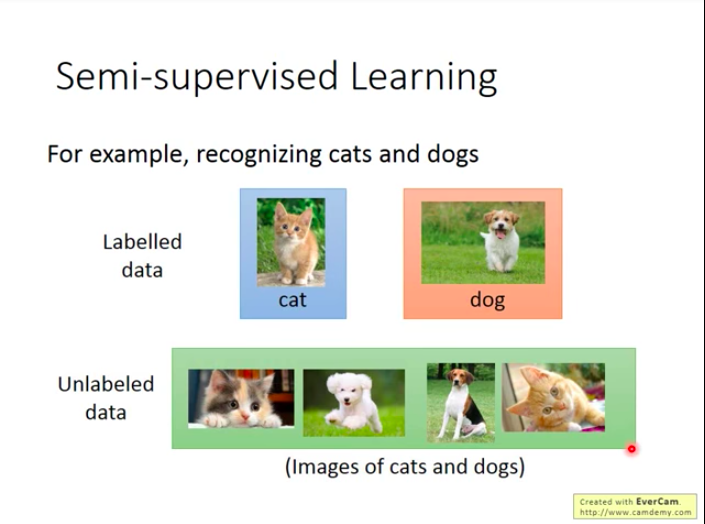
Another way to save data: Transfer Learning
(labelled/unlabelled) Data that are not directly linked with goal problem may be helpful to the goal problem.
What can machine learn without label: Unsupervised Learning


- Machine creates new animals after seeing some animal images


Structured Learning: Output Result with Structure
In speech recognition: input - a voice clip, output - corresponding sentence.
In translation: input - Chinese sentence, output - English sentence.
In object detection: input - images, output - boundary of object.
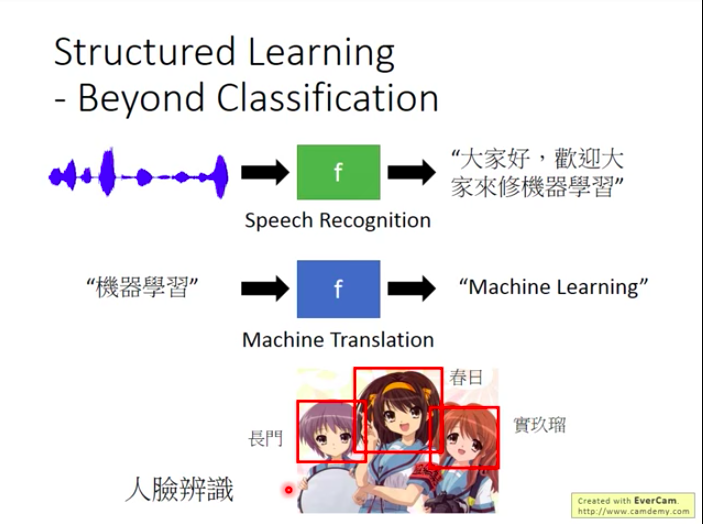
Usually, many people heard of regression and classification, but seldom heard of Structured Learning, even textbooks may ignore it.
However, structured learning is a very important part of ML field!

