SDUST数据结构 - chap8 查找
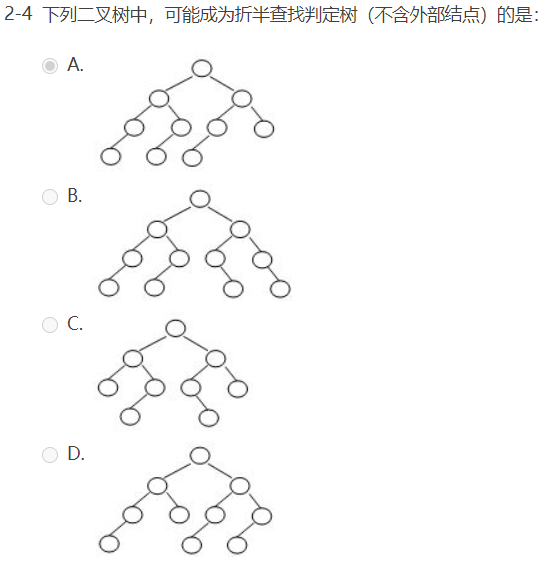
选择题:












函数题:
6-1 二分查找:
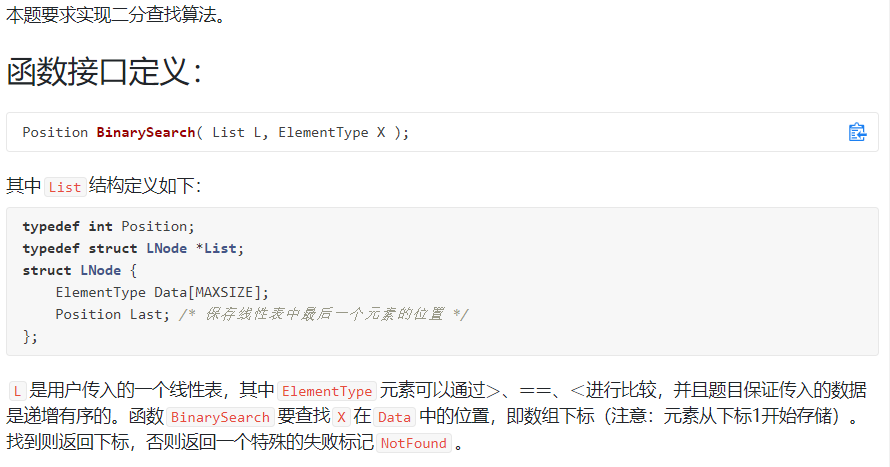
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> #define MAXSIZE 10
#define NotFound 0
typedef int ElementType; typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
}; List ReadInput(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表。元素从下标1开始存储 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X ); int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P; L = ReadInput();
scanf("%d", &X);
P = BinarySearch( L, X );
printf("%d\n", P); return 0;
} /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:
5
12 31 55 89 101
31
输出样例1:
2
输入样例2:
3
26 78 233
31
输出样例2:
0
代码:


Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X )
{
if(L == NULL)
return NotFound;//不符合条件,空
int low=1, high=L->Last;//设置左右指针
int mid;
while(low<=high)//左右指针相遇跳出循环
{
mid = (low+high)/2;
if(X>L->Data[mid])
low = mid+1;
else if(X<L->Data[mid])
high = mid-1;
else
return mid;
}
return NotFound;//未找到,空
}
6-2 线性探测法的查找函数:
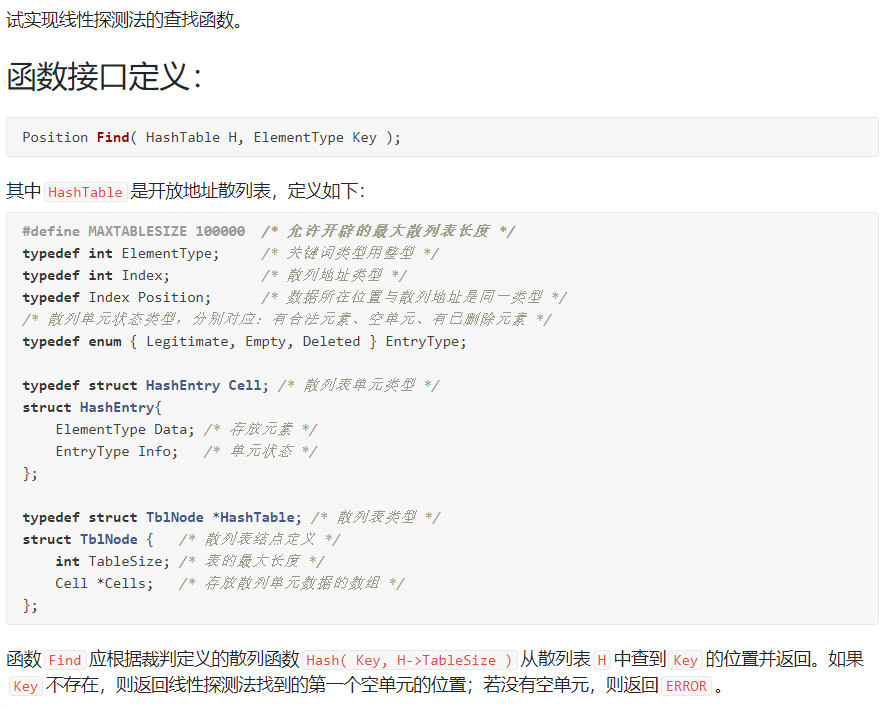
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXTABLESIZE 100000 /* 允许开辟的最大散列表长度 */
typedef int ElementType; /* 关键词类型用整型 */
typedef int Index; /* 散列地址类型 */
typedef Index Position; /* 数据所在位置与散列地址是同一类型 */
/* 散列单元状态类型,分别对应:有合法元素、空单元、有已删除元素 */
typedef enum { Legitimate, Empty, Deleted } EntryType; typedef struct HashEntry Cell; /* 散列表单元类型 */
struct HashEntry{
ElementType Data; /* 存放元素 */
EntryType Info; /* 单元状态 */
}; typedef struct TblNode *HashTable; /* 散列表类型 */
struct TblNode { /* 散列表结点定义 */
int TableSize; /* 表的最大长度 */
Cell *Cells; /* 存放散列单元数据的数组 */
}; HashTable BuildTable(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表 */
Position Hash( ElementType Key, int TableSize )
{
return (Key % TableSize);
} #define ERROR -1
Position Find( HashTable H, ElementType Key ); int main()
{
HashTable H;
ElementType Key;
Position P; H = BuildTable();
scanf("%d", &Key);
P = Find(H, Key);
if (P==ERROR)
printf("ERROR: %d is not found and the table is full.\n", Key);
else if (H->Cells[P].Info == Legitimate)
printf("%d is at position %d.\n", Key, P);
else
printf("%d is not found. Position %d is returned.\n", Key, P); return 0;
} /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:(-1表示该位置为空)
11
11 88 21 -1 -1 5 16 7 6 38 10
38
输出样例1:
38 is at position 9.
输入样例2:
11
11 88 21 -1 -1 5 16 7 6 38 10
41
输出样例2:
41 is not found. Position 3 is returned.
输入样例3:
11
11 88 21 3 14 5 16 7 6 38 10
41
输出样例3:
ERROR: 41 is not found and the table is full.
代码:


