域渗透-Kerberos协议中spn的应用
0x01 关于SPN
服务主体名称(SPN)是Kerberos客户端用于唯一标识给特定Kerberos目标计算机的服务实例名称。
服务主体名称是服务实例(可以理解为一个服务,比如 HTTP、MSSQL)的唯一标识符。Kerberos 身份验证使用 SPN 将服务实例与服务登录帐户相关联。
在内部网络中,SPN扫描通过 查询向域控制器执行服务发现。这对于红队而言,可以帮助他们识别正在运行重要服务的主机,如终端、交换机、微软SQL等,并隐藏他们。此外,SPN的识别也是kerberoasting攻击的第一步。
0x02 SPN基础配置
详细可以查看微软官方手册
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows-server/networking/sdn/security/kerberos-with-spn
在 SPN 的语法中存在四种元素,两个必须元素和两个额外元素,其中<service class>和<host>为必须元素:
<serviceclass>/<host>:<port>/<service name> <service class>:标识服务类的字符串 <host>:服务所在主机名称 <port>:服务端口 <service name>:服务名称
常见服务和spn服务实例名称
MSSQL MSSQLSvc/adsmsSQLAP01.adsecurity.org: Exchange exchangeMDB/adsmsEXCAS01.adsecurity.org RDP TERMSERV/adsmsEXCAS01.adsecurity.org WSMan / WinRM / PS Remoting WSMAN/adsmsEXCAS01.adsecurity.org Hyper-V Host Microsoft Virtual Console Service/adsmsHV01.adsecurity.org VMWare VCenter STS/adsmsVC01.adsecurity.org
提一下SPN的注册
这里以SQL Server服务为例子。
SQL Server在每次启动的时候,都会去尝试用自己的启动账号注册SPN。但是在Windows域里,默认普通机器账号有权注册SPN,但是普通域用户账号是没有权利注册SPN的。这就会导致这样一个现象,SQL Server如果使用“Local System account”来启动,Kerberos就能够成功,因为SQL Server这时可以在DC上注册SPN。如果用一个域用户来启动,Kerberos就不能成功,因为这时SPN注册不上去。
解决的方法之一,当然可以使用工具SetSPN -S来手动注册SPN。但是这不是一个最好的方法,毕竟手工注册不是长久之计。如果SPN下次丢了,又要再次手动注册。所以比较好的方法,是让SQL Server当前的启动账号有注册SPN的权力。要在DC上为域账号赋予“Read servicePrincipalName”和“Write serverPrincipalName”的权限即可。
SetSPN
SetSPN是一个本地windows二进制文件,可用于检索用户帐户和服务之间的映射。该实用程序可以添加,删除或查看SPN注册。
这里在我dc上进行SPN服务(MSSQL)的注册。
Setspn -A MSSQLSvc/DC-1.qing.com:1433 tsvc
注册成功之后可以通过下面两个命令来查看已经注册的 SPN。
setspn -Q */*
setspn -T DC-1.qing.com -Q */*
注意这里是写机器的FQDN


0x03 SPN扫描
附上MSSQL的spn扫描脚本
function Discover-PSMSSQLServers
{ <#
.SYNOPSIS
This script is used to discover Microsoft SQL servers without port scanning.