Reinforcement Learning

- Supervised v.s. Reinforcement
Supervised: Have a supervisor to teach machine; (Learning from teacher)
Reinforcement: Let machine to explore and teach itself. (Learning from critics)
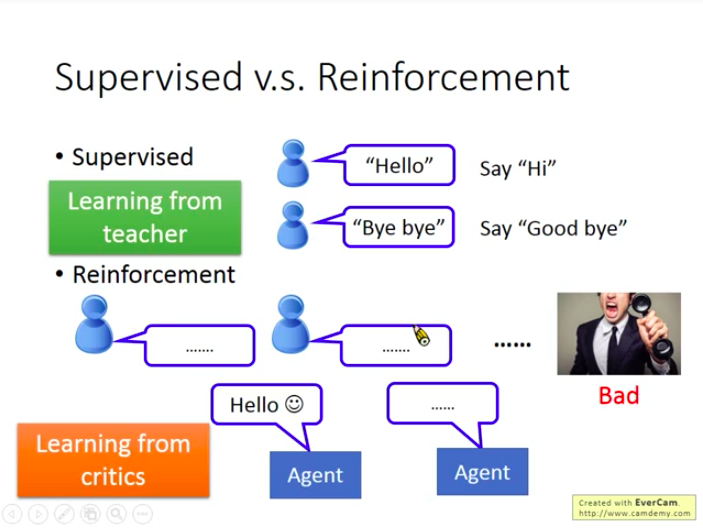
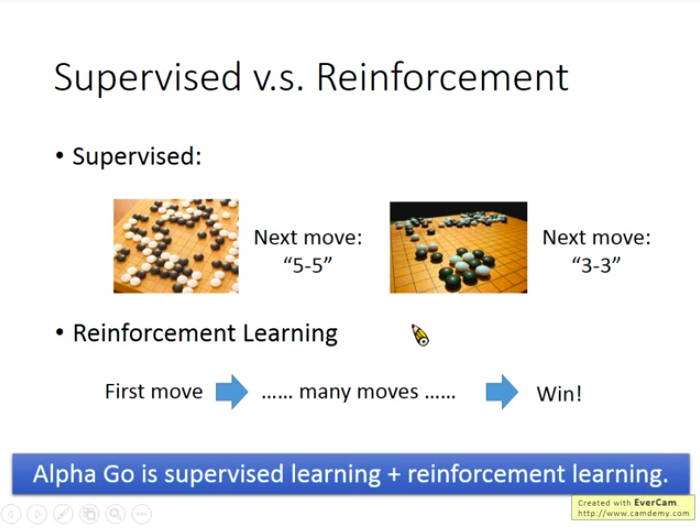
So Reinforcement Learning is closer to how human beings learn.
Example: Plying GO
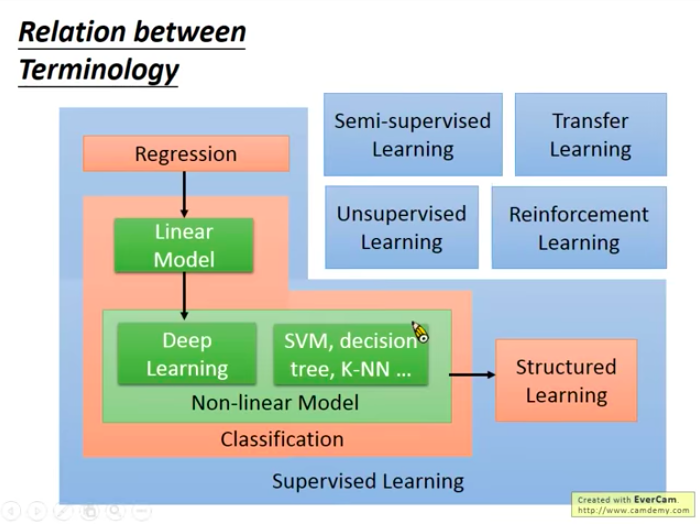
Relation between Terminomogy
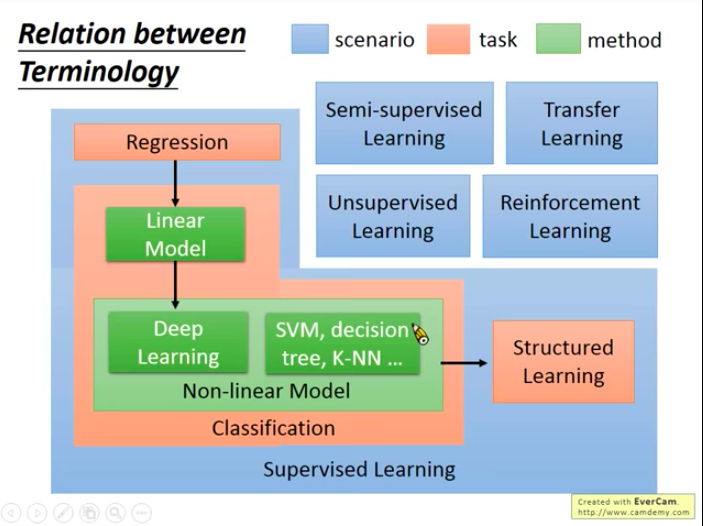
Data you have determines what scenario your problem is in, the type of your problem defines its task, and we can use different models (methods) to solve same problems.