Position Find( HashTable H, ElementType Key )
{
Position p, p1;
int cts=0;
p = p1 =Hash(Key, H->TableSize);
while(H->Cells[p].Data!=Key&&H->Cells[p].Info!=Empty)
{
cts++;
if(cts == MAXTABLESIZE)
return ERROR;//若没有空单元,则返回ERROR
p = (p1 + cts)%H->TableSize;
}
return p;
}
6-3 分离链接法的删除操作函数:
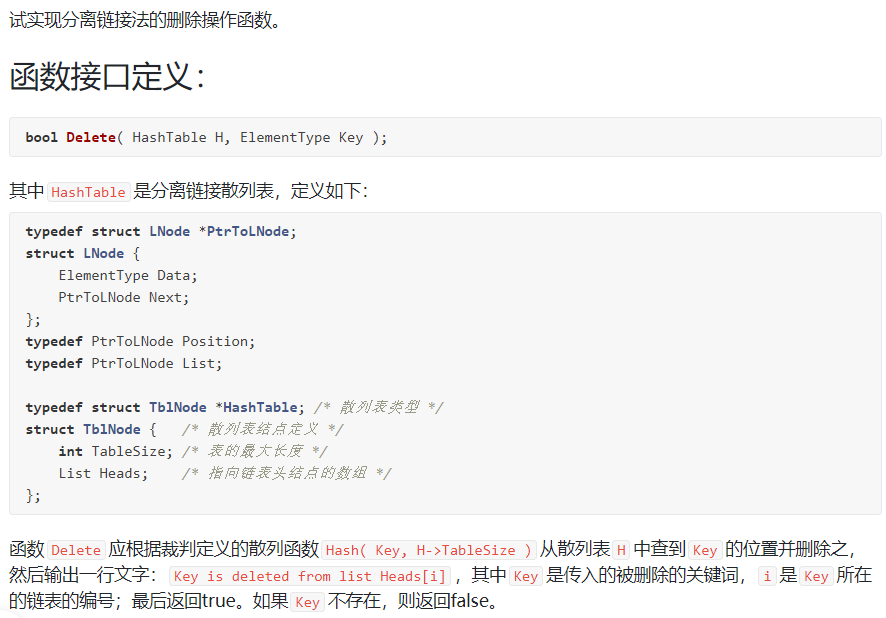
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> #define KEYLENGTH 15 /* 关键词字符串的最大长度 */
typedef char ElementType[KEYLENGTH+1]; /* 关键词类型用字符串 */
typedef int Index; /* 散列地址类型 */
typedef enum {false, true} bool; typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToLNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToLNode Position;
typedef PtrToLNode List; typedef struct TblNode *HashTable; /* 散列表类型 */
struct TblNode { /* 散列表结点定义 */
int TableSize; /* 表的最大长度 */
List Heads; /* 指向链表头结点的数组 */
}; Index Hash( ElementType Key, int TableSize )
{
return (Key[0]-'a')%TableSize;
} HashTable BuildTable(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表 */
bool Delete( HashTable H, ElementType Key ); int main()
{
HashTable H;
ElementType Key; H = BuildTable();
scanf("%s", Key);
if (Delete(H, Key) == false)
printf("ERROR: %s is not found\n", Key);
if (Delete(H, Key) == true)
printf("Are you kidding me?\n");
return 0;
} /* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1: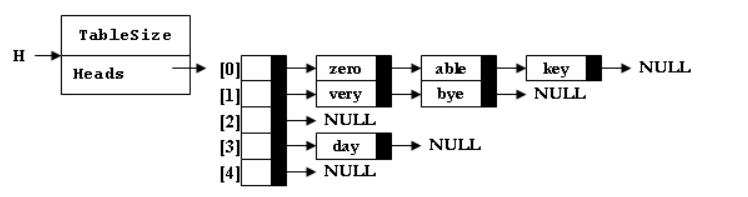
able
输出样例1:
able is deleted from list Heads[0]
输入样例2:(散列表如样例1图)
date
输出样例2:
ERROR: date is not found
代码:


bool Delete( HashTable H, ElementType Key )
{
Position p,q;
Index pos;//关键字地址
pos = Hash(Key, H->TableSize);//初始化散列位置
p = H->Heads[pos].Next;//从该邻接表第一个节点开始
while(p&&strcmp(p->Data, Key))//当未到表尾,并且Key未找到时
{
q = p;
p = p->Next;
}
if(p==NULL)
return false;
else
{
printf("%s is deleted from list Heads[%d]",Key,pos);
q = p->Next;
free(p);//删除p节点,释放p内存
return true;
}
}
编程题:
7-1 两个有序序列的中位数:

输入样例1:
5
1 3 5 7 9
2 3 4 5 6
输出样例1:
4
输入样例2:
6
-100 -10 1 1 1 1
-50 0 2 3 4 5
输出样例2:
1
代码:


#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int a[100001]={0},b[100001]={0},c[200002]={0};//a,b分别用于存储两行数,c用于排序的时候按顺序填入
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)//读入两个数组的元素
{
if(i==0)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&a[j]);
}
if(i==1)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&b[j]);
}
}
int x=0,y=0;
int i=0;
while(x<n&&y<n)//分别进行比较, 按照升序依次填入c数组中,
{
if(a[x] > b[y])
{
c[i] = b[y];
i++;
y++;
}
else
{
c[i] = a[x];
i++;
x++;
}
}
while(y<n)//
{
c[i++] = a[y++];
}
while(x<n)//
{
c[i++] = b[x++];
}
int mid = (i-1)/2;//寻找中位数,
printf("%d",c[mid]);
return 0;
}
7-2 是否同一棵二叉搜索树:

输入样例:
4 2
3 1 4 2
3 4 1 2
3 2 4 1
2 1
2 1
1 2
0
输出样例:
Yes
No
No
代码:


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Tree
{
int data;
struct Tree *Left;
struct Tree *Right;
}TNode, *BTree;
void BuildT(BTree &T, int a)
{
if(T == NULL)
{
T = new Tree;
T->data = a;
T->Left = T->Right = NULL;
}
else
{
if(a<T->data)
BuildT(T->Left, a);
else
BuildT(T->Right, a);
}
}
int panduan(Tree *t1, Tree *t2)
{
if(!t1&&!t2)
return 1;
if(t1&&t2)
if(t1->data==t2->data )
if(panduan(t1->Left,t2->Left )&&panduan(t1->Right,t2->Right ))
return 1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n, l,a;
int flag=0;
while(cin>>n)
{
Tree *t = NULL;
if(n == 0)
return 0;
cin>>l;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
BuildT(t, a);
}
while(l--)
{
Tree *tt = NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a;
BuildT(tt, a);
}
flag = panduan(t, tt);
if(flag==0)
cout<<"No"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
7-3 是否完全二叉搜索树:

输入样例1:
9
38 45 42 24 58 30 67 12 51
输出样例1:
38 45 24 58 42 30 12 67 51
YES
输入样例2:
8
38 24 12 45 58 67 42 51
输出样例2:
38 45 24 58 42 12 67 51
NO
代码:


#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int a[105];
int n,m;
void insert(int p, int data)
{
if(a[p] == 0)
{
a[p] = data;
return ;
}
if(data > a[p])
insert(p*2, data);
else
insert(p*2+1, data);
}
int main()
{
//int n,m;
//int a[105];
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(a, 0, sizeof(int));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&m);
insert(1, m);
}
int nn=0;;
int i=0;;
while(nn<n)
{
while(a[i] == 0)
i++;
if(nn)
printf(" %d", a[i]);
else
printf("%d",a[i]);
i++;
nn++;
}
if(i == n+1)
printf("\nYES\n");
else
printf("\nNO\n");
}
SDUST数据结构 - chap8 查找的更多相关文章
- Go 数据结构--二分查找树
Go 数据结构--二分查找树 今天开始一个Go实现常见数据结构的系列吧.有时间会更新其他数据结构. 一些概念 二叉树:二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构. 完全二叉树:若设二叉树的高度为h,除第 ...
- 【Java】 大话数据结构(11) 查找算法(2)(二叉排序树/二叉搜索树)
本文根据<大话数据结构>一书,实现了Java版的二叉排序树/二叉搜索树. 二叉排序树介绍 在上篇博客中,顺序表的插入和删除效率还可以,但查找效率很低:而有序线性表中,可以使用折半.插值.斐 ...
- 算法与数据结构(九) 查找表的顺序查找、折半查找、插值查找以及Fibonacci查找
今天这篇博客就聊聊几种常见的查找算法,当然本篇博客只是涉及了部分查找算法,接下来的几篇博客中都将会介绍关于查找的相关内容.本篇博客主要介绍查找表的顺序查找.折半查找.插值查找以及Fibonacci查找 ...
- 【Java】 大话数据结构(10) 查找算法(1)(顺序、二分、插值、斐波那契查找)
本文根据<大话数据结构>一书,实现了Java版的顺序查找.折半查找.插值查找.斐波那契查找. 注:为与书一致,记录均从下标为1开始. 顺序表查找 顺序查找 顺序查找(Sequential ...
- 【Java】 大话数据结构(12) 查找算法(3) (平衡二叉树(AVL树))
本文根据<大话数据结构>一书及网络资料,实现了Java版的平衡二叉树(AVL树). 平衡二叉树介绍 在上篇博客中所实现的二叉排序树(二叉搜索树),其查找性能取决于二叉排序树的形状,当二叉排 ...
- 【Java】 大话数据结构(13) 查找算法(4) (散列表(哈希表))
本文根据<大话数据结构>一书,实现了Java版的一个简单的散列表(哈希表). 基本概念 对关键字key,将其值存放在f(key)的存储位置上.由此,在查找时不需比较,只需计算出f(key) ...
- 数据结构---平衡查找树之B树和B+树(转)
本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/Introduce-B-Tree-and-B-Plus-Tree.html 前面讲解了平衡查找树中的2-3树以及其实现红 ...
- 数据结构之查找(图片来源,老师PPT)
顺序查找进行遍历元素,进行查找 总计全部比较次数为:1+2+…+n = (1+n)n/2 若求某一个元素的平均查找次数,还应当除以n(等概率), 即: ASL=(1+n)/2 ,时间效率为 O(n) ...
- 数据结构【查找】—B树
/*********************讲解后期补充*****************/ 先上代码 #include "000库函数.h" #define MAXSIZE 10 ...
随机推荐
- gnuplot设置字体及大小
set term png font 'times.ttf,14'set fontpath '/home/peter/.fonts'set output 'vel-cost.eps'set gridse ...
- druid数据源yml配置
application.yml配置 spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:33 ...
- 深入解析 C# 的 String.Create 的方法
作者:Casey McQuillan 译者:精致码农 原文:http://dwz.win/YVW 说明:原文比较长,翻译时精简了很多内容,对于不重要的细枝末节只用了一句话概括,但不并影响阅读. 你还记 ...
- 本科入行可能吗?做到这3点,斩获BAT offer不是梦
大家好,前两天有一个小伙伴加我微信咨询.他说他不想读研,想要直接本科毕业就参与工作.但是又担心自己由于没有学历优势,无法在校招当中获得机会,于是便来向我请教,能不能指点迷津提供一些具体的实操性措施.与 ...
- 关于 ReentrantLock 中锁 lock() 和解锁 unlock() 的底层原理浅析
关于 ReentrantLock 中锁 lock() 和解锁 unlock() 的底层原理浅析 如下代码,当我们在使用 ReentrantLock 进行加锁和解锁时,底层到底是如何帮助我们进行控制的啦 ...
- [译] ConstraintLayout 可视化[Design]编辑器(这到底是什么)[第四部分]
原文地址:Testing Views in Isolation with Espresso 原文作者:Ataul Munim 译文出自:掘金翻译计划 译者:yazhi1992 校对者:lovexiao ...
- mac 清理磁盘空间
128G mac真的用的很崩溃,发现系统占用80G ,肯定是有问题的,发现了是缓存的原因,删除后好多了,记录一下. 从管理里进入之后,从文稿中选择"文件浏览器"可以看到每一个文件夹 ...
- 在IDEA中的cannot_resolve_method解决方法
打开IDEA编辑器,点击编辑器左上角file,出现菜单栏,点击菜单栏中的Settings选项. 在出现的Settings窗口中的左侧菜单栏中找到Plugins选项,点击进入'Plugins'窗口. ...
- Spring Data JPA简介 Spring Data JPA特点
Spring Data JPA 是Spring基于ORM框架.JPA规范的基础上封装的一套JPA 应用框架,底层使用了Hibernate 的JPA技术实现,可使开发者用极简的代码即可实现对数据的访问和 ...
- 基于Let's Encrypt生成免费证书-支持多域名泛域名证书
目录 客户端 certbot acme.sh 安装acme.sh 1. 自动安装 2. 手动安装 3. 测试收否安装成功 使用acme.sh生成证书 1. HTTP 方式 2. DNS 方式 1. 生 ...