SQL discovery in the Active Directory Forest is performed by querying an Active Directory Gloabl Catalog via ADSI. Discover-PSMSSQLServers
Author: Sean Metcalf, Twitter: @PyroTek3
License: BSD 3-Clause
Required Dependencies: None
Optional Dependencies: None Last Updated: 2/04/2015
Version: 2.3 .DESCRIPTION
This script is used to discover Microsoft SQL servers in the Active Directory Forest. Currently, the script performs the following actions:
* Queries a Global Catalog in the Active Directory root domain for all Microsoft SQL SPNs in the forest
* Displays the Microsoft SQL server FQDNs ports and instances
* Identifies any service accounts associated with the SQL instance and includes the account info REQUIRES: Active Directory user authentication. Standard user access is fine - admin access is not necessary. .EXAMPLE
Discover-PSMSSQLServers
Perform Microsoft SQL Server discovery via AD and returns the results in a custom PowerShell object. .NOTES
This script is used to discover Microsoft SQL servers in the Active Directory Forest and can also provide additional computer information such as OS and last bootup time. .LINK
Blog: http://www.ADSecurity.org
Github repo: https://github.com/PyroTek3/PowerShell-AD-Recon #> Param
( ) Write-Verbose "Get current Active Directory domain... "
$ADForestInfo = [System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Forest]::GetCurrentForest()
$ADForestInfoRootDomain = $ADForestInfo.RootDomain
$ADForestInfoRootDomainDN = "DC=" + $ADForestInfoRootDomain -Replace("\.",',DC=') $ADDomainInfoLGCDN = 'GC://' + $ADForestInfoRootDomainDN Write-Verbose "Discovering Microsoft SQL Servers in the AD Forest $ADForestInfoRootDomainDN "
$root = [ADSI]$ADDomainInfoLGCDN
$ADSearcher = new-Object System.DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher($root,"(serviceprincipalname=mssql*)")
$ADSearcher.PageSize = 50000
$AllADSQLServerSPNs = $ADSearcher.FindAll() $AllADSQLServerSPNsCount = $AllADSQLServerSPNs.Count Write-Output "Processing $AllADSQLServerSPNsCount (user and computer) accounts with MS SQL SPNs discovered in AD Forest $ADForestInfoRootDomainDN `r " $AllMSSQLSPNs = $NULL
$AllMSSQLSPNHashTable =@{}
$AllMSSQLServiceAccountHashTable =@{}
ForEach ($AllADSQLServerSPNsItem in $AllADSQLServerSPNs)
{
$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName = $NULL
[array]$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemArray = $AllADSQLServerSPNsItem.Path -Split(",DC=")
[int]$DomainNameFECount = 0
ForEach ($AllADSQLServerSPNsItemArrayItem in $AllADSQLServerSPNsItemArray)
{
IF ($DomainNameFECount -gt 0)
{ [string]$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName += $AllADSQLServerSPNsItemArrayItem + "." }
$DomainNameFECount++
}
$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName = $AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName.Substring(0,$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName.Length-1) ForEach ($ADSISQLServersItemSPN in $AllADSQLServerSPNsItem.properties.serviceprincipalname)
{
IF ( ($ADSISQLServersItemSPN -like "MSSQL*") -AND ($ADSISQLServersItemSPN -like "*:*") )
{
IF (($AllADSQLServerSPNsItem.properties.objectcategory -like "CN=Person*") -AND ($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN) )
{
$AllMSSQLServiceAccountHashTable.Set_Item($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN,$AllADSQLServerSPNsItem.properties.distinguishedname)
}
$ADSISQLServersItemSPNArray1 = $ADSISQLServersItemSPN -Split("/")
$ADSISQLServersItemSPNArray2 = $ADSISQLServersItemSPNArray1 -Split(":")
[string]$ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN = $ADSISQLServersItemSPNArray2[1]
IF ($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN -notlike "*$AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName*" )
{ $ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN = $ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN + "." + $AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName }
[string]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstancePort = $ADSISQLServersItemSPNArray2[2] $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerName = $ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN -Replace(("."+ $AllADSQLServerSPNsItemDomainName),"") $AllMSSQLSPNHashTableData = $AllMSSQLSPNHashTable.Get_Item($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN)
IF ( ($AllMSSQLSPNHashTableData) -AND ($AllMSSQLSPNHashTableData -notlike "*$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstancePort*") )
{
$AllMSSQLSPNHashTableDataUpdate = $AllMSSQLSPNHashTableData + ";" + $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstancePort
$AllMSSQLSPNHashTable.Set_Item($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN,$AllMSSQLSPNHashTableDataUpdate)
}
ELSE
{ $AllMSSQLSPNHashTable.Set_Item($ADSISQLServersItemSPNServerFQDN,$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstancePort) }
}
}
} ###
Write-Verbose "Loop through the discovered MS SQL SPNs and build the report "
###
$ALLSQLServerReport = @()
#$AllMSSQLServerFQDNs = $NULL
ForEach ($AllMSSQLSPNsItem in $AllMSSQLSPNHashTable.GetEnumerator())
{
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName = $NULL
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN = $NULL
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN = $NULL
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN = $NULL $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN = $AllMSSQLSPNsItem.Name
#[array]$AllMSSQLServerFQDNs += $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArray = ($AllMSSQLSPNsItem.Value) -Split(';') $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDNArray = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN -Split('\.')