ML Lecture 0-1: Introduction of Machine Learning的更多相关文章
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 10—Advice for applying machine learning 机器学习应用建议
Lecture 10—Advice for applying machine learning 10.1 如何调试一个机器学习算法? 有多种方案: 1.获得更多训练数据:2.尝试更少特征:3.尝试更多 ...
- 【Machine Learning is Fun!】1.The world’s easiest introduction to Machine Learning
Bigger update: The content of this article is now available as a full-length video course that walks ...
- Introduction to Machine Learning
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What Is Machine Learning? To solve a problem on a computer, we need an al ...
- Introduction of Machine Learning
李宏毅主页 台湾大学语音处理实验室 人工智慧.机器学习与深度学习间有什么区别? 人工智能——目标 机器学习——手段 深度学习——机器学习的一种方法 人类设定好的天生本能 Machine Learnin ...
- 李宏毅老师机器学习课程笔记_ML Lecture 0-1: Introduction of Machine Learning
引言: 最近开始学习"机器学习",早就听说祖国宝岛的李宏毅老师的大名,一直没有时间看他的系列课程.今天听了一课,感觉非常棒,通俗易懂,而又能够抓住重点,中间还能加上一些很有趣的例子 ...
- Introduction To Machine Learning Self-Evaluation Test
Preface Section 1 - Mathematical background Multivariate calculus take derivatives and integrals; de ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(1)--Introduction
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 目 录 1 Introduction 1 1.1 ...
- 【机器学习Machine Learning】资料大全
昨天总结了深度学习的资料,今天把机器学习的资料也总结一下(友情提示:有些网站需要"科学上网"^_^) 推荐几本好书: 1.Pattern Recognition and Machi ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料【转】
转自:机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料 <Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一 ...
随机推荐
- Spring AOP使用方式
AOP:全称是Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程 Spring AOP的作用和优势: 作用:在程序运行期间,不修改源码对已有方法进行增强 优势:减少重复代码:提高开发 ...
- 达拉草201771010105《面向对象程序设计(java)》第七周学习总结
达拉草201771010105<面向对象程序设计(java)>第七周学习总结 实验七继承附加实验 实验时间 2018-10-11 1.实验目的与要求 (1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符 ...
- 将mysql数据库集成到idea中
将mysql数据库集成到idea中
- 有了这个开源 Java 项目,开发出炫酷的小游戏好像不难?
本文适合有 Java 基础知识的人群,跟着本文可学习和运行 Java 的游戏. 本文作者:HelloGitHub-秦人 HelloGitHub 推出的<讲解开源项目>系列,今天给大家带来一 ...
- 从0开发3D引擎(补充):介绍领域驱动设计
我们使用领域驱动设计(英文缩写为DDD)的方法来设计引擎,在引擎开发的过程中,领域模型会不断地演化. 本文介绍本系列使用的领域驱动设计思想的相关概念和知识点,给出了相关的资料. 上一篇博文 从0开发3 ...
- 使用 Hexo 创建项目文档网站
当我们发布一个开源项目的时候,最重要的事情之一就是要创建项目文档.对使用项目的用户来说,文档是非常有必要的,通常我们可以使用下面这些方式来创建文档: GitHub Wiki:在 Github 上我们可 ...
- Ubuntu 系统下如何安装pip3工具
一.[导读]Ubuntu 系统内置了 Python2 和 Python3 两个版本的开发环境,却没有内置相应的 pip3 管理工具,本文将介绍如何在Ubuntu下如何快速安装 pip3 工具,并升级到 ...
- PC端如何下载B站里面的视频?
此随笔只是记录一下: PC端下载B站的视频,在blibli前面加上一个i 然后在视频上鼠标右键,视频另存为+路径即可 PS:网上其他的方法,比如在blibli前面加上kan,后面加上jj等,这些方 ...
- 22 Specifications动态查询
Specifications动态查询 有时我们在查询某个实体的时候,给定的条件是不固定的,这时就需要动态构建相应的查询语句,在Spring Data JPA中可以通过JpaSpecificationE ...
- Redis06——Redis到底能用在什么地方(上)
之前我们介绍了一些列关于Redis的数据结构.持久化.过期&淘汰策略.集群化等知识点,感兴趣的小伙伴可以在文章的末尾查看往期内容.今天将为大家带来Redis的应用.由于本篇文章较长,所以将拆分 ...