[int]$FQDNArrayFECount = 0
ForEach ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDNArrayItem in $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDNArray)
{
IF ($FQDNArrayFECount -ge 1)
{
[string]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName += $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDNArrayItem + "."
[string]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN += "DC=" + $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDNArrayItem + ","
}
$FQDNArrayFECount++
} $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName.Substring(0,$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName.Length-1)
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN.Substring(0,$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN.Length-1)
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainLDAPDN = "LDAP://$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainDN" $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerName = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN -Replace(("."+$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName),"") $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN = $AllMSSQLServiceAccountHashTable.Get_Item($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN)
IF ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN)
{
$ADServiceAccountSearchInfo = @()
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDNArray = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN -Split(",")
ForEach ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDNArrayItem in $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDNArray)
{
IF ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDNArrayItem -like 'DC=*')
{ [string]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN += "$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDNArrayItem," } }
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN.Substring(0,$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN.Length-1) $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainLDAPDN = "LDAP://$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainDN" $ADServiceAccountSearch = New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([ADSI]"")
$ADServiceAccountSearch.SearchRoot = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDomainLDAPDN
$ADServiceAccountSearch.PageSize = 50000
$ADServiceAccountSearch.Filter = "distinguishedname=$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN"
$ADServiceAccountSearchInfo = $ADServiceAccountSearch.FindAll() IF ($ADServiceAccountSearchInfo)
{
[string]$ADServiceAccountSAMAccountName = $ADServiceAccountInfo[0].Properties.samaccountname
[string]$ADServiceAccountdescription = $ADServiceAccountSearchInfo[0].Properties.description
[string]$ADServiceAccountpwdlastset = $ADServiceAccountSearchInfo[0].Properties.pwdlastset
[string]$ADServiceAccountPasswordLastSetDate = [datetime]::FromFileTimeUTC($ADServiceAccountpwdlastset)
[string]$ADServiceAccountlastlogon = $ADServiceAccountSearchInfo[0].Properties.lastlogon
[string]$ADServiceAccountLastLogonDate = [datetime]::FromFileTimeUTC($ADServiceAccountlastlogon) $ADServiceAccountadmincount = $ADServiceAccountSearchInfo[0].Properties.admincount [string]$ADServiceAccountDistinguishedName = $ADServiceAccountSearchInfo[0].Properties.distinguishedname
}
$ADServiceAccountLDAPDN = "LDAP://"+$ADServiceAccountDistinguishedName
$ADServiceAccountInfo = ([adsi] $ADServiceAccountLDAPDN) }
ForEach ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArrayItem in $AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArray)
{
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerPort = $NULL
$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstance = $NULL $SQLServerReport = New-Object -TypeName System.Object
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Domain -Value $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainName
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name ServerName -Value $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerFQDN IF ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArrayItem -match "^[\d\.]+$")
{ [int]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerPort = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArrayItem }
IF ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArrayItem -NOTmatch "^[\d\.]+$")
{ [string]$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstance = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemInstancePortArrayItem } $SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Port -Value $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerPort
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Instance -Value $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerInstance
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name ServiceAccountDN -Value $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN TRY
{
$ADComputerSearch = New-Object DirectoryServices.DirectorySearcher([ADSI]"")
$ADComputerSearch.SearchRoot = $AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerDomainLDAPDN
$ADComputerSearch.PageSize = 50000
$ADComputerSearch.Filter = "(&(objectCategory=Computer)(name=$AllMSSQLSPNsItemServerName))"
$ADComputerSearchInfo = $ADComputerSearch.FindAll() [string]$ComputerADInfoLastLogonTimestamp = ($ADComputerSearchInfo[0].properties.lastlogontimestamp)
TRY { [datetime]$ComputerADInfoLLT = [datetime]::FromFileTime($ComputerADInfoLastLogonTimestamp) }
CATCH { } #$ComputerADInfo.Values $SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name OperatingSystem -Value ($ADComputerSearchInfo[0].properties.operatingsystem)
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name OSServicePack -Value ($ADComputerSearchInfo[0].properties.operatingsystemservicepack)
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name LastBootup -Value $ComputerADInfoLLT
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name OSVersion -Value ($ADComputerSearchInfo[0].properties.operatingsystemversion)
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name Description -Value ($ADComputerSearchInfo[0].properties.description)
}
CATCH { } IF ($AllMSSQLSPNsItemServiceAccountDN)
{
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name SrvAcctUserID -Value $ADServiceAccountSAMAccountName
$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name SrvAcctDescription -Value $ADServiceAccountdescription
#$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name SrvAcctPasswordLastSet -Value $ADServiceAccountPasswordLastSetDate
#$SQLServerReport | Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -Name SAadmincount -Value $ADServiceAccountadmincount
} [array]$ALLSQLServerReport += $SQLServerReport
}
} # Find all SQL service account that may be a domain-level admin in the domain
# $ALLSQLServerReport | Where {$_.SAadmincount -eq 1} | select ServerName,SrvAcctUserID,SrvAcctPasswordLastSet,SrvAcctDescription | sort SrvAcctUserID -unique | format-table -auto
return $ALLSQLServerReport }
下面列出常见spn扫描工具:
由于每台服务器都需要注册用于Kerberos身份验证服务的SPN,因此这为在不进行端口扫描的情况下收集有关环境的信息提供了一个完美的方法。
PowerShell-AD-Recon
除了Tim Medin开发的工具外,Sean Metcalf也开发了各种PowerShell脚本来执行Kerberos侦察。这些脚本是PowerShell AD Recon存储库的一部分,可以在Active Directory中查询服务,例如Exchange,Microsoft SQL,Terminal等。Sean将每个脚本绑定到一个特定的服务,具体取决于你想要发现的SPN。以下脚本将标识网络上的所有Microsoft SQL实例。
参考
http://en.hackdig.com/?17699.htm
GetUserSPNs:
GetUserSPNs 是 Kerberoast 工具集中的一个 powershell 脚本,用来查询域内注册的 SPN。
查看当前 域 qing.com的spn
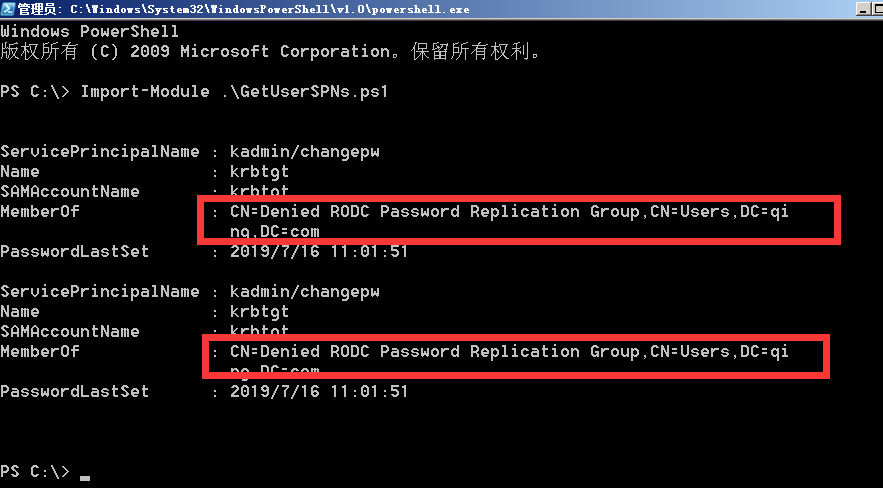
PowerView:
PowerView 是由 Will Schroeder(https://twitter.com/harmj0y)开发的 Powershell 脚本,在 Powersploit 和 Empire 工具里都有集成,PowerView 相对于上面几种是根据不同用户的 objectsid 来返回,返回的信息更加详细。

查看当前 域 qing.com的spn

暂时写到这里,有空后面补充
域渗透-Kerberos协议中spn的应用的更多相关文章
- 域渗透-Kerberos身份验证流程
域渗透-Kerberos身份验证流程 Kerberos协议框架 在 Kerberos 协议中主要是有三个角色的存在: 1. 访问服务的 Client: 2. 提供服务的 Server: 3.KDC(K ...
- 域渗透 | kerberos认证及过程中产生的攻击
文章首发于公众号<Z2O安全攻防> 直接公众号文章复制过来的,排版可能有点乱, 可以去公众号看. https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/WMGkQoMnQdyG8UmS ...
- 内网学习之Kerberos协议
学习了解kerberos协议,有助于我们后期理解黄金票据和白银票据的原理 kerberos协议 kerberos是一种由麻省理工大学提出的一种网络身份验证协议.旨在通过使用密钥加密技术为客户端/服务器 ...
- 域渗透:SPN(ServicePrincipal Names)的利用
SPN 简介:服务主体名称(SPN:ServicePrincipal Names)是服务实例(可以理解为一个服务,比如 HTTP.MSSQL)的唯一标识符.Kerberos 身份验证使用 SPN 将服 ...
- 域渗透基础之NTLM认证协议
域渗透基础的两个认证协议ntlm和Kerberos协议是必须总结的~ 这篇简单总结下ntlm协议 晚上写下kerberos 0x01 NTLM简介 NTLM使用在Windows NT和Windows ...
- 域渗透-企业应用SAML签名攻击
在项目中遇到SAML企业应用 想留个后门时候一脸懵 随便的整理记录 记录项目中SAML渗透的知识点. 0x01 前置知识 SAML单点登陆 SAML(Security Assertion ...
- 初级AD域渗透系列
net group /domain 获得所有域用户组列表 net group “domain admins” /domain 获得域管理员列表 net group “enterprise admi ...
- AD域渗透总结
域渗透总结 学习并做了一段时间域网络渗透,给我直观的感受就是思路问题和耐心,这个不像技术研究,需要对一个点进行研究,而是遇到问题后要从多个方面思考,寻找"捷径"思路,只要思路正确, ...
- 关于Kerberos协议流程的总结
Kerberos协议工作原理分析 这里面借用一下师傅们的图来说明一下  Kerberos协议的流程大致如下(假设A要获取对Server B的访问权限) 第一步(KRB_AS_REQ) 这一步客户 ...
随机推荐
- Git服务端下载
链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1kVshpQ3提取密码:4g36
- thinkphp6 常用方法文档
请求变量 use think\facade\Request; Request::param('name'); Request::param();全部请求变量 返回数组 Request::param([ ...
- 安全性测试:OWASP ZAP 2.8 使用指南(三):ZAP代理设置
ZAP本地代理设置 如前文所言,ZAP的工作机制,是通过“中间代理”的形式实现. ZAP的代理设置可以从菜单中的:工具 - 选项 - Local Proxies加载. 在这里可以设置ZAP用来接受接入 ...
- Java方法调用的字节码指令学习
Java1.8环境下,我们在编写程序时会进行各种方法调用,虚拟机在执行这些调用的时候会用到不同的字节码指令,共有如下五种: invokespecial:调用私有实例方法: invokestatic:调 ...
- Vue学习之vue属性绑定和双向数据绑定
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 基于API和SQL的基本操作【DataFrame】
写在前面: 当得到一个DataFrame对象之后,可以使用对象提供的各种API方法进行直接调用,进行数据的处理. // =====基于dataframe的API=======之后的就都是DataFra ...
- 2019-2020-1 20199303《Linux内核原理与分析》第三周作业
操作系统是如何工作的 除了存储程序计算机和函数调用堆栈机制,还有一个非常基础的概念就是中断,这三个关键性的方法机制可以称作计算机的三个法宝:程序存储计算机.函数调用.中断 堆栈的作用:记录函数调用框架 ...
- 读《深入理解Elasticsearch》点滴-基础概念
Lucene的概念 document:以json的形式体现,搜索和搜索的主要载体 field:document的一个部分 term(词项):代表文本中的一个词 token(词条):term在field ...
- 记录使用echarts的graph类型绘制流程图全过程(一)-x,y位置的计算
先说下本次案例业务需求,输入2个节点,获取数据后绘制出2个节点间的路径,之前使用的是网状图,但是网状图的效果不佳,需要转换成流程图的模式: 那么如何在不修改数据的情况下,实现类似效果尼? 看了下ech ...
- 夯实Java基础系列19:一文搞懂Java集合类框架,以及常见面试题
本系列文章将整理到我在GitHub上的<Java面试指南>仓库,更多精彩内容请到我的仓库里查看 https://github.com/h2pl/Java-Tutorial 喜欢的话麻烦点下 ...
